Title
题目
HiDiff: Hybrid Diffusion Framework for Medical Image Segmentation
HiDiff: 用于医学图像分割的混合扩散框架
01
文献速递介绍
医学图像分割是将医学图像数据转化为有意义的、空间结构化的信息,如器官和肿瘤。随着深度学习(DL)技术的快速发展,这一领域取得了显著进步。基于深度学习的分割方法在划分器官/肿瘤和减少人工成本方面显示了有效性。目前,现有的基于深度学习的分割方法,包括基于卷积神经网络和视觉transformer的变体,通常使用交叉熵或Dice损失来学习从输入医学图像到分割掩码的映射函数。这种范式通常被称为判别方法,直接学习图像像素的分类概率。尽管这种方法很流行,但它们仅关注在像素特征空间中学习类之间的决策边界,而未能捕捉底层数据分布,因此未能捕捉内在的类特征。此外,它们学习到的特征空间不稳定,当远离决策边界时性能迅速下降,使得处理模糊边界和微小物体变得具有挑战性。
相比之下,基于生成的方式首先建模输入数据和分割掩码的联合概率,然后利用学习到的联合概率评估给定输入图像的分割掩码的条件分布,最后输出掩码预测。众多理论和实证研究表明,基于生成的方法由于直接建模底层数据分布,具有缓解其判别对手相关限制的潜力。然而,值得注意的是,现代生成模型也面临挑战,包括训练不稳定和推理速度慢。这些挑战促使人们探索结合判别和生成分割方法的集成方法,以缓解这些问题。
Abstract
摘要
医学图像分割随着深度学习(DL)技术的快速发展取得了显著进步。现有的基于深度学习的分割模型通常是判别性的;即,它们旨在学习从输入图像到分割掩码的映射。然而,这些判别方法忽视了底层数据分布和内在类别特征,导致特征空间不稳定。在这项工作中,我们提出用生成模型的底层数据分布知识来补充判别性分割方法。为此,我们提出了一种用于医学图像分割的新型混合扩散框架,称为HiDiff,它可以协同现有判别性分割模型和新生成扩散模型的优势。HiDiff包含两个关键组件:判别分割器和扩散优化器。
首先,我们利用任何常规训练的分割模型作为判别分割器,可以为扩散优化器提供分割掩码先验。其次,我们提出了一种新颖的二元伯努利扩散模型(BBDM)作为扩散优化器,通过建模底层数据分布,有效、高效和互动地优化分割掩码。第三,我们以交替协作的方式训练判别分割器和BBDM,使它们相互促进。
在腹部器官、脑肿瘤、息肉和视网膜血管分割数据集上进行的大量实验结果,涵盖了四种广泛使用的模态,证明了HiDiff在现有医学分割算法(包括最先进的基于transformer和扩散模型的算法)上的优越性能。此外,HiDiff在分割小物体和推广到新数据集方面表现出色。源码可在https://github.com/takimailto/HiDiff获得。
Method
方法
To effectively, efficiently, and interactively synergize thestrengths of existing discriminative segmentors and the proposed BBDM, we propose a novel hybrid diffusion frameworkfor medical image segmentation, as shown in Fig. 2. In thissection, we first elaborate on existing discriminative segmentors and the proposed diffusion refiner in Secs. II-A and II-B,respectively. Finally, we detail our hybrid diffusion frameworkwith an alternate-collaborative training strategy in Sec. II-C.
