目录
- imageProjection.cpp
- 1. ImageProjection类
- 1.1. imuHandler
- 1.2. odometryHandler
- 1.3. cloudHandler⭐
- 1.3.1. cachePointCloud: 点云消息缓存与检查
- 1.3.2. deskewInfo() : 获得运动补偿信息
- 1.3.2.1. imuDeskewInfo() : imu的补偿信息
- 1.3.2.2. odomDeskewInfo():获取odom的信息
- 1.3.3. projectPointCloud():将点云投影到一个矩阵上,并且保存每个点的信息
- 1.3.3.1. deskewPoint():运动补偿
- 1.3.3.1.1. findRotation() 计算当前点相对起始点的相对旋转
- 1.3.3.1.2. findPosition() 计算当前点相对起始点的相对平移
- 1.3.4. cloudExtraction():提取出有效的点的信息
- 1.3.5. publishClouds()
- 参考
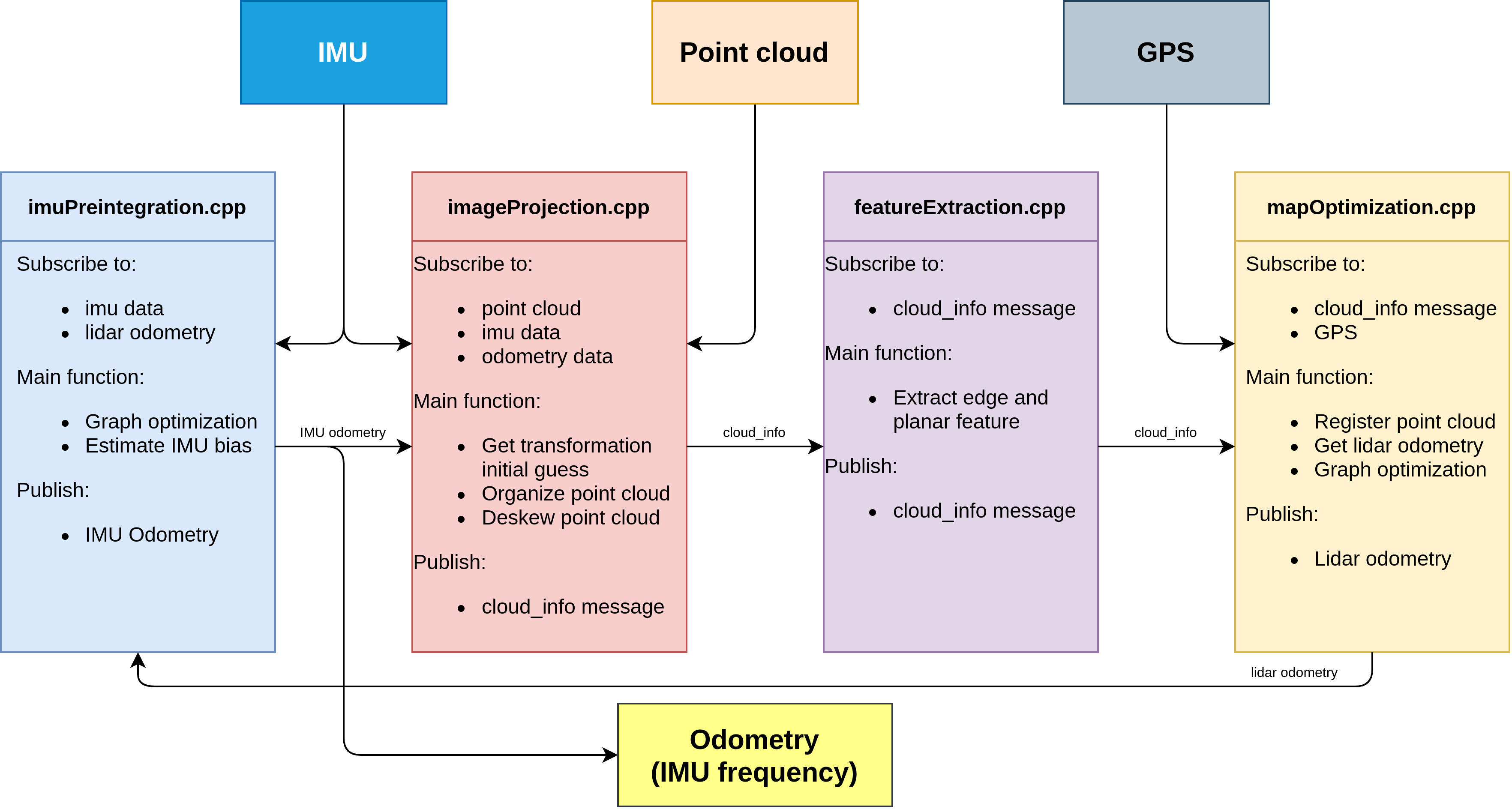 传感器输入: IMU,Point Cloud, GPS(可选)
传感器输入: IMU,Point Cloud, GPS(可选)
输出 : IMU 频率的odometry
imageProjection.cpp: 接受IMU,PointCloud以及IMU预积分输出的IMU odometry(系统刚初始化时没有IMU odometry)。
- 主要功能:
- 基于IMU odometry得到系统的初始位姿
- 将点云投影到cv::mat中,做相应的预处理
- 对原始点云数据做运动补偿(点云的去畸变补偿在代码中只应用于旋转部分,注释掉了平移部分)
featureExtraction.cpp :接收来自imageProjection处理完的lidar帧数据,对应的点云是去畸变的,也就是在同一个坐标系下。对点云进行面点,角点特征的分类。
- 主要功能:
- 提取点云边缘特征和面特征
mapOptimization.cpp:
- 主要功能:
- 将提取到点云特征与地图中的边缘特征和面特征进行配准
- 配准后得到当前帧在地图中的位姿
- 图优化: 将lidar的帧间约束,回环的约束,(GPS因子)添加到因子图中
imuPreintegration.cpp:一开始并没有工作,只有收到lidar odometry后才会工作
- 主要功能:
- 图优化:lidar odometry和IMU的帧间约束添加到因子图中
- 估计IMU零偏
imageProjection.cpp
主函数只存在1个类ImageProjection IP
1. ImageProjection类
ImageProjection():
deskewFlag(0)
{
// 订阅原始imu数据
subImu = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::Imu>(imuTopic, 2000, &ImageProjection::imuHandler, this, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay());
// 订阅IMU激光节点发送的增量数据,由imuPreintegration积分计算得到的每时刻imu位姿
subOdom = nh.subscribe<nav_msgs::Odometry>(odomTopic+"_incremental", 2000, &ImageProjection::odometryHandler, this, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay());
/// 订阅原始lidar数据, 该节点的主要操作都在cloudHandler中
subLaserCloud = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>(pointCloudTopic, 5, &ImageProjection::cloudHandler, this, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay());
// 发布当前激光帧运动畸变校正后的点云,有效点
pubExtractedCloud = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2> ("lio_sam/deskew/cloud_deskewed", 1);
// 发布当前激光帧运动畸变校正后的点云信息
pubLaserCloudInfo = nh.advertise<lio_sam::cloud_info> ("lio_sam/deskew/cloud_info", 1);
// 给指针赋上地址
allocateMemory();
// 参数复位
resetParameters();
pcl::console::setVerbosityLevel(pcl::console::L_ERROR);
}
1.1. imuHandler
功能 :把IMU数据的坐标系转换到lidar系上,从而和lidar数据进行匹配,然后放到容器里去。
void imuHandler(const sensor_msgs::Imu::ConstPtr& imuMsg)
{
