概述
- 在上一篇文章中,我们已经详细了解了开发 Webpack Loader 需要用到的基本技能,包括:Loader 基本形态、如何构建测试环境、如何使用 Loader Context 接口等。接下来我们继续拓展学习一些 Loader 辅助工具,包括:
- 了解
loader-utils,并使用loader-utils拼接文件名; - 了解
schema-tiles,以及其背后的ajv库与 JSON-Schema 协议,学习使用schema-utils实现参数校验
- 了解
- 文章最后还会深入剖析
vue-loader组件源码,通过实战方式帮助大家更深入理解:如何开发一个成熟 Loader
使用 schema-utils
Webpack,以及 Webpack 生态下的诸多 Loader、Plugin 基本上都会提供若干“配置项”,供用户调整组件的运行逻辑,这些组件内部通常都会使用 schema-utils 工具库校验用户传入的配置是否满足要求。
因此,若我们开发的 Loader 需要对外暴露配置项,建议也尽量使用这一工具,基本用法:
-
安装依赖:
yarn add -D schema-utils -
编写配置对象的 Schema 描述,例如:
// options.json { "type": "object", "properties": { "name": { "type": "boolean" } }, "required": ["name"], "additionalProperties": false } -
在 Loader 中调用
schema-utils校验配置对象:import { validate } from "schema-utils"; import schema from "./options.json"; // 调用 schema-utils 完成校验 export default function loader(source) { const options = this.getOptions(); validate(schema, options); return source; } // Webpack5 之后还可以借助 Loader Context 的 `getOptions` 接口完成校验 export default function loader(source) { const options = this.getOptions(schema); return source; }
之后,若用户传入不符合 Schema 描述的参数对象,会报类似下面这种错误提示:
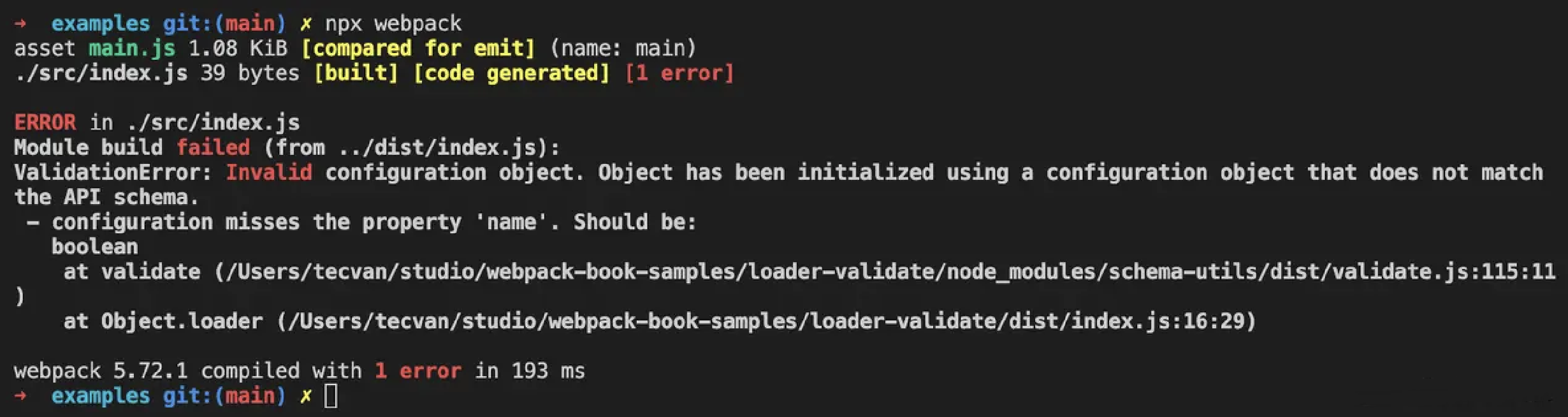
schema-utils 的校验能力很强,能够完美支撑起 Webpack 生态下非常复杂的参数校验需求,但官方文档非常语焉不详,翻阅源码后发现,它底层主要依赖于 ajv ,这是一个应用广泛、功能强大且性能优异的校验工具:
- 提示:
ajv在对象校验、JSON 序列化/反序列化方面的性能表现非常突出,许多知名开源框架 如:ESLint、fast-json-stringify、middy、swagger、tailwind 等底层都依赖于ajv,值得我们学习、复用到业务项目中。
ajv 功能非常完备,基本上已经覆盖了“使用 JSON 描述对象约束”的所有场景,我们不可能在一篇文章里介绍所有细节,所以我下面只摘要介绍一些比较重要的能力与实例,更多信息建议参考 官网。
-
ajv数据描述格式基础知识: -
schema-utils内部使用ajv的 JSON-Schema 模式实现参数校验,而 JSON-Schema 是一种以 JSON 格式描述数据结构的 公共规范,使用时至少需要提供type参数,如:{ "type": "number" }
ajv 默认支持七种基本数据类型。
-
number :数值型,支持整数、浮点数,支持如下校验规则:
maximum、minimum:属性值必须大于等于minimum,且小于等于maximum;exclusiveMaximum、exclusiveMinimum:属性值必须大于exclusiveMinimum,且小于exclusiveMinimum;multipleOf:属性值必须为multipleOf的整数倍,例如对于multipleOf = 5,则10/20/5均符合预期,但8/9/1等不符合预期。
-
interger:整数型,与number类似,也支持上面介绍的maximum等校验规则; -
string :字符串型,支持如下校验规则:
maxLength、minLength:限定字符串的最大长度、最小长度;pattern:以正则表达式方式限定字符串内容;format:声明字符串内容格式,schema-utils底层调用了[ajv-formats](https://github.com/ajv-validator/ajv-formats)插件,开箱支持date/ipv4/regex/uuid等格式。
-
boolean:bool 值; -
array :数组型,支持如下校验属性:
maxItems、minItems:限定数组的最多、最少的元素数量;uniqueItems:限定数组元素是否必须唯一,不可重复;items:声明数组项的 Schema 描述,数组项内可复用 JSON-Schema 的任意规则,从而形成嵌套定义结构;
-
