目录
一. 正则表达式
二. Math类
三. Random类
四. Date类
五. Calendar类
六. SimpDateFormate类
七. BigInteger类
八. BigDecimal类
一. 正则表达式
正则表达式(Regular Expression)就是用一些特殊的符号去匹配一个字符串是否符合规则,利用String类中的matches()方法去匹配字符串
这里只介绍一些常用的正则表达式,当需要使用时可以自己在网上查找
| * | 表示匹配0次或多次 |
| + | 至少匹配一次或多次 |
| [] | 只允许出现括号内的内容 |
| {n} | 只能出现n次 |
| {n,} | 至少出现n次 |
| {n,m} | 只能出现n到m次 |
| \d | 匹配数字 |
| \D | 匹配非数字 |
| \w | 匹配数字,字母,下划线 |
| \W | 匹配非数字,字母,下划线 |
| \s | 匹配空格字符 |
| \S | 匹配非空格字符 |
| | | 逻辑或 |
| . | 匹配除了换行符的任意字符 |
public class RegExDemo1 {
/*
正则表达式 (Regular Expression),简称 regex
正则表达式是一种规则(模式)匹配语法,
可以使用一些正则表达式中定义的特殊符号来定义一种规则,然后用此规则去匹配某个字符串
如果字符串与规则相匹配返回true,否则返回false
验证一个字符串是否是中国大陆地区的手机号格式? //长度是11位 是不是1开头 判断第二位 判断之后的每位是数字
可以使用正则表达式定义一个规则去匹配即可
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "704447306";
System.out.println(s.matches("[0-9]*"));//[0-9]* 允许出现0次或多次数字
System.out.println(s.matches("[0-9]+"));//[0-9]+ 允许出现至少一次或多次数字
System.out.println(s.matches("1[0-9]{3}"));//[0-9]{3}只能是n次
System.out.println(s.matches("1[0-9]{3,}"));//[0-9]{3}至少n次
System.out.println(s.matches("[0-9]{3,6}")); // [0-9]{3,6}至少n次 不大于m次
System.out.println(s.matches("[1-9]{3,6}"));
System.out.println(s.matches("[357]{3,6}"));//只能是3 5 7 3-6位
System.out.println(s.matches("\\d{3,6}")); //\d == [0-9] 匹配数字 \D 匹配非数字
System.out.println(s.matches("1[358]\\d{9}"));//匹配手机号
System.out.println(s.matches("[1-9]\\d{5,9}"));//匹配qq号
}
}public class RegExDemo2 {
/*
正则表达式 (Regular Expression) 简称regex
正则表达式是一种规则(模式)匹配语法
可以使他一些正则表达式中定义的特殊符号来定义一种规则,然后用此规则去匹配某个字符串
如果字符串与规则匹配返回true,否则返回false
[0-9] [1-9] [357] [a-z] [A-z0-9]* + {n} {n,} {n,m}
\d匹配数字
\D匹配非数字
\w匹配数字,字母,下划线
\W匹配非数字 字母 下划线
\s匹配空格字符
\S非空格字符
|逻辑或
.匹配任意字符,要使用本来的.要转义
[\\u4e00-\\u9fa5] 匹配汉字
验证一个字符串是否是中国大陆地区的手机号格式? //长度11位 是不是1开头 判断第二位 判断之后的每位是数字
可以使用正则表达式定义一个规则去匹配
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "704447306@asd.com";
System.out.println(s.matches("[a-z]*"));//匹配小写字母
System.out.println(s.matches("[A-Z]+"));//匹配大写字母
System.out.println(s.matches("[a-zA-Z]*"));//匹配所有字母
System.out.println(s.matches("[0-9A-Z]*"));//匹配数字和大写字母
System.out.println(s.matches("\\w*"));//匹配数字 字母 下划线
System.out.println(s.matches("[\\u4e00-\\u9fa5]*"));//匹配中文
System.out.println(s.matches("[\\w\\s]"));//\s匹配空格
//邮箱格式 xxxx@xx.com.cn
System.out.println(s.matches("\\w{6,10}@\\w{1,5}((\\.com)|(\\.com\\.cn))"));
}
}二. Math类
Math类中有一些用于数学计算的方法,在java.lang包中,下面介绍一些常用的
| PI | 数学中的PI(3.1415926) |
| abs(n) | 计算n的绝对值 |
| sqrt(n) | 对n开根号 |
| pow(n,m) | 计算n的m次方 |
| floor(n) | 对n向下取整 |
| ceil(n) | 对n向上取整 |
| round(n) | 四舍五入 |
| max() | 求两个数之间的较大者 |
| random() | 返回0-1之间的随机数 |
public class MathDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Math.PI);//PI
System.out.println(Math.abs(-3));//绝对值
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(9));//开根号
System.out.println(Math.pow(2,3));//n的m次方
System.out.println(Math.floor(9.9));//向下取整