为了有效、高效且互动地协同现有判别分割器和提出的BBDM的优势,我们提出了一种用于医学图像分割的新型混合扩散框架,如图2所示。在本节中,我们首先分别在II-A和II-B节详细说明现有的判别分割器和提出的扩散优化器。最后,我们在II-C节详细介绍了我们的混合扩散框架及其交替协作的训练策略。
Conclusion
结论
This paper proposed a novel hybrid diffusion framework,HiDiff, for medical image segmentation, which can synergizethe strengths of existing discriminative segmentation modelsand new generative diffusion models, i.e. BBDM. The noveltyof our BBDM lies in three-fold: (i) effective: Bernoulli-baseddiffusion kernel to enhance the diffusion models in modelingthe discrete targets of the segmentation task, (ii) efficient: thebinarized diffusion refiner to significantly improve efficiencyfor inference with negligible computational costs, and (iii)interactive: cross transformer to enable interactive exchangebetween the diffusion generative feature and the discriminativefeature. We train HiDiff in an alternate-collaborative manner,which can mutually boost the discriminative segmentor andthe diffusion refiner during training. Extensive experimentalresults and detailed ablation studies validated the superior performance of HiDiff and the effectiveness of key componentsin HiDiff. We highlight that HiDiff is a principled frameworkfully compatible with existing DL-based segmentation models.
本文提出了一种用于医学图像分割的新型混合扩散框架 HiDiff,它能够协同现有判别分割模型和新的生成扩散模型(即 BBDM)的优势。我们的 BBDM 的创新之处在于以下三点:(i) 有效性:基于伯努利的扩散核以增强扩散模型在分割任务离散目标建模中的能力;(ii) 高效性:二值化扩散优化器显著提高推理效率,同时几乎不增加计算成本;(iii) 交互性:交叉转换器实现了扩散生成特征和判别特征之间的互动交换。我们以交替协作的方式训练 HiDiff,在训练过程中相互促进判别分割器和扩散优化器。大量实验结果和详细的消融研究验证了 HiDiff 的卓越性能和关键组件的有效性。我们强调,HiDiff 是一个与现有基于 DL 的分割模型完全兼容的基本框架。
Figure
图
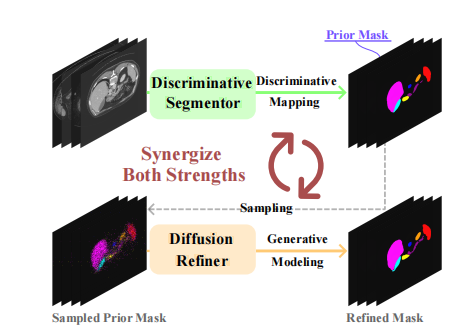
Fig. 1. Conceptual illustration of our HiDiff. We train our HiDiff in analternate-collaborative manner to synergize the strengths of existingdiscriminative segmentation and generative diffusion models.
图 1. HiDiff 的概念示意图。我们以交替协作的方式训练 HiDiff,以协同现有判别分割模型和生成扩散模型的优势。
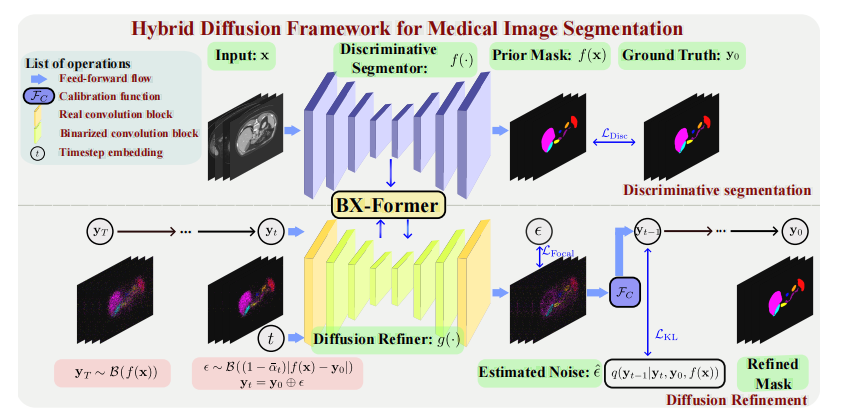
Fig. 2. Overview of the proposed HiDiff for medical image segmentation. Our HiDiff involves two key components: discriminative segmentor anddiffusion refiner, where the discriminative segmentor provides a segmentation mask prior for diffusion models while the diffusion refiner effectively,efficiently, and interactively refines the segmentation mask. Furthermore, we binarize our diffusion refiner and introduce a binary cross transformerto interactively exchange the discriminative and diffusion generative features, effectively refining the segmentation mask with negligible resources.
