目录
前言
原理解释
完整项目
相关文献
文章出处链接:[https://blog.csdn.net/qq_59075481/article/details/140334106]
前言
众所周知,DLL 注入有多种用途,如热修补、日志记录、子类化等。本文重点介绍使用 DLL 注入对窗口进行子类化。子类化是通过更改窗口过程来重新定义窗口的行为。要更改窗口过程,窗口过程应驻留在创建窗口的进程中。我计划通过注入子类化模块在不了解创建窗口的进程的情况下替换窗口行为。本文涉及三个模块。
- GUITestProcess:这是创建窗口的目标进程。称为“GUITestProcess”,DLL(“SubClassModule”)被注入其中。这是一个简单的 Win32 应用程序,它有一个窗口,每当按下鼠标左键时,就会绘制一个圆圈。
- SubClassModule:这是一个 DLL,它具有新的窗口过程,可以挂接到被注入者的窗口。
- Injector:这是实际将注入物注入被注入者的进程。这是一个简单的控制台应用程序。
原理解释
窗口子类化有两种实现方式:一种是 SetWindowLongPtr 指定 GWLP_WNDPROC 参数,替换窗口过程函数,另外一种是使用 ComCtl32.dll (至少 6.0 版本)导出的 SetWindowSubclass 来设置子类化窗口过程(另外几个函数分别是:GetWindowSubclass、RemoveWindowSubclass 和 DefSubclassProc),后者提供更多扩展特性。本文以最基础的 SetWindowLongPtr 子类化进行讲解。
首先是一个桌面窗口程序实例代码:
// GUITestProcess.cpp : 定义应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "framework.h"
#include "GUITestProcess.h"
#include <windowsx.h>
#define MAX_LOADSTRING 100
// Global Variables:
HINSTANCE hInst; // current instance
TCHAR szTitle[MAX_LOADSTRING]; // The title bar text
TCHAR szWindowClass[MAX_LOADSTRING]; // the main window class name
// Forward declarations of functions included in this code module:
ATOM MyRegisterClass(HINSTANCE hInstance);
BOOL InitInstance(HINSTANCE, int);
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND, UINT, WPARAM, LPARAM);
INT_PTR CALLBACK About(HWND, UINT, WPARAM, LPARAM);
int APIENTRY _tWinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance,
HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
LPTSTR lpCmdLine,
int nCmdShow)
{
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(hPrevInstance);
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(lpCmdLine);
// TODO: Place code here.
MSG msg;
HACCEL hAccelTable;
// Initialize global strings
LoadString(hInstance, IDS_APP_TITLE, szTitle, MAX_LOADSTRING);
LoadString(hInstance, IDC_INJECTEE, szWindowClass, MAX_LOADSTRING);
MyRegisterClass(hInstance);
// Perform application initialization:
if (!InitInstance(hInstance, nCmdShow))
{
return FALSE;
}
hAccelTable = LoadAccelerators(hInstance, MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDC_INJECTEE));
// Main message loop:
while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0))
{
if (!TranslateAccelerator(msg.hwnd, hAccelTable, &msg))
{
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
}
return (int)msg.wParam;
}
//
// FUNCTION: MyRegisterClass()
//
// PURPOSE: Registers the window class.
//
// COMMENTS:
//
// This function and its usage are only necessary if you want this code
// to be compatible with Win32 systems prior to the 'RegisterClassEx'
// function that was added to Windows 95. It is important to call this function
// so that the application will get 'well formed' small icons associated
// with it.
//
ATOM MyRegisterClass(HINSTANCE hInstance)
{
WNDCLASSEX wcex;
wcex.cbSize = sizeof(WNDCLASSEX);
wcex.style = CS_HREDRAW | CS_VREDRAW;
wcex.lpfnWndProc = WndProc;
wcex.cbClsExtra = 0;
wcex.cbWndExtra = 0;
wcex.hInstance = hInstance;
wcex.hIcon = LoadIcon(hInstance, MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDI_INJECTEE));
wcex.hCursor = LoadCursor(NULL, IDC_ARROW);
wcex.hbrBackground = (HBRUSH)(COLOR_WINDOW + 1);
wcex.lpszMenuName = MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDC_INJECTEE);
wcex.lpszClassName = szWindowClass;
wcex.hIconSm = LoadIcon(wcex.hInstance, MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDI_SMALL));
return RegisterClassEx(&wcex);
}
//
// FUNCTION: InitInstance(HINSTANCE, int)
//
// PURPOSE: Saves instance handle and creates main window
//
// COMMENTS:
//
// In this function, we save the instance handle in a global variable and
// create and display the main program window.
