目录
- 1.av_write_frame
- 1.1 写入pkt(write_packets_common)
- 1.1.1 检查pkt的信息(check_packet)
- 1.1.2 准备输入的pkt(prepare_input_packet)
- 1.1.3 检查码流(check_bitstream)
- 1.1.4 写入pkt
- 1.1.4.1 从write_packets_from_bsfs写入pkt
- 1.1.4.2 直接写入pkt(write_packet_common)
- 2.小结
FFmpeg相关记录:
示例工程:
【FFmpeg】调用ffmpeg库实现264软编
【FFmpeg】调用ffmpeg库实现264软解
【FFmpeg】调用ffmpeg库进行RTMP推流和拉流
【FFmpeg】调用ffmpeg库进行SDL2解码后渲染
流程分析:
【FFmpeg】编码链路上主要函数的简单分析
【FFmpeg】解码链路上主要函数的简单分析
结构体分析:
【FFmpeg】AVCodec结构体
【FFmpeg】AVCodecContext结构体
【FFmpeg】AVStream结构体
【FFmpeg】AVFormatContext结构体
【FFmpeg】AVIOContext结构体
【FFmpeg】AVPacket结构体
函数分析:
【FFmpeg】avformat_open_input函数
【FFmpeg】avformat_find_stream_info函数
【FFmpeg】avformat_alloc_output_context2函数
【FFmpeg】avio_open2函数
【FFmpeg】avformat_write_header函数
在参考雷博的文章时,发现他在进行函数分析时,分析了av_write_frame但是在实际工程之中应用了av_interleaved_write_frame,为什么有这个区别?这两个函数有什么异同,对于不同的格式而言,应该使用什么函数来实现frame写入比较好?本文先记录av_write_frame是如何实现的,在FFmpeg7.0中,av_write_frame和老版本的av_write_frame有一些改动
av_write_frame函数的内部调用关系如下,其中最核心的部分是调用的write_packet函数

1.av_write_frame
函数的声明位于libavformat/avformat.h中,如下所示
/**
* Write a packet to an output media file.
*
* This function passes the packet directly to the muxer, without any buffering
* or reordering. The caller is responsible for correctly interleaving the
* packets if the format requires it. Callers that want libavformat to handle
* the interleaving should call av_interleaved_write_frame() instead of this
* function.
*
* @param s media file handle
* @param pkt The packet containing the data to be written. Note that unlike
* av_interleaved_write_frame(), this function does not take
* ownership of the packet passed to it (though some muxers may make
* an internal reference to the input packet).
* <br>
* This parameter can be NULL (at any time, not just at the end), in
* order to immediately flush data buffered within the muxer, for
* muxers that buffer up data internally before writing it to the
* output.
* <br>
* Packet's @ref AVPacket.stream_index "stream_index" field must be
* set to the index of the corresponding stream in @ref
* AVFormatContext.streams "s->streams".
* <br>
* The timestamps (@ref AVPacket.pts "pts", @ref AVPacket.dts "dts")
* must be set to correct values in the stream's timebase (unless the
* output format is flagged with the AVFMT_NOTIMESTAMPS flag, then
* they can be set to AV_NOPTS_VALUE).
* The dts for subsequent packets passed to this function must be strictly
* increasing when compared in their respective timebases (unless the
* output format is flagged with the AVFMT_TS_NONSTRICT, then they
* merely have to be nondecreasing). @ref AVPacket.duration
* "duration") should also be set if known.
* @return < 0 on error, = 0 if OK, 1 if flushed and there is no more data to flush
*
* @see av_interleaved_write_frame()
*/
// 将数据包写入输出媒体文件
// 此函数将数据包直接传递给复用器,不进行任何缓冲或重新排序。如果格式要求的话,
// 调用者负责正确地交错数据包。想要libavformat处理交错的调用者应该调用av_interleaved_write_frame()而不是这个函数
// @param :
// 1.这个函数与av_interleaved_write_frame不同,不具有对pkt的所有权
// 2.该参数可以为NULL(在任何时候,而不仅仅是在末尾),以便立即刷新muxer中缓冲的数据,
// 对于在将数据写入输出之前内部缓冲数据的muxer来说
// 3.AVPacket.stream_index必须赋值给AVFormatContext.streams中的index
// 4.pkt中的dts和pts必须设置为流的时基中的正确值
// 5.传递给此函数的后续数据包的dts在各自的时间基中进行比较时必须严格增加
// @return :
// 如果返回值小于0,则出现错误;返回0则成功;返回1则表明已经flush并且没有更多数据要flush
int av_write_frame(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt);
av_write_frame的定义位于libavformat\avformat.c中
int av_write_frame(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *in)
{
FFFormatContext *const si = ffformatcontext(s);
AVPacket *pkt = si->parse_pkt;
int ret;
// 如果没有输入的pkt,并且允许FLUSH,将空的pkt写入,否则直接返回1
if (!in) {
if (ffofmt(s->oformat)->flags_internal & FF_OFMT_FLAG_ALLOW_FLUSH) {
ret = ffofmt(s->oformat)->write_packet(s, NULL);
flush_if_needed(s);
if (ret >= 0 && s->pb && s->pb->error < 0)
ret = s->pb->error;
return ret;
}
return 1;
}
// AV_PKT_FLAG_UNCODED_FRAME表示数据包含未编码的帧,此时直接赋值
if (in->flags & AV_PKT_FLAG_UNCODED_FRAME) {
pkt = in;
} else {
/* We don't own in, so we have to make sure not to modify it.
