一、模型

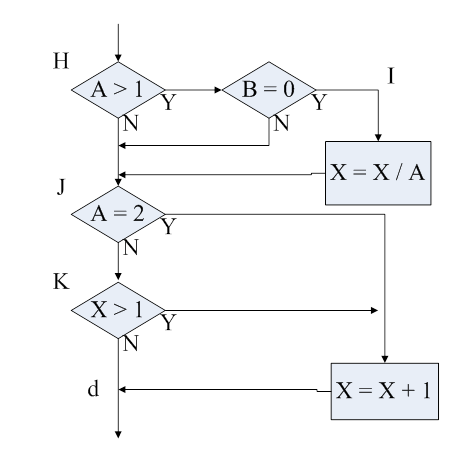
此模型主要由基础网络组成,其后是几个多尺度特征块。基本网络用于从输入图像中提取特征,因此它可以使用深度卷积神经网络。
单发多框检测选用了在分类层之前截断的VGG,现在也常用ResNet替代;可以设计基础网络,使它输出的高和宽较大,使基于该特征图生成的锚框数量较多,可以用来检测尺寸较小的目标。 接下来的每个多尺度特征块将上一层提供的特征图的高和宽缩小(如减半),并使特征图中每个单元在输入图像上的感受野变得更广阔。
1、类别预测层
%matplotlib inline
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from d2l import torch as d2l
def cls_predictor(num_inputs, num_anchors, num_classes):
#类别+1是因为加上了背景类别
return nn.Conv2d(num_inputs, num_anchors * (num_classes + 1),
kernel_size=3, padding=1)
2、边界框预测层
def bbox_predictor(num_inputs, num_anchors):
#边界框预测四个偏移,四条边
return nn.Conv2d(num_inputs, num_anchors * 4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
3、连结多尺度的预测
单发多框检测使用多尺度特征图来生成锚框并预测其类别和偏移量。 在不同的尺度下,特征图的形状或以同一单元为中心的锚框的数量可能会有所不同。 因此,不同尺度下预测输出的形状可能会有所不同。
def forward(x, block):
return block(x)
为了将这两个预测输出链接起来以提高计算效率,我们将把这些张量转换为更一致的格式。
def flatten_pred(pred):
#将通道维移到最后一维,是为了做展平时候同一个像素的框所判断的类是集中在一起的
return torch.flatten(pred.permute(0, 2, 3, 1), start_dim=1)
def concat_preds(preds):
return torch.cat([flatten_pred(p) for p in preds], dim=1)
4、高和宽减半块
def down_sample_blk(in_channels, out_channels):
blk = []
for _ in range(2):
blk.append(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels,
kernel_size=3, padding=1))
blk.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels))
blk.append(nn.ReLU())
in_channels = out_channels
blk.append(nn.MaxPool2d(2))
return nn.Sequential(*blk)
5、基本网络块
def base_net():
blk = []
num_filters = [3, 16, 32, 64]
for i in range(len(num_filters) - 1):
blk.append(down_sample_blk(num_filters[i], num_filters[i+1]))
return nn.Sequential(*blk)
forward(torch.zeros((2, 3, 256, 256)), base_net()).shape
6、完整的模型
def get_blk(i):
if i == 0:
blk = base_net()
elif i == 1:
blk = down_sample_blk(64, 128)
elif i == 4:
blk = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d((1,1))
else:
blk = down_sample_blk(128, 128)
return blk
def blk_forward(X, blk, size, ratio, cls_predictor, bbox_predictor):
Y = blk(X)
anchors = d2l.multibox_prior(Y, sizes=size, ratios=ratio)
cls_preds = cls_predictor(Y)
bbox_preds = bbox_predictor(Y)
return (Y, anchors, cls_preds, bbox_preds)
sizes = [[0.2, 0.272], [0.37, 0.447], [0.54, 0.619], [0.71, 0.79],
[0.88, 0.961]]
ratios = [[1, 2, 0.5]] * 5
num_anchors = len(sizes[0]) + len(ratios[0]) - 1
class TinySSD(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes, **kwargs):
super(TinySSD, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.num_classes = num_classes
idx_to_in_channels = [64, 128, 128, 128, 128]
for i in range(5):
# 即赋值语句self.blk_i=get_blk(i)
setattr(self, f'blk_{i}', get_blk(i))
setattr(self, f'cls_{i}', cls_predictor(idx_to_in_channels[i],
num_anchors, num_classes))
setattr(self, f'bbox_{i}', bbox_predictor(idx_to_in_channels[i],
num_anchors))
def forward(self, X):
anchors, cls_preds, bbox_preds = [None] * 5, [None] * 5, [None] * 5
for i in range(5):
# getattr(self,'blk_%d'%i)即访问self.blk_i
X, anchors[i], cls_preds[i], bbox_preds[i] = blk_forward(
X, getattr(self, f'blk_{i}'), sizes[i], ratios[i],
getattr(self, f'cls_{i}'), getattr(self, f'bbox_{i}'))
anchors = torch.cat(anchors, dim=1)
cls_preds = concat_preds(cls_preds)
cls_preds = cls_preds.reshape(