// 把IMU数据的坐标系转换到lidar系上,从而和lidar数据进行匹配
sensor_msgs::Imu thisImu = imuConverter(*imuMsg);
// 加一个线程锁,把imu数据保存进队列
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock1(imuLock);
imuQueue.push_back(thisImu);
}
imuConverter()定义在utility.h文件里,这个文件定义了全部通用的工具函数。它把线加速度和角速度转化到lidar系下,rot转化为从lidar->world的旋转。
sensor_msgs::Imu imuConverter(const sensor_msgs::Imu& imu_in)
{
sensor_msgs::Imu imu_out = imu_in;
// rotate acceleration
// 这里把imu的数据旋转到前左上坐标系下,可以参考github的issue/6
Eigen::Vector3d acc(imu_in.linear_acceleration.x, imu_in.linear_acceleration.y, imu_in.linear_acceleration.z);
acc = extRot * acc;
imu_out.linear_acceleration.x = acc.x();
imu_out.linear_acceleration.y = acc.y();
imu_out.linear_acceleration.z = acc.z();
// rotate gyroscope
Eigen::Vector3d gyr(imu_in.angular_velocity.x, imu_in.angular_velocity.y, imu_in.angular_velocity.z);
gyr = extRot * gyr;
imu_out.angular_velocity.x = gyr.x();
imu_out.angular_velocity.y = gyr.y();
imu_out.angular_velocity.z = gyr.z();
// rotate roll pitch yaw
// 这是一个九轴IMU,因此还会有姿态信息
Eigen::Quaterniond q_from(imu_in.orientation.w, imu_in.orientation.x, imu_in.orientation.y, imu_in.orientation.z);
Eigen::Quaterniond q_final = q_from * extQRPY;
// 把eigen的消息格式转换为ros的消息格式
imu_out.orientation.x = q_final.x();
imu_out.orientation.y = q_final.y();
imu_out.orientation.z = q_final.z();
imu_out.orientation.w = q_final.w();
// 简单校验一下结果
if (sqrt(q_final.x()*q_final.x() + q_final.y()*q_final.y() + q_final.z()*q_final.z() + q_final.w()*q_final.w()) < 0.1)
{
ROS_ERROR("Invalid quaternion, please use a 9-axis IMU!");
ros::shutdown();
}
return imu_out;
}
1.2. odometryHandler
功能 : 直接把里程计放到buffer里去,注意这里接收的里程计都已经是lidar系在world系下的表示 T(world<-lidar)
// 订阅imu里程计,由imuPreintegration积分计算得到的每时刻imu位姿
void odometryHandler(const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr& odometryMsg)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock2(odoLock);
odomQueue.push_back(*odometryMsg);
}
1.3. cloudHandler⭐
void cloudHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& laserCloudMsg)
{
// 添加一帧激光点云到队列,取出最早一帧作为当前帧,计算起止时间戳,检查数据有效性
if (!cachePointCloud(laserCloudMsg))
return;
// 获取运动补偿
if (!deskewInfo())
return;
// 将点云投影到一个矩阵上,并且保存每个点的信息
projectPointCloud();
// 提取出有效的点的信息,存extractedCloud
cloudExtraction();
// 发布当前帧校正后点云,有效点
publishClouds();
// 重置参数,接收每帧lidar数据都要重置这些参数
resetParameters();
}
1.3.1. cachePointCloud: 点云消息缓存与检查
// 点云消息缓存,并对点云信息进行检查
