matlab绘制二维曲线,如何设置线型、颜色、标记点类型、如何设置坐标轴、matlab 图表如何标注、如何在图中标记想要的点
matlab绘制二维曲线,如何在图中标记想要的点。。。如何设置线型、颜色、标记点类型。。。如何设置坐标轴。。。matlab 图表标注操作。。。
在MATLAB中,可以使用plot函数绘制图形,并使用text函数在图中标记想要的点。
例1:如何在图中标记一个点:
% 创建一个示例图形
x = linspace(0,10,100);
y = sin(x);
figure
plot(x, y);
hold on;
% 在图中标记一个点
x_point = 5;
y_point = sin(x_point);
% plot(x_point, y_point, 'ro');%红色 o 标记
% plot(x_point, y_point, 'r.', 'MarkerSize',12);% 指定标记样式、颜色、大小
% plot(x_point, y_point, 'Color','red', 'Marker','.', 'MarkerSize',12);
plot(x_point, y_point, 'r*');%红色 * 标记
text(x_point, y_point, 'Point');
% 设置图形标题和坐标轴标签
title('示例图');
xlabel('X轴');
ylabel('Y轴');
% 关闭图形保持功能
hold off;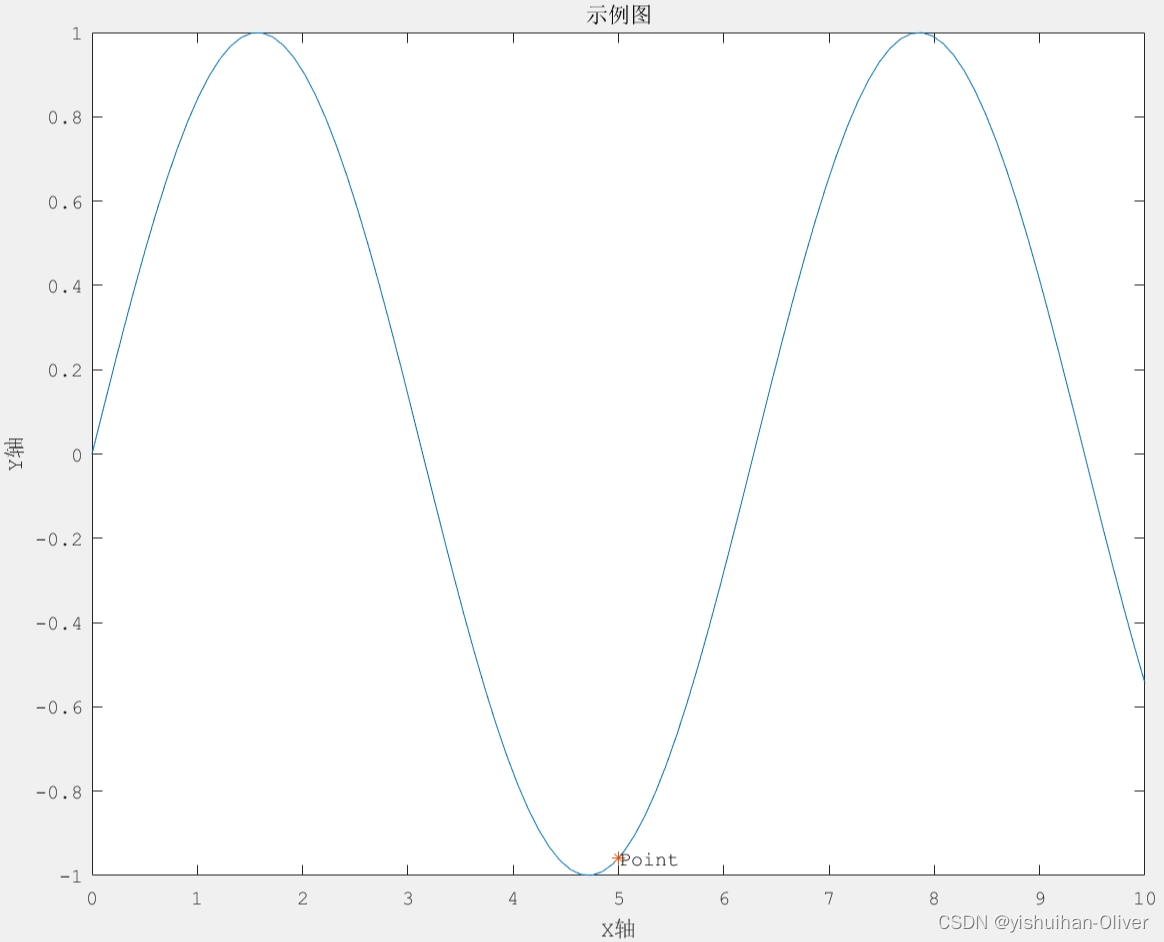
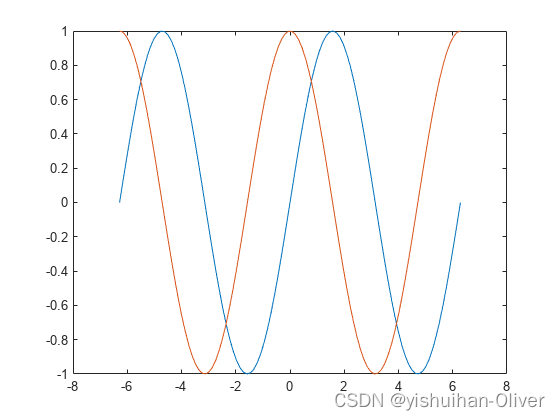
例2:绘制曲线-创建后修改线
将x定义为−2π和2π之间的100个线性间隔值。将y1和y2定义为x的正弦和余弦值。创建两组数据的折线图,并画出曲线。
x = linspace(-2*pi,2*pi);
y1 = sin(x);
