目录
一、前言
二、initHandlerMappings
三、处理器映射器架构
策略接口
请求链
模版类
四、RequestMappingHandlerMapping的初始化
HandlerMethod映射器模版类的初始化
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MappingRegistry:内部类注册中心
五、RequestMappingHandlerMapping映射器模版类的调用
RequestMappingHandlerMapping调用
一、前言
昨天在进行spring的安全升级时,遇到一个奇葩问题:原始版本为4.1.9,升级至5.3.34,由于是几年前的项目,请求路径还是带有.action的老式写法(如login.action),而有的不带(如:index),升级完后,就发现了问题,login.action能访问到,请求index时,日志爆了 no mapping for GET。
我们来看看是怎么回事。
在SpringMVC中会有很多请求,每个请求都需要一个HandlerAdapter处理,具体接收到一个请求之后使用哪个HandlerAdapter进行处理呢,他们的过程是什么。本文将对此问题进行讨论
二、initHandlerMappings
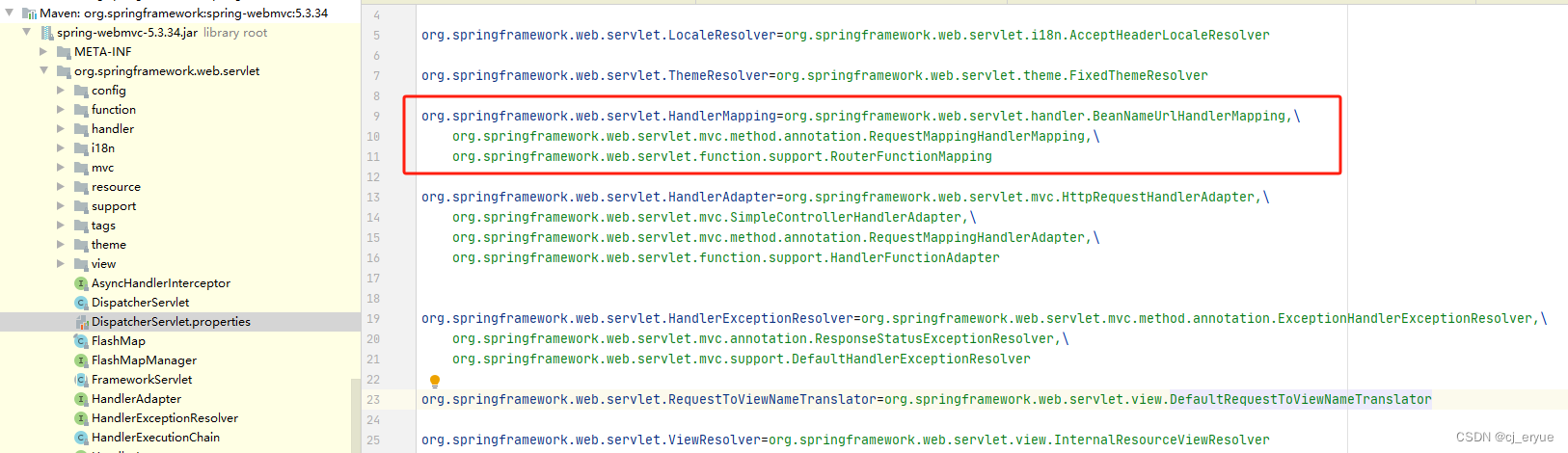
DispatcherServlet在初始化中,会调用其initHandlerMappings方法注册HandlerMapping对象并放到其缓存池中,其过程如下:先查询容器中是否有处理器映射器,如果有就注册到其缓存池中,如果没有就安装默认到规则创建处理器映射器,并注册到其缓存池中。
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
//detectAllHandlerMappings默认为true
//true标志检测所有handlerMapping,false只获取“handlerMapping”bean。
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// 在ApplicationContext中查找所有HandlerMappings,包括祖先上下文。
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
//排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
//只获取“handlerMapping”bean
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
//通过注册,确保我们至少有一个HandlerMapping
//如果找不到其他映射,则为默认HandlerMapping。
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
//从spring-webmvc下的DispatcherServlet.properties读取默认配置
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties");
}
}
}Spring默认HandlerMapping有BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping、RequestMappingHandlerMapping、RouterFunctionMapping