System.out.println(Math.ceil(9.1));//向上取整
System.out.println(Math.round(9.5));//四舍五入
System.out.println(Math.max(5,10));//返回两个数之间的较大者
System.out.println(Math.random());//返回0-1之间的随机数 可能会等于0,小于1
}
}三. Random类
Random类是一个用于产生随机数的类,在java.util包中
| nextBoolean() | 返回一个随机的布尔值 |
| nextInt() | 在int范围内返回一个随机数 |
| nextInt(n) | 在0-(n-1)之间返回一个数 |
| nextLong() | 在Long范围内返回一个随机数 |
| nextBytes(byte[ ]) | 随机取出byte数组个长度的随机数返回 |
public class RandomDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
System.out.println(random.nextBoolean());//返回一个随机的布尔值
System.out.println(random.nextInt());//在int的取值范围内随机获取一个值
System.out.println(random.nextLong());//在long的取值范围内随机获取一个值
System.out.println(random.nextInt(35)+1);//在给定范围内随机获取一个数 0 <= num < 给定数
byte[] bytes = new byte[5];
random.nextBytes(bytes);//随机取出数组长度个byte类型的随机数
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
}
}四. Date类
在java.util包中,Date类主要是一个日期类,Date类的对象主要用来记录对象被创建那一刻的时间,里面有很多获取关于时间的方法,只不过因为该类在JDK1.0时就已经被写好了,很多方法已经被抛弃了,有其他类替换了
| getYear() | 获取年份,不过该方法中用当前年份-1900,所以在使用时要+1900 |
| getMonth() | 获取月份,该方法中用当前月份-1,所以在使用时要+1 |
| getDay() | 获取天数 |
| getHours() | 获取小时 |
| getMinutes() | 获取分钟 |
| getSeconds() | 获取秒 |
| getTime() | 获取该对象被创建那一刻的时间 |
| Date(long date) | 有参构造,传入一个时间戳,返回这个时间戳对应的日期对象 |
public class DateDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date = new Date();//获取程序运行时的时刻
System.out.println(date);
System.out.println(date.getYear()+1900);//Date类中的有些方法已经被后面的代替,但是还可以用
System.out.println(date.getDay());
System.out.println(date.getMonth()+1);//月份
System.out.println(date.getHours());//小时
System.out.println(date.getMinutes());//分钟
System.out.println(date.getSeconds());//秒
//获取的是自1970 1.1 0:0:0至程序运行时刻的毫秒值
System.out.println(date.getTime());//1719925778342 时间戳qa2wesdrxftgyvhbujnki
Date date1 = new Date();
System.out.println(date1.getTime() - date.getTime());
Date date2 = new Date(17119925778342L);//将指定的long类型的时间戳构造出一个时间对象
System.out.println(date2);
}
}五. Calendar类
Calendar类是一个日历类,该类是一个抽象类,所以我们在使用时要创建他的子类对象,一般我们创建GregorianCalendar类的对象,该类就是现在我们使用的公历,Calendar类就是用来替代Date类中的一些方法的类
| get() | 主要用来将GregorianCalendar类中的静态常量转为我们想要的时间 |
| YEAR | 在GregorianCalendar类中是一个静态的常量1,配合get()方法可以返回年份 |
| MONTH | 在GregorianCalendar类中是一个静态的常量2,配合get()方法可以返回月份-1,使用时记得+1 |
| DAY_OF_MONTH | 在GregorianCalendar类中是一个静态的常量5,配合get()方法可以返回今天是这个月的第几天 |
| DAY_OF_WEEK | 在GregorianCalendar类中是一个静态的常量7,配合get()方法可以返回今天是这周的第几天 |
| DAY_OF_YEAR | 在GregorianCalendar类中是一个静态的常量6,配合get()方法可以返回今天是今年的第几天 |
| WEEK_OF_MONTH | 在GregorianCalendar类中是一个静态的常量4,配合get()方法可以返回这周是这个月的第几周 |
| HOUR_OF_DAY | 在GregorianCalendar类中是一个静态的常量11,配合get()方法可以返回现在是今天的第几个小时 |
| getTimeInMillis() | 该方法返回对象被创建的时间,和Date类中的getTime()用法相同 |
六. SimpDateFormate类
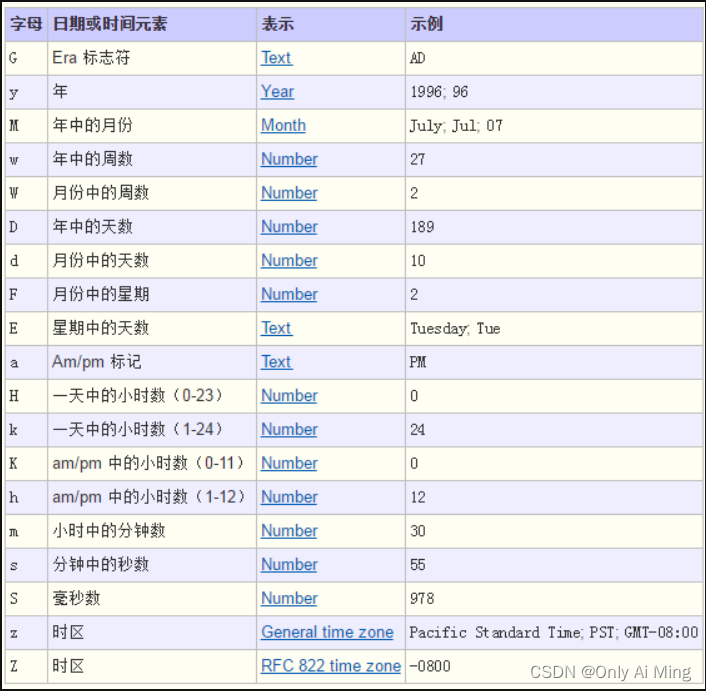
SimpDateFormate类用于将字符串和日期(Date类)进行相互转换
| SimpDateFormate(String pattern) | 传入一种匹配模式,可以将字符串转为该模式的日期对象,也可以将日期对象转为该模式的字符串 |
