一、功能描述

项目设计要求输入三次错误密码后,要求隔段时间才能继续进行登录操作,这里简单记录一下实现思路
二、设计方案
有几个问题需要考虑一下:
1.是只有输错密码才锁定,还是账户名和密码任何一个输错就锁定?
2.输错之后也不是完全冻结,为啥隔了几分钟又可以重新输了?
3.技术栈实现是否麻烦?
参考资料发现,SpringBoot+Redis+Lua脚本这套方案不错,也早有人使用,所以阔以来简单回答以上的问题
1.锁定的是IP(最好还能加上客户端的物理设备ID放于请求头中),不是输入的账户名或者密码,即是任有一个输错3次就会被锁定
2.Redis的Lua脚本中实现了key过期策略,当key消失时锁定自然也就消失了
3.技术栈同SpringBoot+Redis+Lua脚本
三、实现
3.1 前端部分
需要一个账密输入页面,使用很简单HTML加表单提交
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>登录页面</title>
<style>
body {
background-color: #F5F5F5;
}
form {
width: 300px;
margin: 0 auto;
margin-top: 100px;
padding: 20px;
background-color: white;
border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px rgba(0,0,0,0.2);
}
label {
display: block;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
input[type="text"], input[type="password"] {
border: none;
padding: 10px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 0 0 5px rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
width: 100%;
box-sizing: border-box;
font-size: 16px;
}
input[type="submit"] {
background-color: #30B0F0;
color: white;
border: none;
padding: 10px;
border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 0 0 5px rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
width: 100%;
font-size: 16px;
cursor: pointer;
}
input[type="submit"]:hover {
background-color: #1C90D6;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form action="http://localhost:8080/login" method="get">
<label for="username">用户名</label>
<input type="text" id="username" name="username" placeholder="请输入用户名" required>
<label for="password">密码</label>
<input type="password" id="password" name="password" placeholder="请输入密码" required>
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
</body>
</html>
效果是:

3.2 后端部分
1.思路:
首先访问次数的统计与判断不是在登录逻辑执行后,而是执行前就加1; 其次登录逻辑的成功与失败并不会影响到次数的统计; 最后这个次数的统计是有过期时间的,当过期之后又可以重新登录。
2.Redis+Lua脚本的优点:
Redis是实现一个重要的需求-——需要一个用来计数的变量。这个变量既要满足分布式读写需求,还要满足全局递增或递减的需求,那Redis的incr方法是最优选。Lua脚本主要是验证用户操作前有些操作,比如如下这个判断:
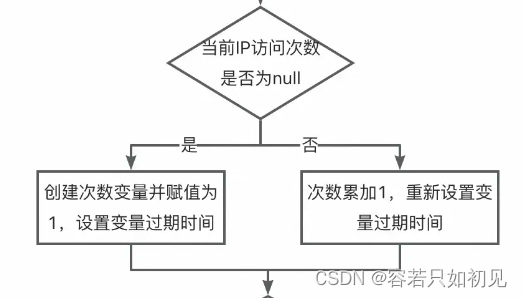
里面至少有3步Redis的操作,get、incr、expire,如果全放到应用里面来操作,有点慢且浪费资源。而Lua脚本阔以:
1.减少网络开销。可以将多个请求通过脚本的形式一次发送,减少网络时延。
2.原子操作。Redis会将整个脚本作为一个整体执行,中间不会被其他请求插入。因此在脚本运行过程中无需担心会出现竞态条件,无需使用事务。
3.复用。客户端发送的脚本会永久存在redis中,这样其他客户端可以复用这一脚本,而不需要使用代码完成相同的逻辑。
最后为增加功能的复用性,使用Java自定义注解的方式实现。
3.代码实现
pom引入依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.11</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>LoginLimit</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>LoginLimit</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Jedis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--切面依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- commons-lang3 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- guava -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>23.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- lombok -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
application.properties配置:
## Redis配置
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.redis.password=
spring.redis.timeout=1000
## Jedis配置
spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=0
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=500
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=2000
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=10000
自定义注解:
package com.example.loginlimit.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* 次数限制注解
* 作用在接口方法上
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface LimitCount {
/**
* 资源名称,用于描述接口功能
*/
String name() default "";
/**
* 资源 key
*/
String key() default "";
/**
* key prefix
*
* @return
*/
String prefix() default "";
/**
* 时间的,单位秒
* 默认60s过期
*/
int period() default 60;
/**
* 限制访问次数
* 默认3次
*/
int count() default 3;
}
注解核心处理逻辑类:LimitCountAspect.java
package com.example.loginlimit.aspect;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Objects;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import com.example.loginlimit.annotation.LimitCount;
import com.example.loginlimit.util.IPUtil;
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.DefaultRedisScript;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.RedisScript;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class LimitCountAspect {
private final RedisTemplate<String, Serializable> limitRedisTemplate;
