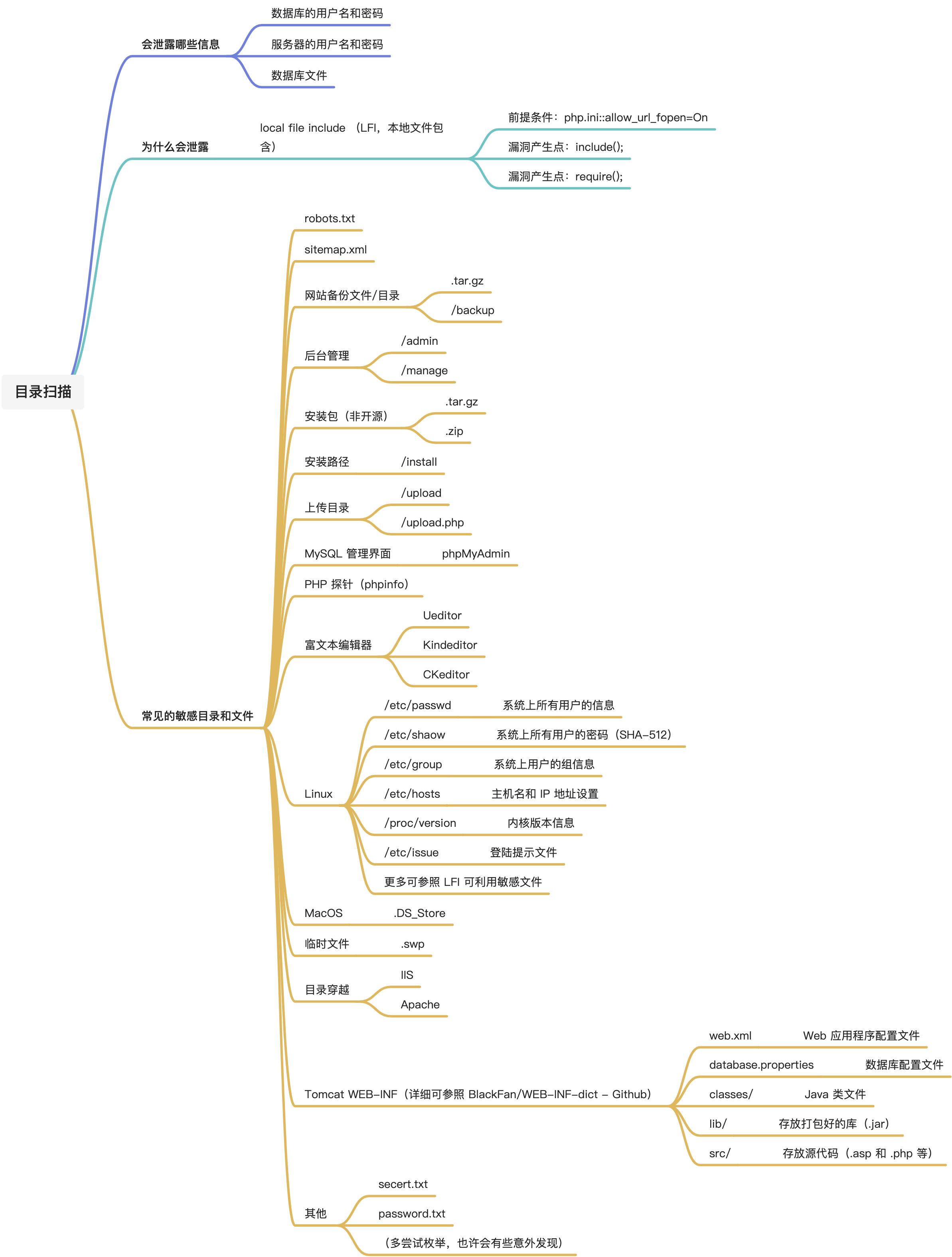
函数定义、合约与面向对象(以太坊solidity合约)
- 1-函数定义、构造与多态
- 2-事件日志
- 3-面向对象特征
1-函数定义、构造与多态
创建合约就是创建类,部署合约就是实例化
合约的方法还支持多态
还能使用第三方的库进行开发
整个合约部署后,函数就是代码的执行单元
https://learnblockchain.cn/docs/solidity/structure-of-a-contract.html#structure-functions
函数也是一种类型是值类型
pragma solidity >=0.6.1 <0.7.0;
// function (<parameter types>) {public private internal(默认)|external} [view|pure] [payable] [returns (<return types>)]
// 合约的函数支持多态(函数名称相同,参数类型或者数量不同)
contract FnDemo{
string _name; // 引用类型 + storage
uint _age; // 值类型不存在Data Location
// 构造函数,合约在部署时自动调用,一般用来初始化状态变量
//deploy部署时,需要输入两个参数
constructor(string memory name,uint age) public{
_name = name;
_age =age;
}
// private 仅仅在合约内部使用(所以合约部署后无法显示进行调用)
// constant 0.4的版本使用,没有修改状态变量时可以设置,0.5版本使用View,Pure代替
// view: 对状态变量(storage),只读但是不能写(状态变量部署会在账本,消耗gas)
function getAll() private view returns (string storage,uint){
return (_name,_age);
}
// public: 公共函数(当前、其它、继承的子合约都能调用), 如果参数引用类型必须设置内存变量memory
//从理论上将每个智能合约只能修改自己的状态变量,而不能修改别人的,即自己的storage不能让别人修改,所以设置为memory
// pure: 对状态变量不可读也不可写,在此函数中既没有操作状态变量,也没有读取
function getAll(string memory name,uint age) public pure returns (string memory,uint){
return (name,age+1);
}
// internal 受保护的函数,只能当前合约或者子合约调用
// payable: 说明此方法有转账的操作,后面金额转账的操作比较多
function getAll(string storage name) internal{
getAll(); // 调用自己的private合约
}
}

