目录
1.RPN
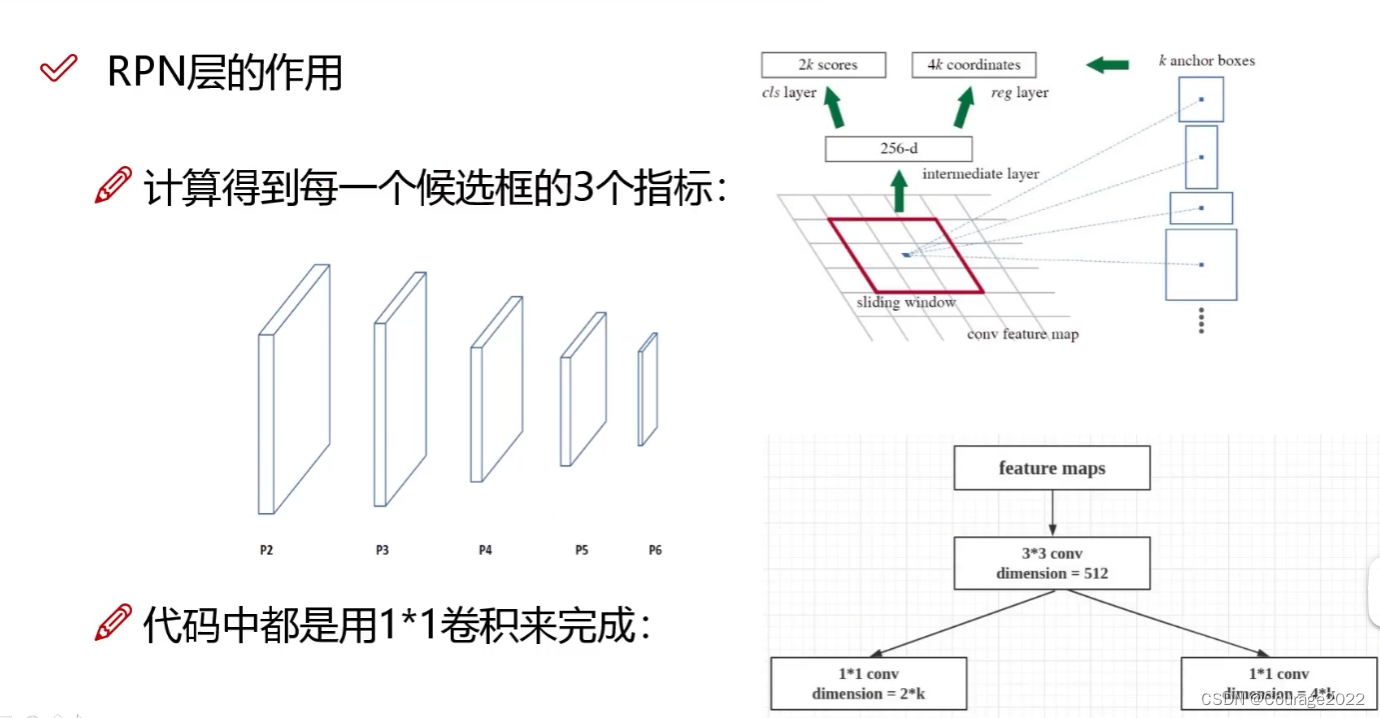
1.1 RPN层的作用与实现解读
1.2 候选框过滤ProposalLayer层
2. DetectionTargetType层
2.1 DetectionTargetType层作用
2.2 正负样本选择与标签定义
1.RPN
1.1 RPN层的作用与实现解读
上篇博客中我们解释了如何通过generate_pyramid_anchors在每一个特征层上生成anchors,而这些框只是一些随便框的一些框而已,而物体检测我们最终框出来的框是物体所在位置的框。
在RPN层中:我们要做的是将由generate_pyramid_anchors函数生成的每一个生成的候选框简单的划分为前景和背景。即是一个物体/不是一个物体。
如上图:对于每个候选框(共k个)我们要得到对其进行二分类(对每个anchor)得到2k个分数,分数代表其是前景/背景概率;要进行候选框参数的回归,因为我们在generate_pyramid_anchors函数中是随机生成的候选框,大小和真实物体大小指定不一样,因此我们要通过回归对k个框体微调其框体的修正值(
)。
# RPN Model rpn = build_rpn_model(config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE, len(config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS), 256)def build_rpn_model(anchor_stride, anchors_per_location, depth): """Builds a Keras model of the Region Proposal Network. It wraps the RPN graph so it can be used multiple times with shared weights. anchors_per_location: number of anchors per pixel in the feature map anchor_stride: Controls the density of anchors. Typically 1 (anchors for every pixel in the feature map), or 2 (every other pixel). depth: Depth of the backbone feature map. Returns a Keras Model object. The model outputs, when called, are: rpn_logits: [batch, H, W, 2] Anchor classifier logits (before softmax) rpn_probs: [batch, W, W, 2] Anchor classifier probabilities. rpn_bbox: [batch, H, W, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))] Deltas to be applied to anchors. """ input_feature_map = KL.Input(shape=[None, None, depth], name="input_rpn_feature_map") outputs = rpn_graph(input_feature_map, anchors_per_location, anchor_stride) return KM.Model([input_feature_map], outputs, name="rpn_model")对于输入:
经过
的卷积层后它的通道数仍然为256。
# Region Proposal Network (RPN) def rpn_graph(feature_map, anchors_per_location, anchor_stride): """Builds the computation graph of Region Proposal Network. feature_map: backbone features [batch, height, width, depth] anchors_per_location: number of anchors per pixel in the feature map anchor_stride: Controls the density of anchors. Typically 1 (anchors for every pixel in the feature map), or 2 (every other pixel). Returns: rpn_logits: [batch, H, W, 2] Anchor classifier logits (before softmax) rpn_probs: [batch, H, W, 2] Anchor classifier probabilities. rpn_bbox: [batch, H, W, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))] Deltas to be applied to anchors. """ # TODO: check if stride of 2 causes alignment issues if the featuremap # is not even. # Shared convolutional base of the RPN shared = KL.Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu', strides=anchor_stride, name='rpn_conv_shared')(feature_map) # Anchor Score. [batch, height, width, anchors per location * 2]. x = KL.Conv2D(2 * anchors_per_location, (1, 1), padding='valid', activation='linear', name='rpn_class_raw')(shared) # Reshape to [batch, anchors, 2] rpn_class_logits = KL.Lambda( lambda t: tf.reshape(t, [tf.shape(t)[0], -1, 2]))(x) # Softmax on last dimension of BG/FG. rpn_probs = KL.Activation( "softmax", name="rpn_class_xxx")(rpn_class_logits) # Bounding box refinement. [batch, H, W, anchors per location, depth] # where depth is [x, y, log(w), log(h)] x = KL.Conv2D(anchors_per_location * 4, (1, 1), padding="valid", activation='linear', name='rpn_bbox_pred')(shared) # Reshape to [batch, anchors, 4] rpn_bbox = KL.Lambda(lambda t: tf.reshape(t, [tf.shape(t)[0], -1, 4]))(x) return [rpn_class_logits, rpn_probs, rpn_bbox]这里shared为共享卷积,即每一特征层都经过这个
的卷积。
得分值:anchors_per_location = 3,即得到6个结果值(前景和背景的三个anchor的分数值)。rpn_class_logits 得到的是[ x , 2 ]的分数值,即对每一个框体的前景/背景的预测分数,在对其进行softmax处理,得到 rpn_probs ,存储着每一个框体的前景/背景的概率。
边界框修正值:存储在rpn_bbox中,shape为[ x , 4 ]的形式。
返回给上层函数的是每一个框体的前景/背景的分数值、前景/背景的概率、边界框的回归微调值。
# Loop through pyramid layers layer_outputs = [] # list of lists for p in rpn_feature_maps: layer_outputs.append(rpn([p]))将我们在上篇博客计算出来的特征图放入layer_outputs列表中。
# Concatenate layer outputs # Convert from list of lists of level outputs to list of lists # of outputs across levels. # e.g. [[a1, b1, c1], [a2, b2, c2]] => [[a1, a2], [b1, b2], [c1, c2]] output_names = ["rpn_class_logits", "rpn_class", "rpn_bbox"] outputs = list(zip(*layer_outputs)) outputs = [KL.Concatenate(axis=1, name=n)(list(o)) for o, n in zip(outputs, output_names)]对每个特征图均进行RPN操作。
1.2 候选框过滤ProposalLayer层
这里主要是处理generate_pyramid_anchors生成的的候选框进行过滤,过滤的依据是1.1节中计算出的参数,具体如下:
①对20W+候选框进行过滤,先按照前景得分排序。(因为20多万个框大部分是没用的)
②取前2000个得分高的,把之前得到的每个框回归值都利用上。(微调)③NMS再过滤。
代码部分如下:
# Generate proposals # Proposals are [batch, N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in normalized coordinates # and zero padded. proposal_count = config.POST_NMS_ROIS_TRAINING if mode == "training"\ else config.POST_NMS_ROIS_INFERENCE rpn_rois = ProposalLayer(proposal_count=proposal_count, nms_threshold=config.RPN_NMS_THRESHOLD, name="ROI", anchors=self.anchors, config=config)([rpn_class, rpn_bbox])这里proposal_count = 2000,即对200000+个候选框只选前两千个前景得分高的框体。
ProposalLayer的类定义如下:
class ProposalLayer(KE.Layer): """Receives anchor scores and selects a subset to pass as proposals to the second stage. Filtering is done based on anchor scores and non-max suppression to remove overlaps. It also applies bounding box refinement deltas to anchors. Inputs: rpn_probs: [batch, anchors, (bg prob, fg prob)] rpn_bbox: [batch, anchors, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))] Returns: Proposals in normalized coordinates [batch, rois, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] """ def __init__(self, proposal_count, nms_threshold, anchors, config=None, **kwargs): """ anchors: [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] anchors defined in image coordinates """ super(ProposalLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs) self.config = config self.proposal_count = proposal_count self.nms_threshold = nms_threshold self.anchors = anchors.astype(np.float32) def call(self, inputs): # Box Scores. Use the foreground class confidence. [Batch, num_rois, 1] scores = inputs[0][:, :, 1] # Box deltas [batch, num_rois, 4] deltas = inputs[1] deltas = deltas * np.reshape(self.config.RPN_BBOX_STD_DEV, [1, 1, 4]) # Base anchors anchors = self.anchors # Improve performance by trimming to top anchors by score # and doing the rest on the smaller subset. pre_nms_limit = min(6000, self.anchors.shape[0]) ix = tf.nn.top_k(scores, pre_nms_limit, sorted=True, name="top_anchors").indices scores = utils.batch_slice([scores, ix], lambda x, y: tf.gather(x, y), self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU) deltas = utils.batch_slice([deltas, ix], lambda x, y: tf.gather(x, y), self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU) anchors = utils.batch_slice(ix, lambda x: tf.gather(anchors, x), self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU, names=["pre_nms_anchors"]) # Apply deltas to anchors to get refined anchors. # [batch, N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] boxes = utils.batch_slice([anchors, deltas], lambda x, y: apply_box_deltas_graph(x, y), self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU, names=["refined_anchors"]) # Clip to image boundaries. [batch, N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] height, width = self.config.IMAGE_SHAPE[:2] window = np.array([0, 0, height, width]).astype(np.float32) boxes = utils.batch_slice(boxes, lambda x: clip_boxes_graph(x, window), self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU, names=["refined_anchors_clipped"]) # Filter out small boxes # According to Xinlei Chen's paper, this reduces detection accuracy # for small objects, so we're skipping it. # Normalize dimensions to range of 0 to 1. normalized_boxes = boxes / np.array([[height, width, height, width]]) # Non-max suppression def nms(normalized_boxes, scores): indices = tf.image.non_max_suppression( normalized_boxes, scores, self.proposal_count, self.nms_threshold, name="rpn_non_max_suppression") proposals = tf.gather(normalized_boxes, indices) # Pad if needed padding = tf.maximum(self.proposal_count - tf.shape(proposals)[0], 0) proposals = tf.pad(proposals, [(0, padding), (0, 0)]) return proposals proposals = utils.batch_slice([normalized_boxes, scores], nms, self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU) return proposals def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape): return (None, self.proposal_count, 4)在ProposalLayer执行中(__call__):