//
BOOL InitInstance(HINSTANCE hInstance, int nCmdShow)
{
HWND hWnd;
hInst = hInstance; // Store instance handle in our global variable
hWnd = CreateWindow(szWindowClass, szTitle, WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW,
CW_USEDEFAULT, 0, CW_USEDEFAULT, 0, NULL, NULL, hInstance, NULL);
if (!hWnd)
{
return FALSE;
}
ShowWindow(hWnd, nCmdShow);
UpdateWindow(hWnd);
return TRUE;
}
//
// FUNCTION: WndProc(HWND, UINT, WPARAM, LPARAM)
//
// PURPOSE: Processes messages for the main window.
//
// WM_COMMAND - process the application menu
// WM_PAINT - Paint the main window
// WM_DESTROY - post a quit message and return
//
//
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hWnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
int wmId, wmEvent;
PAINTSTRUCT ps;
HDC hdc;
switch (message)
{
case WM_LBUTTONDOWN:
{
int x = GET_X_LPARAM(lParam);
int y = GET_Y_LPARAM(lParam);
HDC hDC = ::GetDC(hWnd);
::Ellipse(hDC, x, y, (x + 50), (y + 50));
break;
}
case WM_COMMAND:
wmId = LOWORD(wParam);
wmEvent = HIWORD(wParam);
// Parse the menu selections:
switch (wmId)
{
case IDM_ABOUT:
DialogBox(hInst, MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDD_ABOUTBOX), hWnd, About);
break;
case IDM_EXIT:
DestroyWindow(hWnd);
break;
default:
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam);
}
break;
case WM_PAINT:
hdc = BeginPaint(hWnd, &ps);
// TODO: Add any drawing code here...
EndPaint(hWnd, &ps);
break;
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage(0);
break;
default:
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam);
}
return 0;
}
// Message handler for about box.
INT_PTR CALLBACK About(HWND hDlg, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(lParam);
switch (message)
{
case WM_INITDIALOG:
return (INT_PTR)TRUE;
case WM_COMMAND:
if (LOWORD(wParam) == IDOK || LOWORD(wParam) == IDCANCEL)
{
EndDialog(hDlg, LOWORD(wParam));
return (INT_PTR)TRUE;
}
break;
}
return (INT_PTR)FALSE;
}让我们看一下注入的源代码。众所周知,注入是一个简单的 DLL,当 DllMain 被调用时DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH,我正在进行 Hack。
//
case DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH:
{
//Find the window of the Injectee using its title