| parse(String s) | 将字符串转为日期对象 |
| format(Date d) | 将日期对象转为字符串 |
public class SimpleDateFormatDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
/*
把字符串日期转为Date对象
*/
String s = "2003-02-03";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date date = sdf.parse(s);
System.out.println(date.getYear()+1900);
/*
把Date对象转为字符串
*/
SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("y-M-d H:m:s E");
Date date1 = new Date();
String s1 = sdf1.format(date1);
System.out.println(s1);
}
}七. BigInteger类
主要用于对大数的计算
| add() | 加法运算 |
| subtract() | 减法运算 |
| multiply() | 乘法运算 |
| divide() | 除法运算 |
public class BigIntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigInteger bigInteger1 = new BigInteger("111111111111111111111111111111111111");
BigInteger bigInteger2 = new BigInteger("999999999999999999999999999999999999");
BigInteger bigInteger3 = bigInteger1.add(bigInteger2);
BigInteger bigInteger5 = bigInteger1.subtract(bigInteger2);
BigInteger bigInteger4 = bigInteger1.multiply(bigInteger2);
BigInteger bigInteger6 = bigInteger2.divide(bigInteger1);
System.out.println(bigInteger1);
System.out.println(bigInteger2);
System.out.println(bigInteger3);
System.out.println(bigInteger4);
System.out.println(bigInteger5);
System.out.println(bigInteger6);
}
}
八. BigDecimal类
小数在计算机中存储时也是用二进制的形式,但有的十进制小数对小数部分采取乘2取整的方式时会发生无限不循环的情况,这就导致了计算机在表示小数时有时候只能近似表示的情况.例如:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double result = 1-0.7;
System.out.println(result);
if(result==0.3){
System.out.println("相等");
}else{
System.out.println("不相等");
}
}
} 
此时就需要使用到BigDecimal类,来对小数进行准确的计算
| add() | 加法运算 |
| subtract() | 减法运算 |
| multiply() | 乘法运算 |
| divide() | 除法运算 |
public class BigDecimalDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("0.7");
BigDecimal bigDecimal2 = new BigDecimal("0.3");
BigDecimal bigDecimal3 = bigDecimal1.add(bigDecimal2);
BigDecimal bigDecimal4 = bigDecimal1.subtract(bigDecimal2);
BigDecimal bigDecimal5 = bigDecimal1.multiply(bigDecimal2);
BigDecimal bigDecimal6 = bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2,5,1);
System.out.println(bigDecimal3);
System.out.println(bigDecimal4);
System.out.println(bigDecimal5);
System.out.println(bigDecimal6);
}
}这里注意计算除法时,可能会出现无限循环或者无限不循环的情况,这时会报错,所以注意除法的方法(divide)可以设置两个参数,一个divide(int scale,int roundingMode),scale表示小数点后保留几位小数,roundingMode是1表示舍去后面的位,是2表示进位在舍去后面的位
我们再来看上面的例子
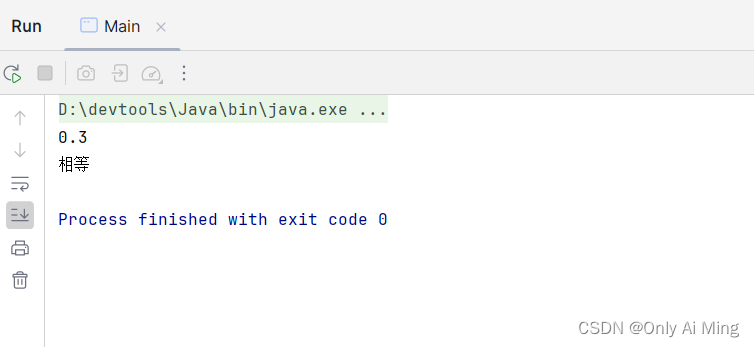
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("1");
BigDecimal bigDecimal2 = new BigDecimal("0.7");
BigDecimal bigDecimal3 = new BigDecimal("0.3");
BigDecimal result = bigDecimal1.subtract(bigDecimal2);
System.out.println(result);
if(result.equals(bigDecimal3)){
System.out.println("相等");
}else{
System.out.println("不相等");
}
}
}
注意:BigDecimal的构造方法中如果用到小数,一定要传字符串,而不是直接传该小数,否则计算机在转换时仍旧无法将该小数准确表示导致构造的BigDecimal对象也是一个不精确的