* (ff_write_chained() relies on this fact.)
* The following avoids copying in's data unnecessarily.
* Copying side data is unavoidable as a bitstream filter
* may change it, e.g. free it on errors. */
// 不拥有pkt的所有权,所以必须确保不修改它。(ff_write_chained()依赖于这个事实。)
// 下面的代码避免不必要地复制in的数据。复制侧数据是不可避免的,因为比特流过滤器可能会改变它
// 例如释放时的错误
pkt->data = in->data;
pkt->size = in->size;
// 将in的一些数据例如pts,buf,size等信息copy到pkt之中
ret = av_packet_copy_props(pkt, in);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
if (in->buf) {
// 创建一个新的buffer给到pkt->buf之中
pkt->buf = av_buffer_ref(in->buf);
if (!pkt->buf) {
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto fail;
}
}
}
// 写入pkt
ret = write_packets_common(s, pkt, 0/*non-interleaved*/);
fail:
// Uncoded frames using the noninterleaved codepath are also freed here
av_packet_unref(pkt);
return ret;
}
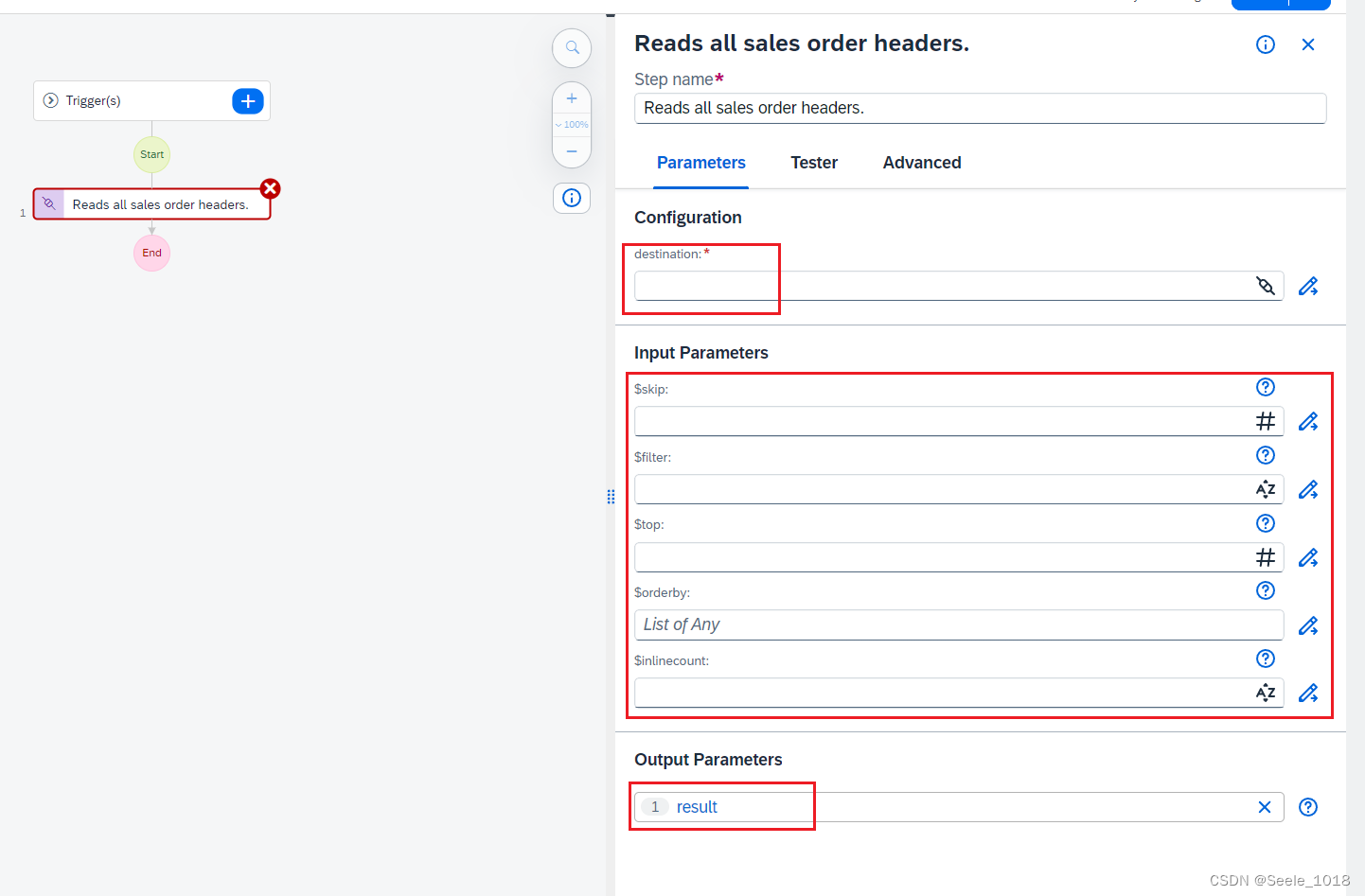
1.1 写入pkt(write_packets_common)
write_packets_common的定义位于libavformat\mux.c中
static int write_packets_common(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt, int interleaved)
{
AVStream *st;
FFStream *sti;
// 1.检查pkt的信息
int ret = check_packet(s, pkt);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
st = s->streams[pkt->stream_index];
sti = ffstream(st);
// 2.准备输入的pkt
ret = prepare_input_packet(s, st, pkt);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
// 3.检查码流
ret = check_bitstream(s, sti, pkt);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
// 4.写入packet
// FFStream中的bsfc变量表示bitstream filter context
// 如果码流过滤器存在,则使用write_packets_from_bsfs写入pkt
// 否则使用write_packet_common写入pkt
if (sti->bsfc) {
return write_packets_from_bsfs(s, st, pkt, interleaved);
} else {
return write_packet_common(s, st, pkt, interleaved);
}
}
函数主要的流程为:
(1)检查pkt的信息(check_packet)
(2)准备输入的pkt(prepare_input_packet)
(3)检查码流(check_bitstream)
(4)根据具体情况写入pkt
(a)如果已经有bsfc,则使用write_packets_from_bsfs,将处理过的数据包从码流过滤器写入pkt
(b)否则,使用write_packet_common写入pkt
1.1.1 检查pkt的信息(check_packet)
static int check_packet(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt)
{
// 检查stream_index
if (pkt->stream_index < 0 || pkt->stream_index >= s->nb_streams) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Invalid packet stream index: %d\n",
pkt->stream_index);
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
// 检查codec_type
if (s->streams[pkt->stream_index]->codecpar->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_ATTACHMENT) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Received a packet for an attachment stream.\n");
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
return 0;
}
1.1.2 准备输入的pkt(prepare_input_packet)
static int prepare_input_packet(AVFormatContext *s, AVStream *st, AVPacket *pkt)
{
FFStream *const sti = ffstream(st);
#if !FF_API_COMPUTE_PKT_FIELDS2 // 默认这里不会使用
/* sanitize the timestamps */
// 清理时间戳
if (!(s->oformat->flags & AVFMT_NOTIMESTAMPS)) {
/* when there is no reordering (so dts is equal to pts), but
* only one of them is set, set the other as well */
// 如果没有重新排序(所以DTS等于pts),但是只设置了其中一个,那么也设置另一个
if (!sti->reorder) {
if (pkt->pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE && pkt->dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE)
pkt->pts = pkt->dts;
if (pkt->dts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE && pkt->pts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE)
pkt->dts = pkt->pts;
}
/* check that the timestamps are set */
// 检查是否设置了时间戳
if (pkt->pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE || pkt->dts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"Timestamps are unset in a packet for stream %d\n", st->index);
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
/* check that the dts are increasing (or at least non-decreasing,