null:空值,常用于复合type类型,如type = ['object', 'null']支持传入对象结构或null值; -
object :对象结构,这是一个比较负责的结构,支持如下校验属性:
-
maxProperties/minProperties:限定对象支持的最多、最少属性数量; -
required:声明哪些属性不可为空,例如required = ['name', 'age']时,传入的值必须至少提供name/age属性; -
properties:定义特定属性的 Schema 描述,与array的items属性类似,支持嵌套规则,例如:{ type: "object", properties: { foo: {type: "string"}, bar: { type: "number", minimum: 2 } } }
-
-
patternProperties:同样用于定义对象属性的 Schema,但属性名支持正则表达式形式,例如:{ type: "object", patternProperties: { "^fo.*$": {type: "string"}, "^ba.*$": {type: "number"} } } -
additionalProperties:限定对象是否可以提供除properties、patternProperties之外的属性;
除此之外,Schema 节点还支持一些通用的规则字段,包括:
-
enum:枚举数组,属性值必须完全等于(Deep equal)这些值之一,例如:// JSON-Schema { "type": "string", "enum": [ "fanwenjie", "tecvan" ] } // 有效值: "fanwenjie"/"tecvan" // 无效值,如: "foo bar" 等 -
const:静态数值,属性值必须完全等于const定义,单独看const似乎作用不大,但配合 $data 指令的 JSON-Pointer 能力,可以实现关联相等的效果,例如:// JSON-Schema { type: "object", properties: { foo: {type: "string"}, bar: {const: {$data: "1/foo"}} } } // bar 必须等于 foo,如: { "foo": "fanwenjie", "bar": "fanwenjie" } // 否则无效: { "foo": "fanwenjie", "bar": "tecvan" } -
这些基础数据类型与校验规则奠定了
ajv的基础校验能力,我们使用schema-utils时大部分时间都需要与之打交道,建议同学们多加学习掌握。 -
使用
ajv复合条件指令
除上述介绍的基本类型与基础校验规则外,ajv 还提供了若干复合校验指令:
-
not:数值必须不符合该条件,例如:
{type: "number", not: {minimum: 3}}时,传入数值必须小于 3; -
anyof:数值必须满足
anyof条件之一,这是一个非常实用的指令,例如在css-loader中:// css-loader/src/options.json { "additionalProperties": false, "properties": { "url": { "description": "Enables/Disables 'url'/'image-set' functions handling (https://github.com/webpack-contrib/css-loader#url).", "anyOf": [ { "type": "boolean" }, { "instanceof": "Function" } ] }, // more properties }, "type": "object" }
这意味着 css-loader 的 url 配置项只接受 Bool 或函数值。
-
oneof:数值必须满足且只能满足
oneof条件之一,例如:{ type: "number", oneOf: [{maximum: 3}, {type: "integer"}] } // 下述数值符合要求: 1.1、2.1、4、5 等 // 下述数值不符合要求: 3.5、2、1 等
数值要么是小于等于3的浮点数,要么是大于3的整数,不在此区间的数值如“3.5/2” 等均不符合要求。
-
allof:数值必须满足
allof指定的所有条件,例如:{ type: "number", allOf: [{maximum: 3}, {type: "integer"}] } // 下述数值符合要求: 1、2、3 等 // 下述数值不符合要求: 1.1、4、5 等
这要求传入的数值必须小于 3,且必须为整型。
-
if/then/else:这是一个稍显复杂的三元组复合条件,大致逻辑为:若传入的数值满足if条件,则必须同时满足then条件;若不满足if则必须同时满足else,其中else可选。例如:{ type: "object", if: {properties: {foo: {minimum: 10}}}, then: {required: ["bar"]}, else: {required: ["baz"]} }
这意味着,若传入的 foo 属性值大于等于 10 时,则必须同时提供 then 所要求的 bar 属性;否则必须同时提供 else 所要求的 baz 属性。
