Linux设备驱动模型和sysfs文件系统
Linux内核在2.6版本中引入设备驱动模型,简化了驱动程序的编写。Linux设备驱动模型包含设备(device)、总线(bus)、类(class)和驱动(driver),它们之间相互关联。其中**设备(device)和驱动(driver)通过总线(bus)**绑定在一起。
Linux内核中,分别用bus_type、device_driver和device结构来描述总线、驱动和设备,结构体定义详见linux/device.h。设备和对应的驱动必须依附于同一种总线,因此device_driver和device结构中都包含struct bus_type指针。
Linux sysfs是一个虚拟的文件系统,它把连接在系统上的设备和总线组织成为一个分级的文件,可以由用户空间存取,向用户空间导出内核数据结构以及它们的属性。
sysfs展示出设备驱动模型中各个组件的层次关系,某个系统上的sysfs顶层目录展示如下:
/sys$ ll
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 0 Aug 20 15:27 block/
drwxr-xr-x 29 root root 0 Aug 20 15:27 bus/
drwxr-xr-x 61 root root 0 Aug 20 15:27 class/
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 0 Aug 20 15:27 dev/
drwxr-xr-x 14 root root 0 Aug 20 15:27 devices/
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 0 Aug 20 15:27 firmware/
drwxr-xr-x 8 root root 0 Aug 20 15:27 fs/
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 0 Sep 2 17:08 hypervisor/
drwxr-xr-x 8 root root 0 Aug 20 15:27 kernel/
drwxr-xr-x 147 root root 0 Aug 20 15:27 module/
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 0 Aug 20 15:27 power/
重要子目录介绍:
block: 包含所有的块设备,如ram,sda等bus: 包含系统中所有的总线类型,如pci,usb,i2c等class: 包含系统中的设备类型,如input,pci_bus,mmc_host等dev: 包含两个子目录:char和block,分别存放字符设备和块设备的主次设备号(major:minor),指向/sys/devices目录下的设备devices:包含系统所有的设备
sysfs中显示的每一个对象都对应一个kobject结构(完整定义位于linux/kobject.h,结构内部包含一个parent指针),而另一个相联系的结构为kset。kset是嵌入相同类型结构的kobject对象的集合。
内核用kobject、kset和parent之间的关系将各个对象连接起来组成一个分层的结构体系,从而与模型化的子系统相匹配。(有机会详细介绍)
sysfs中能清晰地看出device、driver和bus的相互联系,以某系统上pci总线上的igb驱动为例。
/sys/bus/pci/下存在devices和drivers两个目录,分别包含了依附于pci总线上的设备和驱动。进入igb驱动目录,可以发现存在指向设备的链接。
/sys/bus/pci/drivers/igb$ ll
total 0
... 0 Sep 2 17:08 0000:07:00.0 -> ../../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.4/0000:07:00.0/
... 0 Sep 2 17:08 0000:07:00.1 -> ../../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.4/0000:07:00.1/
...
对应地,在/sys/devices/目录下,可以看到设备存在一个指向igb的driver项:
/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.4/0000:07:00.0$ ll
total 0
...
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Aug 20 15:27 driver -> ../../../../bus/pci/drivers/igb/
...
同样地,/sys/bus/pci/devices目录下可以找到指向同样设备的一个链接:
/sys/bus/pci/devices$ ll
total 0
...
... 0 Aug 20 15:27 0000:07:00.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.4/0000:07:00.0/
... 0 Aug 20 15:27 0000:07:00.1 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.4/0000:07:00.1/
...