* if the format allows it */
// 检查DTS是否在增加(或者至少不减少,如果格式允许的话)
if (sti->cur_dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE &&
((!(s->oformat->flags & AVFMT_TS_NONSTRICT) && sti->cur_dts >= pkt->dts) ||
sti->cur_dts > pkt->dts)) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"Application provided invalid, non monotonically increasing "
"dts to muxer in stream %d: %" PRId64 " >= %" PRId64 "\n",
st->index, sti->cur_dts, pkt->dts);
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
if (pkt->pts < pkt->dts) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "pts %" PRId64 " < dts %" PRId64 " in stream %d\n",
pkt->pts, pkt->dts, st->index);
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
}
#endif
/* update flags */
if (sti->is_intra_only)
pkt->flags |= AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY;
if (!pkt->data && !pkt->side_data_elems) {
/* Such empty packets signal EOS for the BSF API; so sanitize
* the packet by allocating data of size 0 (+ padding). */
av_buffer_unref(&pkt->buf);
return av_packet_make_refcounted(pkt);
}
return 0;
}
1.1.3 检查码流(check_bitstream)
函数位于libavformat\mux.c中
static int check_bitstream(AVFormatContext *s, FFStream *sti, AVPacket *pkt)
{
int ret;
if (!(s->flags & AVFMT_FLAG_AUTO_BSF))
return 1;
if (ffofmt(s->oformat)->check_bitstream) {
if (!sti->bitstream_checked) { // 如果没有检查码流,则进行检查
if ((ret = ffofmt(s->oformat)->check_bitstream(s, &sti->pub, pkt)) < 0)
return ret;
else if (ret == 1)
sti->bitstream_checked = 1;
}
}
return 1;
}
这里根据具体的格式进行码流的检查,例如flv格式
const FFOutputFormat ff_flv_muxer = {
.p.name = "flv",
.p.long_name = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL("FLV (Flash Video)"),
.p.mime_type = "video/x-flv",
.p.extensions = "flv",
.priv_data_size = sizeof(FLVContext),
.p.audio_codec = CONFIG_LIBMP3LAME ? AV_CODEC_ID_MP3 : AV_CODEC_ID_ADPCM_SWF,
.p.video_codec = AV_CODEC_ID_FLV1,
.init = flv_init,
.write_header = flv_write_header,
.write_packet = flv_write_packet,
.write_trailer = flv_write_trailer,
.deinit = flv_deinit,
.check_bitstream= flv_check_bitstream,
.p.codec_tag = (const AVCodecTag* const []) {
flv_video_codec_ids, flv_audio_codec_ids, 0
},
.p.flags = AVFMT_GLOBALHEADER | AVFMT_VARIABLE_FPS |
AVFMT_TS_NONSTRICT,
.p.priv_class = &flv_muxer_class,
};
会调用flv_check_bitstream进行码流的检查,如下所示
static int flv_check_bitstream(AVFormatContext *s, AVStream *st,
const AVPacket *pkt)
{ // AAC格式
if (st->codecpar->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AAC) {
if (pkt->size > 2 && (AV_RB16(pkt->data) & 0xfff0) == 0xfff0)
return ff_stream_add_bitstream_filter(st, "aac_adtstoasc", NULL);
}
// H264 or HEVC or AV1 or MPEG4格式
// 添加对应格式的码流过滤器
if (!st->codecpar->extradata_size &&
(st->codecpar->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264 ||
st->codecpar->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_HEVC ||
st->codecpar->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AV1 ||
st->codecpar->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4))
return ff_stream_add_bitstream_filter(st, "extract_extradata", NULL);
return 1;
}
ff_stream_add_bitstream_filter的主要作用是在FFStream中添加码流过滤器(Bitstream Filter),码流过滤器的主要目的是对已编码的码流进行操作,而不涉及解码过程,过滤器通常用于在不解码的情况下对编码数据进行格式转换或者处理,使其能够被解码器正确处理。ff_stream_add_bitstream_filter的定义如下
int ff_stream_add_bitstream_filter(AVStream *st, const char *name, const char *args)
{
int ret;
const AVBitStreamFilter *bsf;
FFStream *const sti = ffstream(st);
AVBSFContext *bsfc;
av_assert0(!sti->bsfc);
if (!(bsf = av_bsf_get_by_name(name))) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Unknown bitstream filter '%s'\n", name);
return AVERROR_BSF_NOT_FOUND;
}
if ((ret = av_bsf_alloc(bsf, &bsfc)) < 0)
return ret;
bsfc->time_base_in = st->time_base;