三、处理器映射器架构
策略接口
处理器映射器使用了策略模式
HandlerMapping是用来查找Handler的。在SpringMVC中会有很多请求,每个请求都需要一个Handler处理,具体接收到一个请求之后使用哪个Handler进行处理呢?这就是HandlerMapping需要做的事
HandlerMapping:负责映射用户的URL和对应的处理类Handler,HandlerMapping并没有规定这个URL与应用的处理类如何映射。所以在HandlerMapping接口中仅仅定义了根据一个URL必须返回一个由HandlerExecutionChain代表的处理链,我们可以在这个处理链中添加任意的HandlerAdapter实例来处理这个URL对应的请求(这样保证了最大的灵活性映射关系)。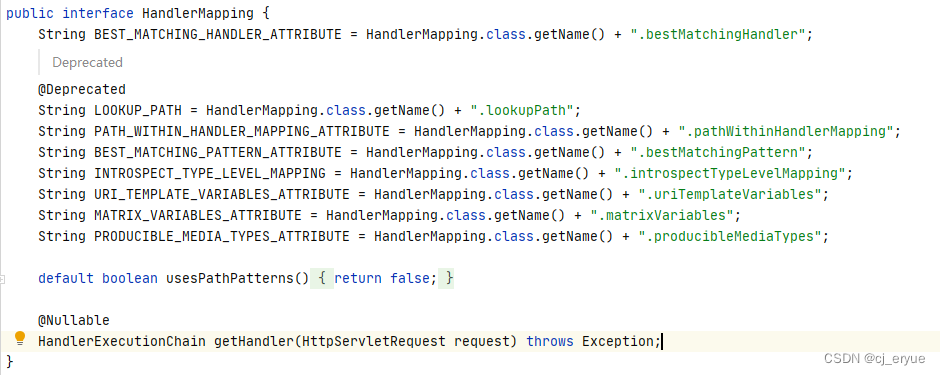
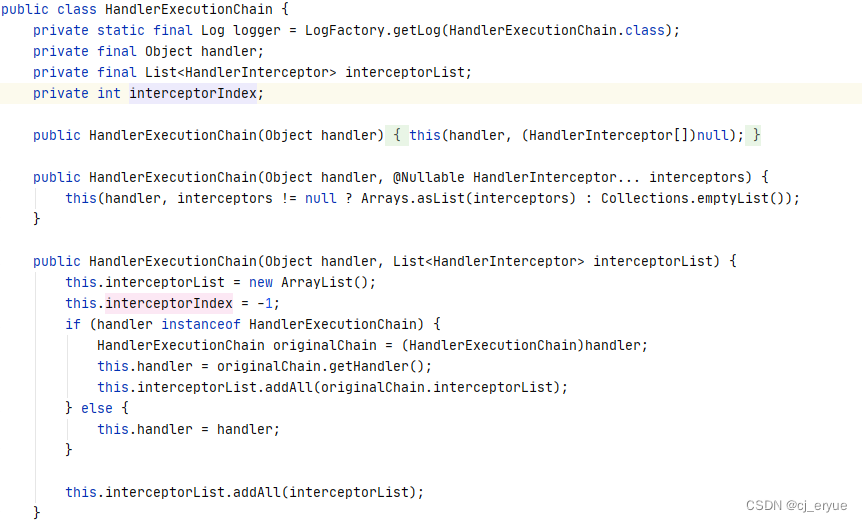
请求链
模版类
处理器映射器都是实现AbstractHandlerMapping,该抽象类完成了所有的Handler以及handler里面所有的HandlerMethod的模版操作,但是怎么获取Handler,这些逻辑都是交给子类自己去实现,所以这层抽象可谓也是非常的灵活,并没有把Handler的实现方式定死。
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
//默认的Handler,这边使用的Obejct,子类实现的时候,使用HandlerMethod,HandlerExecutionChain等
@Nullable
private Object defaultHandler;
// url路径计算的辅助类、工具类
private UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper();
// Ant风格的Path匹配模式~ 解决如/books/{id}场景
private PathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
// 保存着拦截器们~~~
private final List<Object> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
// 从interceptors中解析得到,直接添加给全部handler
private final List<HandlerInterceptor> adaptedInterceptors = new ArrayList<>();
// 跨域相关的配置~
private CorsConfigurationSource corsConfigurationSource = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
private CorsProcessor corsProcessor = new DefaultCorsProcessor();
// 最低的顺序(default: same as non-Ordered)
private int order = Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
@Nullable
private String beanName;
/**
* Initializes the interceptors.
