1. ZooKeeper基本概念
Zookeeper官网:https://zookeeper.apache.org/index.html
- Zookeeper是Apache Hadoop项目中的一个子项目,是一个树形目录服务
- Zookeeper翻译过来就是动物园管理员,用来管理Hadoop(大象)、Hive(蜜蜂)、Pig(小猪)的管理员,简称zk
- Zookeeper的本质是一个分布式的、开源的、提供分布式应用程序协调服务的组件
- Zookeeper提供的主要功能有:
- 配置管理
- 分布式锁
- 集群管理
2. ZooKeeper常用命令
2.1 ZooKeeper数据模型
在正式介绍Zookeeper的常用命令之前,我们先来了解一下Zookeeper的相关数据模型:
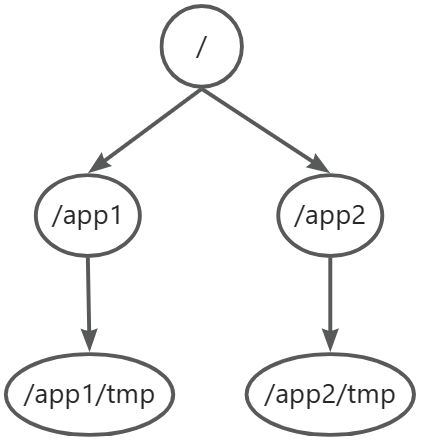
- Zookeeper的是一个树形目录服务,其数据模型与unix文件系统目录树类似,是一个层次化的结构
- 这里面的每一个节点都被称为ZNode,每个节点上都会保存自己的数据以及元数据信息
- 节点也可以拥有子节点,同时允许少量数据(1MB)存储在该节点之下
- 节点类型大致可以分为如下四类:
- PERSISTENT:持久化节点
- EPHEMERAL:临时节点 -e
- PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL:持久化顺序节点 -s
- EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL:临时顺序节点 -e -s
2.2 ZooKeeper常用命令
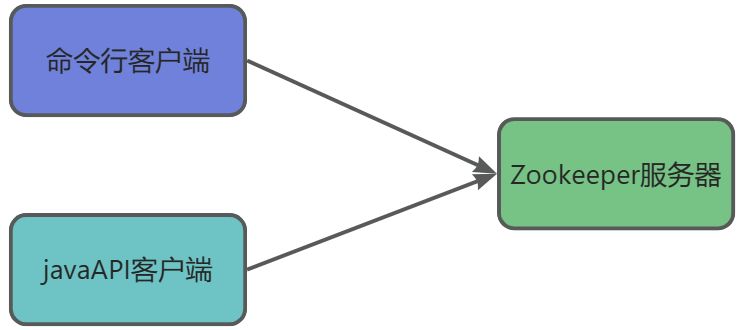
Zookeeper是一个常见的客户端-服务器模型,我们可以使用命令行或者JavaAPI的方式充当客户端进行访问,其架构如下图所示:
- 服务端命令:
./zkServer.sh start启动zookeeper服务
./zkServer.sh status查看zookeeper服务运行状态

./zkServer.sh restart重启zookeeper服务
./zkServer.sh stop关闭zookeeper服务

- 客户端命令:
./zkCli.sh -server ip:port连接指定的zookeeper服务(如连接本地可忽略选项直接使用./zkCli.sh)
quit退出客户端交互界面
help查看命令帮助

ls 目录查看指定目录下的znode节点

ls -s 目录查看节点详细信息
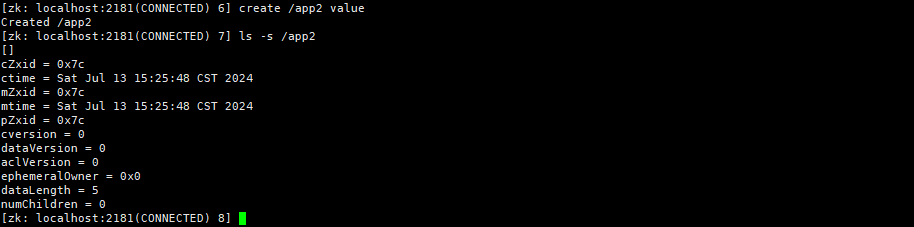
create znode [value]创建znode节点(可以携带data)

create znode -e [value]创建临时节点(会话结束后消失)create znode -s [value]创建顺序节点

get znode查看节点携带数据

set znode value设置节点数据

delete znode删除指定的znode节点(必须为空)