HWND hwnd = ::FindWindow(NULL,TEXT("GUITestProcess") );
//If the window found, then change it's window proc
if( hwnd )
{
oldWindowProc = ::SetWindowLongPtr( hwnd, GWLP_WNDPROC, (LONG_PTR) HackingWndProc );
}
break;
}新的窗口过程看起来像这样,这个窗口过程将替换原窗口的左键单击和右键单击操作:
LRESULT CALLBACK HackingWndProc(HWND hWnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
switch( message )
{
case WM_LBUTTONDOWN:
{
int x = GET_X_LPARAM(lParam);
int y = GET_Y_LPARAM(lParam);
HDC hDC = ::GetDC( hWnd );
//::Rectangle( hDC,x,y,(x+50),(y+50) );
DrawText( hDC,x,y);
break;
}
case WM_RBUTTONDOWN:
{
int x = GET_X_LPARAM(lParam);
int y = GET_Y_LPARAM(lParam);
HDC hDC = ::GetDC( hWnd );
::Ellipse( hDC,x,y,(x+50),(y+50));
break;
}
case WM_DESTROY:
{
PostQuitMessage(0);
break;
}
default:
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam);
}
return 0;
}接下来我们看一下 Injector 的源代码。
这段代码很简单,首先我们要知道要注入到目标进程(injectee)中的 DLL(SubClassModule)的名字。
这个DLL名称应该是目标进程知道的。因此,它必须写入目标进程的地址空间中。
- 使用窗口标题找出 GUITestProcess 的窗口。
- 接下来使用 创建窗口的进程的句柄 GetWindowThreadProcessId。
- 使用句柄打开注入者的进程。
- 通过命令行的参数获取要注入的 DLL 的路径。
- 然后在被注入者的地址空间中分配内存以写入要注入的 DLL 的名称。
- 获取 LoadLibrary 函数的地址。这是将在注入对象的地址空间中创建的线程要调用的方法。
- 然后调用 NtCreateThreadEx 在被注入者的地址空间内创建一个线程,这个线程将调用 LoadLibrary 函数来注入 DLL。
- 当线程调用 LoadLibrary 方法加载 DLL 时,DllMain 被调用的原因为 DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH。参阅注入的代码以查看 DllMain 调用时会发生什么。
- 等待远程线程执行完毕后再调用该 VirtualFree 方法,否则当远程线程查找 DLL 的名称时,保存 DLL 名称的地址块的名称已被注入器进程释放,这可能会导致崩溃!
注入器的命令行参数:注入器程序路径 Dll 文件路径。
注入器主要代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <windows.h>
#include <vector>
#include <tlhelp32.h>
#include <shlwapi.h>
#pragma comment(lib, "Shlwapi.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "advapi32.lib")
#define INJECTEE_NAME TEXT("GUITestProcess")
BOOL ProcessHasLoadDll(
DWORD pid,
const TCHAR* dll
);
BOOL ZwCreateThreadExInjectDll(
DWORD dwProcessId,
const wchar_t* pszDllFileName
);
int wmain(int argc, wchar_t* argv[])
{
SetConsoleTitleW(L"SubClassWindowsInjector v.1.0");
if (argc != 2)
{
std::cerr << "错误:参数不合法!" << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
return -1;
}
const size_t dllpthlen =
wcslen(argv[1]) * sizeof(wchar_t);