* @see #extendInterceptors(java.util.List)
* @see #initInterceptors()
*/
@Override
protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
// 给子类扩展:增加拦截器,默认为空实现.RequestMappingHandlerMapping也没有重写这个方法
extendInterceptors(this.interceptors);
// 找到所有MappedInterceptor(截器是)类型的bean添加到adaptedInterceptors中
detectMappedInterceptors(this.adaptedInterceptors);
// 将interceptors中的拦截器取出放入adaptedInterceptors
// 如果是WebRequestInterceptor类型的拦截器 需要用WebRequestHandlerInterceptorAdapter进行包装适配
initInterceptors();
}
@Override
@Nullable
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//根据请求获取对应的处理器,子类实现
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
//如果获取不到,到默认到处理器中
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
//如果还没有处理器,返回null
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// 意思是如果当前传入的handler是个String类型,那就根据其名字去容器内找这个Bean,当作一个Handler~
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
//到容器中找
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
//根据handler和request构造一个请求处理链~~
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
// 4.2版本提供了对CORS跨域资源共享的支持 此处暂时略过~
if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler)) {
CorsConfiguration config = (this.corsConfigurationSource != null ? this.corsConfigurationSource.getCorsConfiguration(request) : null);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
config = (config != null ? config.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
@Nullable
protected abstract Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
}getHandlerInternal模板方法的实现类:

接下来最重要的就是以getHandlerInternal()方法为主线,看看其子类们的实现。它主要分为两大主线: AbstractUrlHandlerMapping 和 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping。
本文是以AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的子类RequestMappingHandlerMapping为主线
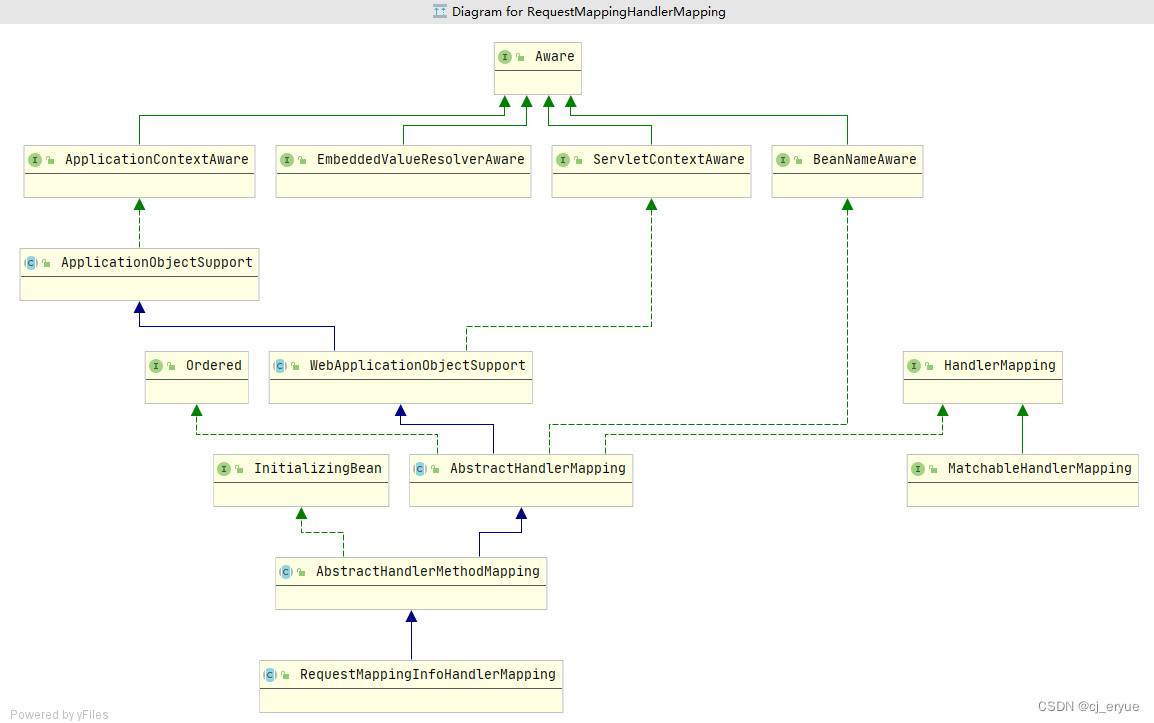
四、RequestMappingHandlerMapping的初始化
HandlerMethod映射器都是处理器映射器类型的映射器。这种类型的映射器有一个模版类AbstractHandlerMethodMapping, 所有的HandlerMethod映射器都是他的实现。
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping包括其初始化和调用过程。为了好讲解,在这里就将其初始化和调用过程代码分开说
HandlerMethod映射器模版类的初始化
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
private static final HandlerMethod PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH =
new HandlerMethod(new EmptyHandler(), ClassUtils.getMethod(EmptyHandler.class, "handle"));
private static final CorsConfiguration ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG = new CorsConfiguration();
static {
ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG.addAllowedOrigin("*");
ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG.addAllowedMethod("*");
ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG.addAllowedHeader("*");
ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG.setAllowCredentials(true);
}
private boolean detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts = false;
@Nullable
private HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy<T> namingStrategy;
//注册表,HandlerMapping在容器启动过程中初始化,把扫描到的handler放到注册表中
private final MappingRegistry mappingRegistry = new MappingRegistry();
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
//循环所有的bean
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
//如果bean名字不是以scopedTarget.开头
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
//日志输出
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
//因为这里我们是研究RequestMappingHandlerMapping,所以这局代码内容如下
//如果beanType不为null,且类上标注@Controller注解或者@RequestMapping注解
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
//底层使用了MappingRegistry的register方法
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
//忽略处理器映射器查询Handler部分代码.....