图 2. 提出的 HiDiff 用于医学图像分割的概述。HiDiff 包含两个关键组件:判别分割器和扩散优化器。判别分割器为扩散模型提供分割掩码先验,而扩散优化器则有效、高效且互动地优化分割掩码。此外,我们将扩散优化器二值化,并引入二值交叉转换器,以互动方式交换判别和生成扩散特征,从而以极少的资源有效地优化分割掩码。
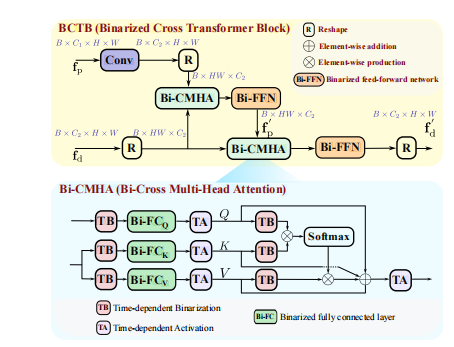
Fig. 3. Illustration of the proposed binarized cross transformer block and its constituent binarized cross multi-head attention modules.
图 3. 提出的二值交叉转换器块及其组成的二值交叉多头注意力模块的示意图。
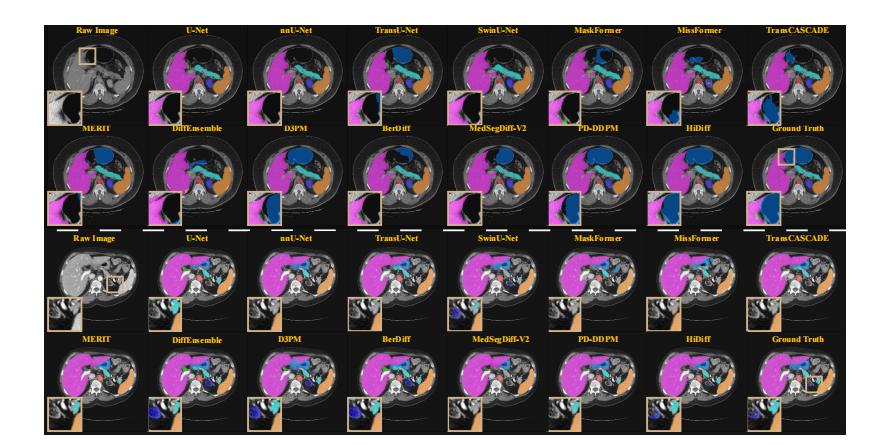
Fig. 4. Qualitative results of different segmentation methods for two cases, 0038 and 0008, from the Synapse testing set.
图 4. 来自 Synapse 测试集的两个案例(0038 和 0008)的不同分割方法的定性结果。
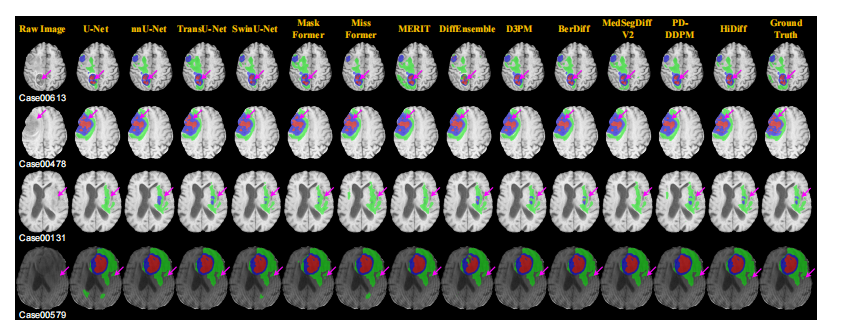
Fig. 5. Qualitative results of different segmentation methods for four cases from the BraTS testing set
图 5. 来自 BraTS 测试集的四个案例中不同分割方法的定性结果。
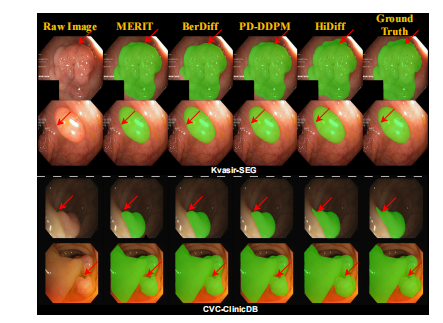
Fig. 6. Qualitative results of different segmentation methods for fourcases from the Kvasir-SEG and CVC-ClinicDB testing sets.