对于早期的Linux内核(2.6版本以前)来说,通常在驱动代码中xxx_driver注册过程中调用probe()函数来对设备进行初始化。
引入Linux设备驱动模型下,设备和驱动可以分开注册,依赖总线完成相互绑定。系统每注册一个设备的时候,会寻找与之匹配的驱动;相反,系统每注册一个驱动的时候,会寻找与之匹配的设备。这个过程中,设备和驱动的匹配工作由总线完成。
下文中将会用关键的内核源码(基于linux 5.2.14 Kernel)说明驱动和设备间匹配机制的实现,分析的过程中以platform总线为例。
platform总线是一种虚拟的总线,与之相对应的是PCI、I2C、SPI等实体总线。引入虚拟platform总线是为了解决某些设备无法直接依附在现有实体总线上的问题,例如SoC系统中集成的独立外设控制器,挂接在SoC内存空间的外设等等。
platform总线的注册
platform总线作为Linux的基础总线,在内核启动阶段便完成了注册,注册的入口函数为platform_bus_init()。内核启动阶段调用该函数的路径为:
start_kernel() --> arch_call_rest_init()[last step in start_kernel]
--> rest_init() --> kernel_init()
--> kernel_init_freeable() --> do_basic_setup()
--> driver_init() --> platform_bus_init()
Linux内核中定义了platform_bus_type结构体来描述platform总线,同时也定义了设备platform_bus,用于管理所有挂载在platform总线下的设备,定义如下:
struct bus_type platform_bus_type = {
.name = "platform",
.dev_groups = platform_dev_groups,
.match = platform_match,
.uevent = platform_uevent,
.dma_configure = platform_dma_configure,
.pm = &platform_dev_pm_ops,
};
struct device platform_bus = {
.init_name = "platform",
};
platform_bus_init()对platform总线的注册主要分为两步:
device_register(&platform_bus)bus_register(&platform_bus_type)。
int __init platform_bus_init(void)
{
int error;
/* Clear up early_platform_device_list, then only remain head_list */
early_platform_cleanup();
/* register platform_bus device (platform_bus is also regarded as a device) */
error = device_register(&platform_bus);
if (error) {
put_device(&platform_bus);
return error;
}
/* Main process to register platform_bus */
error = bus_register(&platform_bus_type);
if (error)
device_unregister(&platform_bus);
of_platform_register_reconfig_notifier();
return error;
}
device_register(&platform_bus)
/***** drivers/base/core.c *****/
int device_register(struct device *dev)
{
device_initialize(dev); // init device structure
return device_add(dev); // add device to device hierarchy
}
device_initialize():对struct device中基本成员进行初始化,包括kobject、struct device_private、struct mutex等。device_add(dev):将platform总线也作为一个设备platform_bus注册到驱动模型中,重要的函数包括device_create_file()、device_add_class_symlinks()、bus_add_device()、bus_probe_device()等,下文中对设备注册的介绍一节,将对这个函数做更详细的介绍。device_add(&platform_bus)主要功能是完成/sys/devices/platform目录的建立。
bus_register(&platform_bus_type)
/***** drivers/base/bus.c *****/
int bus_register(struct bus_type *bus)
{
struct subsys_private *priv;
struct lock_class_key *key = &bus->lock_key;
priv = kzalloc(sizeof(struct subsys_private), GFP_KERNEL);
priv->bus = bus;
bus->p = priv;
BLOCKING_INIT_NOTIFIER_HEAD(&priv->bus_notifier);
retval = kobject_set_name(&priv->subsys.kobj, "%s", bus->name);
if (retval)
goto out;
priv->subsys.kobj.kset = bus_kset;
priv->subsys.kobj.ktype = &bus_ktype;
priv->drivers_autoprobe = 1;
/* Register kset (subsys) */
retval = kset_register(&priv->subsys);
retval = bus_create_file(bus, &bus_attr_uevent);
/* Setup "devices" and "drivers" subfolder under "platform" */
priv->devices_kset = kset_create_and_add("devices", NULL,
&priv->subsys.kobj);
priv->drivers_kset = kset_create_and_add("drivers", NULL,
&priv->subsys.kobj);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&priv->interfaces);
__mutex_init(&priv->mutex, "subsys mutex", key);
klist_init(&priv->klist_devices, klist_devices_get, klist_devices_put);
klist_init(&priv->klist_drivers, NULL, NULL);
/* bus_create_file(bus, &bus_attr_drivers_probe); BUS_ATTR_WO(drivers_probe)
* bus_create_file(bus, &bus_attr_drivers_autoprobe); BUS_ATTR_RW(drivers_autoprobe)
* Add two attribute files for current bus /sys/bus/platform
*/
retval = add_probe_files(bus);
retval = bus_add_groups(bus, bus->bus_groups);
return 0;
}
bus_register(&platform_bus_type)将总线platform注册到Linux的总线系统中,主要完成了subsystem的注册,对struct subsys_private结构进行了初始化,具体包括:
platform_bus_type->p->drivers_autoprobe = 1- 对
struct kset类型成员subsys进行初始化,作为子系统中kobject对象的parent。kset本身也包含kobject对象,在sysfs中也表现为一个目录,即/sys/bus/platform。 - 建立