if ((ret = avcodec_parameters_copy(bsfc->par_in, st->codecpar)) < 0) {
av_bsf_free(&bsfc);
return ret;
}
if (args && bsfc->filter->priv_class) {
if ((ret = av_set_options_string(bsfc->priv_data, args, "=", ":")) < 0) {
av_bsf_free(&bsfc);
return ret;
}
}
if ((ret = av_bsf_init(bsfc)) < 0) {
av_bsf_free(&bsfc);
return ret;
}
sti->bsfc = bsfc;
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_VERBOSE,
"Automatically inserted bitstream filter '%s'; args='%s'\n",
name, args ? args : "");
return 1;
}
1.1.4 写入pkt
在写入pkt时,会分两种情况,如果使用了Bitstream Filter Context,则使用write_packets_from_bsfs,否则就使用write_packet_common将pkt写入到输出的URL当中去
1.1.4.1 从write_packets_from_bsfs写入pkt
static int write_packets_from_bsfs(AVFormatContext *s, AVStream *st, AVPacket *pkt, int interleaved)
{
FFStream *const sti = ffstream(st);
AVBSFContext *const bsfc = sti->bsfc;
int ret;
// 将输入数据包发送到比特流过滤器(Bitstream Filter)进行处理
if ((ret = av_bsf_send_packet(bsfc, pkt)) < 0) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"Failed to send packet to filter %s for stream %d\n",
bsfc->filter->name, st->index);
return ret;
}
do {
// 从比特流过滤器(Bitstream Filter)接收处理后的数据包
ret = av_bsf_receive_packet(bsfc, pkt);
if (ret < 0) {
if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN) || ret == AVERROR_EOF)
return 0;
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Error applying bitstream filters to an output "
"packet for stream #%d: %s\n", st->index, av_err2str(ret));
if (!(s->error_recognition & AV_EF_EXPLODE) && ret != AVERROR(ENOMEM))
continue;
return ret;
}
av_packet_rescale_ts(pkt, bsfc->time_base_out, st->time_base);
// 写入pkt
ret = write_packet_common(s, st, pkt, interleaved);
if (ret >= 0 && !interleaved) // a successful write_packet_common already unrefed pkt for interleaved
av_packet_unref(pkt);
} while (ret >= 0);
return ret;
}
1.1.4.2 直接写入pkt(write_packet_common)
函数会写入一个packet,定义位于libavformat\mux.c中
static int write_packet_common(AVFormatContext *s, AVStream *st, AVPacket *pkt, int interleaved)
{
int ret;
if (s->debug & FF_FDEBUG_TS)
av_log(s, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "%s size:%d dts:%s pts:%s\n", __func__,
pkt->size, av_ts2str(pkt->dts), av_ts2str(pkt->pts));
// 1.猜测pkt的持续时间
guess_pkt_duration(s, st, pkt);
// 2.设置AVPacket的一些属性值
#if FF_API_COMPUTE_PKT_FIELDS2
if ((ret = compute_muxer_pkt_fields(s, st, pkt)) < 0 && !(s->oformat->flags & AVFMT_NOTIMESTAMPS))
return ret;
#endif
// 3.写入packet
if (interleaved) {
if (pkt->dts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE && !(s->oformat->flags & AVFMT_NOTIMESTAMPS))
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
return interleaved_write_packet(s, pkt, 0, 1);
} else {
return write_packet(s, pkt);
}
}
函数执行的过程分为几个部分:
(1)猜测pkt的持续时间(guess_pkt_duration)
(2)设置AVPacket的一些属性值(compute_muxer_pkt_fields)
(3)写入pkt
guess_pkt_duration的定义为
static void guess_pkt_duration(AVFormatContext *s, AVStream *st, AVPacket *pkt)
{
if (pkt->duration < 0 && st->codecpar->codec_type != AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Packet with invalid duration %"PRId64" in stream %d\n",
pkt->duration, pkt->stream_index);
pkt->duration = 0;
}
if (pkt->duration)
return;
switch (st->codecpar->codec_type) {
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO: // 计算视频的duration
if (st->avg_frame_rate.num > 0 && st->avg_frame_rate.den > 0) {
pkt->duration = av_rescale_q(1, av_inv_q(st->avg_frame_rate),
st->time_base);
} else if (st->time_base.num * 1000LL > st->time_base.den)
pkt->duration = 1;
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO: {
int frame_size = av_get_audio_frame_duration2(st->codecpar, pkt->size);
if (frame_size && st->codecpar->sample_rate) {
pkt->duration = av_rescale_q(frame_size,
(AVRational){1, st->codecpar->sample_rate},
st->time_base);
}