总结一下,Webpack 官方选择 ajv 作用配置参数的校验工具,并将其二次封装为 schema-utils 库,供 Webpack 生态下的诸多 Loader、Plugin 使用。
而上面介绍的基础类型、类型校验、复合校验规则等内容是 ajv 非常基础且重要的知识点,三者协作组成 ajv 校验 schema 的框架结构,除此之外还有许多增强 Schema 表述能力的增强指令,包括:$data、$ref、definitions 等,篇幅关系这里不一一列举。同学们也可以参考 Webpack 官方编写的 Schema 文件,学习各种校验规则的写法。
使用 loader-utils
在 Webpack5 之前,loader-utils 是一个非常重要的 Loader 开发辅助工具,为开发者提供了诸如 getOptions/getCurrentRequest/parseQuery 等核心接口,这些接口被诸多 Loader 广泛使用,到 Webpack5 之后干脆将这部分能力迁移到 Loader Context,致使 loader-utils 被大幅裁减简化。
被裁减后的 loader-utils 仅保留了四个接口:
urlToRequest:用于将模块路径转换为文件路径的工具函数;isUrlRequest:用于判定字符串是否为模块请求路径;getHashDigest:用于计算内容 Hash 值;interpolateName:用于拼接文件名的模板工具;
翻阅大量 Loader 源码后发现,前三个接口使用率极低,实用性不大,因此本文直接跳过,仅侧重介绍 interpolateName 接口。
使用 interpolateName 拼接文件名
Webpack 支持以类似 [path]/[name]-[hash].js 方式设定 output.filename 即输出文件的命名,这一层规则通常不需要关注,但在编写类似 webpack-contrib/file-loader 这种自行输出产物文件的 Loader 时,需要由开发者自行处理产物路径逻辑。
此时可以使用 loader-utils 提供的 interpolateName 方法在 Loader 中以类似 Webpack 的 output.filename 规则拼接资源路径及名称,例如:
// file-loader/src/index.js
import { interpolateName } from 'loader-utils';
export default function loader(content) {
const context = options.context || this.rootContext;
const name = options.name || '[contenthash].[ext]';
// 拼接最终输出的名称
const url = interpolateName(this, name, {
context,
content,
regExp: options.regExp,
});
let outputPath = url;
// ...
let publicPath = `__webpack_public_path__ + ${JSON.stringify(outputPath)}`;
// ...
if (typeof options.emitFile === 'undefined' || options.emitFile) {
// ...
// 提交、写出文件
this.emitFile(outputPath, content, null, assetInfo);
}
// ...
const esModule =
typeof options.esModule !== 'undefined' ? options.esModule : true;
// 返回模块化内容
return `${esModule ? 'export default' : 'module.exports ='} ${publicPath};`;
}
export const raw = true;
代码的核心逻辑:
- 根据 Loader 配置,调用
interpolateName方法拼接目标文件的完整路径; - 调用上下文
this.emitFile接口,写出文件; - 返回
module.exports = ${publicPath},其它模块可以引用到该文件路径。
- 提示:除
file-loader外,css-loader、eslint-loader都有用到该接口,感兴趣的同学请自行前往查阅源码。
interpolateName 功能稍弱于 Webpack 的 Template String 规则,仅支持如下占位符:
[ext]:原始资源文件的扩展名,如.js;[name]:原始文件名;[path]:原始文件相对context参数的路径;[hash]:原始文件的内容 Hash 值,与output.file类似同样支持[hash:length]指定 Hash 字符串的长度;[contenthash]:作用、用法都与上述[hash]一模一样。
综合示例:Vue-loader
接下来,我们再结合 vue-loader 源码进一步学习 Loader 开发的进阶技巧。vue-loader 是一个综合性很强的示例,它借助 Webpack 与组件的一系列特性巧妙地解决了:如何区分 Vue SFC 不同代码块,并复用其它 Loader 处理不同区块的内容?