①将RPN层的结果拿出来:前景得分值scores、边界框回归参数deltas、生成的框体anchors。
②判断要留下多少个候选框pre_nms_limit = min(pre_nms_limit / 6000)(proposal_count 没用到吗???开始不是2000怎么变成6000了???NMS用到了)并按照得分值确定我们要保留边界框的索引ix。
③根据索引ix取到框体得分score、边界框回归参数deltas及原始anchor信息anchors。
④apply_box_deltas_graph方法是根据原始anchor信息及边界框回归参数deltas对边界框进行微调将调整后的6000个框体保留在box变量中。
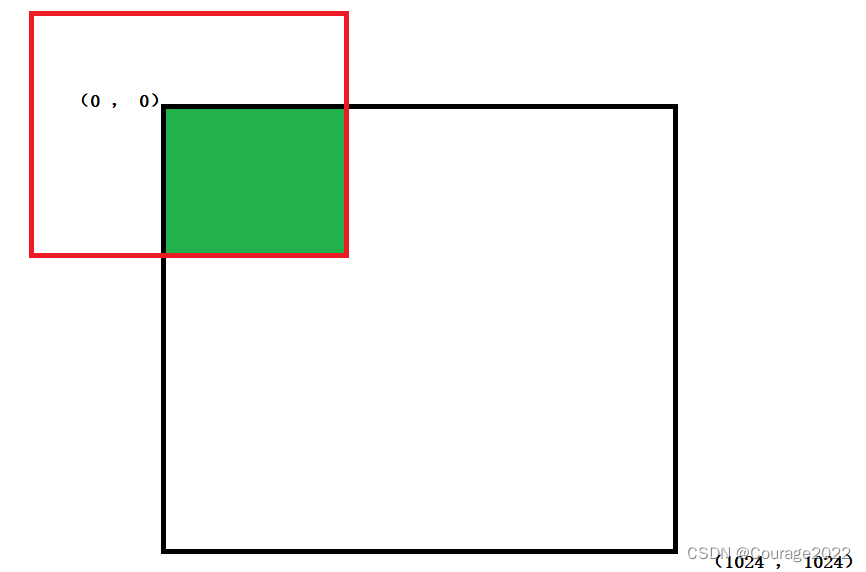
⑤由于微调后的框可能会出现越界问题:
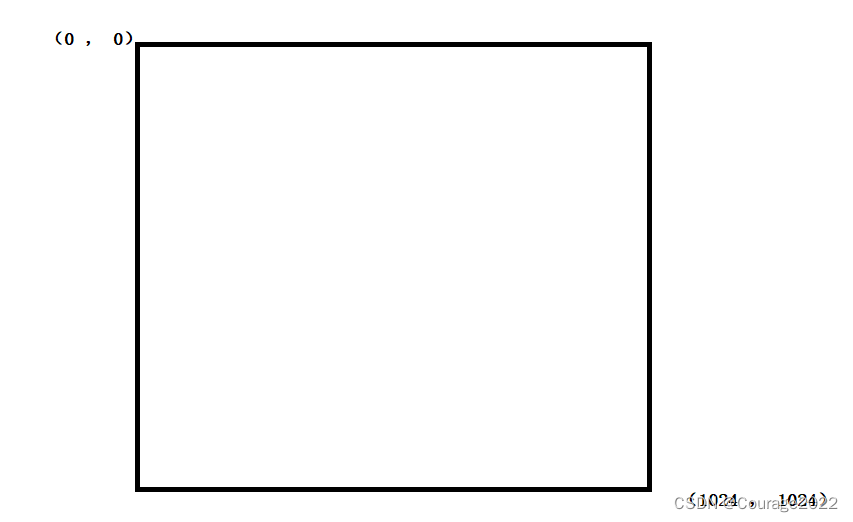
window是一个shape为 [ 0 , 0 , 1024 , 1024] 的定窗体,如下图:
回忆一下,我们的数据集图片也是1024*1024的,如果我们的边界框经过回归后越界了如下图:我们最终只会采用绿色部分作为边界框参数,最后的边界框信息保留在box变量中。
⑥将坐标归一化:将
坐标限制在
之间。
⑦nms处理:经过NMS处理最终保留proposal_count个框体。
rpn_rois = ProposalLayer(proposal_count=proposal_count, nms_threshold=config.RPN_NMS_THRESHOLD, name="ROI", anchors=self.anchors, config=config)([rpn_class, rpn_bbox])保留在rpn_rois变量中,表示为可能的框体要参与到后续计算当中。
2. DetectionTargetType层
2.1 DetectionTargetType层作用
①之前得到了2000个ROI,可能有pad进来的(0充数的)这些去掉(如果不够2000个前景样本则有背景样本充数)
②有的数据集一个框会包括多个物体,这样情况剔除掉。
③判断正负样本,基于ROI和GT,通过IOU与默认阈值0.5判断。
④设置负样本数量是正样本的3倍,总数默认400个。⑤每一个正样本(ROI),需要得到其类别,用IOU最大的那个GT。(通过ROI和标注GT比较,因为可能与多个框重叠猫、狗...,选择IOU最大的框作为预测类别)
⑥每一个正样本(ROI),需要得到其与GT-BOX的偏移量。(做微调用)
⑦每一个正样本(ROl),需要得到其最接近的GT-BOX对应的MASK。
⑧返回所有结果,其中负样本偏移量和MASK都用0填充。(正样本有标注)
2.2 正负样本选择与标签定义
class DetectionTargetLayer(KE.Layer): """Subsamples proposals and generates target box refinement, class_ids, and masks for each. Inputs: proposals: [batch, N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in normalized coordinates. Might be zero padded if there are not enough proposals. gt_class_ids: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES] Integer class IDs. gt_boxes: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in normalized coordinates. gt_masks: [batch, height, width, MAX_GT_INSTANCES] of boolean type Returns: Target ROIs and corresponding class IDs, bounding box shifts, and masks. rois: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in normalized coordinates target_class_ids: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE]. Integer class IDs. target_deltas: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, NUM_CLASSES, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw), class_id)] Class-specific bbox refinements. target_mask: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, height, width) Masks cropped to bbox boundaries and resized to neural network output size. Note: Returned arrays might be zero padded if not enough target