y2 = cos(x);
figure
p = plot(x,y1,x,y2);
将第一行的线宽更改为2。将星形标记添加到第二行。使用点表示法设置特性。
x = linspace(-2*pi,2*pi);
y1 = sin(x);
y2 = cos(x);
figure
p = plot(x,y1,x,y2);
p(1).LineWidth = 2;
p(2).Marker = '*';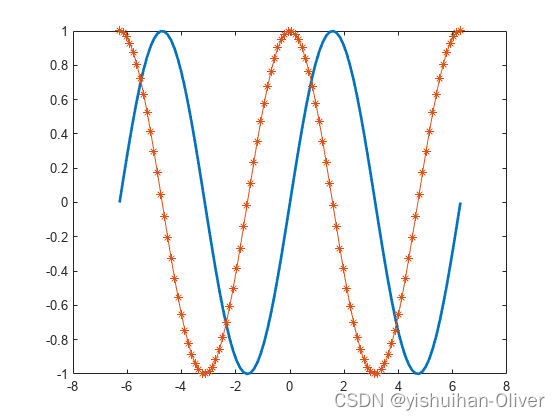
例3:指定绘制曲线的样式
绘制三条正弦曲线,每条线之间有一个小的相移。对第一条线使用默认的线样式。为第二条线指定虚线样式,为第三条线指定点线样式。
x = 0:pi/100:2*pi;
y1 = sin(x);
y2 = sin(x-0.25);
y3 = sin(x-0.5);
figure
plot(x,y1,x,y2,'--',x,y3,':')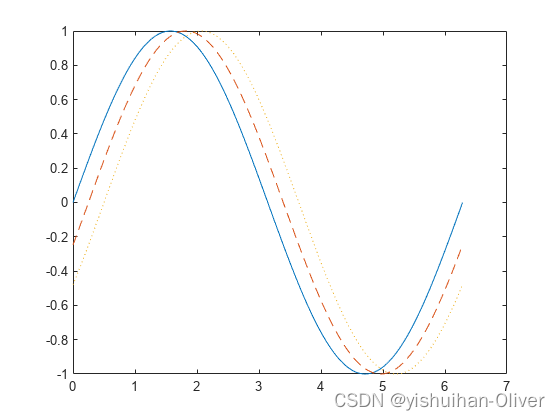
例4:指定线条样式、颜色和标记
x = 0:pi/100:2*pi;
y1 = sin(x);
y2 = sin(x-0.25);
y3 = sin(x-0.5);
figure
plot(x,y1,x,y2,'--',x,y3,':')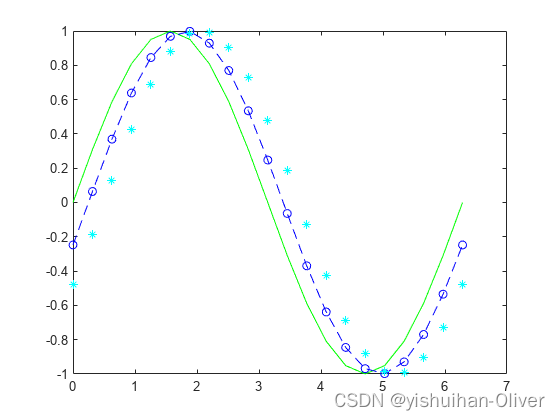
例5:在特定数据点显示标记
x = linspace(0,10);
y = sin(x);
plot(x,y,'-o','MarkerIndices',1:5:length(y))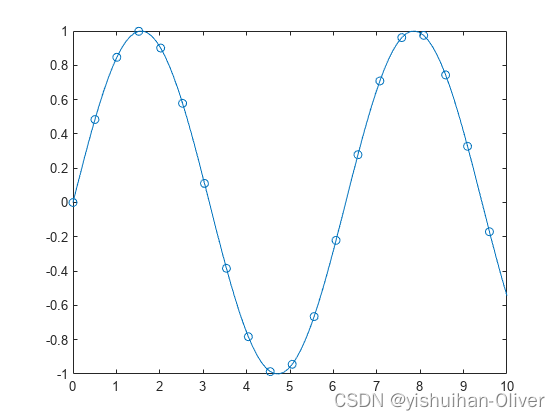
例6:指定线宽、标记大小和标记颜色
x = -pi:pi/10:pi;
y = tan(sin(x)) - sin(tan(x));
figure
plot(x,y,'--gs',...