bool cachePointCloud(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& laserCloudMsg)
{
// cache point cloud
// 点云数据保存进队列
cloudQueue.push_back(*laserCloudMsg);
// 确保队列里大于两帧的点云数据
if (cloudQueue.size() <= 2)
return false;
// convert cloud
// 缓存足够多的点云之后
currentCloudMsg = std::move(cloudQueue.front());
cloudQueue.pop_front();
if (sensor == SensorType::VELODYNE)
{
// 转成pcl的点云格式
pcl::moveFromROSMsg(currentCloudMsg, *laserCloudIn);
}
else if (sensor == SensorType::OUSTER)
{
// Convert to Velodyne format
pcl::moveFromROSMsg(currentCloudMsg, *tmpOusterCloudIn);
laserCloudIn->points.resize(tmpOusterCloudIn->size());
laserCloudIn->is_dense = tmpOusterCloudIn->is_dense;
for (size_t i = 0; i < tmpOusterCloudIn->size(); i++)
{
auto &src = tmpOusterCloudIn->points[i];
auto &dst = laserCloudIn->points[i];
dst.x = src.x;
dst.y = src.y;
dst.z = src.z;
dst.intensity = src.intensity;
dst.ring = src.ring;
dst.time = src.t * 1e-9f;
}
}
else
{
ROS_ERROR_STREAM("Unknown sensor type: " << int(sensor));
ros::shutdown();
}
// get timestamp
cloudHeader = currentCloudMsg.header;
timeScanCur = cloudHeader.stamp.toSec();
// 开始的时间+最后一个点的时间(相对于第一个点的时间) = 最后的时间
timeScanEnd = timeScanCur + laserCloudIn->points.back().time;
// check dense flag
// is_dense 是点云是否有序排列的标志
if (laserCloudIn->is_dense == false)
{
ROS_ERROR("Point cloud is not in dense format, please remove NaN points first!");
ros::shutdown();
}
// check ring channel
// 查看驱动里是否把每个点属于哪一根扫描scan这个信息
static int ringFlag = 0;
if (ringFlag == 0)
{
ringFlag = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)currentCloudMsg.fields.size(); ++i)
{
if (currentCloudMsg.fields[i].name == "ring")
{
ringFlag = 1;
break;
}
}
// 如果没有这个信息就需要像loam或者lego loam那样手动计算scan id,现在velodyne的驱动里都会携带这些信息
if (ringFlag == -1)
{
ROS_ERROR("Point cloud ring channel not available, please configure your point cloud data!");
ros::shutdown();
}
}
// check point time
// 同样,检查是否有时间戳信息
if (deskewFlag == 0)
{
deskewFlag = -1;
for (auto &field : currentCloudMsg.fields)
{
if (field.name == "time" || field.name == "t")
{
deskewFlag = 1;
break;
}
}
if (deskewFlag == -1)
ROS_WARN("Point cloud timestamp not available, deskew function disabled, system will drift significantly!");
}
return true;
}
1.3.2. deskewInfo() : 获得运动补偿信息
获得在当前激光帧范围内的每一个时刻时的相对旋转角,初始时刻的roll,pitch,yaw角,位姿,和起止时刻间位姿的变化量。
bool deskewInfo()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock1(imuLock);
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock2(odoLock);