break;
}
}
}
compute_muxer_pkt_fields的定义如下,主要进行的任务是dts和pts的计算和检查
#if FF_API_COMPUTE_PKT_FIELDS2
FF_DISABLE_DEPRECATION_WARNINGS
//FIXME merge with compute_pkt_fields
static int compute_muxer_pkt_fields(AVFormatContext *s, AVStream *st, AVPacket *pkt)
{
FFFormatContext *const si = ffformatcontext(s);
FFStream *const sti = ffstream(st);
int delay = st->codecpar->video_delay;
int frame_size;
if (!si->missing_ts_warning &&
!(s->oformat->flags & AVFMT_NOTIMESTAMPS) &&
(!(st->disposition & AV_DISPOSITION_ATTACHED_PIC) || (st->disposition & AV_DISPOSITION_TIMED_THUMBNAILS)) &&
(pkt->pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE || pkt->dts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE)) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING,
"Timestamps are unset in a packet for stream %d. "
"This is deprecated and will stop working in the future. "
"Fix your code to set the timestamps properly\n", st->index);
si->missing_ts_warning = 1;
}
if (s->debug & FF_FDEBUG_TS)
av_log(s, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "compute_muxer_pkt_fields: pts:%s dts:%s cur_dts:%s b:%d size:%d st:%d\n",
av_ts2str(pkt->pts), av_ts2str(pkt->dts), av_ts2str(sti->cur_dts), delay, pkt->size, pkt->stream_index);
if (pkt->pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE && pkt->dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE && delay == 0)
pkt->pts = pkt->dts;
//XXX/FIXME this is a temporary hack until all encoders output pts
if ((pkt->pts == 0 || pkt->pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE) && pkt->dts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE && !delay) {
static int warned;
if (!warned) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Encoder did not produce proper pts, making some up.\n");
warned = 1;
}
pkt->dts =
// pkt->pts= st->cur_dts;
pkt->pts = sti->priv_pts.val;
}
//calculate dts from pts
// 计算dts
if (pkt->pts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE && pkt->dts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE && delay <= MAX_REORDER_DELAY) {
sti->pts_buffer[0] = pkt->pts;
for (int i = 1; i < delay + 1 && sti->pts_buffer[i] == AV_NOPTS_VALUE; i++)
sti->pts_buffer[i] = pkt->pts + (i - delay - 1) * pkt->duration;
for (int i = 0; i<delay && sti->pts_buffer[i] > sti->pts_buffer[i + 1]; i++)
FFSWAP(int64_t, sti->pts_buffer[i], sti->pts_buffer[i + 1]);
pkt->dts = sti->pts_buffer[0];
}
if (sti->cur_dts && sti->cur_dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE &&
((!(s->oformat->flags & AVFMT_TS_NONSTRICT) &&
st->codecpar->codec_type != AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE &&
st->codecpar->codec_type != AVMEDIA_TYPE_DATA &&
sti->cur_dts >= pkt->dts) || sti->cur_dts > pkt->dts)) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"Application provided invalid, non monotonically increasing dts to muxer in stream %d: %s >= %s\n",
st->index, av_ts2str(sti->cur_dts), av_ts2str(pkt->dts));
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
if (pkt->dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE && pkt->pts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE && pkt->pts < pkt->dts) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"pts (%s) < dts (%s) in stream %d\n",
av_ts2str(pkt->pts), av_ts2str(pkt->dts),
st->index);
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
if (s->debug & FF_FDEBUG_TS)
av_log(s, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "av_write_frame: pts2:%s dts2:%s\n",
av_ts2str(pkt->pts), av_ts2str(pkt->dts));
sti->cur_dts = pkt->dts;
sti->priv_pts.val = pkt->dts;
/* update pts */
switch (st->codecpar->codec_type) {
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO:
frame_size = (pkt->flags & AV_PKT_FLAG_UNCODED_FRAME) ?