'LineWidth',2,...
'MarkerSize',10,...
'MarkerEdgeColor','b',...
'MarkerFaceColor',[0.5,0.5,0.5])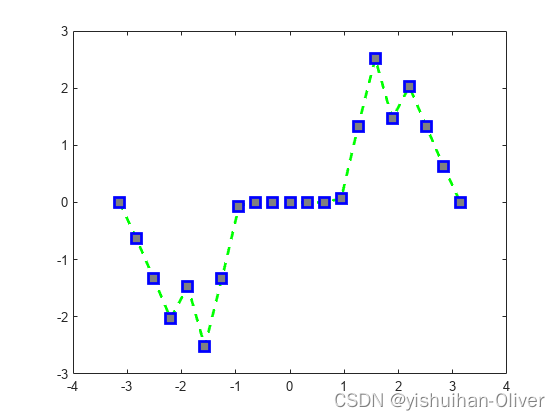
例7:添加标题和轴标签
x = linspace(0,10,150);
y = cos(5*x);
figure
plot(x,y,'Color',[0,0.7,0.9])
txt = '\leftarrow cos(5*x)';
text(5,0,txt,'Color','red','FontSize',12,'FontWeight','bold','Rotation',5, 'HorizontalAlignment', 'right', 'VerticalAlignment', 'top');%, 'BackgroundColor','white', 'EdgeColor','w');%
title('2-D Line Plot')
xlabel('x')
ylabel('cos(5x)')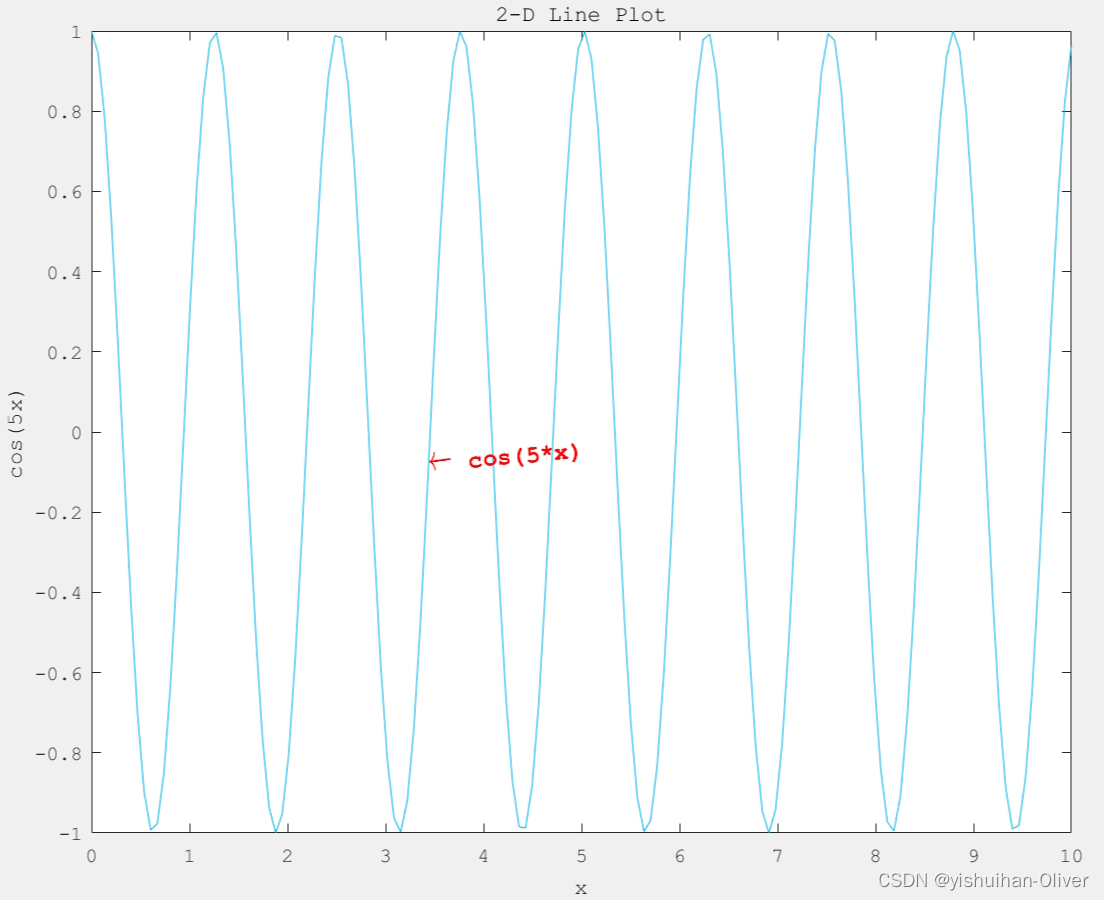
x = 0:0.1:2*pi; y1 = sin(x); y2 = exp(-x);
plot(x, y1, '--*', x, y2, ':o');
xlabel('t = 0 to 2\pi');% 添加X轴标签
ylabel('values of sin(t) and e^{-x}')% 添加Y轴标签
title('Function Plots of sin(t) and e^{-x}');% 添加图表标题
legend('sin(t)','e^{-x}');% 添加图例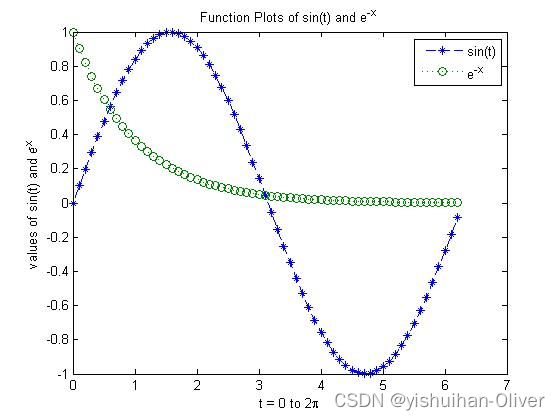
例8:绘制工期和指定刻度格式
t = 0:seconds(30):minutes(3);
y = rand(1,7);
figure