先从结构说起,vue-loader 内部实际上包含了三个组件:
lib/index.js定义的 Normal Loader,负责将 Vue SFC 不同区块转化为 JavaScriptimport语句,具体逻辑下面细讲;lib/loaders/pitcher.js定义的 Pitch Loader,负责遍历的rules数组,拼接出完整的行内引用路径;lib/plugin.js定义的插件,负责初始化编译环境,如复制原始rules配置等;
三者协作共同完成对 SFC 的处理,使用时需要用户同时注册 Normal Loader 和 Plugin,如:
const VueLoaderPlugin = require("vue-loader/lib/plugin");
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /.vue$/,
use: [{ loader: "vue-loader" }],
}
],
},
plugins: [
new VueLoaderPlugin()
],
};
vue-loader 运行过程大致上可以划分为两个阶段:
- 预处理阶段:动态修改 Webpack 配置,注入
vue-loader专用的一系列module.rules; - 内容处理阶段:Normal Loader 配合 Pitch Loader 完成文件内容转译。
预处理阶段
vue-loader 插件会在 apply 函数中动态修改 Webpack 配置,核心代码如下:
class VueLoaderPlugin {
apply (compiler) {
// ...
const rules = compiler.options.module.rules
// ...
const clonedRules = rules
.filter(r => r !== rawVueRules)
.map((rawRule) => cloneRule(rawRule, refs))
// ...
// global pitcher (responsible for injecting template compiler loader & CSS
// post loader)
const pitcher = {
loader: require.resolve('./loaders/pitcher'),
resourceQuery: query => {
if (!query) { return false }
const parsed = qs.parse(query.slice(1))
return parsed.vue != null
}
// ...
}
// replace original rules
compiler.options.module.rules = [
pitcher,
...clonedRules,
...rules
]
}
}
function cloneRule (rawRule, refs) {
// ...
}
module.exports = VueLoaderPlugin
拆开来看,插件主要完成两个任务:
- 初始化并注册 Pitch Loader:代码第16行,定义pitcher对象,指定loader路径为
require.resolve('./loaders/pitcher'),并将pitcher注入到rules数组首位。
这种动态注入的好处是用户不用关注 —— 不去看源码根本不知道还有一个pitcher loader,而且能保证pitcher能在其他rule之前执行,确保运行顺序。
- 复制
rules配置:代码第8行遍历compiler.options.module.rules数组,也就是用户提供的 Webpack 配置中的module.rules项,对每个rule执行cloneRule方法复制规则对象。
之后,将 Webpack 配置修改为 [pitcher, ...clonedRules, ...rules] 。感受一下实际效果,例如:
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /.vue$/i,
use: [{ loader: "vue-loader" }],
},
{
test: /\.css$/i,
use: [MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader, "css-loader"],
},
{
test: /\.js$/i,
exclude: /node_modules/,
use: {
loader: "babel-loader",
options: {
presets: [["@babel/preset-env", { targets: "defaults" }]],
},
},
},
],
},
plugins: [
new VueLoaderPlugin(),
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({ filename: "[name].css" }),
],
};
这里定义了三个 rule,分别对应 vue、js、css 文件。经过 plugin 转换之后的结果大概为:
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
loader: "/node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/pitcher.js",
resourceQuery: () => {},
options: {},
},
{
resource: () => {},
resourceQuery: () => {},
use: [
{
loader: "/node_modules/mini-css-extract-plugin/dist/loader.js",