}1、循环所有的bean,如果bean名字不是以scopedTarget.开头,那么就判断他们是否是Handler(类上标注@Controller注解或者@RequestMapping注解)
2、如果是Handler,获取这个类上所有标注@RequestMapping的方法信息,以RequestMappingInfo形式
3、把他们储存到MappingRegistry中
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MappingRegistry:内部类注册中心
维护几个Map(键值对),用来存储映射的信息, 还有一个MappingRegistration专门保存注册信息 这个注册中心,核心是保存了多个Map映射关系,相当于缓存下来。在请求过来时需要查找的时候,可以迅速定位到处理器
class MappingRegistry {
//对于RequestMappingHandlerMapping来说
//保存着RequestMappingInfo和MappingRegistration的对应关系~
private final Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> registry = new HashMap<>();
// 对于保存着mapping和HandlerMethod的对应关系~
//对于RequestMappingHandlerMapping来说
//保存着RequestMappingInfo和HandlerMethod的对应关系~
private final Map<T, HandlerMethod> mappingLookup = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// 这里的Map不是普通的Map,而是MultiValueMap,它是个多值Map。其实它的value是一个list类型的值
// 至于为何是多值?有这么一种情况 URL都是/api/v1/hello 但是有的是get post delete等方法 所以有可能是会匹配到多个MappingInfo的
//对于RequestMappingHandlerMapping来说,保存着URL和RequestMappingInfo的关系~
private final MultiValueMap<String, T> urlLookup = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
//对于RequestMappingHandlerMapping来说,保存着URL和HandlerMethod的关系~
private final Map<String, List<HandlerMethod>> nameLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>()
// 这两个就不用解释了
private final Map<HandlerMethod, CorsConfiguration> corsLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 读写锁~~~ 读写分离 提高启动效率
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
//5.1版本其子类只有一个RequestMappingHandlerMapping,T就是RequestMappingInfo
//handler一般情况下是处理器方法从属bean的名字
//method是处理器方法
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(method.getDeclaringClass()) && KotlinDelegate.isSuspend(method)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unsupported suspending handler method detected: " + method);
}
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
//断言提供的映射是唯一的。
validateMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);
List<String> directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping);
for (String url : directUrls) {
this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping);
}
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
//初始化跨域配置
//使用的是AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的initCorsConfiguration方法,子类实现
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}这个注册中心,核心是保存了多个Map映射关系,相当于缓存下来。在请求过来时需要查找的时候,可以迅速定位到处理器
在其初始化过程中,其主要模版化的2个方法
protected CorsConfiguration initCorsConfiguration(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
return null;
}
protected abstract boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType);五、RequestMappingHandlerMapping映射器模版类的调用
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
private static final HandlerMethod PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH =
new HandlerMethod(new EmptyHandler(), ClassUtils.getMethod(EmptyHandler.class, "handle"));
private static final CorsConfiguration ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG = new CorsConfiguration();
static {
ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG.addAllowedOrigin("*");
ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG.addAllowedMethod("*");
ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG.addAllowedHeader("*");
ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG.setAllowCredentials(true);
}
private boolean detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts = false;
@Nullable
private HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy<T> namingStrategy;
//注册表,HandlerMapping在容器启动过程中初始化,把扫描到的handler放到注册表中
private final MappingRegistry mappingRegistry = new MappingRegistry();
//忽略初始化部分代码.....