图 6.来自 Kvasir-SEG 和 CVC-ClinicDB 测试集的四个案例中不同分割方法的定性结果。
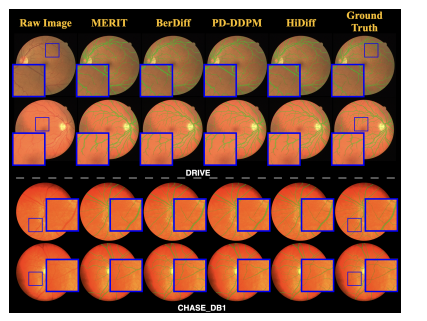
Fig. 7. Qualitative results of different segmentation methods for fourcases from the Drive and CHASE DB1 testing sets.
图 7.来自 DRIVE 和 CHASE_DB1 测试集的四个案例中不同分割方法的定性结果。
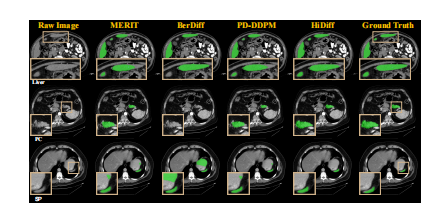
Fig. 8. Cross-dataset qualitative results of different segmentationmethods for four cases from the MSD testing set.
图 8. 不同分割方法在 MSD 测试集中四个案例的跨数据集定性结果。
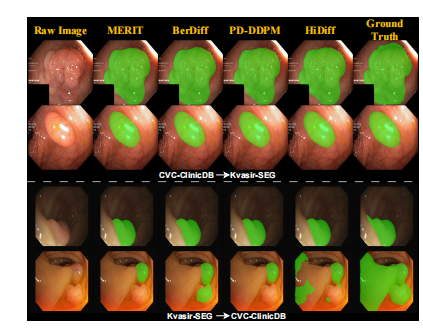
Fig. 9. Cross-dataset qualitative results of different methods on thepolyps segmentation task.
图 9. 在息肉分割任务中,不同方法的跨数据集定性结果。
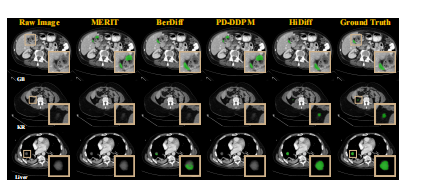
Fig. 10. Qualitative results of different segmentation methods for threecases from the small organ subset of the Synapse testing set.
图 10. 来自 Synapse 测试集小器官子集的三个案例中不同分割方法的定性结果。
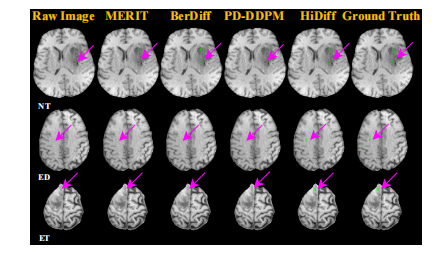
Fig. 11. Qualitative results of different segmentation methods for threecases from the small tumor subset of the BraTS testing set.
图 11. 来自 BraTS 测试集小肿瘤子集的三个案例中不同分割方法的定性结果。
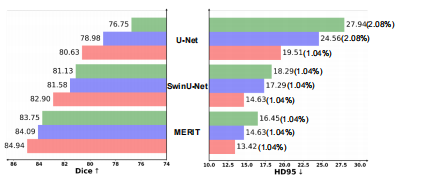
Fig. 12. Quantitative results of our HiDiff with three different discriminative segmentors: U-Net, SwinU-Net, and MERIT. HD95 is representedas HD95(NaN Ratio).
