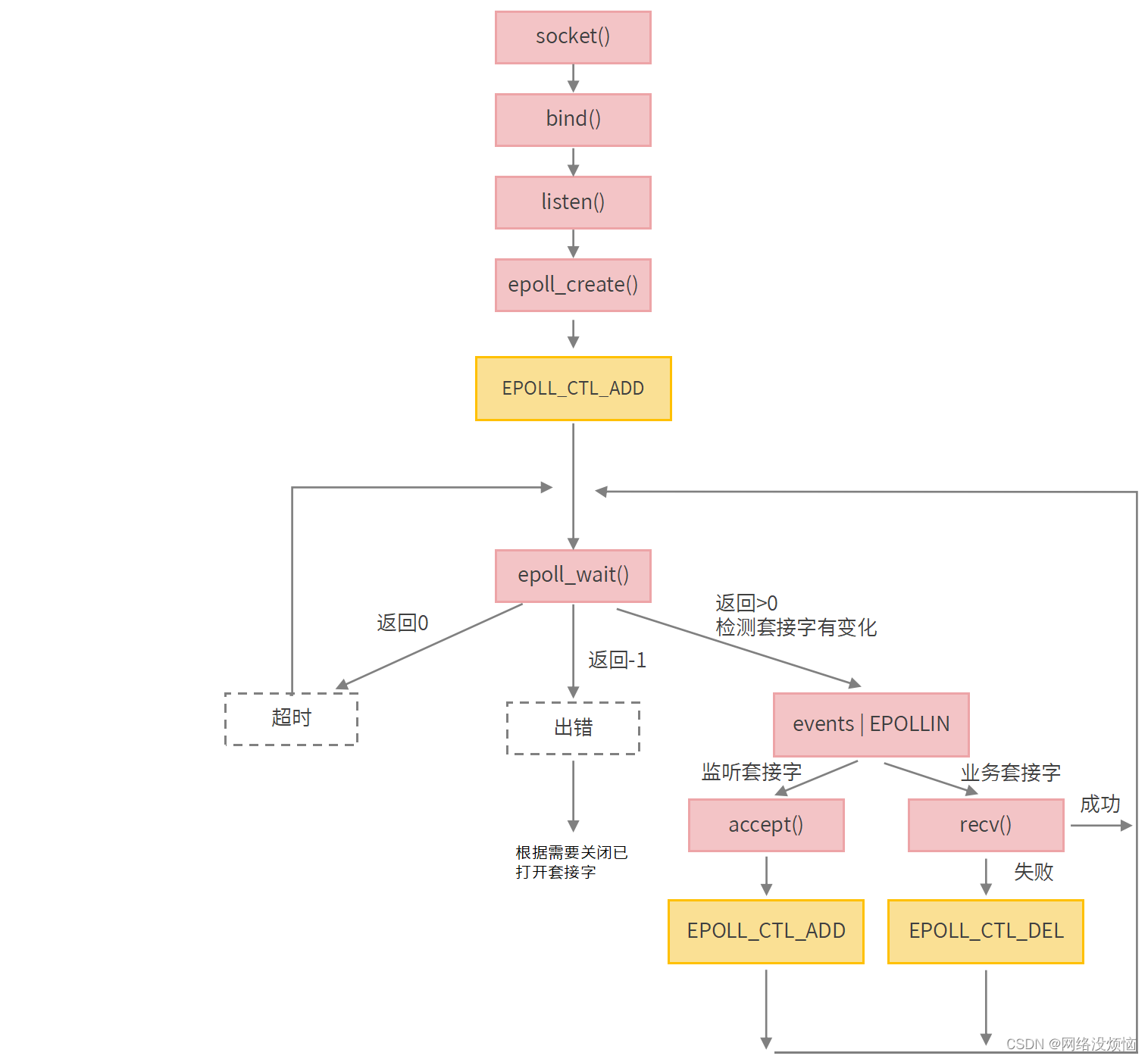
Scan
Scan操作是许多应用程序中常见的操作。扫描操作采用一个二元运算符⊕和一个输入数组并计算输出数组如下:
[x0,(x0⊕x1),…,( x0⊕x1⊕…..⊕xn-1)]
分层扫描和多种Scan算法介绍
Kogge-Stone's Algorithm
Kogge-Stone's Algorithm最初是为设计快速加法电路而发明的。该算法如今被用于设计高速计算机算术硬件。
图1是该算法的示例。

图1
Kogge-Stone's Algorithm,所有线程将迭代直到log2N步骤。
Kogge-Stone's Algorithm完成Scan操作所需的工作量接近Nlog2N。
Kogge-Stone's Algorithm将需要大约Nlog2N/P的时间步骤才能完成(P 执行单元的个数)。
Brent-Kung's Algorithm
Brent-Kung's Algorithm是Kogge-Stone's Algorithm的一个变种,它在计算中间结果时采取策略,以减少算法执行的工作量。
算法分为两个阶段:
降维树阶段
分发树阶段
图2是算法示例。

图2
Brent-Kung's Algorithm中,所有线程将迭代2log2N的步数。
Brent-Kung's Algorithm完成Scan操作所需的工作量接近于 2N - 2 - log2N。
Brent-Kung's Algorithm将需要大约(N / 2) * (2 * log2N - 1) / P的时间步数来完成(P 执行单元的个数)。 (由于 CUDA 设备设计该算法非常接近 Kogge-Stone's Algorithm)
三阶段Scan算法
三阶段Scan算法旨在实现比其他两种更高的工作效率。
该算法分为三个阶段:
独立扫描阶段(按块)
对先前独立扫描的最后元素进行扫描操作
将前一阶段的每个元素重新添加回块的最后阶段
图3是算法展示:

图3
具有T个线程完成的工作量是
1阶段N – 1
2阶段 Tlog2T
3阶段N- T
工作总量是 N – 1 + Tlog2T +N- T
如果我们使用P个执行单元,可以预计执行所需的时间。
花费(N – 1 + Tlog2T +N- T)/ P
分层Scan
上述描述的kernel在数据的输入大小方面有限制。
Kogge-Stone's Algorithm可以处理最多 threads-per-block个元素。
Brent-Kung's Algorithm可以处理最多2 * threads-per-block个元素。
三阶段扫描可以处理至多shared-memory / sizeof(T)个元素。
分层Scan算法旨在处理任意长度的输入。
图4是该算法展示:

图4
算法首先使用上述三种算法之一扫描输入的块,并将每个扫描的最后一个元素写入辅助数组。
然后扫描辅助数组。
并将每个元素i添加到index为 i + 1 的块中。
如果辅助数组足够大,它将使用相同的算法对其进行扫描。
Code
Host
host代码使用随机值初始化输入向量,并调用kernel执行Scan运算。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <ctime>
#include <cmath>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <thrust/host_vector.h>
#include <thrust/device_vector.h>
#include "helper_cuda.h"
#include "error.cuh"
#include "scanKernels.cuh"
const double EPSILON = 1.0e-10;
const int FORTIME = 50;
void check_result(thrust::host_vector<int>& h_res, thrust::host_vector<int> d_res, int n, std::string name) {
bool success = true;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (abs(h_res[i] - d_res[i]) > 0.001) {
std::cout << "Error at " << i << ":" << h_res[i] << "!=" << d_res[i] << std::endl;
success = false;
break;
}
}
std::cout << (success ? "Success!" : "Failed..") << "(" << name << ")" << std::endl;
}
int main(void)
{
int n1, n2, n3, n4, n5, n6;
n1 = 1024;
n2 = 1024;
n3 = 1024;
n4 = 2048;
n5 = 2048;
n6 = 2048;
thrust::host_vector<int> h_vec1(n1), h_vec2(n2), h_vec3(n3),
h_vec4(n4), h_vec5(n5), h_vec6(n6);
thrust::host_vector<int> h_res1(n1), h_res2(n2), h_res3(n3),
h_res4(n4), h_res5(n5), h_res6(n6);
thrust::device_vector<int> d_vec1(n1), d_vec2(n2), d_vec3(n3),
d_vec4(n4), d_vec5(n5), d_vec6(n6);