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//获取请求路径
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
//放到请求属性中
request.setAttribute(LOOKUP_PATH, lookupPath);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
//根据请求和路径获取对应的处理方法,注册表中取
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// Match是一个private class,内部就两个属性:T mapping和HandlerMethod handlerMethod
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
// 根据lookupPath去注册中心里查找RequestMappingInfo,因为一个具体的url可能匹配上多个RequestMappingInfo
// 至于为何是多值?有这么一种情况 URL都是/api/v1/hello 但是有的是get post delete等方法 等不一样,都算多个的 所以有可能是会匹配到多个MappingInfo的
// 所有这个里可以匹配出多个出来。比如/hello 匹配出GET、POST、PUT都成,所以size可以为3
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
// 依赖于子类实现的抽象方法:getMatchingMapping() 看看到底匹不匹配,而不仅仅是URL匹配就行
// 比如还有method、headers、consumes等等这些不同都代表着不同的MappingInfo的
// 最终匹配上的,会new Match()放进matches里面去
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
// 当还没有匹配上的时候,别无选择,只能浏览所有映射
// 这里为何要浏览所有的mappings呢?而不是报错404呢?
// 增加路径匹配对范围,如:/rest 匹配 /rest.ssss
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
}
// 只要找到了一个匹配的 就进来这里了~~~
// 请注意:因为到这里 匹配上的可能还不止一个 所以才需要继续处理~~
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
//如果匹配到多个,就取第一个
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
throw new IllegalStateException(" ");
}
}
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.handlerMethod);
//请求域增加一些属性,子类重写
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
//请求域增加一些属性,子类重写
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
}
protected void handleMatch(T mapping, String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) {
request.setAttribute(HandlerMapping.PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE, lookupPath);
}
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod handleNoMatch(Set<T> mappings, String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request)
throws Exception {
return null;
}RequestMappingHandlerMapping调用
public abstract class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<RequestMappingInfo> {
private static final Method HTTP_OPTIONS_HANDLE_METHOD;
/**
* Expose URI template variables, matrix variables, and producible media types in the request.
* @see HandlerMapping#URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE
* @see HandlerMapping#MATRIX_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE
* @see HandlerMapping#PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE
*/
@Override
protected void handleMatch(RequestMappingInfo info, String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) {
super.handleMatch(info, lookupPath, request);
String bestPattern;
Map<String, String> uriVariables;
Set<String> patterns = info.getPatternsCondition().getPatterns();
if (patterns.isEmpty()) {
bestPattern = lookupPath;
uriVariables = Collections.emptyMap();
}
else {
bestPattern = patterns.iterator().next();
uriVariables = getPathMatcher().extractUriTemplateVariables(bestPattern, lookupPath);
}
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE, bestPattern);
if (isMatrixVariableContentAvailable()) {
Map<String, MultiValueMap<String, String>> matrixVars = extractMatrixVariables(request, uriVariables);
request.setAttribute(HandlerMapping.MATRIX_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE, matrixVars);
}
Map<String, String> decodedUriVariables = getUrlPathHelper().decodePathVariables(request, uriVariables);
request.setAttribute(HandlerMapping.URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE, decodedUriVariables);
if (!info.getProducesCondition().getProducibleMediaTypes().isEmpty()) {
Set<MediaType> mediaTypes = info.getProducesCondition().getProducibleMediaTypes();
request.setAttribute(PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE, mediaTypes);
}
}
private boolean isMatrixVariableContentAvailable() {
return !getUrlPathHelper().shouldRemoveSemicolonContent();
}
private Map<String, MultiValueMap<String, String>> extractMatrixVariables(
HttpServletRequest request, Map<String, String> uriVariables) {
Map<String, MultiValueMap<String, String>> result = new LinkedHashMap<>();
uriVariables.forEach((uriVarKey, uriVarValue) -> {
int equalsIndex = uriVarValue.indexOf('=');
if (equalsIndex == -1) {
return;
}
int semicolonIndex = uriVarValue.indexOf(';');
if (semicolonIndex != -1 && semicolonIndex != 0) {
uriVariables.put(uriVarKey, uriVarValue.substring(0, semicolonIndex));
}
String matrixVariables;
if (semicolonIndex == -1 || semicolonIndex == 0 || equalsIndex < semicolonIndex) {
matrixVariables = uriVarValue;
}
else {
matrixVariables = uriVarValue.substring(semicolonIndex + 1);
}
MultiValueMap<String, String> vars = WebUtils.parseMatrixVariables(matrixVariables);
result.put(uriVarKey, getUrlPathHelper().decodeMatrixVariables(request, vars));
});
return result;
}
/**
* Iterate all RequestMappingInfo's once again, look if any match by URL at
* least and raise exceptions according to what doesn't match.