deleteall znode删除指定的znode节点及其子节点

2.3 ZooKeeper的JavaAPI操作
2.3.1 Curator介绍
Curator:是一个Zookeeper的Java客户端库
- 常见的Zookeeper Java客户端有如下几种:
- 原生JavaAPI
- ZkClient
- Curator
- Curator的目标就是简化Zookeeper客户端的使用
- Curator项目最初有Netflix公司研发,后来捐给了Apache基金会,成为顶级项目
Curator官网:http://curator.apache.org/
2.3.2 Curator API操作
2.3.2.1 建立连接
我们可以使用CuratorFrameworkFactory静态工厂类进行创建,可以通过如下两种方式配置:
- 使用
newClient()方法 - 使用
build()方法
下面我们就给出对应两种代码的实现方式:
newClient:
/**
* ZooKeeper测试类
*/
public class ZooKeeperTest {
private CuratorFramework client = null;
@Before
public void initByNewClient() {
CuratorFramework client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.newClient("127.0.0.1:2181",
3000,
3000,
new ExponentialBackoffRetry(3000, 1));
this.client = client;
this.client.start();
}
}
build:
/**
* ZooKeeper测试类
*/
public class ZooKeeperTest {
private CuratorFramework client = null;
@Before
public void init() {
CuratorFramework client = CuratorFrameworkFactory
.builder()
.connectString("127.0.0.1:2181")
.sessionTimeoutMs(3000)
.connectionTimeoutMs(3000)
.retryPolicy(new ExponentialBackoffRetry(3000, 1))
.namespace("")
.build();
client.start();
this.client = client;
}
}
其中各个配置项含义如下:
connectString:连接字符串,配置服务器地址,格式为ip:portsessionTimeoutMs:会话超时时间connectionTimeoutMs:连接超时时间retryPolicy:重试策略namespace:设置根目录位置
2.3.2.2 创建节点
创建节点有如下常见的四种方式:
Case1:创建节点(不携带数据)
@Test
public void testCreate1() throws Exception {
String path = client.create().forPath("/app1");
System.out.println(path);
}
Case2:创建节点(携带数据)
@Test
public void testCreate2() throws Exception {
String path = client.create().forPath("/app2", "curator java api".getBytes());
System.out.println(path);
}
Case3:创建多级节点
@Test
public void testCreate4() throws Exception {
client.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().forPath("/test/test1/test2");
}
Case4:创建节点并指定类型
@Test
public void testCreate3() throws Exception {
client.create().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL).forPath("/app3");
client.create().withMode(CreateMode.PERSISTENT).forPath("/app4");
client.create().withMode(CreateMode.PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL).forPath("/app5");
client.create().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL).forPath("/app6");
}
2.3.2.3 删除节点
删除节点有如下常见的两种方式:
Case1:删除节点(不含子节点)
@Test
public void testDelete() throws Exception {
client.delete().forPath("/app1");
}
Case2:删除节点(递归删除子节点)
@Test
public void testDeleteAll() throws Exception {
client.delete().deletingChildrenIfNeeded().forPath("/test");
}
2.3.2.4 查询节点
查询节点有如下常见的三种方式:
Case1:查询子节点信息
@Test
public void testGetChildren() throws Exception {
List<String> childrenList = client.getChildren().forPath("/");
System.out.println(childrenList);
}
Case2:查询节点数据
@Test
public void testGetData() throws Exception {
byte[] bytes = client.getData().forPath("/app2");
System.out.println("data: " + new String(bytes));
}
Case3:查询节点详细信息
@Test
public void testGetData3() throws Exception {
Stat stat = new Stat();
client.getData().storingStatIn(stat).forPath("/app2");
System.out.println(stat);
}
2.3.2.5 修改节点
修改节点有如下常见的两种方式:
Case1:修改节点数据
@Test
public void testSetData() throws Exception {
Stat stat = client.setData().forPath("/app1", "some data".getBytes());
System.out.println(stat);
}
Case2:修改节点数据(带有版本号)
@Test
public void testSetData2() throws Exception {
Stat stat = new Stat();
client.getData().storingStatIn(stat).forPath("/app2");
int version = stat.getVersion();
System.out.println(version);
client.setData().withVersion(version).forPath("/app2", "set with version".getBytes());
}
3. ZooKeeper的事件监听机制
Watcher事件监听机制:
- ZooKeeper允许用户在指定节点上注册一些Watcher,当一些特定事件发生时,ZooKeeper就会将事件通知给对其感兴趣的客户端,这是ZooKeeper提供分布式协调服务的重要特性
- ZooKeeper引入了Watcher机制来实现发布 / 订阅功能,能够让多个订阅者同时监听某一个对象,当一个对象状态发生变化时就会通知所有订阅者
- ZooKeeper提供原生Watcher的方式,但是比较麻烦,因此Curator使用Cache数据结构进行了优化实现监听机制
- Curator提供了如下三种Cache:
- NodeCache:只监听某一个指定的节点变化
- PathChildrenCache:监控一个节点的所有子节点