// make sure IMU data available for the scan
// 确保imu的数据覆盖这一帧的点云
if (imuQueue.empty() || imuQueue.front().header.stamp.toSec() > timeScanCur || imuQueue.back().header.stamp.toSec() < timeScanEnd)
{
ROS_DEBUG("Waiting for IMU data ...");
return false;
}
// 准备imu补偿的信息
imuDeskewInfo();
// 获取odom的信息
odomDeskewInfo();
return true;
}
1.3.2.1. imuDeskewInfo() : imu的补偿信息
特别的,此处代码记录了第一个时刻IMU的roll,pitch,yaw给cloudinfo。这是cloudinfo第一次出现的地方,它是整个cpp文件的输出文件,即去畸变后的lidar帧信息。即虽然每一个IMU都有记录roll,pitch,yaw角,但是我们只要了第一个IMU
// 获得在当前激光帧范围内的每一个时刻时的相对旋转角,初始时刻的rollpitchyaw角,位姿,和起止时刻间位姿的变化量。
bool deskewInfo()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock1(imuLock);
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock2(odoLock);
// make sure IMU data available for the scan
// 确保imu的数据覆盖这一帧的点云
if (imuQueue.empty() || imuQueue.front().header.stamp.toSec() > timeScanCur || imuQueue.back().header.stamp.toSec() < timeScanEnd)
{
ROS_DEBUG("Waiting for IMU data ...");
return false;
}
// 准备imu补偿的信息
imuDeskewInfo();
// 获取odom的信息
odomDeskewInfo();
return true;
}
// 准备imu的补偿信息
void imuDeskewInfo()
{
cloudInfo.imuAvailable = false;
// 从imu队列中删除当前激光帧0.01s前面时刻的imu数据
while (!imuQueue.empty())
{
if (imuQueue.front().header.stamp.toSec() < timeScanCur - 0.01)
imuQueue.pop_front();
else
break;
}
if (imuQueue.empty())
return;
imuPointerCur = 0;
// 遍历当前激光帧起止时刻(前后扩展0.01s)之间的imu数据
for (int i = 0; i < (int)imuQueue.size(); ++i)
{
sensor_msgs::Imu thisImuMsg = imuQueue[i];
double currentImuTime = thisImuMsg.header.stamp.toSec();
// get roll, pitch, and yaw estimation for this scan
// 获取离当前帧之前最近时刻的imu姿态角RPY,作为当前lidar帧初始姿态角
if (currentImuTime <= timeScanCur)
// 把imu的姿态转成欧拉角
imuRPY2rosRPY(&thisImuMsg, &cloudInfo.imuRollInit, &cloudInfo.imuPitchInit, &cloudInfo.imuYawInit);
if (currentImuTime > timeScanEnd + 0.01) // 超过当前激光帧结束时刻0.01s,结束
break;
// 令第一个IMU时刻的累计x,y,z方向的旋转角为0,则之后每一个IMU时刻的旋转角都是基于当前IMU角速度和之前旋转角的累加。
if (imuPointerCur == 0){ // 起始帧
imuRotX[0] = 0;
imuRotY[0] = 0;
imuRotZ[0] = 0;
imuTime[0] = currentImuTime;
++imuPointerCur;
continue;
}
// get angular velocity
double angular_x, angular_y, angular_z;
// 取出当前帧imu的角速度
imuAngular2rosAngular(&thisImuMsg, &angular_x, &angular_y, &angular_z);
// integrate rotation
// imu帧间时差
double timeDiff = currentImuTime - imuTime[imuPointerCur-1];
// 计算每一个时刻的姿态角,方便后续查找对应每个点云时间的值
imuRotX[imuPointerCur] = imuRotX[imuPointerCur-1] + angular_x * timeDiff; // 简单的角度积分