plot(t,y,'DurationTickFormat','mm:ss')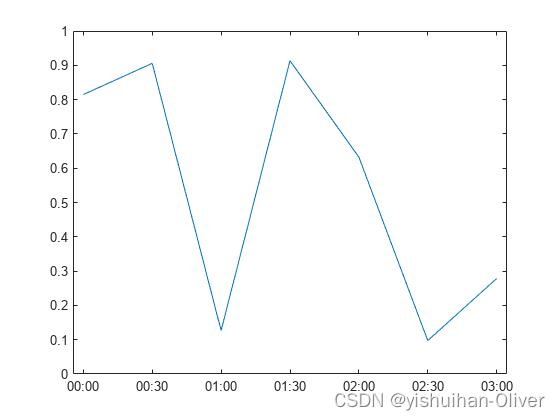
例9:从表中打印坐标

tbl = readtimetable("weather.csv");
tbl = sortrows(tbl);
head(tbl,3)
p = plot(tbl,"RainInchesPerMinute");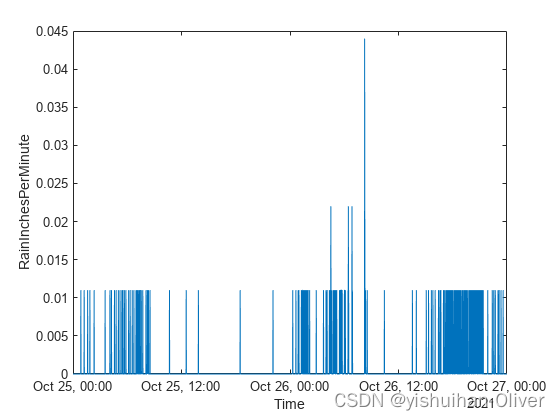
tbl = readtimetable("weather.csv");
tbl = sortrows(tbl);
head(tbl,3)
p = plot(tbl,"RainInchesPerMinute");
p.LineStyle = ":";
p.Color = "red";
p.Marker = ".";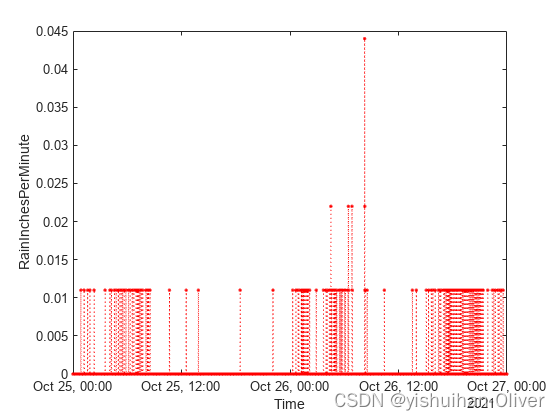
例10:在一个轴上绘制多个图表,并添加图例
tbl = readtimetable("weather.csv");
head(tbl,3)
添加图例。请注意,图例标签与变量名称匹配。
plot(tbl,["Temperature" "PressureHg"])
legend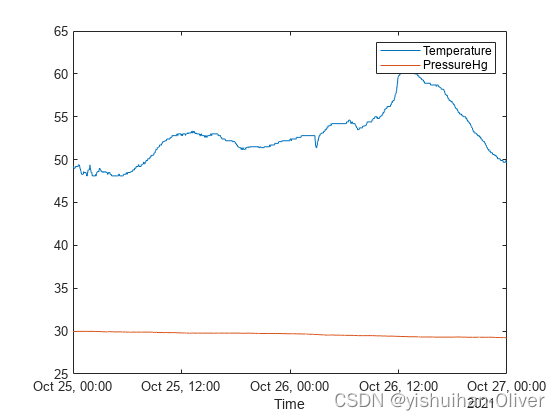
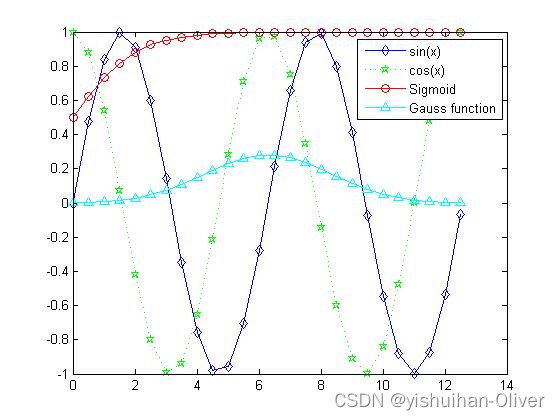
x=0:0.5:4*pi;
y=sin(x); h=cos(x); w=1./(1+exp(-x)); g=(1/(2*pi*2)^0.5).*exp((-1.*(x-2*pi).^2)./(2*2^2));
plot(x,y,'bd-' ,x,h,'gp:',x,w,'ro-' ,x,g,'c^-'); % 绘制多条图线
legend('sin(x)','cos(x)','Sigmoid','Gauss function'); % 添加图例
例11:指定直线打印的轴