if (dllpthlen < 1)
{
std::cerr << "错误:文件路径错误!" << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
return -1;
}
wchar_t* dllpth = new wchar_t[dllpthlen];
wcscpy_s(dllpth, dllpthlen, argv[1]);
BOOL dllextflag = PathFileExistsW(dllpth);
if (FALSE == dllextflag)
{
std::cerr << "错误:文件不存在或者无法访问!" << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
return -1;
}
if (PathGetDriveNumberW(dllpth) == -1)
{
TCHAR szPath[_MAX_PATH] = { 0 };
TCHAR szDrive[_MAX_DRIVE] = { 0 };
TCHAR szDir[_MAX_DIR] = { 0 };
TCHAR szFname[_MAX_FNAME] = { 0 };
TCHAR szExt[_MAX_EXT] = { 0 };
TCHAR CurBinPath[MAX_PATH] = { 0 };
GetModuleFileNameW(NULL, szPath, sizeof(szPath) / sizeof(TCHAR));
ZeroMemory(CurBinPath, sizeof(CurBinPath));
_wsplitpath_s(szPath, szDrive, szDir, szFname, szExt);
wsprintf(CurBinPath, L"%s%s", szDrive, szDir);
wcscat_s(CurBinPath, dllpth);
dllextflag = PathFileExistsW(CurBinPath);
if (FALSE == dllextflag)
{
std::cerr << "错误:文件不存在或者无法访问!" << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
return -1;
}
dllpth = CurBinPath;
}
DWORD dwProcessID = 0;
//Find the main window of the Injectee
HWND hwnd = ::FindWindow(NULL, INJECTEE_NAME);
//Get the process hanlde of injectee
GetWindowThreadProcessId(hwnd, &dwProcessID);
if (dwProcessID == 0) {
std::cerr << "错误:找不到目标窗口!"<< std::endl;
return 0;
}
if (ProcessHasLoadDll(dwProcessID, dllpth) != NULL)
{
std::cerr << "警告:PID 为 " << dwProcessID << " 的进程已经包含目标 DLL。" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
if (ZwCreateThreadExInjectDll(dwProcessID, dllpth) == FALSE)
{
std::cerr << "错误:注入 PID 为 " << dwProcessID << " 的进程时失败。" << std::endl;
std::cerr << "原因:" << GetLastError() << std::endl;
return 1;
}
std::cout << "操作已经完成。" << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
return 0;
}
BOOL ProcessHasLoadDll(DWORD pid, const TCHAR* dll) {
/*
* 参数为TH32CS_SNAPMODULE 或 TH32CS_SNAPMODULE32时,如果函数失败并返回ERROR_BAD_LENGTH,则重试该函数直至成功
* 进程创建未初始化完成时,CreateToolhelp32Snapshot会返回error 299,但其它情况下不会
*/
HANDLE hSnapshot = CreateToolhelp32Snapshot(TH32CS_SNAPMODULE | TH32CS_SNAPMODULE32, pid);
while (INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE == hSnapshot) {