},
{ loader: "css-loader" },
],
},
{
resource: () => {},
resourceQuery: () => {},
exclude: /node_modules/,
use: [
{
loader: "babel-loader",
options: {
presets: [["@babel/preset-env", { targets: "defaults" }]],
},
ident: "clonedRuleSet-2[0].rules[0].use",
},
],
},
{
test: /\.vue$/i,
use: [
{ loader: "vue-loader", options: {}, ident: "vue-loader-options" },
],
},
{
test: /\.css$/i,
use: [
{
loader: "/node_modules/mini-css-extract-plugin/dist/loader.js",
},
{ loader: "css-loader" },
],
},
{
test: /\.vue$/i,
exclude: /node_modules/,
use: [
{
loader: "babel-loader",
options: {
presets: [["@babel/preset-env", { targets: "defaults" }]],
},
ident: "clonedRuleSet-2[0].rules[0].use",
},
],
},
],
},
};
转换之后生成6个rule,按定义的顺序分别为:
- 针对
xx.vue&vue格式路径生效的规则,只用了vue-loader的 Pitch 作为 Loader; - 被复制的 CSS 处理规则,
use数组与开发者定义的规则相同; - 被复制的 JS 处理规则,
use数组也跟开发者定义的规则相同; - 开发者定义的
vue-loader规则,内容及配置都不变; - 开发者定义的css规则,用到
css-loader、mini-css-extract-plugin loader; - 开发者定义的js规则,用到
babel-loader。
可以看到,第2、3项是从开发者提供的配置中复制过来的,内容相似,只是 cloneRule 在复制过程会给这些规则重新定义 resourceQuery 函数:
function cloneRule (rawRule, refs) {
const rules = ruleSetCompiler.compileRules(`clonedRuleSet-${++uid}`, [{
rules: [rawRule]
}], refs)
const conditions = rules[0].rules
.map(rule => rule.conditions)
// shallow flat
.reduce((prev, next) => prev.concat(next), [])
// ...
const res = Object.assign({}, rawRule, {
resource: resources => {
currentResource = resources
return true
},
resourceQuery: query => {
if (!query) { return false }
const parsed = qs.parse(query.slice(1))
if (parsed.vue == null) {
return false
}
if (!conditions) {
return false
}
// 用import路径的lang参数测试是否适用于当前rule
const fakeResourcePath = `${currentResource}.${parsed.lang}`
for (const condition of conditions) {
// add support for resourceQuery
const request = condition.property === 'resourceQuery' ? query : fakeResourcePath
if (condition && !condition.fn(request)) {
return false
}
}
return true
}
})
// ...
return res
}
cloneRule 内部定义的 resourceQuery 函数对应 module.rules.resourceQuery 配置项,与我们经常用的 test 差不多,都用于判断资源路径是否适用这个rule。这里 resourceQuery 核心逻辑就是取出路径中的lang参数,伪造一个以 lang 结尾的路径,传入rule的condition中测试路径名对该rule是否生效,例如下面这种会命中 /\.js$/i 规则:
import script from "./index.vue?vue&type=script&lang=js&"
vue-loader 正是基于这一规则,为不同内容块 (css/js/template) 匹配、复用用户所提供的 rule 设置。
内容处理阶段
插件处理完配置,webpack 运行起来之后,Vue SFC 文件会被多次传入不同的 Loader,经历多次中间形态变换之后才产出最终的 js 结果,大致上可以分为如下步骤:
- 路径命中
/\.vue$/i规则,调用vue-loader生成中间结果 A; - 结果 A 命中
xx.vue?vue规则,调用vue-loaderPitch Loader 生成中间结果 B; - 结果 B 命中具体 Loader,直接调用 Loader 做处理。
过程大致为:
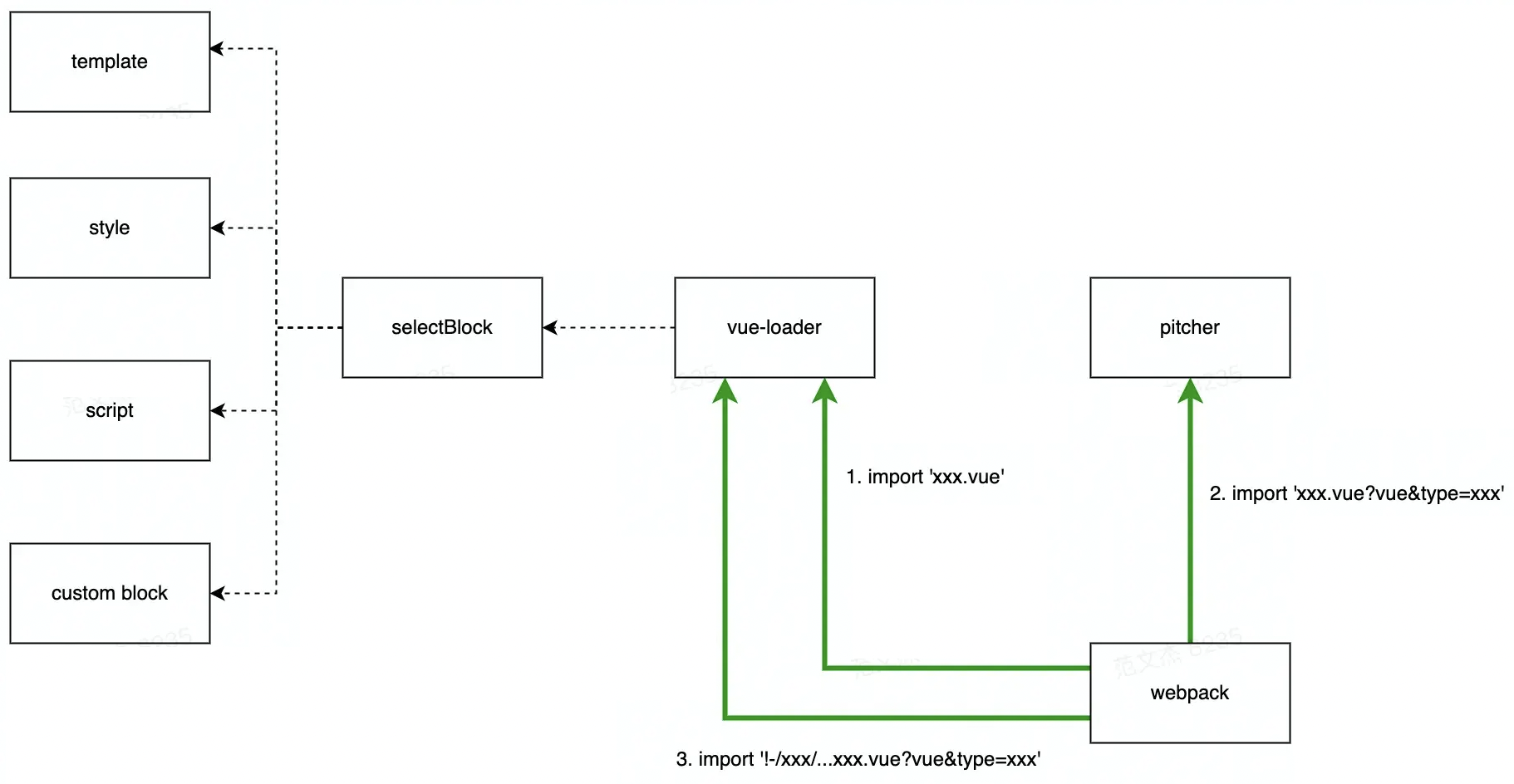