* @throws HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException if there are matches by URL
* but not by HTTP method
* @throws HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException if there are matches by URL
* but not by consumable/producible media types
*/
@Override
protected HandlerMethod handleNoMatch(
Set<RequestMappingInfo> infos, String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws ServletException {
PartialMatchHelper helper = new PartialMatchHelper(infos, request);
if (helper.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
if (helper.hasMethodsMismatch()) {
Set<String> methods = helper.getAllowedMethods();
if (HttpMethod.OPTIONS.matches(request.getMethod())) {
HttpOptionsHandler handler = new HttpOptionsHandler(methods);
return new HandlerMethod(handler, HTTP_OPTIONS_HANDLE_METHOD);
}
throw new HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException(request.getMethod(), methods);
}
if (helper.hasConsumesMismatch()) {
Set<MediaType> mediaTypes = helper.getConsumableMediaTypes();
MediaType contentType = null;
if (StringUtils.hasLength(request.getContentType())) {
try {
contentType = MediaType.parseMediaType(request.getContentType());
}
catch (InvalidMediaTypeException ex) {
throw new HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException(ex.getMessage());
}
}
throw new HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException(contentType, new ArrayList<>(mediaTypes));
}
if (helper.hasProducesMismatch()) {
Set<MediaType> mediaTypes = helper.getProducibleMediaTypes();
throw new HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException(new ArrayList<>(mediaTypes));
}
if (helper.hasParamsMismatch()) {
List<String[]> conditions = helper.getParamConditions();
throw new UnsatisfiedServletRequestParameterException(conditions, request.getParameterMap());
}
return null;
}
}RequestMappingHandlerMapping根据请求获取对应的handlerMethod过程是:
1、获取请求路径
2、根据路径到注册表中查询对应路径的RequestMappingInfo
3、如果匹配到多个,就取第一个。
4、如果匹配不到,就到注册表中查询所有RequestMappingInfo,匹配规则我们可以自定义。
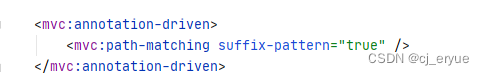
Spring MVC请求URL带后缀匹配的情况,如/hello.json也能匹配/hello
RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping 在处理http请求的时候, 如果 请求url 有后缀,如果找不到精确匹配的那个@RequestMapping方法。 那么,就把后缀去掉,然后.*去匹配,这样,一般都可以匹配,默认这个行为是被开启的。4.3以后是关闭的
比如有一个@RequestMapping("/rest"), 那么精确匹配的情况下, 只会匹配/rest请求。 但如果我前端发来一个 /rest.abcdef 这样的请求, 又没有配置 @RequestMapping("/rest.abcdef") 这样映射的情况下, 那么@RequestMapping("/rest") 就会生效。
这样会带来什么问题呢?绝大多数情况下是没有问题的,但是如果你是一个对权限要求非常严格的系统,强烈关闭此项功能,否则你会有意想不到的"收获"。本文的一开始夜抛出了这个问题
究其原因咱们可以接着上面的分析,其实就到了PatternsRequestCondition这个类上,具体实现是它的匹配逻辑来决定的。
public final class PatternsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<PatternsRequestCondition> {
...