cls_preds.shape[0], -1, self.num_classes + 1)
bbox_preds = concat_preds(bbox_preds)
return anchors, cls_preds, bbox_preds
net = TinySSD(num_classes=1)
X = torch.zeros((32, 3, 256, 256))
anchors, cls_preds, bbox_preds = net(X)
print('output anchors:', anchors.shape)
print('output class preds:', cls_preds.shape)
print('output bbox preds:', bbox_preds.shape)
二、训练模型
1、定义损失函数和评价函数
第一种有关锚框类别的损失,可以简单地复用之前图像分类问题里一直使用的交叉熵损失函数来计算; 第二种有关正类锚框偏移量的损失:预测偏移量是一个回归问题
cls_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none')
#因为L2是平方,可能会特别大,我们就用绝对值的L1
bbox_loss = nn.L1Loss(reduction='none')
def calc_loss(cls_preds, cls_labels, bbox_preds, bbox_labels, bbox_masks):
batch_size, num_classes = cls_preds.shape[0], cls_preds.shape[2]
cls = cls_loss(cls_preds.reshape(-1, num_classes),
cls_labels.reshape(-1)).reshape(batch_size, -1).mean(dim=1)
bbox = bbox_loss(bbox_preds * bbox_masks,
bbox_labels * bbox_masks).mean(dim=1)
return cls + bbox
def cls_eval(cls_preds, cls_labels):
# 由于类别预测结果放在最后一维,argmax需要指定最后一维。
return float((cls_preds.argmax(dim=-1).type(
cls_labels.dtype) == cls_labels).sum())
def bbox_eval(bbox_preds, bbox_labels, bbox_masks):
return float((torch.abs((bbox_labels - bbox_preds) * bbox_masks)).sum())
2、训练模型
num_epochs, timer = 20, d2l.Timer()
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs],
legend=['class error', 'bbox mae'])
net = net.to(device)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# 训练精确度的和,训练精确度的和中的示例数
# 绝对误差的和,绝对误差的和中的示例数
metric = d2l.Accumulator(4)
net.train()
for features, target in train_iter:
timer.start()
trainer.zero_grad()
X, Y = features.to(device), target.to(device)
# 生成多尺度的锚框,为每个锚框预测类别和偏移量
anchors, cls_preds, bbox_preds = net(X)
# 为每个锚框标注类别和偏移量
bbox_labels, bbox_masks, cls_labels = d2l.multibox_target(anchors, Y)
# 根据类别和偏移量的预测和标注值计算损失函数
l = calc_loss(cls_preds, cls_labels, bbox_preds, bbox_labels,
bbox_masks)
l.mean().backward()
trainer.step()
metric.add(cls_eval(cls_preds, cls_labels), cls_labels.numel(),
bbox_eval(bbox_preds, bbox_labels, bbox_masks),
bbox_labels.numel())
cls_err, bbox_mae = 1 - metric[0] / metric[1], metric[2] / metric[3]
animator.add(epoch + 1, (cls_err, bbox_mae))
print(f'class err {cls_err:.2e}, bbox mae {bbox_mae:.2e}')
print(f'{len(train_iter.dataset) / timer.stop():.1f} examples/sec on '
f'{str(device)}')
三、预测目标
#根据锚框及其预测偏移量得到预测边界框,通过非极大值抑制来移除相似的预测边界框
def predict(X):
net.eval()
anchors, cls_preds, bbox_preds = net(X.to(device))
cls_probs = F.softmax(cls_preds, dim=2).permute(0, 2, 1)
output = d2l.multibox_detection(cls_probs, bbox_preds, anchors)
#筛选有效结果
idx = [i for i, row in enumerate(output[0]) if row[0] != -1]
return output[0, idx]
output = predict(X)
#筛选所有置信度不低于0.9的边界框
def display(img, output, threshold):
d2l.set_figsize((5, 5))
fig = d2l.plt.imshow(img)
for row in output:
score = float(row[1])
if score < threshold:
continue
h, w = img.shape[0:2]
bbox = [row[2:6] * torch.tensor((w, h, w, h), device=row.device)]
d2l.show_bboxes(fig.axes, bbox, '%.2f' % score, 'w')
display(img, output.cpu(), threshold=0.9)













![[职场] MARKETINGSPECIALIST是什么 #笔记#微信#知识分享](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/8f50fe4d19dba2d8913f70ce27c76c4d.png)