举个转换过程的例子:
// 原始代码
import xx from './index.vue';
// 第一步,命中 vue-loader,转换为:
import { render, staticRenderFns } from "./index.vue?vue&type=template&id=2964abc9&scoped=true&"
import script from "./index.vue?vue&type=script&lang=js&"
export * from "./index.vue?vue&type=script&lang=js&"
import style0 from "./index.vue?vue&type=style&index=0&id=2964abc9&scoped=true&lang=css&"
// 第二步,命中 pitcher,转换为:
export * from "-!../../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/templateLoader.js??vue-loader-options!../../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/index.js??vue-loader-options!./index.vue?vue&type=template&id=2964abc9&scoped=true&"
import mod from "-!../../node_modules/babel-loader/lib/index.js??clonedRuleSet-2[0].rules[0].use!../../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/index.js??vue-loader-options!./index.vue?vue&type=script&lang=js&";
export default mod; export * from "-!../../node_modules/babel-loader/lib/index.js??clonedRuleSet-2[0].rules[0].use!../../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/index.js??vue-loader-options!./index.vue?vue&type=script&lang=js&"
export * from "-!../../node_modules/mini-css-extract-plugin/dist/loader.js!../../node_modules/css-loader/dist/cjs.js!../../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/stylePostLoader.js!../../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/index.js??vue-loader-options!./index.vue?vue&type=style&index=0&id=2964abc9&scoped=true&lang=css&"
// 第三步,根据行内路径规则按序调用loader
第一次执行 vue-loader
在运行阶段,根据配置规则, Webpack 首先将原始的 SFC 内容传入 vue-loader,例如对于下面的代码:
// main.js
import xx from 'index.vue';
// index.vue 代码
<template>
<div class="root">hello world</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {},
mounted() {
console.log("hello world");
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.root {
font-size: 12px;
}
</style>
此时第一次执行 vue-loader ,执行如下逻辑:
- 调用
@vue/component-compiler-utils包的parse函数,将SFC 文本解析为AST对象; - 遍历 AST 对象属性,转换为特殊的引用路径;
- 返回转换结果。
对于上述 index.vue 内容,转换结果为:
import { render, staticRenderFns } from "./index.vue?vue&type=template&id=2964abc9&scoped=true&"
import script from "./index.vue?vue&type=script&lang=js&"
export * from "./index.vue?vue&type=script&lang=js&"
import style0 from "./index.vue?vue&type=style&index=0&id=2964abc9&scoped=true&lang=css&"
/* normalize component */
import normalizer from "!../../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/runtime/componentNormalizer.js"
var component = normalizer(
script,
render,
staticRenderFns,
false,
null,
"2964abc9",
null
)
...