thrust::device_vector<int> d_res1(n1), d_res2(n2), d_res3(n3),
d_res4(n4), d_res5(n5), d_res6(n6);
std::fill(h_vec1.begin(), h_vec1.end(), 1);
std::fill(h_vec2.begin(), h_vec2.end(), 1);
std::fill(h_vec3.begin(), h_vec3.end(), 1);
std::fill(h_vec4.begin(), h_vec4.end(), 1);
std::fill(h_vec5.begin(), h_vec5.end(), 1);
std::fill(h_vec6.begin(), h_vec6.end(), 1);
thrust::inclusive_scan(h_vec1.begin(), h_vec1.end(), h_res1.begin());
thrust::inclusive_scan(h_vec2.begin(), h_vec2.end(), h_res2.begin());
thrust::inclusive_scan(h_vec3.begin(), h_vec3.end(), h_res3.begin());
thrust::inclusive_scan(h_vec4.begin(), h_vec4.end(), h_res4.begin());
thrust::inclusive_scan(h_vec5.begin(), h_vec5.end(), h_res5.begin());
thrust::inclusive_scan(h_vec6.begin(), h_vec6.end(), h_res6.begin());
cudaEvent_t start, stop;
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventCreate(&start));
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventCreate(&stop));
d_vec1 = h_vec1;
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventRecord(start));
for (int i = 0; i < FORTIME; i++)
Kogge_Stone_inclusive_scan<int> <<<1, 1024, 2048 * sizeof(int) >>> (
thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_vec1.data()), thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_res1.data()), n1
);
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventRecord(stop));
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventSynchronize(stop));
float elapsed_time;
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventElapsedTime(&elapsed_time, start, stop));
printf("Time = %g ms.\n", elapsed_time / FORTIME);
check_result(h_res1, d_res1, n1, std::string("Kogge Stone"));
d_vec2 = h_vec1;
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventRecord(start));
for (int i = 0; i < FORTIME; i++)
Brent_Kung_inclusive_scan<int> <<<1, 1024, 2048 * sizeof(int) >>> (
thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_vec2.data()), thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_res2.data()), n2
);
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventRecord(stop));
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventSynchronize(stop));
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventElapsedTime(&elapsed_time, start, stop));
printf("Time = %g ms.\n", elapsed_time / FORTIME);
check_result(h_res2, d_res2, n2, std::string("Brent Kung"));
d_vec3 = h_vec3;
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventRecord(start));
for (int i = 0; i < FORTIME; i++)