图 12. 我们的 HiDiff 与三种不同判别分割器(U-Net、SwinU-Net 和 MERIT)的定量结果。HD95 以 HD95(NaN 比率) 表示。
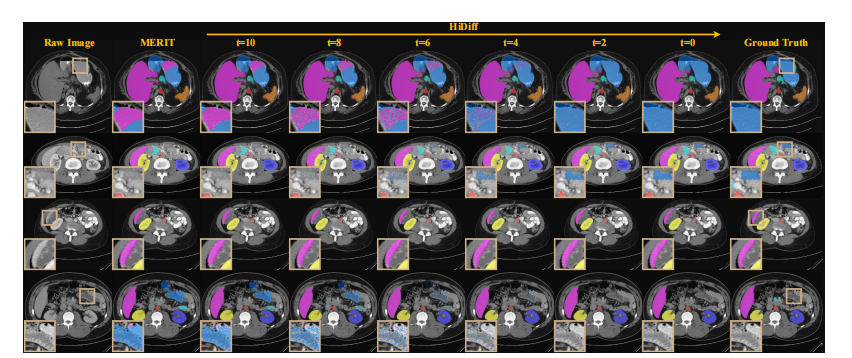
Fig. 13. Qualitative case study on the effectiveness of diffusion refinement process for four cases from the Synapse testing set (0025, 0004, 0002,and 0036).
图 13. 来自 Synapse 测试集(0025、0004、0002 和 0036)的四个案例中扩散优化过程有效性的定性案例研究。
Table
表
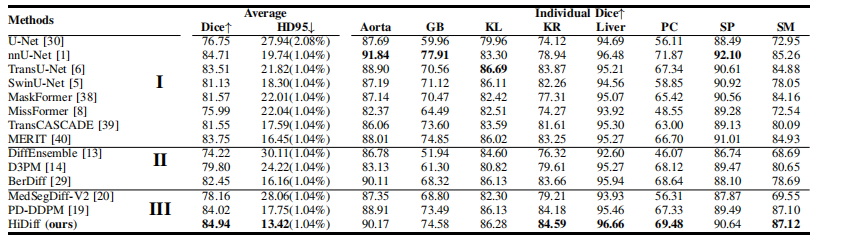
TABLE Iquantitative results on the synapse testing set. the hd95 is represented as hd95(nan ratio). i, ii, and iii represent discriminative, generative diffusion, and integrated methods, respectively.
表 ISynapse 测试集上的定量结果。HD95 以 HD95(NAN 比率) 表示。I、II 和 III 分别代表判别方法、生成扩散方法和集成方法。
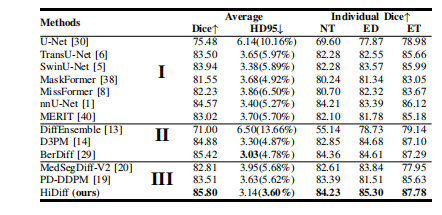
TABLE II quantitative results on the brats testing set. hd95 is represented as hd95(nan ratio). i, ii, and iii represent discriminative, generative diffusion, and integrated methods, respectively.
表 II BraTS 测试集上的定量结果。HD95 以 HD95(NAN 比率) 表示。I、II 和 III 分别代表判别方法、生成扩散方法和集成方法。
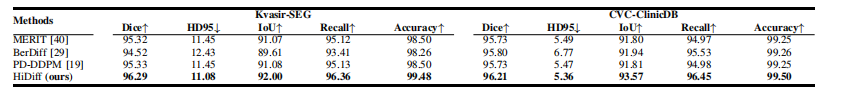
TABLE III quantitative results on the kvasir-seg and cvc-clinicdb testing sets. nan ratios are omitted because they are all 0.