DWORD dwError = GetLastError();
if (dwError == ERROR_BAD_LENGTH) {
hSnapshot = CreateToolhelp32Snapshot(TH32CS_SNAPMODULE | TH32CS_SNAPMODULE32, pid);
continue;
}
else {
printf("CreateToolhelp32Snapshot failed: %d\ncurrentProcessId: %d \t targetProcessId:%d\n",
dwError, GetCurrentProcessId(), pid);
return FALSE;
}
}
MODULEENTRY32W mi{};
mi.dwSize = sizeof(MODULEENTRY32W); //第一次使用必须初始化成员
BOOL bRet = Module32FirstW(hSnapshot, &mi);
while (bRet) {
// mi.szModule是短路径
if (wcsstr(dll, mi.szModule) || wcsstr(mi.szModule, dll)) {
if (hSnapshot != NULL) CloseHandle(hSnapshot);
return TRUE;
}
mi.dwSize = sizeof(MODULEENTRY32W);
bRet = Module32NextW(hSnapshot, &mi);
}
if (hSnapshot != NULL) CloseHandle(hSnapshot);
return FALSE;
}
BOOL ZwCreateThreadExInjectDll(
DWORD dwProcessId,
const wchar_t* pszDllFileName
)
{
size_t pathSize = (wcslen(pszDllFileName) + 1) * sizeof(wchar_t);
// 1.打开目标进程
HANDLE hProcess = OpenProcess(
PROCESS_ALL_ACCESS, // 打开权限
FALSE, // 是否继承
dwProcessId); // 进程 PID
if (hProcess == nullptr)
{
printf("错误:打开目标进程失败!\n");
return FALSE;
}
// 2.在目标进程中申请空间
LPVOID lpPathAddr = VirtualAllocEx(
hProcess, 0, pathSize,
MEM_RESERVE | MEM_COMMIT,
PAGE_READWRITE);
if (lpPathAddr == nullptr)
{
printf("错误:在目标进程中申请空间失败!\n");
CloseHandle(hProcess);
return FALSE;
}
// 3.在目标进程中写入Dll路径
if (FALSE == WriteProcessMemory(
hProcess, lpPathAddr,
pszDllFileName, pathSize,
NULL)) // 实际写入大小
{
printf("错误:目标进程中写入Dll路径失败!\n");
CloseHandle(hProcess);
return FALSE;
}
//4.加载ntdll.dll
HMODULE hNtdll = GetModuleHandleW(L"ntdll.dll");
if (hNtdll == nullptr)
{
printf("错误:加载ntdll.dll失败!\n");
CloseHandle(hProcess);
return FALSE;
}
//5.获取LoadLibraryA的函数地址
//FARPROC可以自适应32位与64位
FARPROC pFuncProcAddr = GetProcAddress(GetModuleHandle(L"Kernel32.dll"),
"LoadLibraryW");
if (pFuncProcAddr == nullptr)
{
printf("错误:获取LoadLibrary函数地址失败!\n");
CloseHandle(hProcess);
return FALSE;
}
//6.获取ZwCreateThreadEx函数地址,该函数在32位与64位下原型不同
//_WIN64用来判断编译环境 ,_WIN32用来判断是否是Windows系统
#ifdef _WIN64
typedef DWORD(WINAPI* typedef_ZwCreateThreadEx)(
PHANDLE ThreadHandle,
ACCESS_MASK DesiredAccess,
LPVOID ObjectAttributes,
HANDLE ProcessHandle,
LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE lpStartAddress,