@Override
@Nullable
public PatternsRequestCondition getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
// patterns表示此MappingInfo可以匹配的值们。一般对应@RequestMapping注解上的patters数组的值
if (this.patterns.isEmpty()) {
return this;
}
// 拿到待匹配的值,比如此处为"/hello.json"
String lookupPath = this.pathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
// 最主要就是这个方法了,它拿着这个lookupPath匹配~~~~
List<String> matches = getMatchingPatterns(lookupPath);
// 此处如果为empty,就返回null了~~~~
return (!matches.isEmpty() ? new PatternsRequestCondition(matches, this.pathHelper, this.pathMatcher, this.useSuffixPatternMatch, this.useTrailingSlashMatch, this.fileExtensions) : null);
}
public List<String> getMatchingPatterns(String lookupPath) {
List<String> matches = new ArrayList<>();
for (String pattern : this.patterns) {
// 最最最重点就是在getMatchingPattern()这个方法里~~~ 拿着lookupPath和pattern看它俩合拍不~
String match = getMatchingPattern(pattern, lookupPath);
if (match != null) {
matches.add(match);
}
}
// 解释一下为何匹配的可能是多个。因为url匹配上了,但是还有可能@RequestMapping的其余属性匹配不上啊,所以此处需要注意 是可能匹配上多个的 最终是唯一匹配就成~
if (matches.size() > 1) {
matches.sort(this.pathMatcher.getPatternComparator(lookupPath));
}
return matches;
}
// // ===============url的真正匹配规则 非常重要~~~===============
// 注意这个方法的取名,上面是负数,这里是单数~~~~命名规范也是有艺术感的
@Nullable
private String getMatchingPattern(String pattern, String lookupPath) {
// 完全相等,那就不继续聊了~~~
if (pattern.equals(lookupPath)) {
return pattern;
}
// 注意了:useSuffixPatternMatch 这个属性就是我们最终要关闭后缀匹配的关键
// 这个值默外部给传的true(其实内部默认值是boolean类型为false)
if (this.useSuffixPatternMatch) {
// 这个意思是若useSuffixPatternMatch=true我们支持后缀匹配。我们还可以配置fileExtensions让只支持我们自定义的指定的后缀匹配,而不是下面最终的.*全部支持
if (!this.fileExtensions.isEmpty() && lookupPath.indexOf('.') != -1) {
for (String extension : this.fileExtensions) {
if (this.pathMatcher.match(pattern + extension, lookupPath)) {
return pattern + extension;
}
}
}
// 若你没有配置指定后缀匹配,并且你的handler也没有.*这样匹配的,那就默认你的pattern就给你添加上后缀".*",表示匹配所有请求的url的后缀~~~
else {
boolean hasSuffix = pattern.indexOf('.') != -1;
if (!hasSuffix && this.pathMatcher.match(pattern + ".*", lookupPath)) {
return pattern + ".*";
}
}
}
// 若匹配上了 直接返回此patter
if (this.pathMatcher.match(pattern, lookupPath)) {
return pattern;
}
// 这又是它支持的匹配规则。默认useTrailingSlashMatch它也是true
// 这就是为何我们的/hello/也能匹配上/hello的原因
// 从这可以看出,Spring MVC的宽容度是很高的,容错处理做得是非常不错的~~~~~~~
if (this.useTrailingSlashMatch) {
if (!pattern.endsWith("/") && this.pathMatcher.match(pattern + "/", lookupPath)) {
return pattern + "/";
}
}
return null;
}
}分析了URL的匹配原因,现在肯定知道为何默认情况下"/hello.aaaa"或者"/hello.aaaa/“或者”"/hello/""能匹配上我们/hello的原因了吧~~~
Spring和SpringBoot中如何关闭此项功能呢?
为何要关闭的理由,上面其实已经说了。当我们涉及到严格的权限校验(强权限控制)的时候。特备是一些银行系统、资产系统等等,关闭后缀匹配事非常有必要的。
高版本直接默认就是关闭的
可以看到这两个属性值都直接冒泡到RequestMappingHandlerMapping这个实现类上来了,所以我们直接通过配置来改变它的默认行为就成。
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
// 开启后缀名匹配,开启最后一个/匹配
@Override
public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.setUseSuffixPatternMatch(true);
configurer.setUseTrailingSlashMatch(true);
}
}或者通过xml方式开启