imuRotY[imuPointerCur] = imuRotY[imuPointerCur-1] + angular_y * timeDiff;
imuRotZ[imuPointerCur] = imuRotZ[imuPointerCur-1] + angular_z * timeDiff;
imuTime[imuPointerCur] = currentImuTime;
++imuPointerCur;
}
--imuPointerCur;
// 没有合规的imu数据
if (imuPointerCur <= 0)
return;
// 表示可以使用imu数据进行运动补偿
cloudInfo.imuAvailable = true;
}
1.3.2.2. odomDeskewInfo():获取odom的信息
void odomDeskewInfo()
{
cloudInfo.odomAvailable = false;
// 从imu里程计队列中删除当前激光帧0.01s前面时刻的imu数据
while (!odomQueue.empty())
{
if (odomQueue.front().header.stamp.toSec() < timeScanCur - 0.01)
odomQueue.pop_front();
else
break;
}
if (odomQueue.empty())
return;
/// 点云做运动补偿需要覆盖整个odom的时间戳
// 点云时间 : ××××××××
// odom时间: ×××××
// 显然不能覆盖整个点云的时间
if (odomQueue.front().header.stamp.toSec() > timeScanCur)
return;
// get start odometry at the beinning of the scan
nav_msgs::Odometry startOdomMsg;
// 提取当前激光帧起始时刻的imu里程计
for (int i = 0; i < (int)odomQueue.size(); ++i)
{
startOdomMsg = odomQueue[i];
if (ROS_TIME(&startOdomMsg) < timeScanCur)
continue;
else
break;
}
// 将ros消息格式中的姿态转成tf的格式
tf::Quaternion orientation;
tf::quaternionMsgToTF(startOdomMsg.pose.pose.orientation, orientation);
// 然后将四元数转成欧拉角
double roll, pitch, yaw;
tf::Matrix3x3(orientation).getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
// Initial guess used in mapOptimization
// 用当前激光帧起始时刻的imu里程计,初始化lidar位姿,后面用于mapOptmization
cloudInfo.initialGuessX = startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.x;
cloudInfo.initialGuessY = startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.y;
cloudInfo.initialGuessZ = startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.z;
cloudInfo.initialGuessRoll = roll;
cloudInfo.initialGuessPitch = pitch;
cloudInfo.initialGuessYaw = yaw;
cloudInfo.odomAvailable = true; // odom提供了这一帧点云的初始位姿
// get end odometry at the end of the scan
odomDeskewFlag = false;
// 这里发现没有覆盖到最后的点云,那就不能用odom数据来做运动补偿
if (odomQueue.back().header.stamp.toSec() < timeScanEnd)
return;
nav_msgs::Odometry endOdomMsg;
// 提取当前激光帧结束时刻的imu里程计
for (int i = 0; i < (int)odomQueue.size(); ++i)
{
endOdomMsg = odomQueue[i];
if (ROS_TIME(&endOdomMsg) < timeScanEnd)
continue;
else
break;
}
// 这个代表odom退化了,置信度不高了
if (int(round(startOdomMsg.pose.covariance[0])) != int(round(endOdomMsg.pose.covariance[0])))
return;
// 起始位姿和结束位姿都转成Affine3f这个数据格式