struct kset类型的drivers_kset和devices_kset,作为总线下挂载的所有驱动和设备的集合,sysfs中表现为/sys/bus/platform/drivers和/sys/bus/platform/devices。 - 初始化链表
klist_drivers和klist_devices,将总线下的驱动和设备分别链接在一起。 - 增加
probe文件,对应/sys/bus/platform目录的文件drivers_autoprobe和drivers_probe。
注册完成后platform_bus_type结构重要的成员列举如下:
struct bus_type platform_bus_type = {
.name = "platform",
.dev_groups = platform_dev_groups,
.match = platform_match,
.uevent = platform_uevent,
.dma_configure = platform_dma_configure,
.pm = &platform_dev_pm_ops,
.p (struct subsys_private) = {
.bus = &platform_bus_type,
.subsys (struct kset) = {
.kobj = {
.name = “platform”
.kref->refcount->refs = 1, // kset_init()
INIT_LIST_HEAD(.entry),
.state_in_sysfs = 0,
.state_add_uevent_sent = 1, // kset_register()
.state_remove_uevent_sent = 0,
.state_initialized = 1,
.kset = bus_kset, // attached to /sys/bus/
.ktype= bus_ktype,
.parent = bus_kset->kobj,
.sd (kernfs_node) = { // create_dir, kobject_add_internal
.parent = bus_kset->kobj->sd,
.dir.root = bus_kset->kobj->sd->dir.root,
.ns = NULL,
.priv = .kobj
}
}
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&k->list);
spin_lock_init(&k->list_lock);
}
/* key point for driver to autoprobe device, set in bus_register() */
. drivers_autoprobe = 1
klist_init(&priv->klist_devices, klist_devices_get, klist_devices_put);
klist_init(&priv->klist_drivers, NULL, NULL);
.devices_kset = kset_create_and_add("devices", NULL, &.p->subsys.kobj);
/* .drivers_kset = kset_create_and_add("drivers", NULL, &.p->subsys.kobj) */
.drivers_kset = {
.kobj = {
.name = “drivers”,
.parent = &.subsys.kobj,
.ktype = &kset_ktype,
.kset = NULL,
.kref->refcount->refs = 1, // kset_init
INIT_LIST_HEAD(.entry),
.state_in_sysfs = 0,
.state_add_uevent_sent = 1, // kset_register
.state_remove_uevent_sent = 0,
.state_initialized = 1,
.sd = { // create_dir: /sys/bus/platform/drivers
/* kobject_add_internal */
.parent = &.subsys.kobj.sd,
.dir.root = = &.subsys.kobj.sd->dir.root
.ns = NULL,
.priv = .kobj
}
}
INIT_LIST_HEAD(.list);
spin_lock_init(.list_lock);
.uevent_ops = NULL,
}
}
};
platform驱动的注册
Linux内核中对依赖于platform总线的驱动定义了platform_driver结构体,内部封装了前述的struct device_driver。
struct platform_driver {
int (*probe)(struct platform_device *);
int (*remove)(struct platform_device *);
void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *);
int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct platform_device *);
struct device_driver driver;
const struct platform_device_id *id_table;
bool prevent_deferred_probe;
};
为了更好地说明platform驱动的注册过程,以驱动globalfifo_driver为实例,globalfifo_driver结构成员定义如下:
static struct platform_driver globalfifo_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "globalfifo_platform",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
},
.probe = globalfifo_probe,
.remove = globalfifo_remove,
};
globalfifo_driver注册的入口函数为platform_driver_register(&globalfifo_driver),具体实现为__platform_driver_register(&globalfifo_driver, THIS_MODULE)。
该函数会对struct device_driver的bus、probe、remove等回调函数进行初始化,紧接着调用driver_register(&globalfifo_driver->driver)。
/***** drivers/base/platform.c *****/
/**
* __platform_driver_register - register a driver for platform-level devices
* @drv: platform driver structure
* @owner: owning module/driver
*/
int __platform_driver_register(struct platform_driver *drv,
struct module *owner)
{
drv->driver.owner = owner;
drv->driver.bus = &platform_bus_type;
drv->driver.probe = platform_drv_probe;
drv->driver.remove = platform_drv_remove;
drv->driver.shutdown = platform_drv_shutdown;
return driver_register(&drv->driver);
}
driver_register(&(globalfifo_driver.driver))
/***** drivers/base/driver.c *****/
/**
* driver_register - register driver with bus
* @drv: driver to register
*
* We pass off most of the work to the bus_add_driver() call,
* since most of the things we have to do deal with the bus
* structures.