ROIs. """ def __init__(self, config, **kwargs): super(DetectionTargetLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs) self.config = config def call(self, inputs): proposals = inputs[0] gt_class_ids = inputs[1] gt_boxes = inputs[2] gt_masks = inputs[3] # Slice the batch and run a graph for each slice # TODO: Rename target_bbox to target_deltas for clarity names = ["rois", "target_class_ids", "target_bbox", "target_mask"] outputs = utils.batch_slice( [proposals, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, gt_masks], lambda w, x, y, z: detection_targets_graph( w, x, y, z, self.config), self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU, names=names) return outputs def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape): return [ (None, self.config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, 4), # rois (None, 1), # class_ids (None, self.config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, 4), # deltas (None, self.config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, self.config.MASK_SHAPE[0], self.config.MASK_SHAPE[1]) # masks ] def compute_mask(self, inputs, mask=None): return [None, None, None, None]先看一下传入的参数:
@proposals:经过RPN层处理后剩下来的比较好的候选框
@gt_class_ids:类别信息
@gt_boxes:真实值(标注文件中的)框体信息
@gt_masks:真实值(标注文件中的)mask信息
返回的信息:
@rois:框体
@target_class_ids:roi对应的类别信息
@target_deltas:roi框体对应的修正信息
@target_mask:mask信息
函数执行流程如下:
①先取出我们传入的参数的值存放在proposals、gt_class_ids、gt_boxes、gt_masks中
②通过detection_targets_graph方法
def detection_targets_graph(proposals, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, gt_masks, config): """Generates detection targets for one image. Subsamples proposals and generates target class IDs, bounding box deltas, and masks for each. Inputs: proposals: [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in normalized coordinates. Might be zero padded if there are not enough proposals. gt_class_ids: [MAX_GT_INSTANCES] int class IDs gt_boxes: [MAX_GT_INSTANCES, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in normalized coordinates. gt_masks: [height, width, MAX_GT_INSTANCES] of boolean type. Returns: Target ROIs and corresponding class IDs, bounding box shifts, and masks. rois: [TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in normalized coordinates class_ids: [TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE]. Integer class IDs. Zero padded. deltas: [TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, NUM_CLASSES, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))] Class-specific bbox refinements. masks: [TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, height, width). Masks cropped to bbox boundaries and resized to neural network output