three_phase_parallel_inclusive_scan<int> <<<1, 512, 4096 * sizeof(int) >>> (
thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_vec3.data()), thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_res3.data()), n3, 4096
);
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventRecord(stop));
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventSynchronize(stop));
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventElapsedTime(&elapsed_time, start, stop));
printf("Time = %g ms.\n", elapsed_time / FORTIME);
check_result(h_res3, d_res3, n3, std::string("Three Phase Parallel"));
return 0;
}
Note:
helper_cuda.h 与error.cuh头文件为错误查验工具。后续会发布到Github。
去除checkCudaErrors等错误查验函数不影响程序运行。
以下是kernel的展示。
Kogge-Stone's Scan
// This kernel can handle up to min(shared_mem_size, max threads per block) / 2 elements
template<typename T> __global__
void Kogge_Stone_inclusive_scan(T *X, T *Y, int n, T *S = NULL){
extern __shared__ uint8_t shared_mem[];
T *XY = reinterpret_cast<T*>(shared_mem);
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
// Load elements into shared memory
if(i < n) XY[threadIdx.x] = X[i];
__syncthreads();
// Perform scan operation
for (unsigned int stride = 1; stride < blockDim.x; stride <<= 1){
if (threadIdx.x >= stride) XY[blockDim.x + threadIdx.x] = XY[threadIdx.x] + XY[threadIdx.x - stride];
__syncthreads();
if (threadIdx.x >= stride) XY[threadIdx.x] = XY[blockDim.x + threadIdx.x];
__syncthreads();
}
// Write results
// Write result to global memory
if (i < n) Y[i] = XY[threadIdx.x];
// Write last element to global memory
if (S != NULL && threadIdx.x == blockDim.x - 1)
S[blockIdx.x] = XY[blockDim.x - 1];
}kernel首先将输入数组中的元素加载到共享内存中。
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
// Load elements into shared memory
if(i < n) XY[threadIdx.x] = X[i];
__syncthreads();然后它执行扫描操作。
// Perform scan operation
for (unsigned int stride = 1; stride < blockDim.x; stride <<= 1){
if (threadIdx.x >= stride) XY[blockDim.x + threadIdx.x] = XY[threadIdx.x] + XY[threadIdx.x - stride];
__syncthreads();
if (threadIdx.x >= stride) XY[threadIdx.x] = XY[blockDim.x + threadIdx.x];
__syncthreads();
}元素写入输出数组,最后一个元素写入辅助数组。
// Write results to global memory
if (i < n) Y[i] = XY[threadIdx.x];
// Write last element to global memory
if (S != NULL && threadIdx.x == blockDim.x - 1)
S[blockIdx.x] = XY[blockDim.x - 1];Brent-Kung's Scan
// This kernel can handle up to min(shared_mem_size, max threads per block) elements
template<typename T> __global__