*/
int driver_register(struct device_driver *drv)
{
int ret;
struct device_driver *other;
if (!drv->bus->p) {
pr_err("Driver '%s' was unable to register with bus_type '%s' because the bus was not initialized.\n",
drv->name, drv->bus->name);
return -EINVAL;
}
if ((drv->bus->probe && drv->probe) ||
(drv->bus->remove && drv->remove) ||
(drv->bus->shutdown && drv->shutdown))
printk(KERN_WARNING "Driver '%s' needs updating - please use "
"bus_type methods\n", drv->name);
other = driver_find(drv->name, drv->bus);
ret = bus_add_driver(drv);
ret = driver_add_groups(drv, drv->groups);
kobject_uevent(&drv->p->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);
return ret;
}
driver_register(&(globalfifo_driver.driver))主要的工作包括:
- 确认驱动依附的总线
platform_bus已经被注册并初始化(必要条件)。 - 对
probe、remove、shutdown等回调函数初始化进行判断,保证总线和驱动上相应的函数只能存在一个。 driver_find()查找总线上是否已存在当前驱动的同名驱动。bus_add_driver(&(globalfifo_driver.driver)),将驱动注册到总线上,下文详述。- 发起
KOBJ_ADD类型uevent,指示驱动已经添加完成,TODO。
bus_add_driver(&(globalfifo_driver.driver))
/***** drivers/base/bus.c *****/
/**
* bus_add_driver - Add a driver to the bus.
* @drv: driver.
*/
int bus_add_driver(struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct bus_type *bus;
struct driver_private *priv;
int error = 0;
bus = bus_get(drv->bus);
priv = kzalloc(sizeof(*priv), GFP_KERNEL);
klist_init(&priv->klist_devices, NULL, NULL);
priv->driver = drv;
drv->p = priv;
priv->kobj.kset = bus->p->drivers_kset;
error = kobject_init_and_add(&priv->kobj, &driver_ktype, NULL,
"%s", drv->name);
klist_add_tail(&priv->knode_bus, &bus->p->klist_drivers);
/* Entrance to match device: try to bind driver to devices */
if (drv->bus->p->drivers_autoprobe) {
error = driver_attach(drv);
}
module_add_driver(drv->owner, drv);
error = driver_create_file(drv, &driver_attr_uevent);
error = driver_add_groups(drv, bus->drv_groups);
if (!drv->suppress_bind_attrs) {
error = add_bind_files(drv);
}
return 0;
}
bus_add_driver(&(globalfifo_driver.driver))的主要工作包括:
- 为
struct device_driver中结构struct driver_private动态分配空间,并完成后者kobject对象初始化。对应地,在/sys/bus/platform/drivers下建立目录globalfifo_platform。 - 初始化
klist_devices链表,用来维护驱动相关联的设备。对应sysfs中在每个驱动目录下关联的设备。 klist_add_tail()将当前驱动加入到总线对应的klist_drivers链表中。- 如果总线使能
drivers_autoprobe,将调用driver_attach()尝试匹配设备。下文中将详述此过程。 module_add_driver(drv->owner, drv)通过sysfs_create_link(),在globalfifo_platform目录下新建module项指向/sys/module/globalfifo_platform。同时,也在/sys/module/globalfifo_platform/目录下新建driver目录,建立bus->name:drv->name链接到/sys/bus/platform/drivers/globalfifo_platform。uevent设置。
初始化后globalfifo_driver结构主要的成员列举如下:
static struct platform_driver globalfifo_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "globalfifo_platform",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.bus = &platform_bus_type,
.probe = platform_drv_probe
.remove = platform_drv_remove,
.shutdown = platform_drv_shutdown,
.p (struct driver_private) = {
.driver = & globalfifo_driver.driver,
klist_init(&.klist_devices, NULL, NULL);
klist_add_tail(&priv->knode_bus, &bus->p->klist_drivers);
.kobj = {
.kset = platform_bus_type->p->drivers_kset,
.ktype = driver_ktype,
.kref->refcount->refs = 1, // kset_init
INIT_LIST_HEAD(.entry),
.state_in_sysfs = 1,
.state_add_uevent_sent = 0,
.state_remove_uevent_sent = 0,
.state_initialized = 1,
.name = "globalfifo_platform",
.parent = platform_bus_type->p->drivers_kset->kobj,
}
}
},
.probe = globalfifo_probe,
.remove = globalfifo_remove,
};
driver_attach(&(globalfifo_driver.driver))
/***** drivers/base/dd.c *****/
/**
* driver_attach - try to bind driver to devices.
* @drv: driver.
*/
int driver_attach(struct device_driver *drv)
{
return bus_for_each_dev(drv->bus, NULL, drv, __driver_attach);
}
/***** drivers/base/bus.c *****/
/**
* bus_for_each_dev - device iterator.
* @bus: bus type.
* @start: device to start iterating from.
* @data: data for the callback.
* @fn: function to be called for each device.