可以使用tiledlayout和nexttile函数显示绘图的平铺。调用tiledlayout函数来创建一个2乘1的平铺图表布局。调用nexttile函数来创建一个axs对象,并将该对象返回为ax1。通过将ax1传递给绘图函数来创建顶部绘图。通过将轴传递给title和ylabel函数,将title和y轴标签添加到绘图中。重复该过程以创建底部绘图。
% Create data and 2-by-1 tiled chart layout
x = linspace(0,3);
y1 = sin(5*x);
y2 = sin(15*x);
tiledlayout(2,1)
% Top plot
ax1 = nexttile;
plot(ax1,x,y1)
title(ax1,'Top Plot')
ylabel(ax1,'sin(5x)')
% Bottom plot
ax2 = nexttile;
plot(ax2,x,y2)
title(ax2,'Bottom Plot')
ylabel(ax2,'sin(15x)')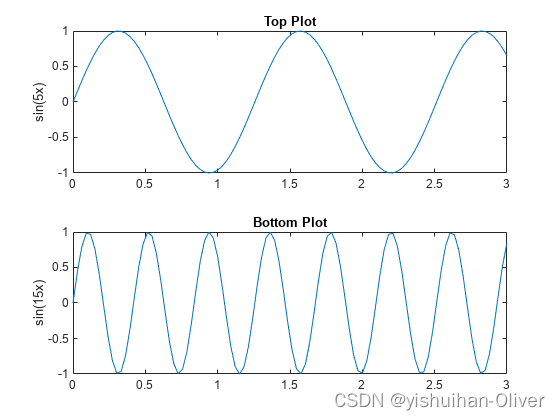
例12:给图表添加注释
x = linspace(0,3); y = x.^2.*sin(x); plot(x,y);
line([2,2],[0,2^2*sin(2)]);
str = '$$ \int_{0}^{2} x^2\sin(x) dx $$';
text(0.25,2.5,str,'Interpreter','latex');% 向数据点添加文本说明
annotation('arrow','X',[0.32,0.5],'Y',[0.6,0.4]);% 创建注释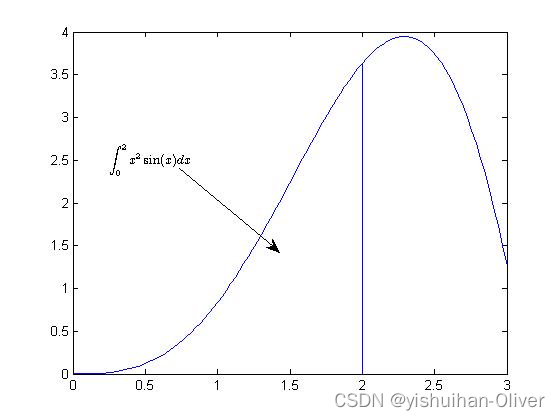
plot()函数
2-D line plot
图线的绘制与装饰
plot(x,y,LineSpec)参数说明:
- x : 图线上点的x坐标
- y : 图线上点的y坐标
- LineSpec : 图线的线条设定,三个指定 线型 , 标记符号 和 颜色 的 设定符 组成一个字符串,设定符不区分先后.具体细节请参考 官方文档 .