表 III KVASIR-SEG 和 CVC-CLINICDB 测试集上的定量结果。NAN 比率省略,因为它们均为 0。
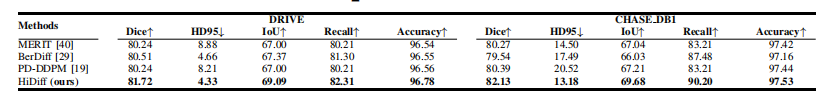
TABLE IVquantitative results on the drive and chase_db1 testing sets. nan ratios are omitted because they are all 0.
表 IVDRIVE 和 CHASE_DB1 测试集上的定量结果。NAN 比率省略,因为它们均为 0。
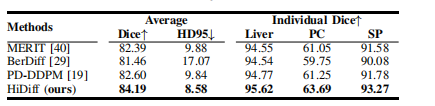
TABLE Vcross-dataset quantitative results of ct organ segmentation task. nan ratios are omitted because they are all 0.
表 VCT 器官分割任务的跨数据集定量结果。NAN 比率省略,因为它们均为 0。
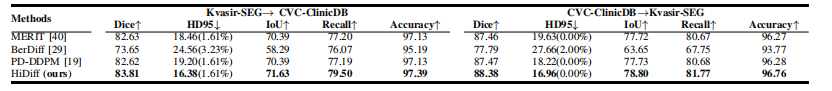
TABLE VI cross-dataset quantitative results of the polyps segmentation task using the kvasir-seg and cvc-clinicdb datasets. hd95 is represented as hd95(nan ratio).
表 VI使用 KVASIR-SEG 和 CVC-ClinicDB 数据集进行息肉分割任务的跨数据集定量结果。HD95 以 HD95(NAN 比率) 表示。
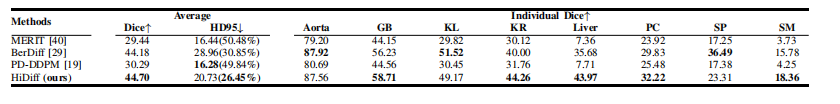
TABLE VII quantitative results on a small organ subset of the synapse testing set. the hd95 is represented as hd95(nan ratio).
表 VIISynapse 测试集小器官子集上的定量结果。HD95 以 HD95(NAN 比率) 表示
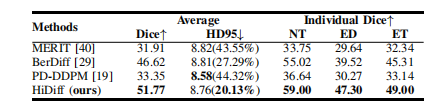
TABLE VIIIquantitative results on a small tumor subset of the brats testing set. the hd95 is represented as hd95(nan ratio).
表 VIIIBraTS 测试集小肿瘤子集上的定量结果。HD95 以 HD95(NAN 比率) 表示。

TABLE IX ablation results of diffusion refinement. nan ratios are omitted because they are all 1.04%
表 IX扩散优化的消融结果。NAN 比率省略,因为它们均为 1.04%。

TABLE X ablation results of training strategy, focal loss, x-former, and binarization. v1, v2, v3, v4, and v5 represent 5 implementations. nan ratios are omitted because they are all 1.04%.
表 X训练策略、Focal Loss、X-Former 和二值化的消融结果。V1、V2、V3、V4 和 V5 代表 5 种实现。NAN 比率省略,因为它们均为 1.04%。
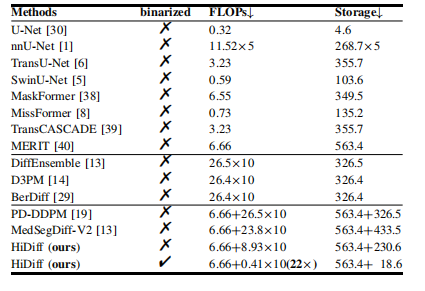
TABLE XI flops (×1010) and storage (mb) of different methods. note that for integrated methods, flops are presented as flops of discriminative segmentor + flops of a single forward process of the diffusion refiner × diffusion steps, and storage is presented as storage of discriminative segmentor + storage of diffusion refiner.
表 XI不同方法的 FLOPS(×1010)和存储(MB)。注意,对于集成方法,FLOPS 表示为判别分割器的 FLOPS + 单次前向过程的扩散优化器 FLOPS × 扩散步骤,存储表示为判别分割器的存储 + 扩散优化器的存储。