*/
int bus_for_each_dev(struct bus_type *bus, struct device *start,
void *data, int (*fn)(struct device *, void *))
{
struct klist_iter i;
struct device *dev;
int error = 0;
if (!bus || !bus->p)
return -EINVAL;
klist_iter_init_node(&bus->p->klist_devices, &i,
(start ? &start->p->knode_bus : NULL));
while (!error && (dev = next_device(&i)))
error = fn(dev, data);
klist_iter_exit(&i);
return error;
}
driver_attach()函数找到驱动依附的总线信息,遍历总线上链表klist_devices得到当前总线上存在的设备,然后调用__driver_attach(dev, drv)函数,尝试将驱动和设备绑定。
__driver_attach(dev, drv)函数包含两个主要的部分:
driver_match_device(drv, dev): 尝试将驱动和设备匹配,返回值指示是否能匹配。device_driver_attach(drv, dev): 将驱动和设备绑定。
static int __driver_attach(struct device *dev, void *data)
{
struct device_driver *drv = data;
int ret;
/*
* Lock device and try to bind to it. We drop the error
* here and always return 0, because we need to keep trying
* to bind to devices and some drivers will return an error
* simply if it didn't support the device.
*
* driver_probe_device() will spit a warning if there
* is an error.
*/
ret = driver_match_device(drv, dev);
if (ret == 0) {
/* no match */
return 0;
} else if (ret == -EPROBE_DEFER) {
dev_dbg(dev, "Device match requests probe deferral\n");
driver_deferred_probe_add(dev);
} else if (ret < 0) {
dev_dbg(dev, "Bus failed to match device: %d", ret);
return ret;
} /* ret > 0 means positive match */
... ...
device_driver_attach(drv, dev);
return 0;
}
driver_match_device(drv, dev)
static inline int driver_match_device(struct device_driver *drv,
struct device *dev)
{
return drv->bus->match ? drv->bus->match(dev, drv) : 1;
}
driver_match_device(drv, dev)回调drv->bus->match()函数,对于platform_bus为platform_match()。
platform_match()函数会依次尝试如下几种方式:
driver_override有效时,尝试将驱动名字和driver_override匹配- 基于设备树风格的匹配
- 基于ACPI风格的匹配
- 匹配ID表
- 匹配
platform_device设备名和驱动的名字
/**
* platform_match - bind platform device to platform driver.
* @dev: device.
* @drv: driver.
*/
static int platform_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);
struct platform_driver *pdrv = to_platform_driver(drv);
/* When driver_override is set, only bind to the matching driver */
if (pdev->driver_override)
return !strcmp(pdev->driver_override, drv->name);
/* Attempt an OF style match first */
if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then try ACPI style match */
if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then try to match against the id table */
if (pdrv->id_table)
return platform_match_id(pdrv->id_table, pdev) != NULL;
/* fall-back to driver name match */
return (strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name) == 0);
}
device_driver_attach(drv, dev)
/**
* device_driver_attach - attach a specific driver to a specific device
* @drv: Driver to attach
* @dev: Device to attach it to
*/
int device_driver_attach(struct device_driver *drv, struct device *dev)
{
int ret = 0;
__device_driver_lock(dev, dev->parent);
/*
* If device has been removed or someone has already successfully
* bound a driver before us just skip the driver probe call.
*/
if (!dev->p->dead && !dev->driver)
ret = driver_probe_device(drv, dev);
__device_driver_unlock(dev, dev->parent);
return ret;
}
在驱动和设备匹配成功之后,便将驱动和设备进行绑定。调用driver_probe_device(drv, dev)完成此工作,进一步调用really_probe(dev, drv)。
/**
* driver_probe_device - attempt to bind device & driver together
* @drv: driver to bind a device to
* @dev: device to try to bind to the driver
*/
int driver_probe_device(struct device_driver *drv, struct device *dev)
{
int ret = 0;
if (!device_is_registered(dev))
return -ENODEV;
... ...
if (initcall_debug)
ret = really_probe_debug(dev, drv);
else
ret = really_probe(dev, drv);
... ...
return ret;
}
really_probe(dev, drv)
/***** drivers/base/dd.c *****/
static int really_probe(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
dev->driver = drv;
... ...
driver_sysfs_add(dev);
... ...