语法:
plot(X,Y)
plot(X,Y,LineSpec)
plot(X1,Y1,...,Xn,Yn)
plot(X1,Y1,LineSpec1,...,Xn,Yn,LineSpecn)
plot(Y)
plot(Y,LineSpec)
plot(tbl,xvar,yvar)
plot(tbl,yvar)
plot(ax,___)
plot(___,Name,Value)
p = plot(___)参数说明:
Vector and Matrix Data
plot(X,Y) creates a 2-D line plot of the data in Y versus the corresponding values in X.
-
To plot a set of coordinates connected by line segments, specify
XandYas vectors of the same length. -
To plot multiple sets of coordinates on the same set of axes, specify at least one of
XorYas a matrix.
plot(X,Y,LineSpec) creates the plot using the specified line style, marker, and color.
plot(X1,Y1,...,Xn,Yn) plots multiple pairs of x- and y-coordinates on the same set of axes. Use this syntax as an alternative to specifying coordinates as matrices.
plot(X1,Y1,LineSpec1,...,Xn,Yn,LineSpecn) assigns specific line styles, markers, and colors to each x-y pair. You can specify LineSpec for some x-y pairs and omit it for others. For example, plot(X1,Y1,"o",X2,Y2) specifies markers for the first x-y pair but not for the second pair.
plot(Y) plots Y against an implicit set of x-coordinates.
-
If
Yis a vector, the x-coordinates range from 1 tolength(Y). - If
Yis a matrix, the plot contains one line for each column inY. The x-coordinates range from 1 to the number of rows inY.
If Y contains complex numbers, MATLAB plots the imaginary part of Y versus the real part of Y. If you specify both X and Y, the imaginary part is ignored.
plot(Y,LineSpec) plots Y using implicit x-coordinates, and specifies the line style, marker, and color.
Table Data
plot(tbl,xvar,yvar)plots the variablesxvarandyvarfrom the tabletbl. To plot one data set, specify one variable forxvarand one variable foryvar. To plot multiple data sets, specify multiple variables forxvar,yvar, or both. If both arguments specify multiple variables, they must specify the same number of variables. (since R2022a)plot(tbl,yvar)plots the specified variable from the table against the row indices of the table. If the table is a timetable, the specified variable is plotted against the row times of the timetable. (since R2022a)
Additional Options
plot(ax,___)displays the plot in the target axes. Specify the axes as the first argument in any of the previous syntaxes.plot(___,Name,Value)specifiesLineproperties using one or more name-value arguments. The properties apply to all the plotted lines. Specify the name-value arguments after all the arguments in any of the previous syntaxes. For a list of properties, see Line Properties.p = plot(___)returns aLineobject or an array ofLineobjects. Usepto modify properties of the plot after creating it. For a list of properties, see Line Properties.
设置线型、标记点样式、颜色:
LineSpec — Line style, marker, and color
string scalar | character vector
Line style, marker, and color, specified as a string scalar or character vector containing symbols. The symbols can appear in any order. You do not need to specify all three characteristics (line style, marker, and color). For example, if you omit the line style and specify the marker, then the plot shows only the marker and no line.
Example: "--or" is a red dashed line with circle markers.
| Line Style | Description | Resulting Line |
|---|---|---|
"-" | Solid line |
|
"--" | Dashed line |
|
":" | Dotted line |
|
"-." | Dash-dotted line |
|
| Marker | Description | Resulting Marker |
|---|---|---|
"o" | Circle |
|
"+" | Plus sign |
|
"*" | Asterisk |
|
"." | Point |
|
"x" | Cross |
|
"_" | Horizontal line |
|
"|" | Vertical line |
|
"square" | Square |
|
"diamond" | Diamond |
|
"^" | Upward-pointing triangle |
|
"v" | Downward-pointing triangle |
|
">" | Right-pointing triangle |
|
"<" | Left-pointing triangle |
|
"pentagram" | Pentagram |
|
"hexagram" | Hexagram |
|
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] |
|
"cyan" | "c" | [0 1 1] |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] |
|
tbl — Source table
table | timetable
Source table containing the data to plot, specified as a table or a timetable.
xvar — Table variables containing x-coordinates
string array | character vector | cell array | pattern | numeric scalar or vector | logical vector | vartype()
Table variables containing the x-coordinates, specified using one of the indexing schemes from the table.
| Indexing Scheme | Examples |
|---|---|
| Variable names:
|
|
| Variable index:
|
|
| Variable type:
|
|
The table variables you specify can contain numeric, categorical, datetime, or duration values. If xvar and yvar both specify multiple variables, the number of variables must be the same.
Example: plot(tbl,["x1","x2"],"y") specifies the table variables named x1 and x2 for the x-coordinates.
Example: plot(tbl,2,"y") specifies the second variable for the x-coordinates.