void Brent_Kung_inclusive_scan(T *X, T *Y, int n, T *S = NULL){
extern __shared__ uint8_t shared_mem[];
T *XY = reinterpret_cast<T*>(shared_mem);
int i = 2 * blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
int tx = threadIdx.x;
// Load elements into shared memory
XY[tx] = (i < n) ? X[i] : 0;
XY[tx + blockDim.x] = (i + blockDim.x < n) ? X[i + blockDim.x] : 0;
__syncthreads();
// Perform scan operation (Phase 1 - Reduction)
for (unsigned int stride = 1; stride <= blockDim.x; stride <<= 1){
unsigned int index = (tx + 1) * stride * 2 - 1;
if(index < 2 * blockDim.x) XY[index] += XY[index - stride];
__syncthreads();
}
// Perform scan operation (Phase 2 - Reverse-Tree)
for (unsigned int stride = blockDim.x / 2; stride > 0; stride >>= 1){
unsigned int index = (tx + 1) * stride * 2 - 1;
if(index + stride < 2 * blockDim.x) XY[index + stride] += XY[index];
__syncthreads();
}
// Write results
// Write result to global memory
if(i < n) Y[i] = XY[tx];
if(i + blockDim.x < n) Y[i + blockDim.x] = XY[tx + blockDim.x];
// Write last element to global memory
if (S != NULL && tx == blockDim.x - 1)
S[blockIdx.x] = XY[2 * blockDim.x - 1];
}kernel首先从全局内存中加载两组元素。
int i = 2 * blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
int tx = threadIdx.x;
// Load elements into shared memory
XY[tx] = (i < n) ? X[i] : 0;
XY[tx + blockDim.x] = (i + blockDim.x < n) ? X[i + blockDim.x] : 0;
__syncthreads();然后它进入了第一阶段的reduction。
// Perform scan operation (Phase 1 - Reduction)
for (unsigned int stride = 1; stride <= blockDim.x; stride <<= 1){
unsigned int index = (tx + 1) * stride * 2 - 1;
if(index < 2 * blockDim.x) XY[2 * blockDim.x + index] = XY[index] + XY[index - stride];
__syncthreads();
if(index < 2 * blockDim.x) XY[index] = XY[2 * blockDim.x + index];
__syncthreads();
}然后它进入了分发树的第二阶段。
// Perform scan operation (Phase 2 - Reverse-Tree)
for (unsigned int stride = blockDim.x / 2; stride > 0; stride >>= 1){
unsigned int index = (tx + 1) * stride * 2 - 1;
if(index + stride < 2 * blockDim.x) XY[2 * blockDim.x + index + stride] = XY[index + stride] + XY[index];
__syncthreads();
if(index + stride < 2 * blockDim.x) XY[index + stride] = XY[2 * blockDim.x + index + stride];
__syncthreads();
}元素被写入输出数组,最后一个元素写入辅助数组。
// Write results to global memory
if(i < n) Y[i] = XY[tx];
if(i + blockDim.x < n) Y[i + blockDim.x] = XY[tx + blockDim.x];
// Write last element to global memory
if (S != NULL && tx == blockDim.x - 1)
S[blockIdx.x] = XY[2 * blockDim.x - 1];Three-Phase-Scan Algorithm
template<typename T> __global__