/* Routine to probe device */
if (dev->bus->probe) {
ret = dev->bus->probe(dev);
if (ret)
goto probe_failed;
} else if (drv->probe) {
ret = drv->probe(dev);
if (ret)
goto probe_failed;
}
... ...
driver_bound(dev);
}
really_probe(dev, drv)主要完成的工作包括:
- 将设备
struct device中driver指针指向globalfifo_driver->driver。 driver_sysfs_add(dev)完成sysfs中设备和驱动的链接,包括在驱动目录下建立到设备的链接,和在设备目录下建立到驱动的链接。- 设备
probe函数的调用:优先使用platform_device->bus->probe函数,其次使用platform_driver->probe函数。对于globalfifo_driver,会回调globalfifo_probe(),完成设备的初始化。 driver_bound(dev)将设备添加到驱动维护的设备链表中,并发起KOBJ_BIND事件。
platform设备的注册
最后,对设备的注册过程进行简要梳理。
和驱动类似,Linux内核中对依赖于platform总线的设备也定义了特有的结构:platform_device,内部封装了struct device结构。
struct platform_device {
const char *name;
int id;
bool id_auto;
struct device dev;
u32 num_resources;
struct resource *resource;
const struct platform_device_id *id_entry;
char *driver_override; /* Driver name to force a match */
/* MFD cell pointer */
struct mfd_cell *mfd_cell;
/* arch specific additions */
struct pdev_archdata archdata;
};
与globalfifo_driver相对应,同样定义globalfifo_device结构体,成员定义如下:
static struct platform_device globalfifo_device = {
.name = "globalfifo_platform",
.id = -1,
};
对设备globalfifo_device进行注册的入口函数为platform_device_register(&globalfifo_device)。
int platform_device_register(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
device_initialize(&pdev->dev);
arch_setup_pdev_archdata(pdev);
return platform_device_add(pdev);
}
其中device_initialize(&pdev->dev)在第一节platform_bus注册中也提到过,主要对struct device中基本成员进行初始化,包括kobject、struct device_private、struct mutex等。着重介绍platform_device_add(pdev)。
platform_device_add(&globalfifo_device)
int platform_device_add(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int i, ret;
if (!pdev->dev.parent)
pdev->dev.parent = &platform_bus;
pdev->dev.bus = &platform_bus_type;
switch (pdev->id) {
default:
dev_set_name(&pdev->dev, "%s.%d", pdev->name, pdev->id);
break;
case PLATFORM_DEVID_NONE:
dev_set_name(&pdev->dev, "%s", pdev->name);
break;
case PLATFORM_DEVID_AUTO:
/*
* Automatically allocated device ID. We mark it as such so
* that we remember it must be freed, and we append a suffix
* to avoid namespace collision with explicit IDs.
*/
ret = ida_simple_get(&platform_devid_ida, 0, 0, GFP_KERNEL);
pdev->id = ret;
pdev->id_auto = true;
dev_set_name(&pdev->dev, "%s.%d.auto", pdev->name, pdev->id);
break;
}
for (i = 0; i < pdev->num_resources; i++) {
struct resource *p, *r = &pdev->resource[i];
if (r->name == NULL)
r->name = dev_name(&pdev->dev);
p = r->parent;
if (!p) {
if (resource_type(r) == IORESOURCE_MEM)
p = &iomem_resource;
else if (resource_type(r) == IORESOURCE_IO)
p = &ioport_resource;
}
if (p) {
ret = insert_resource(p, r);
}
}
ret = device_add(&pdev->dev);
if (ret == 0)
return ret;
... ...
}
platform_device_add(&globalfifo_device)主要工作如下:
- 对
globalfifo_device.dev.parent和globalfifo_device->dev.bus初始化,分别指向platform_bus和platform_bus_type。 globalfifo_device.dev.kobj->name初始化为globalfifo_device.name(“globalfifo_platform”)。- 调用
device_add(&globalfifo_device.dev)添加设备。
device_add(&globalfifo_device.dev)
int device_add(struct device *dev)
{
struct device *parent;
struct kobject *kobj;
int error = -EINVAL;
/* This will incr the ref_count */
dev = get_device(dev);
/* Init dev->p->device = dev */
if (!dev->p)
error = device_private_init(dev);
/* if init_name exists, use it to initialize dev.kobj->name */
if (dev->init_name) {
dev_set_name(dev, "%s", dev->init_name);
dev->init_name = NULL;
}
/* subsystems can specify simple device enumeration */
if (!dev_name(dev) && dev->bus && dev->bus->dev_name)
dev_set_name(dev, "%s%u", dev->bus->dev_name, dev->id);
/* Return ERROR if dev name is not specified */
if (!dev_name(dev)) {
error = -EINVAL;
goto name_error;
}
... ...
parent = get_device(dev->parent);
/* get_device_parent(dev, parent) --> platform_bus.kobj */
kobj = get_device_parent(dev, parent);
if (kobj)
dev->kobj.parent = kobj;
... ...