2-事件日志
Solidity无打印功能,调试不便
使用事件event和log日志
https://learnblockchain.cn/docs/solidity/structure-of-a-contract.html#event
通过事件写入日志
间接使用事件实现打印的功能
pragma solidity >=0.6.1 <0.7.0;
// solidity没有print,console.log方法,因此增加了调试的难度 ==> event + log来解决
contract LogTest{
// 事件名称采用驼峰命名法
event LogData(string,uint);
event LogData(string,string);
function show(string memory name,uint age) public{
age = age + 1;// 此处实现业务操作
emit LogData(name,age);
}
function show(string memory name,string memory age) public{
emit LogData(name,age);
}
}

这些日志也会随着合约的调用存储到分布式账本
如支付宝转账有备注,此日志也具有此功能,后续进行调用转账函数的时候,可以写日志的,一旦交易成功会跟随数据一起写入分布式账本中,交易往来
单机一个区块
有交易,合约交易(合约的创建、调用、销毁(以后合约不能再使用))
https://cn.etherscan.com/txsInternal?block=12548200
一般众筹完毕不再接受新的众筹金币,合约就会销毁


只要每笔交易确认,当前交易日志就会写到分布式账本(测试时解决打印难题)
3-面向对象特征
https://learnblockchain.cn/docs/solidity/contracts.html
Solidity多继承,python单继承
抽象合约,函数只有声明没有实现,交给自合约实现,抽象合约无法编译
https://learnblockchain.cn/docs/solidity/contracts.html#abstract-contract
库在后续课程实战调用第三方的库
好的需求,可维护,设计
pragma solidity >=0.6.0 <0.7.0;
// 手机OOP实现
// 每个手机都有一样的开机与关机功能
// 每个手机都有闹钟功能,但不同品牌的手机闹钟设计不同
// 品牌手机实现Wifi与BlueTooth,但有些老年机只实现Wifi或者BlueTooth.
interface Wifi{
// external 说明当前函数只能被外界调用
function wifi() external returns (string memory);
}
interface BlueTooth{
// external 说明当前函数只能被外界调用
function blue() external returns (string memory);
}
abstract contract Phone{ // 手机的父类(完成开机关机子)
event ShowCall(string);//事件方式调用手机开机功能
function start() internal{
emit ShowCall('调用手机开机功能');
}
function close() internal{
emit ShowCall('调用手机关机功能');
}
function alarm() virtual internal;//只有声明无实现(闹钟函数只能设计成抽象,每台手机对闹钟的实现各有不同,virtual 代表函数为抽象函数,solidity6)
}
继承抽象合约phone
contract Mi is Phone,Wifi{
//internal 不能被外界访问
function alarm() internal override(Phone){
emit ShowCall('小米实现闹钟功能');
}
function wifi() external override(Wifi) returns (string memory){
return "小米实现wifi功能";
}
}
contract Iphone is Phone,Wifi,BlueTooth{
function alarm() internal override(Phone){
emit ShowCall('华为实现闹钟功能');
}
function wifi() external override(Wifi) returns (string memory){
return "华为实现wifi功能";
}
function blue() external override(BlueTooth) returns (string memory){
return "华为实现blueTooth功能";
}
function callAlarm() public{
alarm();
}
}

需要再回来好好的看看
返回华为实现了wifi功能
接口、抽象函数、抽象方法、乃至于实现