Eigen::Affine3f transBegin = pcl::getTransformation(startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.x, startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.y, startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.z, roll, pitch, yaw);
tf::quaternionMsgToTF(endOdomMsg.pose.pose.orientation, orientation);
tf::Matrix3x3(orientation).getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
Eigen::Affine3f transEnd = pcl::getTransformation(endOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.x, endOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.y, endOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.z, roll, pitch, yaw);
// 计算起始位姿和结束位姿之间IMU里程计的delta pose
Eigen::Affine3f transBt = transBegin.inverse() * transEnd;
// 将这个增量转成xyz和欧拉角的形式
float rollIncre, pitchIncre, yawIncre;
pcl::getTranslationAndEulerAngles(transBt, odomIncreX, odomIncreY, odomIncreZ, rollIncre, pitchIncre, yawIncre);
odomDeskewFlag = true; // 表示可以用odom做运动补偿
}
1.3.3. projectPointCloud():将点云投影到一个矩阵上,并且保存每个点的信息
// 这个函数的作用是把当前帧的所有点云的序号找到,同时变换到帧初始时刻所在的坐标系下,这个函数才是去畸变。
void projectPointCloud()
{
int cloudSize = laserCloudIn->points.size();
// range image projection
// 遍历当前帧激光点云
for (int i = 0; i < cloudSize; ++i)
{
PointType thisPoint;
// 取出对应的某个点
thisPoint.x = laserCloudIn->points[i].x;
thisPoint.y = laserCloudIn->points[i].y;
thisPoint.z = laserCloudIn->points[i].z;
thisPoint.intensity = laserCloudIn->points[i].intensity;
// 计算这个点距离lidar中心的距离
float range = pointDistance(thisPoint);
// 距离太小或者太远都认为是异常点
if (range < lidarMinRange || range > lidarMaxRange)
continue;
// 取出对应的在第几根scan上
int rowIdn = laserCloudIn->points[i].ring;
// scan id必须合理
if (rowIdn < 0 || rowIdn >= N_SCAN)
continue;
// 如果需要降采样,就根据scan id适当跳过
if (rowIdn % downsampleRate != 0)
continue;
// 计算水平角
float horizonAngle = atan2(thisPoint.x, thisPoint.y) * 180 / M_PI;
static float ang_res_x = 360.0/float(Horizon_SCAN);
// 计算水平线束id,转换到x负方向e为起始,顺时针为正方向,范围[0,H]
int columnIdn = -round((horizonAngle-90.0)/ang_res_x) + Horizon_SCAN/2;
if (columnIdn >= Horizon_SCAN)
columnIdn -= Horizon_SCAN;
// 对水平id进行检查
if (columnIdn < 0 || columnIdn >= Horizon_SCAN)
continue;
// 如果这个位置已经填充了,就跳过
if (rangeMat.at<float>(rowIdn, columnIdn) != FLT_MAX)
continue;
// 对点做运动补偿
/// 利用当前帧起始和结束时刻之间的imu数据计算旋转增量,imu里程计数据计算平移增量,进而将每一时刻激光点位置变换到第一个激光点坐标系下,进行运动补偿
thisPoint = deskewPoint(&thisPoint, laserCloudIn->points[i].time);
// 将这个点的距离数据保存进这个range矩阵块
rangeMat.at<float>(rowIdn, columnIdn) = range;
// 算出这个点的索引
int index = columnIdn + rowIdn * Horizon_SCAN;
// 保存这个点的坐标