Example: plot(tbl,vartype("numeric"),"y") specifies all numeric variables for the x-coordinates.
yvar — Table variables containing y-coordinates
string array | character vector | cell array | pattern | numeric scalar or vector | logical vector | vartype()
Table variables containing the y-coordinates, specified using one of the indexing schemes from the table.
| Indexing Scheme | Examples |
|---|---|
| Variable names:
|
|
| Variable index:
|
|
| Variable type:
|
|
The table variables you specify can contain numeric, categorical, datetime, or duration values. If xvar and yvar both specify multiple variables, the number of variables must be the same.
Example: plot(tbl,"x",["y1","y2"]) specifies the table variables named y1 and y2 for the y-coordinates.
Example: plot(tbl,"x",2) specifies the second variable for the y-coordinates.
Example: plot(tbl,"x",vartype("numeric")) specifies all numeric variables for the y-coordinates.
ax — Target axes
Axes object | PolarAxes object | GeographicAxes object
Target axes, specified as an Axes object, a PolarAxes object, or a GeographicAxes object. If you do not specify the axes, MATLAB plots into the current axes or it creates an Axes object if one does not exist.
To create a polar plot or geographic plot, specify ax as a PolarAxes or GeographicAxes object. Alternatively, call the polarplot or geoplot function.
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is the argument name and Value is the corresponding value. Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the pairs does not matter.
Example: plot([0 1],[2 3],LineWidth=2)
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose Name in quotes.
Example: plot([0 1],[2 3],"LineWidth",2)
Note:The properties listed here are only a subset. For a complete list, see Line Properties.
Color — Line color
[0 0.4470 0.7410] (default) | RGB triplet | hexadecimal color code | "r" | "g" | "b" | ...
Line color, specified as an RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color code, a color name, or a short name.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan" | "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
"none" | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable | No color |
Here are the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for the default colors MATLAB uses in many types of plots.
| RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
[0 0.4470 0.7410] | "#0072BD" |
|
[0.8500 0.3250 0.0980] | "#D95319" |
|
[0.9290 0.6940 0.1250] | "#EDB120" |
|
[0.4940 0.1840 0.5560] | "#7E2F8E" |
|
[0.4660 0.6740 0.1880] | "#77AC30" |
|
[0.3010 0.7450 0.9330] | "#4DBEEE" |
|
[0.6350 0.0780 0.1840] | "#A2142F" |
|
Example: "blue"
Example: [0 0 1]
Example: "#0000FF"
LineStyle — Line style
"-" (default) | "--" | ":" | "-." | "none"
Line style, specified as one of the options listed in this table.
| Line Style | Description | Resulting Line |
|---|---|---|
"-" | Solid line |
|
"--" | Dashed line |
|
":" | Dotted line |
|
"-." | Dash-dotted line |
|
"none" | No line | No line |
LineWidth — Line width
0.5 (default) | positive value
Marker — Marker symbol
"none" (default) | "o" | "+" | "*" | "." | ...
Marker symbol, specified as one of the values listed in this table. By default, the object does not display markers. Specifying a marker symbol adds markers at each data point or vertex.
| Marker | Description | Resulting Marker |
|---|---|---|
"o" | Circle |
|
"+" | Plus sign |
|
"*" | Asterisk |
|
"." | Point |
|
"x" | Cross |
|
"_" | Horizontal line |
|
"|" | Vertical line |
|
"square" | Square |
|
"diamond" | Diamond |
|
"^" | Upward-pointing triangle |
|
"v" | Downward-pointing triangle |
|
">" | Right-pointing triangle |
|
"<" | Left-pointing triangle |
|
"pentagram" | Pentagram |
|
"hexagram" | Hexagram |
|
"none" | No markers | Not applicable |
MarkerIndices — Indices of data points at which to display markers
1:length(YData) (default) | vector of positive integers | scalar positive integer
Indices of data points at which to display markers, specified as a vector of positive integers. If you do not specify the indices, then MATLAB displays a marker at every data point.
Note:To see the markers, you must also specify a marker symbol.
Example: plot(x,y,"-o","MarkerIndices",[1 5 10]) displays a circle marker at the first, fifth, and tenth data points.
Example: plot(x,y,"-x","MarkerIndices",1:3:length(y)) displays a cross marker every three data points.
Example: plot(x,y,"Marker","square","MarkerIndices",5) displays one square marker at the fifth data point.
MarkerEdgeColor — Marker outline color
"auto" (default) | RGB triplet | hexadecimal color code | "r" | "g" | "b" | ...
Marker outline color, specified as "auto", an RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color code, a color name, or a short name. The default value of "auto" uses the same color as the Color property.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
-
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1], for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7]. -
A hexadecimal color code is a string scalar or character vector that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Therefore, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan" | "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
"none" | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable | No color |
Here are the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for the default colors MATLAB uses in many types of plots.
| RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
[0 0.4470 0.7410] | "#0072BD" |
|
[0.8500 0.3250 0.0980] | "#D95319" |
|
[0.9290 0.6940 0.1250] | "#EDB120" |
|
[0.4940 0.1840 0.5560] | "#7E2F8E" |
|
[0.4660 0.6740 0.1880] | "#77AC30" |
|
[0.3010 0.7450 0.9330] | "#4DBEEE" |
|
[0.6350 0.0780 0.1840] | "#A2142F" |
|
MarkerFaceColor — Marker fill color
"none" (default) | "auto" | RGB triplet | hexadecimal color code | "r" | "g" | "b" | ...
