LangChain 是面向大模型的开发框架,是 AGI 时代软件工程的探索和原型。学习 LangChain 需要关注接口的变更。
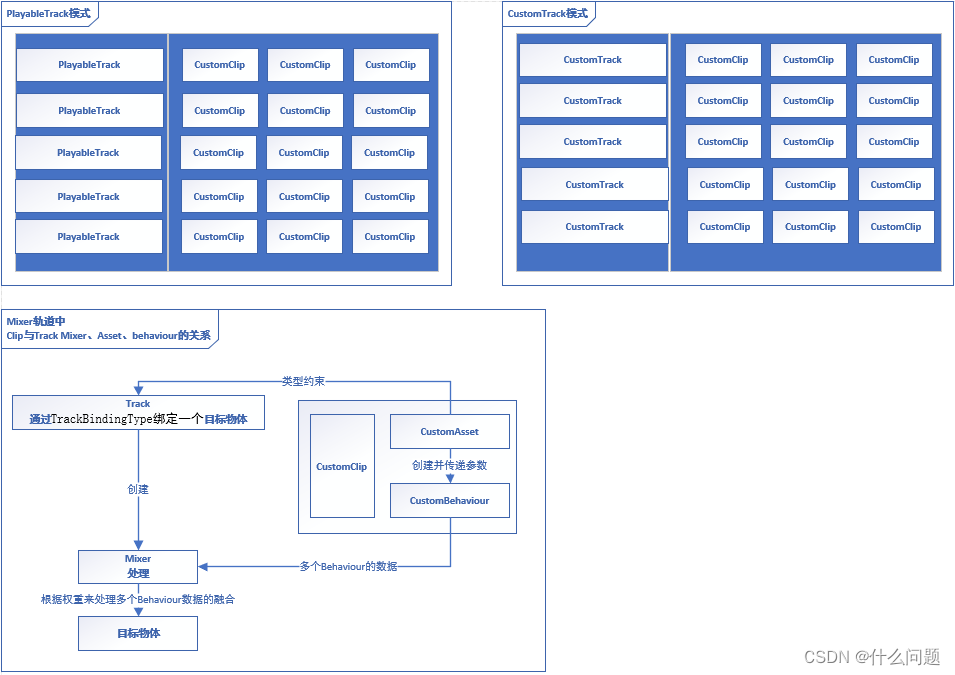
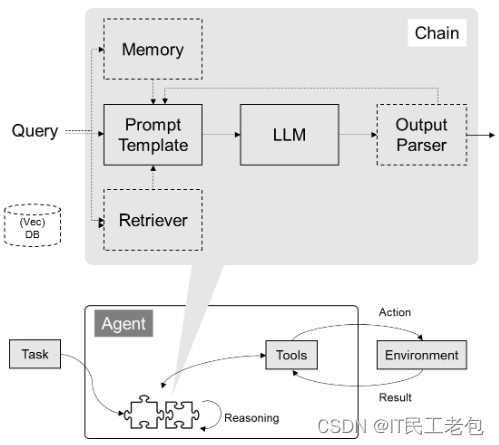
LangChain 的核心组件
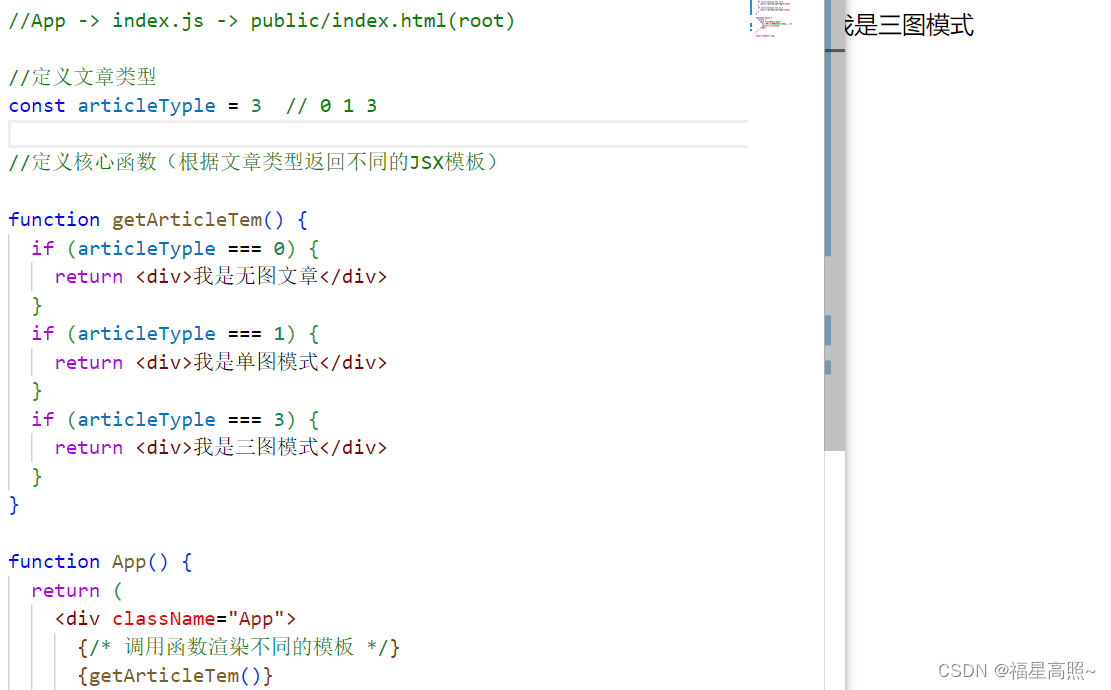
1.模型 I/O 封装
- LLMS 大语言模型
- Chat Models 一套基于 LLMS,但按对话结构重新封装
- PromptTemplate 提示词模板
- OutputParser 解析输出
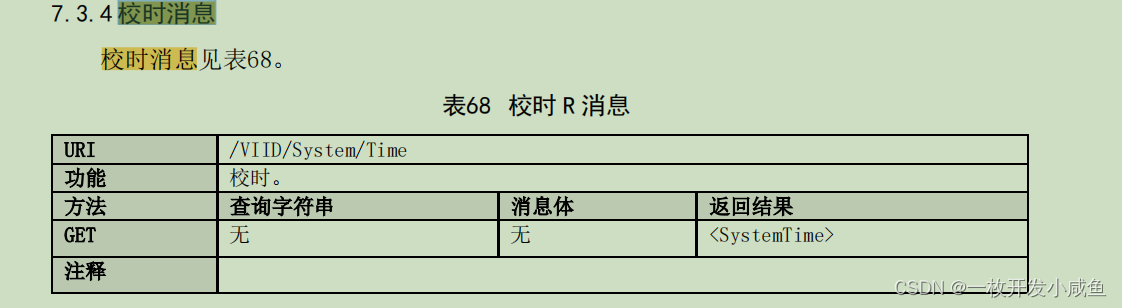
2.数据连接封装
- Document Loaders 各种格式文件的加载器
- Document Transformers 对文档的常用操作,如 split, filter,translate,extract, metadata, etc
- Text Embedding Models 文本向量化表示,用于检索等操作
- Verctorstores 向量存储
- Retrievers 向量检索
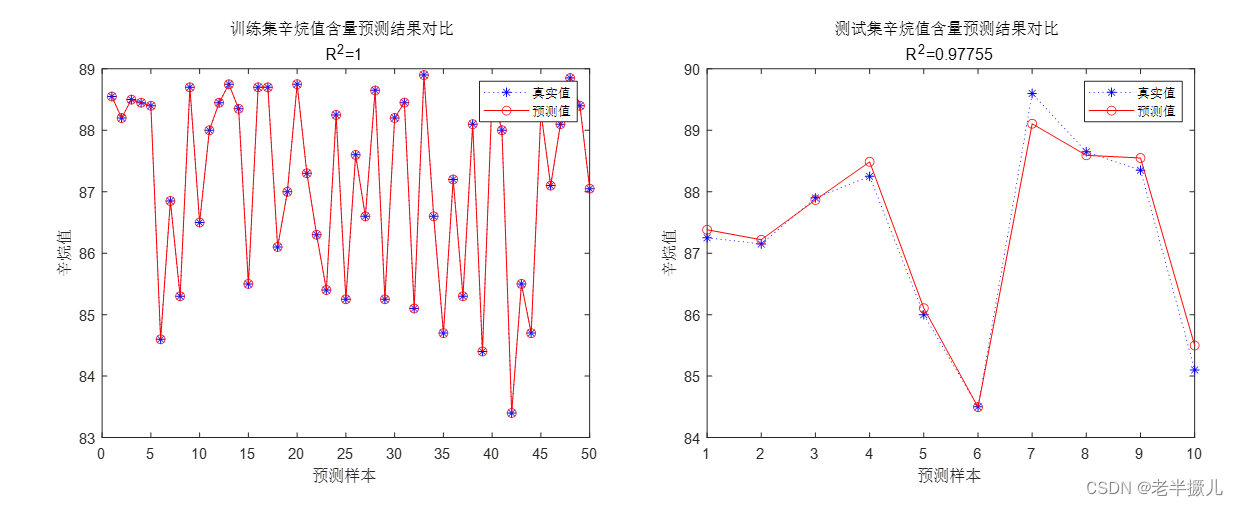
3.记忆封装
- Memory 这里不是物理内存,从文本的角度可以理解为“上文”,“历史记录”或者说“记忆”的管理
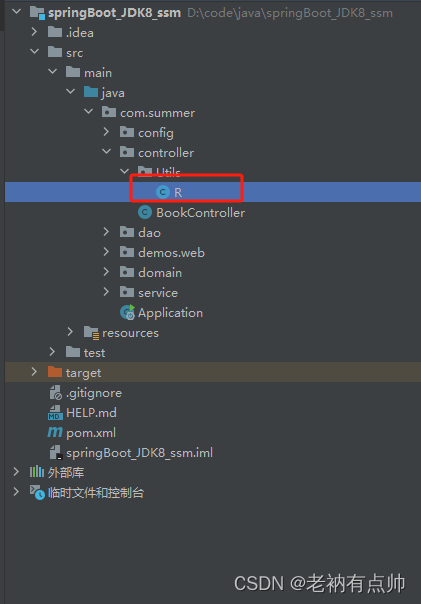
4.架构封装
- Chain 实现一个功能或者一系列顺序功能组合
