参考:GLib – 2.0: The Main Event Loop
The Main Event Loop
主事件循环管理所有可用的事件源,事件可以是各种类型、各种数量的。比如说文件描述符(普通文件、管道以及套接字)和超时。
新类型的事件源可以通过函数g_source_attach来添加。为了使多个相互独立的事件源集能在不同的线程中进行处理,每个事件源都会关联一个GMainContext。一个GMainContext只能在一个线程中运行,但, 事件源可以添加到一个线程中的GmainContext,而从另外一个线程中移除。
我们来先来看看GLib中对事件源的定义。
struct _GSource
{
/*< private >*/
gpointer callback_data;
GSourceCallbackFuncs *callback_funcs;
const GSourceFuncs *source_funcs;
guint ref_count;
GMainContext *context;
gint priority;
guint flags;
guint source_id;
GSList *poll_fds;
GSource *prev;
GSource *next;
char *name;
GSourcePrivate *priv;
};由定义可以看到,事件源的定义中包含 GMainContext,结构体中还包含成员priority,这表示每个事件源都被指定一个优先级,默认的优先级是G_PRIORITY_DEFAULT,其值为0,当优先级的值小于0表示高优先级,高优先级的事件源优先处理。
GMainLoop 用于表示主事件循环。它由函数g_main_loop_new()函数创建。在为其添加完事件后,调用函数g_main_loop_run()来运行主事件循环。从代码层面上看,GMainLoop就是一个loop,在loop中它,循环会运行GMainContext来持续检查事件源中的事件并对事件进行分发。最终,会有一个事件源中的事件导致函数g_main_loop_quit()被调用,这就意味着程序退出主循环,函数g_main_loop_run()返回。
我们看一下GLib中GMainLoop是如何定义的。
struct _GMainLoop
{
GMainContext *context;
gboolean is_running; /* (atomic) */
gint ref_count; /* (atomic) */
};/**
* g_main_loop_run:
* @loop: a #GMainLoop
*
* Runs a main loop until g_main_loop_quit() is called on the loop.
* If this is called for the thread of the loop's #GMainContext,
* it will process events from the loop, otherwise it will
* simply wait.
**/
void
g_main_loop_run (GMainLoop *loop)
{
......
g_atomic_int_set (&loop->is_running, TRUE);
while (g_atomic_int_get (&loop->is_running))
g_main_context_iterate_unlocked (loop->context, TRUE, TRUE, self);
......
}Creating new source types
GMainLoop允许创建和使用不同于GLib中内置的事件源类型的事件源。
新的事件源类型要继承自GSource结构,与GObject中的有继承关系的数据结构的成员的写法类似,新的事件源类型的数据结构的第一个成员是GSource。创建新的事件源类型实例是通过函数g_source_new()实现的。函数的第一个参数GsourceFuncs中的函数决定了新事件源类型的功能。
GLIB_AVAILABLE_IN_ALL
GSource *g_source_new (GSourceFuncs *source_funcs,
guint struct_size);我们举例看看在GTK中,新事件源类型数据结构的定义情况。
typedef struct _GdkMacosEventSource
{
GSource source;
GdkDisplay *display;
} GdkMacosEventSource;
新的事件源类型与其所属GMainContext之间有两种交互方式。第一种方式是通过GSourceFuncs结构中的prepare函数设置一个超时,来指定在主事件循环在检查此事件源之前最大的睡眠时间,另一种方式是,事件源通过调用函数g_source_add_poll()将文件描述符添加到集合中,GMainContext会对集合进行检查。
GSourceFuncs结构的定义如下:
/**
* GSourceDummyMarshal:
*
* This is just a placeholder for #GClosureMarshal,
* which cannot be used here for dependency reasons.
*/
typedef void (*GSourceDummyMarshal) (void);
struct _GSourceFuncs
{
gboolean (*prepare) (GSource *source,
gint *timeout_);/* Can be NULL */
gboolean (*check) (GSource *source);/* Can be NULL */
gboolean (*dispatch) (GSource *source,
GSourceFunc callback,
gpointer user_data);
void (*finalize) (GSource *source); /* Can be NULL */
/*< private >*/
/* For use by g_source_set_closure */
GSourceFunc closure_callback;
GSourceDummyMarshal closure_marshal; /* Really is of type GClosureMarshal */
};Customizing the main loop iteration
函数g_main_context_iteration()就能实现单纯的GMainContext迭代。然而,很多时候,我们需要对主事件循环的运行增加精确控制。比如说,GMainLoop在迭代时使用了另外一个主事件循环,此时,你可以调用g_main_context_iteration()的组成函数g_main_context_prepare(), g_main_context_query(), g_main_context_check() and g_main_context_dispatch()。
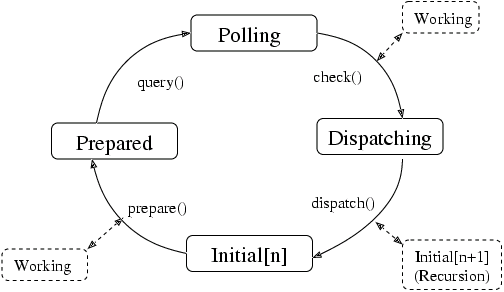
State of a Main Context
MainContext的状态图如下:
Main Contexts
What is GMainContext?