(*(AVFrame **)pkt->data)->nb_samples :
av_get_audio_frame_duration2(st->codecpar, pkt->size);
/* HACK/FIXME, we skip the initial 0 size packets as they are most
* likely equal to the encoder delay, but it would be better if we
* had the real timestamps from the encoder */
if (frame_size >= 0 && (pkt->size || sti->priv_pts.num != sti->priv_pts.den >> 1 || sti->priv_pts.val)) {
frac_add(&sti->priv_pts, (int64_t)st->time_base.den * frame_size);
}
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO:
frac_add(&sti->priv_pts, (int64_t)st->time_base.den * st->time_base.num);
break;
}
return 0;
}
FF_ENABLE_DEPRECATION_WARNINGS
#endif
如果使用了交错(interleaved)格式,则使用interleaved_write_packet写入packet,否则使用write_packet写入packet。其中interleaved_write_packet的定义如下
static int interleaved_write_packet(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt,
int flush, int has_packet)
{
FFFormatContext *const si = ffformatcontext(s);
for (;; ) {
// interleave_packet能够将多个视频和音频数据包交错组合成一个完整的帧
int ret = si->interleave_packet(s, pkt, flush, has_packet);
if (ret <= 0)
return ret;
has_packet = 0;
// 写入pkt
ret = write_packet(s, pkt);
av_packet_unref(pkt);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
}
}
在FFmpeg-7.0的代码中,查了一下interleave_packet使用的地方,发现只有在gxf和mxf两个地方有定义(不确定是否哪里有遗漏),如下所示
const FFOutputFormat ff_mxf_muxer = {
.p.name = "mxf",
.p.long_name = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL("MXF (Material eXchange Format)"),
.p.mime_type = "application/mxf",
.p.extensions = "mxf",
.priv_data_size = sizeof(MXFContext),
.p.audio_codec = AV_CODEC_ID_PCM_S16LE,
.p.video_codec = AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG2VIDEO,
.init = mxf_init,
.write_packet = mxf_write_packet,
.write_trailer = mxf_write_footer,
.deinit = mxf_deinit,
.p.flags = AVFMT_NOTIMESTAMPS,
.interleave_packet = mxf_interleave,
.p.priv_class = &mxf_muxer_class,
.check_bitstream = mxf_check_bitstream,
};
const FFOutputFormat ff_gxf_muxer = {
.p.name = "gxf",
.p.long_name = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL("GXF (General eXchange Format)"),
.p.extensions = "gxf",
.priv_data_size = sizeof(GXFContext),
.p.audio_codec = AV_CODEC_ID_PCM_S16LE,
.p.video_codec = AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG2VIDEO,
.write_header = gxf_write_header,
.write_packet = gxf_write_packet,
.write_trailer = gxf_write_trailer,
.deinit = gxf_deinit,
.interleave_packet = gxf_interleave_packet,
};
由于interleave比较复杂,不做记录,先考虑write_packet。其实如果不使用interleave,上面的一些判断也不会进行,会直接使用write_packet进行pkt的写入,write_packet的定义如下
/**
* Shift timestamps and call muxer; the original pts/dts are not kept.
*
* FIXME: this function should NEVER get undefined pts/dts beside when the
* AVFMT_NOTIMESTAMPS is set.
* Those additional safety checks should be dropped once the correct checks
* are set in the callers.
*/
// 移位时间戳和调用复用器;不保留原始的pts/dts
// 这个函数应该永远不会得到未定义的pts/dts,除非AVFMT_NOTIMESTAMPS被设置
// 一旦在调用程序中设置了正确的检查,就应该删除这些额外的安全检查
static int write_packet(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt)
{
FFFormatContext *const si = ffformatcontext(s);
AVStream *const st = s->streams[pkt->stream_index];
FFStream *const sti = ffstream(st);
int ret;
// If the timestamp offsetting below is adjusted, adjust
// ff_interleaved_peek similarly.