- TreeCache:监控整个树上的节点,类似于前两者的组合
3.1 Node Cache
代码实现:
@Test
public void testCuratorCache() throws Exception {
NodeCache cache = new NodeCache(client, "/app1");
cache.getListenable().addListener(new NodeCacheListener() {
@Override
public void nodeChanged() throws Exception {
System.out.println("监听到节点变化...");
}
});
cache.start();
while (true) {
}
}
3.2 PathChildren Cache
代码实现:
@Test
public void testPathChildrenCache() throws Exception {
PathChildrenCache cache = new PathChildrenCache(client, "/app1", true);
cache.getListenable().addListener(new PathChildrenCacheListener() {
@Override
public void childEvent(CuratorFramework curatorFramework, PathChildrenCacheEvent pathChildrenCacheEvent) throws Exception {
System.out.println("监听到子节点变化...");
PathChildrenCacheEvent.Type type = pathChildrenCacheEvent.getType();
if (type.equals(PathChildrenCacheEvent.Type.CHILD_UPDATED)) {
System.out.println("监听到子节点数据变化...");
System.out.println("更新后数据: " + pathChildrenCacheEvent.getData().getData());
}
}
});
cache.start();
while (true) {
}
}
3.3 Tree Cache
代码实现:
@Test
public void testTreeCache() throws Exception {
TreeCache cache = new TreeCache(client, "/app1");
cache.getListenable().addListener(new TreeCacheListener() {
@Override
public void childEvent(CuratorFramework curatorFramework, TreeCacheEvent treeCacheEvent) throws Exception {
System.out.println("监听到节点发生变化...");
System.out.println(treeCacheEvent);
}
});
cache.start();
while (true) {
}
}
4. ZooKeeper分布式锁
4.1 ZooKeeper分布式锁原理
- 核心思想:当用户获取到锁时就创建节点,使用完锁就删除节点
- 每当一个用户想要获取锁时就在
/lock节点下创建一个 **临时顺序 **节点 - 然后获取
/lock节点下的全部子节点,如果发现当前节点编号是最小的,则该节点对应的客户端获取到锁,使用完锁后,删除该节点 - 如果发现节点编号不是最小的,则对前一个比自己小的编号节点,并注册事件监听器,监听删除事件
- 如果后续发现比自己小的节点被删除,则客户端会接收到来自ZooKeeper的通知,然后再次判断所对应节点编号是否是最小的,重复上述步骤
注意:这里创建临时节点是因为防止获取到锁的客户端宕机了,进而导致锁永远不会被删的情况;这是创建顺序节点是方便编号的排序
Cutator提供了下面五种分布式锁的方式:
- InterProcessMutex(分布式可重入排他锁)
- InterProcessSemaphoreMutex(分布式不可重入排他锁)
- InterProcessReadWriteLock(分布式读写锁)
- InterProcessMutliLock(将多个锁作为单个实体管理的容器)
- InterProcessSemaphoreV2(共享信号量)
4.2 分布式锁实战(模拟12306抢票)
代码如下:
package org.example;
import org.apache.curator.framework.CuratorFramework;
import org.apache.curator.framework.CuratorFrameworkFactory;
import org.apache.curator.framework.recipes.locks.InterProcessMutex;
import org.apache.curator.retry.ExponentialBackoffRetry;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ZooKeeperLockTest {
private static int tickets = 10; // 票数
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 建立连接
CuratorFramework client = CuratorFrameworkFactory
.builder()
.connectString("127.0.0.1:2181")
.sessionTimeoutMs(3000)
.connectionTimeoutMs(3000)
.retryPolicy(new ExponentialBackoffRetry(3000, 1))
.namespace("")
.build();
client.start();
// 获取分布式锁
InterProcessMutex lock = new InterProcessMutex(client, "/lock");
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
boolean hasLock = lock.acquire(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (hasLock && tickets > 0) {
// 不断抢票
System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "抢到了当前第" + tickets + "张票");
tickets--;
if (tickets <= 0) {
break;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
lock.release();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}, "携程");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
boolean hasLock = lock.acquire(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (hasLock && tickets > 0) {
// 不断抢票
System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "抢到了当前第" + tickets + "张票");
tickets--;
if (tickets <= 0) {
break;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
lock.release();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}, "飞猪");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
5. ZooKeeper集群管理
Leader选举过程:
- ServerId:服务器ID
比如有三台服务器,编号分别是1,2,3。则编号越大在选择算法中的权重就越大
- Zxid:数据ID
服务器中存放的数据ID越大,值越大说明更新的越频繁,则在选择算法中的权重就越大
- 在Leader选举的过程中如果某台ZooKeeper超过了半数选票,则直接当选为Leader