void three_phase_parallel_inclusive_scan(T *X, T *Y, int n, int shared_mem_size, T *S = NULL){
extern __shared__ uint8_t shared_mem[];
T *XY = reinterpret_cast<T*>(shared_mem);
int start_pos = blockIdx.x * shared_mem_size;
int tx = threadIdx.x;
for(int j = tx; j < shared_mem_size; j += blockDim.x)
XY[j] = start_pos + j < n ? X[start_pos + j] : 0;
__syncthreads();
// Phase 1
// Scan each section
int size = shared_mem_size / blockDim.x;
int start = size * tx;
int stop = start + size;
T acc = 0;
if(start_pos + start < n) { // Threads that all their values are 0 do not execute (start > n)
for(int i = start; i < stop; ++i) {
acc += XY[i];
XY[i] = acc;
}
}
__syncthreads();
// Phase 2
// Use Brent-Kung algorithm to scan the last elements of each section
for (unsigned int stride = 1; stride <= blockDim.x; stride <<= 1){
__syncthreads();
unsigned int index = (tx + 1) * stride * 2 * size - 1;
if(index < shared_mem_size) XY[index] += XY[index - (stride * size)];
}
for (unsigned int stride = shared_mem_size / 4; stride >= size; stride >>= 1){
__syncthreads();
unsigned int index = (tx + 1) * stride * 2 - 1;
if(index + stride < shared_mem_size) XY[index + stride] += XY[index];
}
__syncthreads();
// Phase 3
// Add the last elements of each section to the next section
if(tx != 0) {
int value = XY[start - 1];
for(int i = start; i < stop - 1; ++i)
XY[i] += value;
}
__syncthreads();
// Write results
// Write result to global memory
for(int i = tx; i < shared_mem_size; i += blockDim.x)
if(start_pos + i < n)
Y[start_pos + i] = XY[i];
// Write last element to global memory
if (S != NULL && tx == blockDim.x - 1)
S[blockIdx.x] = XY[shared_mem_size - 1];
}kernel首先从全局内存加载元素。
int start_pos = blockIdx.x * shared_mem_size;
int tx = threadIdx.x;
for(int j = tx; j < shared_mem_size; j += blockDim.x)
XY[j] = start_pos + j < n ? X[start_pos + j] : 0;
__syncthreads();然后每个线程在自己的部分执行顺序扫描。
// Phase 1
// Scan each section
int size = shared_mem_size / blockDim.x;
int start = size * tx;
int stop = start + size;
T acc = 0;
if(start_pos + start < n) { // Threads that all their values are 0 do not execute (start > n)
for(int i = start; i < stop; ++i) {
acc += XY[i];
XY[i] = acc;
}
}
__syncthreads();然后使用Brent-Kung algorithm扫描每个部分的最后一个元素。
然后除了第一个线程外,所有线程将对应于前一个线程的元素写入它们的元素。
// Phase 3
// Add the last elements of each section to the next section
if(tx != 0) {
int value = XY[start - 1];
for(int i = start; i < stop - 1; ++i)
XY[i] += value;
}
__syncthreads();元素被写入输出数组,最后一个元素写入辅助数组。
// Write results
