string对象的构造
//string() string(const string &s) string(const char *s) string(first,last)
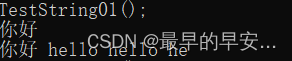
void TestString01()
{
string s1;
string s2("hello");
string s3(s2);
const char* p = "hello";
string s4(p, p + 2);
cin >> s1;
cout << s1 << " " << s2 << " " << s3 << " " << s4 << endl;
}
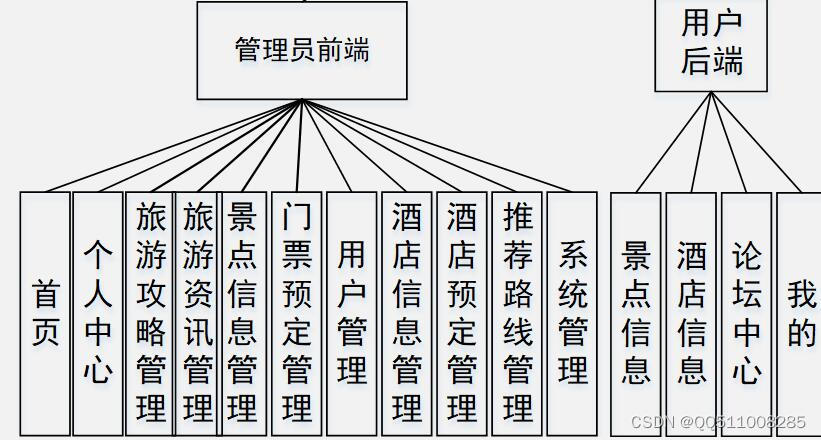
上机实践:
容器:
size() length() :获取字符串长度
capacity():获取空间大小
empty():检测字符串是否为空串
clear():将有效元素清空
reserve(size_t newcapacity):进行扩容
resize(size_t newcapacity,char ch):修改空间,多余空间使用ch填充,未多余不用补充
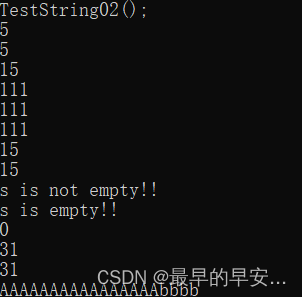
void TestString02()
{
string s("hello");
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.length() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
s.reserve(100);
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
s.reserve(20);
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
//缩小时临界位置
s.reserve(16);
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
s.reserve(15);
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
s.reserve(2);
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
if (s.empty())
{
cout << "s is empty!!" << endl;
}
else
cout << "s is not empty!!" << endl;
s.clear();
if (s.empty())
{
cout << "s is empty!!" << endl;
}
else
cout << "s is not empty!!" << endl;
cout << s.size() << endl;
string ss(16, 'A');
cout << ss.capacity() << endl;
ss.reserve(10);
cout << ss.capacity() << endl;
ss.resize(20, 'b');
cout << ss << endl;
}
上机实践:
修改:
operator+=:在string之后拼接:单个字符 C格式的字符串 string对象
append:在string之后拼接:单个字符 C格式的字符串 string对象
push_back(char ch):往string尾部插入ch
insert(size_t poosl,size_t n,char c):在poosl位置插入n个c
erase(size_t pos,size_t n):在pos位置删除n个
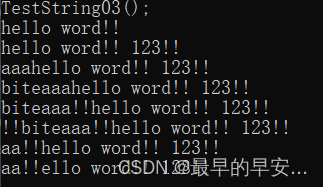
void TestString03()
{
string s = ("hello");
s.push_back(' ');
//拼接 C格式字符串
s += "word";
//拼接对象
string ss("!!");
s += ss;
cout << s << endl;
s.append(1, ' ');
s.append("123");
s.append(ss);
cout << s << endl;
s.insert(0, 3, 'a');
cout << s << endl;
s.insert(0, "bite");
cout << s << endl;
s.insert(7, ss);
cout << s << endl;
s.insert(s.begin(), ss.begin(), ss.end());
cout << s << endl;
s.erase(0, 7);
cout << s << endl;
s.erase(s.begin()+4);//删除s第四个字符
cout << s << endl;
s.erase(s.begin(), s.end());//清空
cout << s << endl;
}
上机实践:
借助push_back方式演示string的扩容机制(在VS2019,string按照1.5倍扩容)
void TestString04()
{
//扩容需要 申请新空间 拷贝旧空间 释放旧空间
string s;
s.reserve(100);
size_t cap = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
s.push_back('A');//s+='A
if (cap != s.capacity())
{
cap = s.capacity();
cout << cap << endl;
}
}
}
上机实践:
迭代器:
正向:begin()|end() 反向:rbegin()|rend()
void TestString05()
{
string s("123456789");
//string 遍历
//for下标方式
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
cout << s[i];
}
cout << endl;
//其次使用范围for
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e;
}
cout << endl;
//使用迭代器遍历
//string::iterator it = s.begin();
auto it = s.begin();//C++11
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it;
it++;
}
cout << endl;
//反向迭代器
//string::reverse_iterator rit = s.rbegin();
auto rit = s.rbegin();//C++11
while (rit != s.rend())
{
cout << *rit;
rit++;
}
cout << endl;
}
上机实践:

#include<algorithm>
void TestString06()
{
string s("123456789");
cout << s << endl;
//对s逆序
reverse(s.begin(), s.end());
cout << s << endl;
sort(s.begin(), s.end());
cout << s << endl;
}
上机实践:
int atoi(const char* s):字符串转换整型数字
c_str():返回string对象中存储字符串的空间首地址
size_t find(char c,size_t pos=0):从pos位置开始查找字符c
size_t rfind(char c):从后往前找
string substr(size_t pos = 0,size_t n = npos):从pos位置开始,截取n个字符 如果n没有传递,则从pos一直到末尾,如果pos和n都没有传递,则将字符串整个截取
void TestString07()
{
string s("1234512");
int ret = atoi(s.c_str());
cout << ret << endl;
//找到s中1
int pos = 0;
while (true)
{
pos = s.find('1', pos);
if (pos == string::npos)//没有找到find返回npos
break;
cout << pos << endl;
pos += 1;
}
//获取文件的后缀
string ss("123.txt.cpp");
size_t Pos = ss.rfind('.') + 1;//返回c位置
string posFix = ss.substr(Pos);
cout << posFix << endl;
}
void GetLastWordLength()
{
string s;
while (getline(cin,s))//getlin获取一整行字符包含空格
{
size_t start = s.rfind(' ') + 1;
string word = s.substr(start);
cout << word << endl;
}
}
上机实践:

int atoi(const char* s):字符串转换整型数字
char* itoa(int value,char* str,int base):将数字转换为字符串,base为2~36进制
int sprintf(char* str,const char* format,int value):将value转换为format类型存放在str
void TestString08()//字符串相加
{
string s1, s2;
cin >> s1 >> s2;
int value = atoi(s1.c_str());
value += atoi(s2.c_str());
char ch[32] = { 0 };
sprintf(ch, "%d", value);
}