fullCloud->points[index] = thisPoint;
}
}
1.3.3.1. deskewPoint():运动补偿
利用当前帧起始和结束时刻之间的imu数据计算旋转增量,imu里程计数据计算平移增量,进而将每一时刻激光点位置变换到第一个激光点坐标系下,进行运动补偿
PointType deskewPoint(PointType *point, double relTime)
{
if (deskewFlag == -1 || cloudInfo.imuAvailable == false)
return *point;
// relTime是当前激光点相对于激光帧起始时刻的时间,pointTime则是当前激光点的时间戳
double pointTime = timeScanCur + relTime;
float rotXCur, rotYCur, rotZCur;
// 计算当前点相对起始点的相对旋转(旋转增量)
findRotation(pointTime, &rotXCur, &rotYCur, &rotZCur);
float posXCur, posYCur, posZCur;
// 计算当前点相对起始点的相对平移(平移增量)
// 这里没有计算
findPosition(relTime, &posXCur, &posYCur, &posZCur);
if (firstPointFlag == true)
{
// 计算第一个点的相对位姿
transStartInverse = (pcl::getTransformation(posXCur, posYCur, posZCur, rotXCur, rotYCur, rotZCur)).inverse();
firstPointFlag = false;
}
// transform points to start
// 计算当前点和第一个点的相对位姿
Eigen::Affine3f transFinal = pcl::getTransformation(posXCur, posYCur, posZCur, rotXCur, rotYCur, rotZCur);
Eigen::Affine3f transBt = transStartInverse * transFinal;
PointType newPoint;
// 就是R * p + t,把点补偿到第一个点对应时刻的位姿
newPoint.x = transBt(0,0) * point->x + transBt(0,1) * point->y + transBt(0,2) * point->z + transBt(0,3);
newPoint.y = transBt(1,0) * point->x + transBt(1,1) * point->y + transBt(1,2) * point->z + transBt(1,3);
newPoint.z = transBt(2,0) * point->x + transBt(2,1) * point->y + transBt(2,2) * point->z + transBt(2,3);
newPoint.intensity = point->intensity;
return newPoint;
}
这里面有findRotation()和findPosition(),作用是根据当前点的时间,起止时间内位姿变化量,插值计算获取当前点云相对于帧初始时刻的x,y,z,roll,pitch,yaw角的增量。这两个函数你可以看到,短时间内的旋转对位姿的影响远大于平移。
1.3.3.1.1. findRotation() 计算当前点相对起始点的相对旋转
计算当前点相对起始点的相对旋转(旋转增量)
void findRotation(double pointTime, float *rotXCur, float *rotYCur, float *rotZCur)
{
*rotXCur = 0; *rotYCur = 0; *rotZCur = 0;
int imuPointerFront = 0;
// 查找当前时刻在imuTime下的索引
// imuPointCur 是 imu 计算的旋转buffer的总共大小,这里用的就是一种朴素的确保不越界的方法
while (imuPointerFront < imuPointerCur)
{
if (pointTime < imuTime[imuPointerFront])
break;
++imuPointerFront;
}
// 如果时间戳不在两个imu的旋转之间,就直接设为离当前时刻最近的旋转增量
if (pointTime > imuTime[imuPointerFront] || imuPointerFront == 0)
{
*rotXCur = imuRotX[imuPointerFront];
*rotYCur = imuRotY[imuPointerFront];
*rotZCur = imuRotZ[imuPointerFront];
} else {
// 否则做一个线性插值,得到相对旋转
// imuPointerBack imuPointerFront
// × ×
// ×
// imuPointerCur(对两个时间戳之间的时间的imu数据,需要计算插值才能得到)
int imuPointerBack = imuPointerFront - 1;