- Agent 根据用户输入,自动规划执行不搜,自动选择每个步骤需要的工具,最终完成用户指定的功能
- Tools 调用外部功能的函数,例如:调用 google 搜索,文件I/O,Linux Shell 等等。
- Toolkits 操作某软件的一组工具集, 例如:操作 DB, 操作 Gmail 等等
5.Callbacks
准备工作
依赖包安装
!pip install --upgrade langchain
!pip install --upgrade langchain-openai
设置环境变量
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-xxxxx"
os.environ["OPENAI_BASE_URL"] = "https://your.proxy.address/v1"模型 I/O 封装
OpenAI 模型封装
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI() # 默认是gpt-3.5-turbo
response = llm.invoke("你是谁")
print(response.content)输出:
我是一个人工智能助手,可以回答你的问题和提供帮助。有什么可以帮助你的吗?
多轮对话 Session 封装
from langchain.schema import (
AIMessage, # 等价于OpenAI接口中的assistant role
HumanMessage, # 等价于OpenAI接口中的user role
SystemMessage # 等价于OpenAI接口中的system role
)
messages = [
SystemMessage(content="你是文档编写小能手。"),
HumanMessage(content="我是学生,我叫 Gem"),
AIMessage(content="欢迎!"),
HumanMessage(content="我是谁")
]
ret = llm.invoke(messages)
print(ret.content)输出:
您是Gem,一个学生。您有什么问题需要帮助吗?
换国产大模型
安装依赖包
pip install qianfan
# 其它模型分装在 langchain_community 底包中
from langchain_community.chat_models import QianfanChatEndpoint
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
import os
llm = QianfanChatEndpoint(
qianfan_ak=os.getenv('ERNIE_CLIENT_ID'), # 需要到百度智能云平台 https://cloud.baidu.com/ 开通应用
qianfan_sk=os.getenv('ERNIE_CLIENT_SECRET')
)
messages = [
HumanMessage(content="你是谁")
]
ret = llm.invoke(messages)
print(ret.content)输出:
你好,我是一名文本生成的人工智能模型,我没有具体的身份和实体形态。我可以回答问题和提供信息,帮助你解决问题。有什么我可以帮助你的吗?