// Write result to global memory
for(int i = tx; i < shared_mem_size; i += blockDim.x)
if(start_pos + i < n)
Y[start_pos + i] = XY[i];
// Write last element to global memory
if (S != NULL && tx == blockDim.x - 1)
S[blockIdx.x] = XY[shared_mem_size - 1];分层Scan
template<typename T>
void hierarchical_scan_using_algorithm(T *X, T *Y, int n, int t_x, int shared_mem_size, int elems_per_block){
T *d_S;
int blocks = (n + elems_per_block - 1) / elems_per_block;
// Allocate memory on the device for the intermediate results
cudaMalloc((void **)&d_S, blocks * sizeof(T));
// Perform scan operation
algorithm<T><<<blocks, t_x, shared_mem_size * sizeof(T), launch.get_stream()>>>(
X, Y, n, shared_mem_size, d_S);
if(blocks > elems_per_block)
hierarchical_scan_three_phase<T>(d_S, d_S, blocks, t_x, shared_mem_size, elems_per_block, launch);
if(blocks > 1){
if(blocks <= elems_per_block)
algorithm<T><<<1, t_x, shared_mem_size * sizeof(T), launch.get_stream()>>>(
d_S, d_S, blocks, shared_mem_size, NULL);
// Add the intermediate results to the final results
add_intermediate_results<T><<<blocks - 1, t_x, 0, launch.get_stream()>>>(
Y + elems_per_block, n - elems_per_block, d_S, elems_per_block);
}
// Free memory on the device
cudaFree(d_S);
}kernel首先计算输入将被分割成多少块。
int blocks = (n + elems_per_block - 1) / elems_per_block;然后它在设备上为中间结果分配内存。
// Allocate memory on the device for the intermediate results
cudaMalloc((void **)&d_S, blocks * sizeof(T));然后,它对每个块执行扫描操作,并将最后一个元素写入辅助数组。
// Perform scan operation
algorithm<T><<<blocks, t_x, shared_mem_size * sizeof(T), launch.get_stream()>>>(
X, Y, n, shared_mem_size, d_S);如果块的数量大于每个块的元素数量,则递归调用该算法来扫描整个辅助数组。
if(blocks > elems_per_block)
hierarchical_scan_three_phase<T>(d_S, d_S, blocks, t_x, shared_mem_size, elems_per_block, launch);或者我们使用基本算法来扫描辅助阵列。
if(blocks <= elems_per_block)
algorithm<T><<<1, t_x, shared_mem_size * sizeof(T), launch.get_stream()>>>(
d_S, d_S, blocks, shared_mem_size, NULL);最后,如果块的数量大于1(意味着我们需要分发结果),我们调用kernel,将辅助数组添加到最终输出中。
// Add the intermediate results to the final results
add_intermediate_results<T><<<blocks - 1, t_x, 0, launch.get_stream()>>>(
Y + elems_per_block, n - elems_per_block, d_S, elems_per_block);性能分析
运行时间:
向量维度:1024
线程块维度:1024 (Three-Phase-Scan Algorithm为512)

Kogge_Stone 比 Brent_Kung 加法次数多,但是在计算资源充足情况下,纵向计算要小于Brent_Kung。计算资源充足情况下,在计算时间上Kogge_Stone 可能比 Brent_Kung 占优势,这也可能是因为Brent_Kung算法的复杂性增加。Three Phase Scan Algorithm优势在于可以计算shared-memory / sizeof(T)个元素,在不分层的情况下,一次能计算元素最多。
笔者采用设备:RTX3060 6GB
参考文献:
1、大规模并行处理器编程实战(第2版)
2、PPMP