// 如果调整了下面的时间戳偏移量,请类似地调整ff_interleaved_peek
if (s->output_ts_offset) {
int64_t offset = av_rescale_q(s->output_ts_offset, AV_TIME_BASE_Q, st->time_base);
if (pkt->dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE)
pkt->dts += offset;
if (pkt->pts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE)
pkt->pts += offset;
}
handle_avoid_negative_ts(si, sti, pkt);
// AV_PKT_FLAG_UNCODED_FRAME表示数据包含未编码的帧
if ((pkt->flags & AV_PKT_FLAG_UNCODED_FRAME)) {
AVFrame **frame = (AVFrame **)pkt->data;
av_assert0(pkt->size == sizeof(*frame));
// 写入未编码的帧信息
ret = ffofmt(s->oformat)->write_uncoded_frame(s, pkt->stream_index, frame, 0);
} else {
ret = ffofmt(s->oformat)->write_packet(s, pkt);
}
if (s->pb && ret >= 0) {
flush_if_needed(s);
if (s->pb->error < 0)
ret = s->pb->error;
}
if (ret >= 0)
st->nb_frames++;
return ret;
}
上面函数中的核心部分是write_packet,以FLV格式为例,则会调用flv_write_packet
static int flv_write_packet(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt)
{
AVIOContext *pb = s->pb;
AVCodecParameters *par = s->streams[pkt->stream_index]->codecpar;
FLVContext *flv = s->priv_data;
unsigned ts;
int size = pkt->size;
uint8_t *data = NULL;
uint8_t frametype = pkt->flags & AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY ? FLV_FRAME_KEY : FLV_FRAME_INTER;
int flags = -1, flags_size, ret = 0;
int64_t cur_offset = avio_tell(pb);
if (par->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO && !pkt->size) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Empty audio Packet\n");
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
// 确定flag_size的大小
if (par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_VP6F || par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_VP6A ||
par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_VP6 || par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AAC)
flags_size = 2;
else if (par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264 || par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4 ||
par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_HEVC || par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AV1 ||
par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_VP9)
flags_size = 5;
else
flags_size = 1;
if (par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_HEVC && pkt->pts != pkt->dts)
flags_size += 3;
// side data的处理
if (par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AAC || par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264
|| par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4 || par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_HEVC
|| par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AV1 || par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_VP9) {
size_t side_size;
uint8_t *side = av_packet_get_side_data(pkt, AV_PKT_DATA_NEW_EXTRADATA, &side_size);
if (side && side_size > 0 && (side_size != par->extradata_size || memcmp(side, par->extradata, side_size))) {
ret = ff_alloc_extradata(par, side_size);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
memcpy(par->extradata, side, side_size);
flv_write_codec_header(s, par, pkt->dts);
}
flv_write_metadata_packet(s, par, pkt->dts);
}
if (flv->delay == AV_NOPTS_VALUE)
flv->delay = -pkt->dts;
if (pkt->dts < -flv->delay) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING,
"Packets are not in the proper order with respect to DTS\n");
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
if (par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264 || par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4 ||
par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_HEVC || par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AV1 ||
par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_VP9) {
if (pkt->pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Packet is missing PTS\n");
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
}
ts = pkt->dts;
if (s->event_flags & AVSTREAM_EVENT_FLAG_METADATA_UPDATED) {
write_metadata(s, ts);
s->event_flags &= ~AVSTREAM_EVENT_FLAG_METADATA_UPDATED;
}
avio_write_marker(pb, av_rescale(ts, AV_TIME_BASE, 1000),
pkt->flags & AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY && (flv->video_par ? par->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO : 1) ? AVIO_DATA_MARKER_SYNC_POINT : AVIO_DATA_MARKER_BOUNDARY_POINT);
switch (par->codec_type) {
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO:
// 视频的TAG类型
// 1.写入Tag header当中的type
avio_w8(pb, FLV_TAG_TYPE_VIDEO);
flags = ff_codec_get_tag(flv_video_codec_ids, par->codec_id);
// frame类型,是否是key_frame
flags |= frametype;
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO:
flags = get_audio_flags(s, par);
av_assert0(size);
avio_w8(pb, FLV_TAG_TYPE_AUDIO);
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE:
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_DATA:
avio_w8(pb, FLV_TAG_TYPE_META);
break;
default:
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
if (par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264 || par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4) {
/* check if extradata looks like mp4 formatted */
if (par->extradata_size > 0 && *(uint8_t*)par->extradata != 1)
if ((ret = ff_avc_parse_nal_units_buf(pkt->data, &data, &size)) < 0)
return ret;
} else if (par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_HEVC) {
if (par->extradata_size > 0 && *(uint8_t*)par->extradata != 1)
if ((ret = ff_hevc_annexb2mp4_buf(pkt->data, &data, &size, 0, NULL)) < 0)
return ret;
} else if (par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AAC && pkt->size > 2 &&
(AV_RB16(pkt->data) & 0xfff0) == 0xfff0) {
if (!s->streams[pkt->stream_index]->nb_frames) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Malformed AAC bitstream detected: "
"use the audio bitstream filter 'aac_adtstoasc' to fix it "
"('-bsf:a aac_adtstoasc' option with ffmpeg)\n");
return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
}
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING, "aac bitstream error\n");
}
/* check Speex packet duration */
if (par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_SPEEX && ts - flv->last_ts[pkt->stream_index] > 160)
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Warning: Speex stream has more than "
"8 frames per packet. Adobe Flash "
"Player cannot handle this!\n");
if (flv->last_ts[pkt->stream_index] < ts)
flv->last_ts[pkt->stream_index] = ts;
if (size + flags_size >= 1<<24) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Too large packet with size %u >= %u\n",
size + flags_size, 1<<24);
ret = AVERROR(EINVAL);
goto fail;
}
// 2.写入Tag Header当中的DataSize
avio_wb24(pb, size + flags_size);
/*
// FLV timestamps are 32 bits signed, RTMP timestamps should be 32-bit unsigned
static void put_timestamp(AVIOContext *pb, int64_t ts) {
avio_wb24(pb, ts & 0xFFFFFF); // 3.写入Tag Header当中的Timestamp
avio_w8(pb, (ts >> 24) & 0x7F); // 4.写入Tag Header当中的Timestamp_ex,timestamps are 32 bits _signed_
}
*/
put_timestamp(pb, ts);
// 5.写入Tag Header当中的StreamID
avio_wb24(pb, flv->reserved);
if (par->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_DATA ||
par->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE ) {
int data_size;
int64_t metadata_size_pos = avio_tell(pb);
if (par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_TEXT) {
// legacy FFmpeg magic?