/* first, register with generic layer. */
/* we require the name to be set before, and pass NULL */
error = kobject_add(&dev->kobj, dev->kobj.parent, NULL);
/* notify platform of device entry */
error = device_platform_notify(dev, KOBJ_ADD);
error = device_create_file(dev, &dev_attr_uevent);
error = device_add_class_symlinks(dev);
error = device_add_attrs(dev);
/* Main Entrance to add device into existing bus */
error = bus_add_device(dev);
error = dpm_sysfs_add(dev);
device_pm_add(dev);
/* Create related node in devfs */
if (MAJOR(dev->devt)) {
error = device_create_file(dev, &dev_attr_dev);
error = device_create_sys_dev_entry(dev);
devtmpfs_create_node(dev);
}
... ...
kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);
/* Try to find driver to bind this device */
bus_probe_device(dev);
... ...
}
主要工作如下:
globalfifo_device.dev.kobj.parent初始化为&platform_bus.kobj。kobject_add()函数初始化globalfifo_device.dev.kobj对象,在sysfs中建立相关的目录,例如/sys/devices/platform/globalfifo_platform。bus_add_device(&globalfifo_device.dev):将globalfifo_device注册到总线系统里,并建立sysfs的相关目录:总线系统中建立到设备的链接,同时也在设备目录下建立到总线的subsystem链接。bus_probe_device(dev):尝试在总线上寻找可以绑定的驱动。下文详细介绍。
globalfifo_devices初步初始化后主要成员列举如下:
static struct platform_device globalfifo_device = {
.name = "globalfifo_platform",
.id = -1,
.dev = {
.parent = &platform_bus,
.bus = &platform_bus_type,
.p = {
.device = & globalfifo_device.dev,
INIT_LIST_HEAD(.klist_children->k_list),
spin_lock_init(.klist_children->k_lock),
.klist_children->get = klist_children_get,
.klist_children->put = klist_children_put,
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&.deferred_probe)
},
.kobj = {
.name = "globalfifo_platform",
.kref->refcount->refs = 1,
INIT_LIST_HEAD(.entry),
.state_in_sysfs = 0,
.state_add_uevent_sent = 0,
.state_remove_uevent_sent = 0,
.state_initialized = 1,
.kset = devices_kset,
.ktype = device_ktype,
.name = "globalfifo_platform",
.parent = & platform_bus.kobj,
.sd = { //create_dir: /sys/devices/platform/globalfifo_platform
.parent = platform_bus.kobj.sd,
.dir.root = platform_bus.kobj.sd->dir.root,
.ns = NULL,
.priv = .kobj
}
},
INIT_LIST_HEAD(.dma_pools),
Mutex_init(.mutex),
spin_lock_init(.devres_lock),
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->devres_head),
device_pm_init(.),
.numa_node = -1,
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->msi_list),
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->links.consumers);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->links.suppliers);
dev->links.status = DL_DEV_NO_DRIVER;
},
};
bus_probe_device(&globalfifo_device.dev)
/***** drivers/base/bus.c *****/
/**
* bus_probe_device - probe drivers for a new device
* @dev: device to probe
*
* - Automatically probe for a driver if the bus allows it.
*/
void bus_probe_device(struct device *dev)
{
struct bus_type *bus = dev->bus;
if (!bus)
return;
if (bus->p->drivers_autoprobe)
device_initial_probe(dev);
... ...
}
/***** drivers/base/dd.c *****/
void device_initial_probe(struct device *dev)
{
__device_attach(dev, true);
}
static int __device_attach(struct device *dev, bool allow_async)
{
... ...
ret = bus_for_each_drv(dev->bus, NULL, &data,
__device_attach_driver);
... ...