模型的输入输出
Prompt 模板封装
1. promptTemplate 可以在模板中自定义变量
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
template = PromptTemplate.from_template("给我讲个关于{subject}的笑话")
print("===Template===")
print(template)
print("===Prompt===")
print(template.format(subject='小明'))===Template===
input_variables=['subject'] template='给我讲个关于{subject}的笑话'
===Prompt===
给我讲个关于小明的笑话
2.ChatPromptTemplate 用模板表示的对话上下文
from langchain.prompts import (
ChatPromptTemplate,
HumanMessagePromptTemplate,
SystemMessagePromptTemplate,
)
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
SystemMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(
"你是{product}助手。你的名字叫{name}"),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{query}"),
]
)
llm = ChatOpenAI()
prompt = template.format_messages(
product="中式美食专家",
name="瓜瓜",
query="你是谁"
)
ret = llm.invoke(prompt)
print(ret.content)输出:
我是一个人工智能助手,可以回答您关于中式美食的问题。如果您有任何疑问或需要帮助,请随时告诉我哦!
3.MessagesPlaceholder 把多轮对话变成模板
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, HumanMessagePromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
human_prompt = "Translate your answer to {language}."
human_message_template = HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(human_prompt)
chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
# conversation 是 message placeholder 中的变量名用于在赋值时使用
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="conversation"),
human_message_template
]
)from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage, HumanMessage
human_message = HumanMessage(content="who is Elon Musk?")
ai_message = AIMessage(
content="Elon Musk is a billionaire entrepreneur, inventor, and industrial designer"
)
messages = chat_prompt.format_prompt(
conversation=[human_message, ai_message],
language="韩语"
)
result = llm.invoke(messages)
print(result.content)输出:
Elon Musk는 억만장자 기업가, 발명가 및 산업 디자이너입니다.
重点:可以把 Prompt 模板看做带有参数的函数,可类比为 SK 的 Semantic Function
4. Prompt 模板也可以直接从文件加载
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
template = PromptTemplate.from_file("example_prompt_template.txt") # 文件内容:举一个关于{topic}的例子
print("===Template===")
print(template)
print("===Prompt===")
print(template.format(topic='黑色幽默'))输出:
===Template===
input_variables=['topic'] template='举一个关于{topic}的例子'
===Prompt===
举一个关于黑色幽默的例子
输出封装 OutputParser
自动把 LLM 输出的字符串按指定格式加载。
LangChain 内置的 OutputParser 包括:
- ListParser
- DatetimeParser
- EnumParser
- JsonOutputParser
- PydanticParser
- XMLParser
等等
Pydantic (JSON) Parser
可以根据 Pydantic 类的定义生成输出的格式说明
from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field, validator
from typing import List, Dict
# 定义你的输出对象
class Date(BaseModel):
year: int = Field(description="Year")
month: int = Field(description="Month")
day: int = Field(description="Day")
era: str = Field(description="BC or AD")
# ----- 可选机制 --------
# 你可以添加自定义的校验机制
@validator('month')
def valid_month(cls, field):
if field <= 0 or field > 12:
raise ValueError("月份必须在1-12之间")
return field
@validator('day')
def valid_day(cls, field):
if field <= 0 or field > 31:
raise ValueError("日期必须在1-31日之间")
return field
@validator('day', pre=True, always=True)
def valid_date(cls, day, values):
year = values.get('year')
month = values.get('month')
# 确保年份和月份都已经提供
if year is None or month is None:
return day # 无法验证日期,因为没有年份和月份
# 检查日期是否有效
if month == 2:
if cls.is_leap_year(year) and day > 29:
raise ValueError("闰年2月最多有29天")
elif not cls.is_leap_year(year) and day > 28:
raise ValueError("非闰年2月最多有28天")
elif month in [4, 6, 9, 11] and day > 30:
raise ValueError(f"{month}月最多有30天")
return day
@staticmethod
def is_leap_year(year):
if year % 400 == 0 or (year % 4 == 0 and year % 100 != 0):
return True
return Falsefrom langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate, ChatPromptTemplate, HumanMessagePromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser
model_name = 'gpt-3.5-turbo'
temperature = 0
model = ChatOpenAI(model_name=model_name, temperature=temperature)
# 根据Pydantic对象的定义,构造一个OutputParser
parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=Date)
template = """提取用户输入中的日期。
{format_instructions}
用户输入:
{query}"""
prompt = PromptTemplate(
template=template,
input_variables=["query"],
# 直接从OutputParser中获取输出描述,并对模板的变量预先赋值
partial_variables={"format_instructions": parser.get_format_instructions()}
)
print("====Format Instruction=====")
print(parser.get_format_instructions())
query = "2023年四月6日天气晴..."