double ratioFront = (pointTime - imuTime[imuPointerBack]) / (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - imuTime[imuPointerBack]);
double ratioBack = (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - pointTime) / (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - imuTime[imuPointerBack]);
*rotXCur = imuRotX[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuRotX[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
*rotYCur = imuRotY[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuRotY[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
*rotZCur = imuRotZ[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuRotZ[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
}
}
1.3.3.1.2. findPosition() 计算当前点相对起始点的相对平移
void findPosition(double relTime, float *posXCur, float *posYCur, float *posZCur)
{
*posXCur = 0; *posYCur = 0; *posZCur = 0;
// If the sensor moves relatively slow, like walking speed, positional deskew seems to have little benefits. Thus code below is commented.
// 如果传感器移动速度较慢,例如人行走的速度,那么可以认为激光在一帧时间范围内,平移量小到可以忽略不计
// if (cloudInfo.odomAvailable == false || odomDeskewFlag == false)
// return;
// float ratio = relTime / (timeScanEnd - timeScanCur);
// *posXCur = ratio * odomIncreX;
// *posYCur = ratio * odomIncreY;
// *posZCur = ratio * odomIncreZ;
}
1.3.4. cloudExtraction():提取出有效的点的信息
void cloudExtraction()
{
// 有效激光点数量
int count = 0;
// extract segmented cloud for lidar odometry
// 遍历所有激光点
for (int i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i)
{
// 记录每根扫描线起始第5个激光点在一维数组中的索引(计算曲率需要左右各五个点)
cloudInfo.startRingIndex[i] = count - 1 + 5;
for (int j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j)
{
// 每个点的默认值设定为FLT_MAX,如果当前点不是该值。则认为该点是一个有用的点
if (rangeMat.at<float>(i,j) != FLT_MAX)
{
// mark the points' column index for marking occlusion later
// 这个点对应这哪一根垂直线
cloudInfo.pointColInd[count] = j;
// save range info
// 它的距离信息
cloudInfo.pointRange[count] = rangeMat.at<float>(i,j);
// save extracted cloud
// 它的3d坐标
extractedCloud->push_back(fullCloud->points[j + i*Horizon_SCAN]);
// size of extracted cloud
// count只有在有效点时才会增加
++count;
}
}
// 记录每根扫描线倒数第5个激光点在一维数组中的索引
cloudInfo.endRingIndex[i] = count -1 - 5;
}
}
1.3.5. publishClouds()
void publishClouds()
{
cloudInfo.header = cloudHeader;
cloudInfo.cloud_deskewed = publishCloud(&pubExtractedCloud, extractedCloud, cloudHeader.stamp, lidarFrame);
pubLaserCloudInfo.publish(cloudInfo);
}
};
参考
https://blog.csdn.net/iwanderu/article/details/123058727