@Autowired
public LimitCountAspect(RedisTemplate<String, Serializable> limitRedisTemplate) {
this.limitRedisTemplate = limitRedisTemplate;
}
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.loginlimit.annotation.LimitCount)")
public void pointcut() {
// do nothing
}
@Around("pointcut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes)Objects.requireNonNull(
RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes())).getRequest();
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature)point.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
LimitCount annotation = method.getAnnotation(LimitCount.class);
//注解名称
String name = annotation.name();
//注解key
String key = annotation.key();
//访问IP
String ip = IPUtil.getIpAddr(request);
//过期时间
int limitPeriod = annotation.period();
//过期次数
int limitCount = annotation.count();
ImmutableList<String> keys = ImmutableList.of(StringUtils.join(annotation.prefix() + "_", key, ip));
String luaScript = buildLuaScript();
RedisScript<Number> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>(luaScript, Number.class);
Number count = limitRedisTemplate.execute(redisScript, keys, limitCount, limitPeriod);
log.info("IP:{} 第 {} 次访问key为 {},描述为 [{}] 的接口", ip, count, keys, name);
if (count != null && count.intValue() <= limitCount) {
return point.proceed();
} else {
return "接口访问超出频率限制";
}
}
/**
* 限流脚本
* 调用的时候不超过阈值,则直接返回并执行计算器自加。
*
* @return lua脚本
*/
private String buildLuaScript() {
return "local c" +
"\nc = redis.call('get',KEYS[1])" +
"\nif c and tonumber(c) > tonumber(ARGV[1]) then" +
"\nreturn c;" +
"\nend" +
"\nc = redis.call('incr',KEYS[1])" +
"\nif tonumber(c) == 1 then" +
"\nredis.call('expire',KEYS[1],ARGV[2])" +
"\nend" +
"\nreturn c;";
}
}
获取IP地址功能工具类IPUtil.java
package com.example.loginlimit.util;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
public class IPUtil {
private static final String UNKNOWN = "unknown";
protected IPUtil() {
}
/**
* 获取 IP地址
* 使用 Nginx等反向代理软件, 则不能通过 request.getRemoteAddr()获取 IP地址
* 如果使用了多级反向代理的话,X-Forwarded-For的值并不止一个,而是一串IP地址,
* X-Forwarded-For中第一个非 unknown的有效IP字符串,则为真实IP地址
*/
public static String getIpAddr(HttpServletRequest request) {
String ip = request.getHeader("x-forwarded-for");
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || UNKNOWN.equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getHeader("Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || UNKNOWN.equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getHeader("WL-Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || UNKNOWN.equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getRemoteAddr();
}
return "0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1".equals(ip) ? "127.0.0.1" : ip;
}
}
Lua限流脚本:
private String buildLuaScript() {
return "local c" +
"\nc = redis.call('get',KEYS[1])" +
"\nif c and tonumber(c) > tonumber(ARGV[1]) then" +
"\nreturn c;" +
"\nend" +
"\nc = redis.call('incr',KEYS[1])" +
"\nif tonumber(c) == 1 then" +
"\nredis.call('expire',KEYS[1],ARGV[2])" +
"\nend" +
"\nreturn c;";
}
判断: tonumber© > tonumber(ARGV[1]);这行表示如果当前key 的值大于了limitCount,直接返回;否则调用incr方法进行累加1,且调用expire方法设置过期时间。
redis配置类RedisConfig.java
package com.example.loginlimit.config;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.Arrays;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisPassword;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisStandaloneConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisClientConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.SerializationException;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig;
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
@Value("${spring.redis.host}")
private String host;
@Value("${spring.redis.port}")
private int port;
@Value("${spring.redis.password}")
private String password;
@Value("${spring.redis.timeout}")
private int timeout;
@Value("${spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle}")
private int maxIdle;
@Value("${spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait}")
private long maxWaitMillis;
@Value("${spring.redis.database:0}")
private int database;
@Bean
public JedisPool redisPoolFactory() {
JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig();