model_input = prompt.format_prompt(query=query)
print("====Prompt=====")
print(model_input.to_string())
output = model.invoke(model_input.to_messages())
print("====模型原始输出=====")
print(output.content)
print("====Parse后的输出=====")
date = parser.parse(output.content)
print(date.dict())输出:
====Format Instruction=====
The output should be formatted as a JSON instance that conforms to the JSON schema below.
As an example, for the schema {"properties": {"foo": {"title": "Foo", "description": "a list of strings", "type": "array", "items": {"type": "string"}}}, "required": ["foo"]}
the object {"foo": ["bar", "baz"]} is a well-formatted instance of the schema. The object {"properties": {"foo": ["bar", "baz"]}} is not well-formatted.
Here is the output schema:
```
{"properties": {"year": {"title": "Year", "description": "Year", "type": "integer"}, "month": {"title": "Month", "description": "Month", "type": "integer"}, "day": {"title": "Day", "description": "Day", "type": "integer"}, "era": {"title": "Era", "description": "BC or AD", "type": "string"}}, "required": ["year", "month", "day", "era"]}
```
====Prompt=====
提取用户输入中的日期。
The output should be formatted as a JSON instance that conforms to the JSON schema below.
As an example, for the schema {"properties": {"foo": {"title": "Foo", "description": "a list of strings", "type": "array", "items": {"type": "string"}}}, "required": ["foo"]}
the object {"foo": ["bar", "baz"]} is a well-formatted instance of the schema. The object {"properties": {"foo": ["bar", "baz"]}} is not well-formatted.
Here is the output schema:
```
{"properties": {"year": {"title": "Year", "description": "Year", "type": "integer"}, "month": {"title": "Month", "description": "Month", "type": "integer"}, "day": {"title": "Day", "description": "Day", "type": "integer"}, "era": {"title": "Era", "description": "BC or AD", "type": "string"}}, "required": ["year", "month", "day", "era"]}
```
用户输入:
2023年四月6日天气晴...
====模型原始输出=====
{
"year": 2023,
"month": 4,
"day": 6,
"era": "AD"
}
====Parse后的输出=====
{'year': 2023, 'month': 4, 'day': 6, 'era': 'AD'}
Auto-Fixing Parser
利用 LLM 自动根据解析异常重新解析修复
from langchain.output_parsers import OutputFixingParser
new_parser = OutputFixingParser.from_llm(
parser=parser, llm=ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo")
)
# 将前面的 output 格式改错
output = output.content.replace("4", "四月")
print("===格式错误的Output===")
print(output)
try:
date = parser.parse(output)
except Exception as e:
print("===出现异常===")
print(e)
# 用 OutputFixingParser 自动修复并解析
date = new_parser.parse(output)
print("===重新解析结果===")
print(date.json())输出:
===格式错误的Output===
{
"year": 2023,
"month": 四月,
"day": 6,
"era": "AD"
}
===出现异常===
Invalid json output: {
"year": 2023,
"month": 四月,
"day": 6,
"era": "AD"
}
===重新解析结果===
{"year": 2023, "month": 4, "day": 6, "era": "AD"}
小结:
- LangChain 统一封装了各种模型的调用接口,包括补全型和对话型两种
- LangChain 提供了 PromptTemplate 类,可以自定义带变量的模板
- LangChain 提供了一些列输出解析器,用于将大模型的输出解析成结构化对象;额外带有自动修复功能。
- 上述模型属于 LangChain 中较为优秀的部分;美中不足的是 OutputParser 自身的 Prompt 维护在代码中,耦合度较高。