GMainContexts是对事件循环的一个通用实现。一个GMaintext会有多个事件源与之相关,每个事件源都可以被认为是一个拥有回调函数的事件,当事件发生时,回调函数就会执行,也可以认为是一个待检测的文件描述符集。例如,超时可以是一个事件,从套接字上首受到的数据也可以是一个事件。
我们来看看GMainContext的定义。
struct _GMainContext
{
/* The following lock is used for both the list of sources
* and the list of poll records
*/
GMutex mutex;
GCond cond;
GThread *owner;
guint owner_count;
GMainContextFlags flags;
GSList *waiters;
gint ref_count; /* (atomic) */
GHashTable *sources; /* guint -> GSource */
GPtrArray *pending_dispatches;
gint timeout; /* Timeout for current iteration */
guint next_id;
GList *source_lists;
gint in_check_or_prepare;
GPollRec *poll_records;
guint n_poll_records;
GPollFD *cached_poll_array;
guint cached_poll_array_size;
GWakeup *wakeup;
GPollFD wake_up_rec;
/* Flag indicating whether the set of fd's changed during a poll */
gboolean poll_changed;
GPollFunc poll_func;
gint64 time;
gboolean time_is_fresh;
};一个完整的事件循环会经过一下几个步骤,如上图所示:
1. 准备事件源。这个步骤用于确定事件源中是否有准备好立即分发事件的事件源
2.监听事件源。阻塞当前线程,直到事件源中有事件发生。
3.检查哪个源中有事件发生。
4.从事件源中分发回调函数。
对于上述的步骤,我们来看看GLib中的实现。
/**
* g_main_context_iteration:
* @context: (nullable): a #GMainContext (if %NULL, the global-default
* main context will be used)
* @may_block: whether the call may block.
*
* Runs a single iteration for the given main loop. This involves
* checking to see if any event sources are ready to be processed,
* then if no events sources are ready and @may_block is %TRUE, waiting
* for a source to become ready, then dispatching the highest priority
* events sources that are ready. Otherwise, if @may_block is %FALSE
* sources are not waited to become ready, only those highest priority
* events sources will be dispatched (if any), that are ready at this
* given moment without further waiting.
*
* Note that even when @may_block is %TRUE, it is still possible for
* g_main_context_iteration() to return %FALSE, since the wait may
* be interrupted for other reasons than an event source becoming ready.
*
* Returns: %TRUE if events were dispatched.
**/
gboolean
g_main_context_iteration (GMainContext *context, gboolean may_block)
{
gboolean retval;
if (!context)
context = g_main_context_default();
LOCK_CONTEXT (context);
retval = g_main_context_iterate_unlocked (context, may_block, TRUE, G_THREAD_SELF);
UNLOCK_CONTEXT (context);
return retval;
}
/* HOLDS context lock */
static gboolean
g_main_context_iterate_unlocked (GMainContext *context,
gboolean block,
gboolean dispatch,
GThread *self)
{
......
g_main_context_prepare_unlocked (context, &max_priority);
while ((nfds = g_main_context_query_unlocked (
context, max_priority, &timeout, fds,
allocated_nfds)) > allocated_nfds)
{
......
}
......
g_main_context_poll_unlocked (context, timeout, max_priority, fds, nfds);
some_ready = g_main_context_check_unlocked (context, max_priority, fds, nfds);
if (dispatch)
g_main_context_dispatch_unlocked (context);
......
return some_ready;
}GMainContext的核心,其实就是一个poll()循环,prepare函数作为循环的先导,check和disapatch函数作为后续。
static void
g_main_context_poll_unlocked (GMainContext *context,
int timeout,
int priority,
GPollFD *fds,
int n_fds)
{
......
poll_func = context->poll_func;
......
}在用户没有调用函数g_main_context_set_poll_func设置poll_func时,GLib的默认poll_func为g_poll.
void
g_main_context_set_poll_func (GMainContext *context,
GPollFunc func)
{
if (!context)
context = g_main_context_default ();
g_return_if_fail (g_atomic_int_get (&context->ref_count) > 0);
LOCK_CONTEXT (context);
if (func)
context->poll_func = func;
else
context->poll_func = g_poll;
UNLOCK_CONTEXT (context);
}
/**
* g_poll:
* @fds: file descriptors to poll
* @nfds: the number of file descriptors in @fds
* @timeout: amount of time to wait, in milliseconds, or -1 to wait forever
*
* Polls @fds, as with the poll() system call, but portably. (On
* systems that don't have poll(), it is emulated using select().)
* This is used internally by #GMainContext, but it can be called
* directly if you need to block until a file descriptor is ready, but
* don't want to run the full main loop.
*
* Each element of @fds is a #GPollFD describing a single file
* descriptor to poll. The @fd field indicates the file descriptor,
* and the @events field indicates the events to poll for. On return,
* the @revents fields will be filled with the events that actually
* occurred.
*
* On POSIX systems, the file descriptors in @fds can be any sort of
* file descriptor, but the situation is much more complicated on
* Windows. If you need to use g_poll() in code that has to run on
* Windows, the easiest solution is to construct all of your
* #GPollFDs with g_io_channel_win32_make_pollfd().
*
* Returns: the number of entries in @fds whose @revents fields
* were filled in, or 0 if the operation timed out, or -1 on error or
* if the call was interrupted.
*
* Since: 2.20
**/
gint
g_poll (GPollFD *fds,
guint nfds,
gint timeout)
{
return poll ((struct pollfd *)fds, nfds, timeout);
}