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxIdle(maxIdle);
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(maxWaitMillis);
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(password)) {
return new JedisPool(jedisPoolConfig, host, port, timeout, password, database);
} else {
return new JedisPool(jedisPoolConfig, host, port, timeout, null, database);
}
}
@Bean
JedisConnectionFactory jedisConnectionFactory() {
RedisStandaloneConfiguration redisStandaloneConfiguration = new RedisStandaloneConfiguration();
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setHostName(host);
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setPort(port);
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setPassword(RedisPassword.of(password));
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setDatabase(database);
JedisClientConfiguration.JedisClientConfigurationBuilder jedisClientConfiguration = JedisClientConfiguration
.builder();
jedisClientConfiguration.connectTimeout(Duration.ofMillis(timeout));
jedisClientConfiguration.usePooling();
return new JedisConnectionFactory(redisStandaloneConfiguration, jedisClientConfiguration.build());
}
@Bean(name = "redisTemplate")
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes"})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "redisTemplate")
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
//使用 fastjson 序列化
JacksonRedisSerializer jacksonRedisSerializer = new JacksonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);
// value 值的序列化采用 fastJsonRedisSerializer
template.setValueSerializer(jacksonRedisSerializer);
template.setHashValueSerializer(jacksonRedisSerializer);
// key 的序列化采用 StringRedisSerializer
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
//缓存管理器
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisCacheManager.RedisCacheManagerBuilder builder = RedisCacheManager.RedisCacheManagerBuilder
.fromConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return builder.build();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(StringRedisTemplate.class)
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
@Bean
public KeyGenerator wiselyKeyGenerator() {
return (target, method, params) -> {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(target.getClass().getName());
sb.append(method.getName());
Arrays.stream(params).map(Object::toString).forEach(sb::append);
return sb.toString();
};
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Serializable> limitRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Serializable> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
}
class JacksonRedisSerializer<T> implements RedisSerializer<T> {
private Class<T> clazz;
private ObjectMapper mapper;
JacksonRedisSerializer(Class<T> clazz) {
super();
this.clazz = clazz;
this.mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
}
@Override
public byte[] serialize(T t) throws SerializationException {
try {
return mapper.writeValueAsBytes(t);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
@Override
public T deserialize(byte[] bytes) throws SerializationException {
if (bytes.length <= 0) {
return null;
}
try {
return mapper.readValue(bytes, clazz);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}
登录控制类LoginController.java
package com.example.loginlimit.controller;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import com.example.loginlimit.annotation.LimitCount;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class LoginController {
@GetMapping("/login")
@LimitCount(key = "login", name = "登录接口", prefix = "limit")
public String login(
@RequestParam(required = true) String username,
@RequestParam(required = true) String password, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (StringUtils.equals("张三", username) && StringUtils.equals("123456", password)) {
return "登录成功";
}
return "账户名或密码错误";
}
}
实现类LoginLimitApplication.java
package com.example.loginlimit;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class LoginLimitApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(LoginLimitApplication.class, args);
}
}
测试:
1.连续三次输错密码,均提示账户或密码错误
2.第四次输错:提示登录请求超出3次限制
3.一分钟后再次正确输入,即可登录成功
总结:在实际项目中,这套限流的逻辑可用,不过目前的登录很少有直接锁定账号不能输入的,一般都是弹出一个验证码框,让输入验证码再提交。这套逻辑也能用来处理短信验证码,防止机器刷验证码短信收费或者接口尝试次数的限制。