avio_w8(pb, AMF_DATA_TYPE_STRING);
put_amf_string(pb, "onTextData");
avio_w8(pb, AMF_DATA_TYPE_MIXEDARRAY);
avio_wb32(pb, 2);
put_amf_string(pb, "type");
avio_w8(pb, AMF_DATA_TYPE_STRING);
put_amf_string(pb, "Text");
put_amf_string(pb, "text");
avio_w8(pb, AMF_DATA_TYPE_STRING);
put_amf_string(pb, pkt->data);
put_amf_string(pb, "");
avio_w8(pb, AMF_END_OF_OBJECT);
} else {
// just pass the metadata through
avio_write(pb, data ? data : pkt->data, size);
}
/* write total size of tag */
data_size = avio_tell(pb) - metadata_size_pos;
avio_seek(pb, metadata_size_pos - 10, SEEK_SET);
avio_wb24(pb, data_size);
avio_seek(pb, data_size + 10 - 3, SEEK_CUR);
avio_wb32(pb, data_size + 11);
} else {
av_assert1(flags>=0);
// hevc格式
if (par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_HEVC) {
int pkttype = (pkt->pts != pkt->dts) ? PacketTypeCodedFrames : PacketTypeCodedFramesX;
avio_w8(pb, FLV_IS_EX_HEADER | pkttype | frametype); // ExVideoTagHeader mode with PacketTypeCodedFrames(X)
avio_write(pb, "hvc1", 4);
if (pkttype == PacketTypeCodedFrames)
avio_wb24(pb, pkt->pts - pkt->dts);
} else if (par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AV1 || par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_VP9) { // av1格式或者是vp9格式
avio_w8(pb, FLV_IS_EX_HEADER | PacketTypeCodedFrames | frametype);
avio_write(pb, par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AV1 ? "av01" : "vp09", 4);
} else {
avio_w8(pb, flags);
}
if (par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_VP6)
avio_w8(pb,0);
if (par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_VP6F || par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_VP6A) {
if (par->extradata_size)
avio_w8(pb, par->extradata[0]);
else
avio_w8(pb, ((FFALIGN(par->width, 16) - par->width) << 4) |
(FFALIGN(par->height, 16) - par->height));
} else if (par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AAC)
avio_w8(pb, 1); // AAC raw
else if (par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264 || par->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4) {
avio_w8(pb, 1); // AVC NALU
avio_wb24(pb, pkt->pts - pkt->dts);
}
// 6.写入Tag Data
avio_write(pb, data ? data : pkt->data, size);
avio_wb32(pb, size + flags_size + 11); // previous tag size
flv->duration = FFMAX(flv->duration,
pkt->pts + flv->delay + pkt->duration);
}
// FLV_ADD_KEYFRAME_INDEX的作用是在FLV文件中添加关键索引,以提高文件的搜索(seek)性能
if (flv->flags & FLV_ADD_KEYFRAME_INDEX) {
switch (par->codec_type) {
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO:
flv->videosize += (avio_tell(pb) - cur_offset);
flv->lasttimestamp = pkt->dts / 1000.0;
if (pkt->flags & AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY) {
flv->lastkeyframetimestamp = flv->lasttimestamp;
flv->lastkeyframelocation = cur_offset;
ret = flv_append_keyframe_info(s, flv, flv->lasttimestamp, cur_offset);
if (ret < 0)
goto fail;
}
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO:
flv->audiosize += (avio_tell(pb) - cur_offset);
break;
default:
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING, "par->codec_type is type = [%d]\n", par->codec_type);
break;
}
}
fail:
av_free(data);
return ret;
}
FLV格式为

从代码上看,核心的部分是完成了6个部分的内容:
(1)写入Tag Header中的Type
avio_w8(pb, FLV_TAG_TYPE_VIDEO); // 写入视频类型的type
(2)写入Tag Header中的Datasize
avio_wb24(pb, size + flags_size);
(3&4)写入Tag Header中的Timestamp和Timestamp_ex
// FLV timestamps are 32 bits signed, RTMP timestamps should be 32-bit unsigned
static void put_timestamp(AVIOContext *pb, int64_t ts) {
avio_wb24(pb, ts & 0xFFFFFF); // 3.写入Tag Header当中的Timestamp
// timestamps are 32 bits _signed_
avio_w8(pb, (ts >> 24) & 0x7F); // 4.写入Tag Header当中的Timestamp_ex
}
(5)写入Tag Header中的StreamID
avio_wb24(pb, flv->reserved);
(6)写入Tag Data
avio_write(pb, data ? data : pkt->data, size);
这样就完成了FLV格式的写入
2.小结
av_write_frame实现了将数据信息写入到输出的功能,它将外部输入的pkt写入到指定的输出url当中,在执行的过程之中考虑了interleaved的情况,这种情况比较复杂,不做记录,另外,在写入信息时,涉及到很多pts和dts的计算。最后就是需要注意根据不同的媒体格式来进行文件的写入,
CSDN : https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42877471
Github : https://github.com/DoFulangChen









![Linux[高级管理]——Squid代理服务器的部署和应用(反向代理详解)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/bc4e327b85534edb9af8560428086a59.png)