LPVOID lpParameter,
ULONG CreateThreadFlags,
SIZE_T ZeroBits,
SIZE_T StackSize,
SIZE_T MaximumStackSize,
LPVOID pUnkown
);
#else
typedef DWORD(WINAPI* typedef_ZwCreateThreadEx)(
PHANDLE ThreadHandle,
ACCESS_MASK DesiredAccess,
LPVOID ObjectAttributes,
HANDLE ProcessHandle,
LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE lpStartAddress,
LPVOID lpParameter,
BOOL CreateSuspended,
DWORD dwStackSize,
DWORD dw1,
DWORD dw2,
LPVOID pUnkown
);
#endif
typedef_ZwCreateThreadEx ZwCreateThreadEx =
(typedef_ZwCreateThreadEx)GetProcAddress(hNtdll, "ZwCreateThreadEx");
if (ZwCreateThreadEx == nullptr)
{
printf("错误:获取ZwCreateThreadEx函数地址失败!\n");
CloseHandle(hProcess);
return FALSE;
}
//7.在目标进程中创建远线程
HANDLE hRemoteThread = NULL;
DWORD lpExitCode = 0;
DWORD dwStatus = ZwCreateThreadEx(&hRemoteThread, PROCESS_ALL_ACCESS, NULL,
hProcess,
(LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE)pFuncProcAddr, lpPathAddr, 0, 0, 0, 0, NULL);
if (hRemoteThread == nullptr)
{
printf("错误:目标进程中创建线程失败!\n");
CloseHandle(hProcess);
return FALSE;
}
// 8.等待线程结束
WaitForSingleObject(hRemoteThread, -1);
GetExitCodeThread(hRemoteThread, &lpExitCode);
if (lpExitCode == 0)
{
printf("错误:目标进程中注入 DLL 失败,请检查提供的 DLL 是否有效!\n");
CloseHandle(hProcess);
return FALSE;
}
// 9.清理环境
VirtualFreeEx(hProcess, lpPathAddr, 0, MEM_RELEASE);
CloseHandle(hRemoteThread);
CloseHandle(hProcess);
FreeLibrary(hNtdll);
return TRUE;
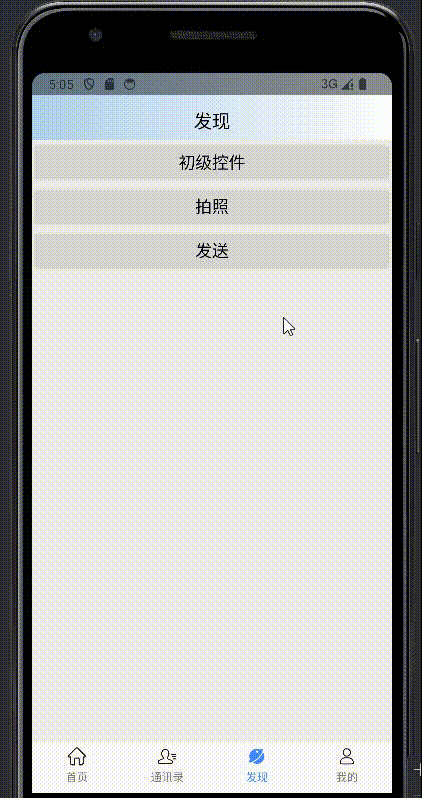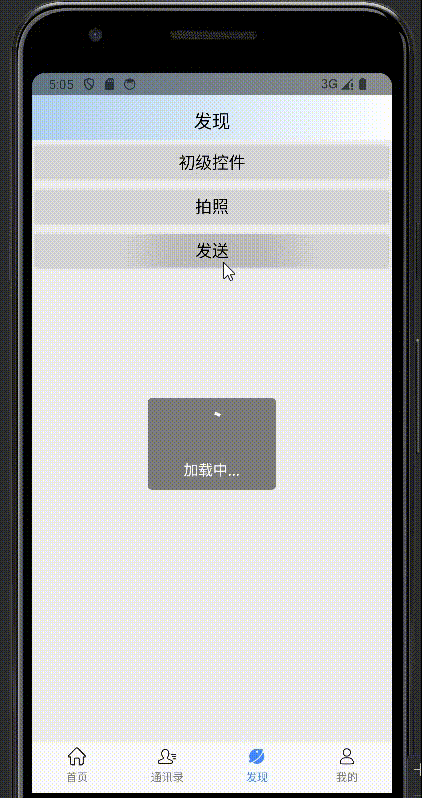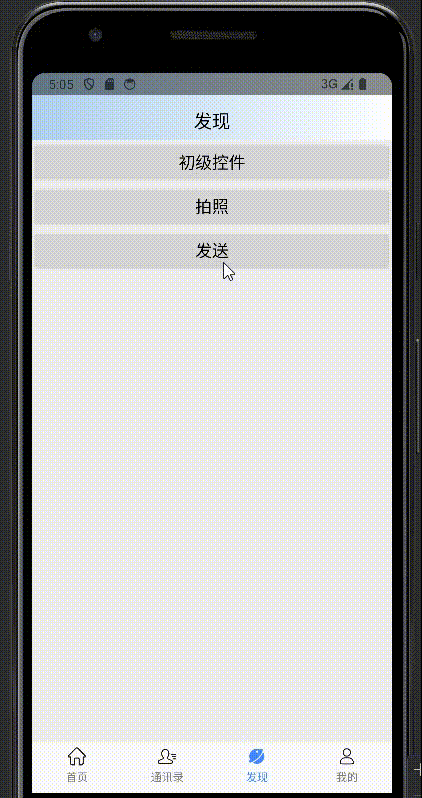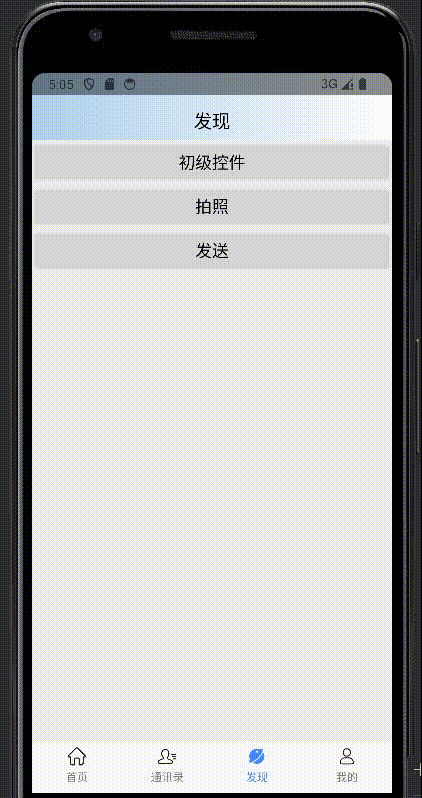
}子类化效果:

完整项目
你可以从这里获取完整的项目代码:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Q3og8dgv7lyzXsrGqZy4kg?pwd=6666
提取码:6666
相关文献
- https://www.cnblogs.com/1yzq/p/12939791.html
- https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/windows/win32/api/commctrl/nf-commctrl-setwindowsubclass
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/65695710/how-to-subclass-another-application-control-using-dll-hook-in-win32
- https://www.purebasic.fr/english/viewtopic.php?t=81714
文章出处链接:[https://blog.csdn.net/qq_59075481/article/details/140334106]。
本文发布于:2024.07.10,修改于:2024.07.10。