size. Note: Returned arrays might be zero padded if not enough target ROIs. """ # Assertions asserts = [ tf.Assert(tf.greater(tf.shape(proposals)[0], 0), [proposals], name="roi_assertion"), ] with tf.control_dependencies(asserts): proposals = tf.identity(proposals) # Remove zero padding proposals, _ = trim_zeros_graph(proposals, name="trim_proposals") gt_boxes, non_zeros = trim_zeros_graph(gt_boxes, name="trim_gt_boxes") gt_class_ids = tf.boolean_mask(gt_class_ids, non_zeros, name="trim_gt_class_ids") gt_masks = tf.gather(gt_masks, tf.where(non_zeros)[:, 0], axis=2, name="trim_gt_masks") # Handle COCO crowds # A crowd box in COCO is a bounding box around several instances. Exclude # them from training. A crowd box is given a negative class ID. crowd_ix = tf.where(gt_class_ids < 0)[:, 0] non_crowd_ix = tf.where(gt_class_ids > 0)[:, 0] crowd_boxes = tf.gather(gt_boxes, crowd_ix) crowd_masks = tf.gather(gt_masks, crowd_ix, axis=2) gt_class_ids = tf.gather(gt_class_ids, non_crowd_ix) gt_boxes = tf.gather(gt_boxes, non_crowd_ix) gt_masks = tf.gather(gt_masks, non_crowd_ix, axis=2) # Compute overlaps matrix [proposals, gt_boxes] overlaps = overlaps_graph(proposals, gt_boxes) # Compute overlaps with crowd boxes [anchors, crowds] crowd_overlaps = overlaps_graph(proposals, crowd_boxes) crowd_iou_max = tf.reduce_max(crowd_overlaps, axis=1) no_crowd_bool = (crowd_iou_max < 0.001) # Determine postive and negative ROIs roi_iou_max = tf.reduce_max(overlaps, axis=1) # 1. Positive ROIs are those with >= 0.5 IoU with a GT box positive_roi_bool = (roi_iou_max >= 0.5) positive_indices = tf.where(positive_roi_bool)[:, 0] # 2. Negative ROIs are those with < 0.5 with every GT box. Skip crowds. negative_indices = tf.where(tf.logical_and(roi_iou_max < 0.5, no_crowd_bool))[:, 0] # Subsample ROIs. Aim for 33% positive # Positive ROIs positive_count = int(config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE * config.ROI_POSITIVE_RATIO) positive_indices = tf.random_shuffle(positive_indices)[:positive_count] positive_count = tf.shape(positive_indices)[0] # Negative ROIs. Add enough to maintain positive:negative ratio. r = 1.0 / config.ROI_POSITIVE_RATIO negative_count = tf.cast(r * tf.cast(positive_count, tf.float32), tf.int32) - positive_count negative_indices = tf.random_shuffle(negative_indices)[:negative_count] # Gather selected ROIs positive_rois = tf.gather(proposals, positive_indices) negative_rois = tf.gather(proposals, negative_indices) # Assign positive ROIs to GT boxes. positive_overlaps = tf.gather(overlaps, positive_indices) roi_gt_box_assignment = tf.argmax(positive_overlaps, axis=1) roi_gt_boxes = tf.gather(gt_boxes, roi_gt_box_assignment) roi_gt_class_ids = tf.gather(gt_class_ids, roi_gt_box_assignment) # Compute bbox refinement for positive ROIs deltas = utils.box_refinement_graph(positive_rois, roi_gt_boxes) deltas /= config.BBOX_STD_DEV # Assign positive ROIs to GT masks # Permute masks to [N, height, width, 1] transposed_masks = tf.expand_dims(tf.transpose(gt_masks, [2, 0, 1]), -1) # Pick the right mask for each ROI roi_masks = tf.gather(transposed_masks, roi_gt_box_assignment) # Compute mask targets boxes = positive_rois if config.USE_MINI_MASK: # Transform ROI corrdinates from normalized image space # to normalized mini-mask space. y1, x1, y2, x2 = tf.split(positive_rois, 4, axis=1) gt_y1, gt_x1, gt_y2, gt_x2 = tf.split(roi_gt_boxes, 4, axis=1) gt_h = gt_y2 - gt_y1 gt_w = gt_x2 - gt_x1 y1 = (y1 - gt_y1) / gt_h x1 = (x1 - gt_x1) / gt_w y2 = (y2 - gt_y1) / gt_h x2 = (x2 - gt_x1) / gt_w boxes = tf.concat([y1, x1, y2, x2], 1) box_ids = tf.range(0, tf.shape(roi_masks)[0]) masks = tf.image.crop_and_resize(tf.cast(roi_masks, tf.float32), boxes, box_ids, config.MASK_SHAPE) # Remove the extra dimension from masks. masks = tf.squeeze(masks, axis=3) # Threshold mask pixels at 0.5 to have GT masks be 0 or 1 to use with # binary cross entropy loss. masks = tf.round(masks) # Append negative ROIs and pad bbox deltas and masks that # are not used for negative ROIs with zeros. rois = tf.concat([positive_rois, negative_rois], axis=0) N = tf.shape(negative_rois)[0] P = tf.maximum(config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE - tf.shape(rois)[0], 0) rois = tf.pad(rois, [(0, P), (0, 0)]) roi_gt_boxes = tf.pad(roi_gt_boxes, [(0, N + P), (0, 0)]) roi_gt_class_ids = tf.pad(roi_gt_class_ids, [(0, N + P)]) deltas = tf.pad(deltas, [(0, N + P), (0, 0)]) masks = tf.pad(masks, [[0, N + P], (0, 0), (0, 0)]) return rois, roi_gt_class_ids, deltas, masksⅠ.移除掉充数的proposal:之前提取候选框的时候有2000个候选框,有可能有前景候选框不够2000个有背景凑数的情况,我们把它们剔除掉并将前景框体存储在proposals中。
Ⅱ.有的数据集一个框会包括多个物体,这样情况剔除掉(处理COCO数据集的数据重叠现象)并剔除掉有重叠的部分。
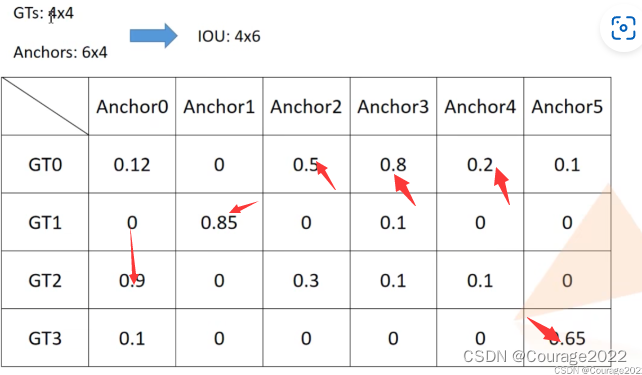
Ⅲ.计算IOU矩阵,即每一个proposals和gtbox的IOU值放在overlaps中
Ⅳ.tf.reduce_max方法是将每个proposal与gtbox的最大IOU值的信息取出,信息索引存放在roi_iou_max中(如下图红色箭头指向部分)。
positive_roi_bool为最大值大于0.5的蒙版
, positive_indice为根据蒙版选出的正样本,negative_indices为根据蒙版选出的负样本。
设置正负样本的数目:positive_count = 66 (最多66)再将正样本打乱,如果不够66个正样本则选择全部正样本作为正样本,最终的索引信息记录在positive_indices中,正样本的数目记录在positive_count中,负样本数量为200(TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE) - positive_count,过程同理。
其中的细节见我的MaskRCNN部分的讲解即可。
函数最终返回的是框体的rois, roi_gt_class_ids, deltas, masks信息。(正负样本数据、标签、边界框、mask信息)



![[数字媒体] PR视频剪辑之自定义音频、视频加速转场和特显停顿](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3186ea5b5add4c70a41b460741e9e9ef.png#pic_center)