export default component.exports
注意,这里并没有真的处理 block 里面的内容,而是简单地针对不同类型的内容块生成 import 语句:
- Script:
"./index.vue?vue&type=script&lang=js&" - Template:
"./index.vue?vue&type=template&id=2964abc9&scoped=true&" - Style:
"./index.vue?vue&type=style&index=0&id=2964abc9&scoped=true&lang=css&"
这些路径都对应原始的 .vue 路径基础上增加了 vue 标志符及 type、lang 等参数。
执行 Pitch Loader
如前所述,vue-loader 插件会在预处理阶段插入带 resourceQuery 函数的 Pitch Loader:
const pitcher = {
loader: require.resolve('./loaders/pitcher'),
resourceQuery: query => {
if (!query) { return false }
const parsed = qs.parse(query.slice(1))
return parsed.vue != null
}
}
其中, resourceQuery 函数命中 xx.vue?vue 格式的路径,也就是说上面 vue-loader 转换后的 import 路径会被 Pitch Loader 命中,做进一步处理。Pitch Loader 的逻辑比较简单,做的事情也只是转换 import 路径:
const qs = require('querystring')
...
const dedupeESLintLoader = loaders => {...}
const shouldIgnoreCustomBlock = loaders => {...}
// 正常的loader阶段,直接返回结果
module.exports = code => code
module.exports.pitch = function (remainingRequest) {
const options = loaderUtils.getOptions(this)
const { cacheDirectory, cacheIdentifier } = options
// 关注点1: 通过解析 resourceQuery 获取loader参数
const query = qs.parse(this.resourceQuery.slice(1))
let loaders = this.loaders
// if this is a language block request, eslint-loader may get matched
// multiple times
if (query.type) {
// if this is an inline block, since the whole file itself is being linted,
// remove eslint-loader to avoid duplicate linting.
if (/\.vue$/.test(this.resourcePath)) {
loaders = loaders.filter(l => !isESLintLoader(l))
} else {
// This is a src import. Just make sure there's not more than 1 instance
// of eslint present.
loaders = dedupeESLintLoader(loaders)
}
}
// remove self
loaders = loaders.filter(isPitcher)
// do not inject if user uses null-loader to void the type (#1239)
if (loaders.some(isNullLoader)) {
return
}
const genRequest = loaders => {
...
}
// Inject style-post-loader before css-loader for scoped CSS and trimming
if (query.type === `style`) {
const cssLoaderIndex = loaders.findIndex(isCSSLoader)
if (cssLoaderIndex > -1) {
...
return query.module
? `export { default } from ${request}; export * from ${request}`
: `export * from ${request}`
}
}
// for templates: inject the template compiler & optional cache
if (query.type === `template`) {
...
// console.log(request)
// the template compiler uses esm exports
return `export * from ${request}`
}
// if a custom block has no other matching loader other than vue-loader itself
// or cache-loader, we should ignore it
if (query.type === `custom` && shouldIgnoreCustomBlock(loaders)) {
return ``
}
const request = genRequest(loaders)
return `import mod from ${request}; export default mod; export * from ${request}`
}
核心功能是遍历用户定义的rule数组,拼接出完整的行内引用路径,例如:
// 开发代码:
import xx from 'index.vue'
// 第一步,通过vue-loader转换成带参数的路径
import script from "./index.vue?vue&type=script&lang=js&"
// 第二步,在 pitcher 中解读loader数组的配置,并将路径转换成完整的行内路径格式
import mod from "-!../../node_modules/babel-loader/lib/index.js??clonedRuleSet-2[0].rules[0].use!../../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/index.js??vue-loader-options!./index.vue?vue&type=script&lang=js&";
第二次执行vue-loader
通过上面 vue-loader -> Pitch Loader 处理后,会得到一个新的行内路径,例如:
import mod from "-!../../node_modules/babel-loader/lib/index.js??clonedRuleSet-2[0].rules[0].use!../../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/index.js??vue-loader-options!./index.vue?vue&type=script&lang=js&";
以这个 import 语句为例,之后 Webpack 会按照下述逻辑运行:
- 调用
vue-loader处理index.js文件; - 调用
babel-loader处理上一步返回的内容。
这就给了 vue-loader 第二次执行的机会,再回过头来看看 vue-loader 的代码:
module.exports = function (source) {
// ...