}
static int __device_attach_driver(struct device_driver *drv, void *_data)
{
struct device_attach_data *data = _data;
struct device *dev = data->dev;
bool async_allowed;
int ret;
ret = driver_match_device(drv, dev);
if (ret == 0) {
/* no match */
return 0;
} else if (ret == -EPROBE_DEFER) {
dev_dbg(dev, "Device match requests probe deferral\n");
driver_deferred_probe_add(dev);
} else if (ret < 0) {
dev_dbg(dev, "Bus failed to match device: %d", ret);
return ret;
} /* ret > 0 means positive match */
async_allowed = driver_allows_async_probing(drv);
if (async_allowed)
data->have_async = true;
if (data->check_async && async_allowed != data->want_async)
return 0;
return driver_probe_device(drv, dev);
}
bus_probe_device(&globalfifo_device.dev)的执行函数路线分析如下所示,经过层层调用,最终又调用到driver_match_device()和driver_probe_device()函数,查找总线上能和当前设备匹配的驱动,并将驱动和设备绑定在了一起。
struct device *dev = &globalfifo_device.dev;
struct device_attach_data *data = {
.dev = dev,
.check_async = allow_async,
.want_async = false,
};
struct device_driver *drv;
---------------------------------------------------
bus_probe_device(dev)
|
V
device_initial_probe(dev)
|
V
__device_attach(dev, true)
|
V
bus_for_each_drv(dev->bus, NULL, &data, __device_attach_driver)
|
V
__device_attach_driver(drv, data)
|
V
driver_match_device(drv, dev) / driver_probe_device(drv, dev)
总结
综上述分析,可以看到驱动注册的过程中,会尝试寻找总线上可以与之匹配的设备;同样地,设备注册的过程中,也会尝试寻找总线上可以与之绑定的驱动。整个过程中,总线、设备、驱动的关键注册函数分别为:
- 总线注册:
bus_register() - 驱动注册:
platform_driver_register() --> driver_register() --> bus_add_driver() - 设备注册:
platform_device_add() --> device_add() --> bus_add_device() / bus_probe_device()
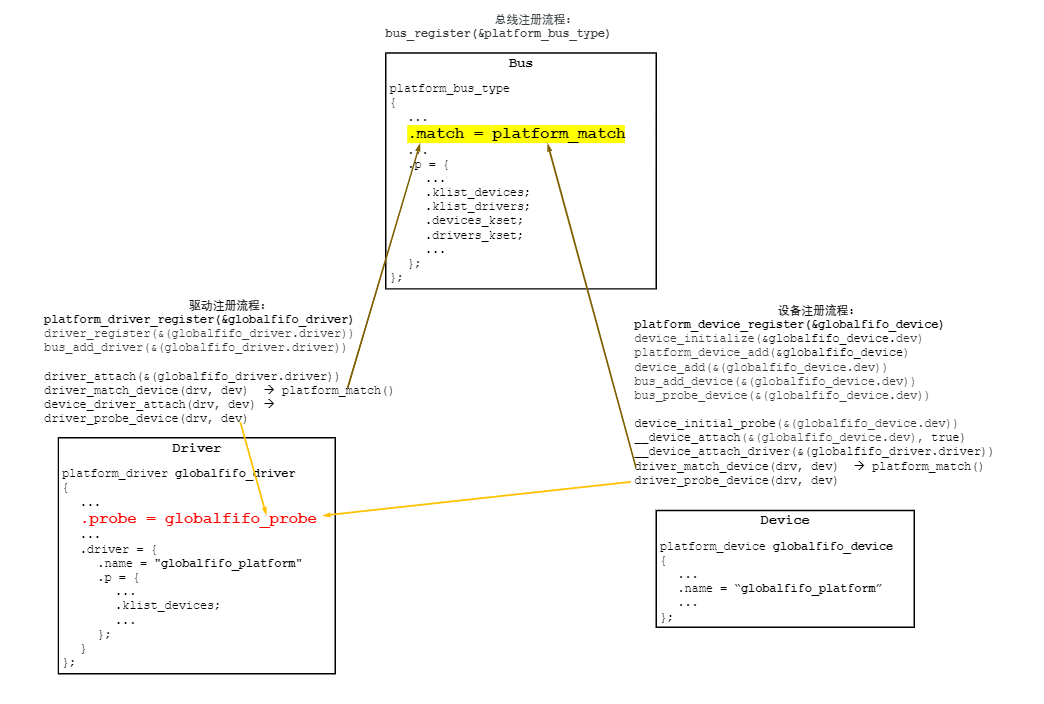
从sysfs的角度,可以清楚地看到platform_device、platform_driver、platform_bus之间的联系:
/sys/bus/platform/drivers/globalfifo_platform$ ll
total 0
bind
globalfifo_platform -> ../../../../devices/platform/globalfifo_platform/
module -> ../../../../module/globalfifo_platform/
uevent
unbind
/sys/bus/platform/devices$ ll
total 0
... ...
globalfifo_platform -> ../../../devices/platform/globalfifo_platform/
/sys/devices/platform/globalfifo_platform$ ll
total 0
driver -> ../../../bus/platform/drivers/globalfifo_platform/
modalias
power/
subsystem -> ../../../bus/platform/
uevent
/sys/module/globalfifo_platform/drivers$ ll
total 0
platform:globalfifo_platform -> ../../../bus/platform/drivers/globalfifo_platform/
参考资料
[1] Linux设备驱动开发详解(基于最新的Linux4.0内核),宋宝华编著,2016年
[2] 知识整理–linux设备驱动模型:https://blog.csdn.net/TongxinV/article/details/54853122
[3] linux设备驱动模型:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40732350/article/details/82992904
原文链接
- Linux设备驱动模型简述(源码剖析)