Marker fill color, specified as "auto", an RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color code, a color name, or a short name. The "auto" option uses the same color as the Color property of the parent axes. If you specify "auto" and the axes plot box is invisible, the marker fill color is the color of the figure.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
-
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1], for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7]. -
A hexadecimal color code is a string scalar or character vector that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Therefore, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan" | "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
"none" | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable | No color |
Here are the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for the default colors MATLAB uses in many types of plots.
| RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
[0 0.4470 0.7410] | "#0072BD" |
|
[0.8500 0.3250 0.0980] | "#D95319" |
|
[0.9290 0.6940 0.1250] | "#EDB120" |
|
[0.4940 0.1840 0.5560] | "#7E2F8E" |
|
[0.4660 0.6740 0.1880] | "#77AC30" |
|
[0.3010 0.7450 0.9330] | "#4DBEEE" |
|
[0.6350 0.0780 0.1840] | "#A2142F" |
|
MarkerSize — Marker size
6 (default) | positive value
Marker size, specified as a positive value in points, where 1 point = 1/72 of an inch.
DatetimeTickFormat — Format for datetime tick labels
character vector | string
Format for datetime tick labels, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of "DatetimeTickFormat" and a character vector or string containing a date format. Use the letters A-Z and a-z to construct a custom format. These letters correspond to the Unicode® Locale Data Markup Language (LDML) standard for dates. You can include non-ASCII letter characters such as a hyphen, space, or colon to separate the fields.
If you do not specify a value for "DatetimeTickFormat", then plot automatically optimizes and updates the tick labels based on the axis limits.
Example: "DatetimeTickFormat","eeee, MMMM d, yyyy HH:mm:ss" displays a date and time such as Saturday, April 19, 2014 21:41:06.
The following table shows several common display formats and examples of the formatted output for the date, Saturday, April 19, 2014 at 9:41:06 PM in New York City.
Value of DatetimeTickFormat | Example |
|---|---|
"yyyy-MM-dd" | 2014-04-19 |
"dd/MM/yyyy" | 19/04/2014 |
"dd.MM.yyyy" | 19.04.2014 |
"yyyy年 MM月 dd日" | 2014年 04月 19日 |
"MMMM d, yyyy" | April 19, 2014 |
"eeee, MMMM d, yyyy HH:mm:ss" | Saturday, April 19, 2014 21:41:06 |
"MMMM d, yyyy HH:mm:ss Z" | April 19, 2014 21:41:06 -0400 |
For a complete list of valid letter identifiers, see the Format property for datetime arrays.
DatetimeTickFormat is not a chart line property. You must set the tick format using the name-value pair argument when creating a plot. Alternatively, set the format using the xtickformat and ytickformat functions.
The TickLabelFormat property of the datetime ruler stores the format.
DurationTickFormat — Format for duration tick labels
character vector | string
Format for duration tick labels, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of "DurationTickFormat" and a character vector or string containing a duration format.
If you do not specify a value for "DurationTickFormat", then plot automatically optimizes and updates the tick labels based on the axis limits.
To display a duration as a single number that includes a fractional part, for example, 1.234 hours, specify one of the values in this table.
Value of DurationTickFormat | Description |
|---|---|
"y" | Number of exact fixed-length years. A fixed-length year is equal to 365.2425 days. |
"d" | Number of exact fixed-length days. A fixed-length day is equal to 24 hours. |
"h" | Number of hours |
"m" | Number of minutes |
"s" | Number of seconds |
Example: "DurationTickFormat","d" displays duration values in terms of fixed-length days.
To display a duration in the form of a digital timer, specify one of these values.
-
"dd:hh:mm:ss" -
"hh:mm:ss" -
"mm:ss" -
"hh:mm"
In addition, you can display up to nine fractional second digits by appending up to nine S characters.
Example: "DurationTickFormat","hh:mm:ss.SSS" displays the milliseconds of a duration value to three digits.
DurationTickFormat is not a chart line property. You must set the tick format using the name-value pair argument when creating a plot. Alternatively, set the format using the xtickformat and ytickformat functions.
The TickLabelFormat property of the duration ruler stores the format.
其他参考:
MATLAB04:基础绘图-CSDN博客
【matlab进阶学习-7】matlab 图表标注操作_matlab怎么给每条线标注-CSDN博客










![[Go Web] Kratos 验证码业务](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/3273f0bcb96e461487da7ae04432e140.png)