const {
target,
request,
minimize,
sourceMap,
rootContext,
resourcePath,
resourceQuery = "",
} = loaderContext;
// ...
const descriptor = parse({
source,
compiler: options.compiler || loadTemplateCompiler(loaderContext),
filename,
sourceRoot,
needMap: sourceMap,
});
// if the query has a type field, this is a language block request
// e.g. foo.vue?type=template&id=xxxxx
// and we will return early
if (incomingQuery.type) {
return selectBlock(
descriptor,
loaderContext,
incomingQuery,
!!options.appendExtension
);
}
//...
return code;
};
module.exports.VueLoaderPlugin = plugin;
第二次运行时由于路径已经带上了 type 参数,会命中上面第26行的判断语句,进入 selectBlock 函数,这个函数的逻辑很简单:
module.exports = function selectBlock (
descriptor,
loaderContext,
query,
appendExtension
) {
// template
if (query.type === `template`) {
if (appendExtension) {
loaderContext.resourcePath += '.' + (descriptor.template.lang || 'html')
}
loaderContext.callback(
null,
descriptor.template.content,
descriptor.template.map
)
return
}
// script
if (query.type === `script`) {
if (appendExtension) {
loaderContext.resourcePath += '.' + (descriptor.script.lang || 'js')
}
loaderContext.callback(
null,
descriptor.script.content,
descriptor.script.map
)
return
}
// styles
if (query.type === `style` && query.index != null) {
const style = descriptor.styles[query.index]
if (appendExtension) {
loaderContext.resourcePath += '.' + (style.lang || 'css')
}
loaderContext.callback(
null,
style.content,
style.map
)
return
}
// custom
if (query.type === 'custom' && query.index != null) {
const block = descriptor.customBlocks[query.index]
loaderContext.callback(
null,
block.content,
block.map
)
return
}
}
至此,就可以完成从 Vue SFC 文件中抽取特定 Block 内容,并复用用户定义的其它 Loader 加载这些 Block
综上,我们可以将 vue-loader 的核心逻辑总结为:
- 首先给原始文件路径增加不同的参数,后续配合
resourceQuery参数就可以分开处理这些内容,这样的实现相比于一次性处理,逻辑更清晰简洁,更容易理解; - 经过 Normal Loader、Pitch Loader 两个阶段后,SFC 内容会被转化为
import xxx from '!-babel-loader!vue-loader?xxx'格式的引用路径,以此复用用户配置。
总结
-
使用
schema-utils与loader-utils工具实现更多 Loader 进阶特性,并进一步剖析vue-loader源码,讲解如何构建一个成熟的 Webpack Loader 组件。 -
我们可以总结一些常用的开发方法论,包括:
- Loader 主要负责将资源内容转译为 Webpack 能够理解、处理的标准 JavaScript 形式,所以通常需要做 Loader 内通过
return/this.callback方式返回翻译结果; - Loader Context 提供了许多实用接口,我们可以借助这些接口读取上下文信息,或改变 Webpack 运行状态(相当于产生 Side Effect,例如通过
emitFile接口); - 假若我们开发的 Loader 需要对外提供配置选项,建议使用
schema-utils校验配置参数是否合法; - 假若 Loader 需要生成额外的资源文件,建议使用
loader-utils拼接产物路径; - 执行时,Webpack 会按照
use定义的顺序从前到后执行 Pitch Loader,从后到前执行 Normal Loader,我们可以将一些预处理逻辑放在 Pitch 中(如vue-loader) 等等
- Loader 主要负责将资源内容转译为 Webpack 能够理解、处理的标准 JavaScript 形式,所以通常需要做 Loader 内通过
-
最后,参考一些知名 Loader 的源码,如:css-loader/babel-loader/file-loader