文章目录
- 七、进程间通信
- 1. 进程间通信分类
- 管道
- 未完待续
七、进程间通信
1. 进程间通信分类
管道
管道的四种情况:
①管道内部没有数据,并且具有写端的进程没有关闭写端,读端就要阻塞等待,知道管道pipe内部有数据。
②管道内部被写满,并且具有读端的继承没有关闭读端,写端写满管道pipe后,就需要阻塞等待,直到管道清空。
③对于写端而言:关闭了写端管道,读端会将管道pipe中的数据读完,最后会读到返回值0,表示读取完毕。
④对于读端而言:关闭了读端管道,操作系统会直接终止具有写端的进程,通过十三号信号 SIGPIPE 杀掉进程。
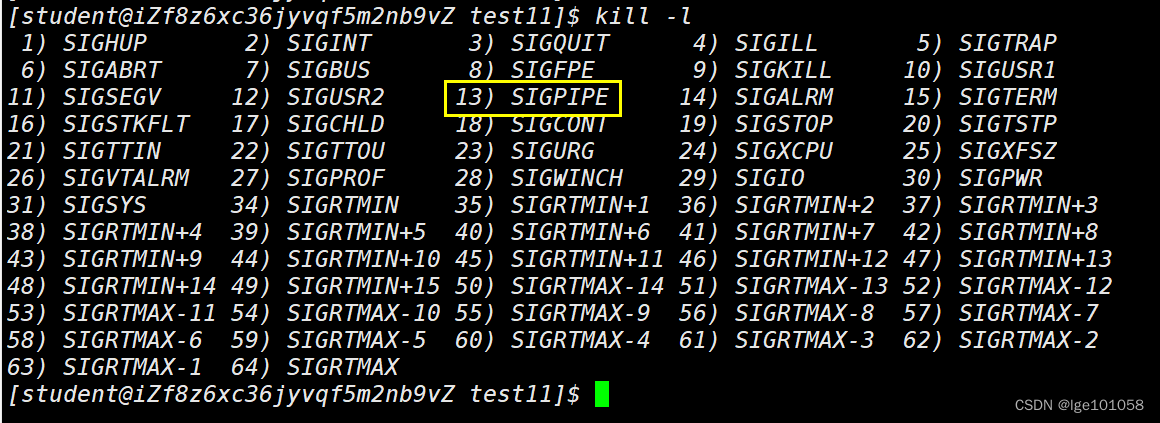
管道的五种特性:
①自带同步机制
②通过血缘关系进程进行通信,常见为父子进程
③pipe是面向字节流的
④父子退出,管道自动释放,文件的生命周期是随进程的
⑤管道只能单向通信
我们曾经学的命令行管道 | 本质上就是pipe。
接下来我们根据我们所学的管道知识来实现一个 进程池 。
Makefile:
processpool:processpool.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11 -g
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f processpool
任务文件 task.hpp:
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
// 函数指针类型
typedef void (*work_t)(int);
typedef void (*task_t)(int, pid_t);
void PrintLog(int fd, pid_t pid)
{
cout << "sub process: " << pid << ", fd : " << fd << ", task is : print log task\n" << endl;
}
void ReloadConf(int fd, pid_t pid)
{
cout << "sub process: " << pid << ", fd : " << fd << ", task is : reload conf task\n" << endl;
}
void ConnectMysql(int fd, pid_t pid)
{
cout << "sub process: " << pid << ", fd : " << fd << ", task is : connect mysql task\n" << endl;
}
// 任务列表
task_t tasks[3] = {PrintLog, ReloadConf, ConnectMysql};
// 随机选择一个任务
uint32_t NextTask()
{
return rand() % 3;
}
// 执行任务
void worker(int fd)
{
while (true)
{
uint32_t task_id = 0;
ssize_t n = read(0, &task_id, sizeof(task_id));
if (n == sizeof(task_id))
{
if (task_id >= 3) continue;
tasks[task_id](fd, getpid());
}
else if (n == 0)
{
cout << "sub process: " << getpid() << " exit" << endl;
break;
}
}
}
进程池主逻辑 processpool.cc:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <vector>
#include <ctime>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include "task.hpp"
using namespace std;
// 枚举错误类型
enum
{
UsageError = 1,
ArgError,
PipeError
};
// 打印使用说明
void Usage(const std::string &proc)
{
cout << "Usage: " << proc << " number of processes" << endl;
}
// 将信道信息封装成一个类
class Channel
{
public:
Channel(int wfd, pid_t sub_id, const string &name)
: _wfd(wfd), _sub_process_id(sub_id), _name(name)
{}
string name()
{
return _name;
}
int wfd()
{
return _wfd;
}
pid_t pid()
{
return _sub_process_id;
}
void Close()
{
close(_wfd);
}
~Channel() {}
private:
// 信道的写端
int _wfd;
// 子进程的id
pid_t _sub_process_id;
// 信道的编号名称
string _name;
};
// 进程池管理类
class ProcessPool
{
public:
ProcessPool(int num_processes)
: _num_processes(num_processes)
{}
// 创建子进程和信道
int CreateProcess(work_t work)
{
for (int i = 0; i < _num_processes; i++)
{
// 创建管道
int pipefd[2]{0};
int n = pipe(pipefd);
if (n < 0)
return PipeError;
// 创建子进程
pid_t id = fork();
if (id == 0)
{
// 这里是子进程, 读端
close(pipefd[1]);
// 这里需要注意的是, 子进程需要从父进程那里接收任务, 所以需要将父进程的写端重定向到标准输入
dup2(pipefd[0], 0);
// 子进程执行任务
work(pipefd[0]);
exit(0);
}
string cname = "Channel-" + to_string(i);
// 这里是父进程, 写端
close(pipefd[0]);
// 放到vector中管理起来
_channels.push_back(Channel{pipefd[1], id, cname});
}
return 0;
}
// 向下一个信道发送任务(目的是负载均衡)
int NextChannel()
{
static int next = 0;
int c = next++;
next %= _num_processes;
return c;
}
// 向index进程执行code任务
void SendTaskCode(int index, uint32_t code)
{
cout << "send code: " << code << " to " << _channels[index].name() << " sub process id: " << _channels[index].pid() << endl;
// 父进程向管道内发送任务,让子进程读取任务
write(_channels[index].wfd(), &code, sizeof(code));
}
// 杀死所有子进程
void KillAll()
{
for (auto& c : _channels)
{
// 父进程关闭写端,子进程读端读到0会自动结束进程
c.Close();
cout << c.name() << " close done," << " sub process id: " << c.pid() << endl;
}
}
// 等待所有子进程退出
void WaitAll()
{
for (auto& c : _channels)
{
pid_t pid = c.pid();
// 回收子进程返回信息
pid_t rid = waitpid(pid, nullptr, 0);
if (rid == pid)
{
cout << c.name() << " sub process id: " << c.pid() << " exit done" << endl;
}
}
}
~ProcessPool() {}
private:
// 进程池的大小
int _num_processes;
// 信道管理容器
vector<Channel> _channels;
};
// 控制进程池
void CtrlProcessPool(ProcessPool* pp, int cnt)
{
while (cnt)
{
// 选择通道
int c = pp->NextChannel();
// 选择任务
uint32_t code = NextTask();
// 发送任务到子进程
pp->SendTaskCode(c, code);
sleep(1);
cnt--;
}
}
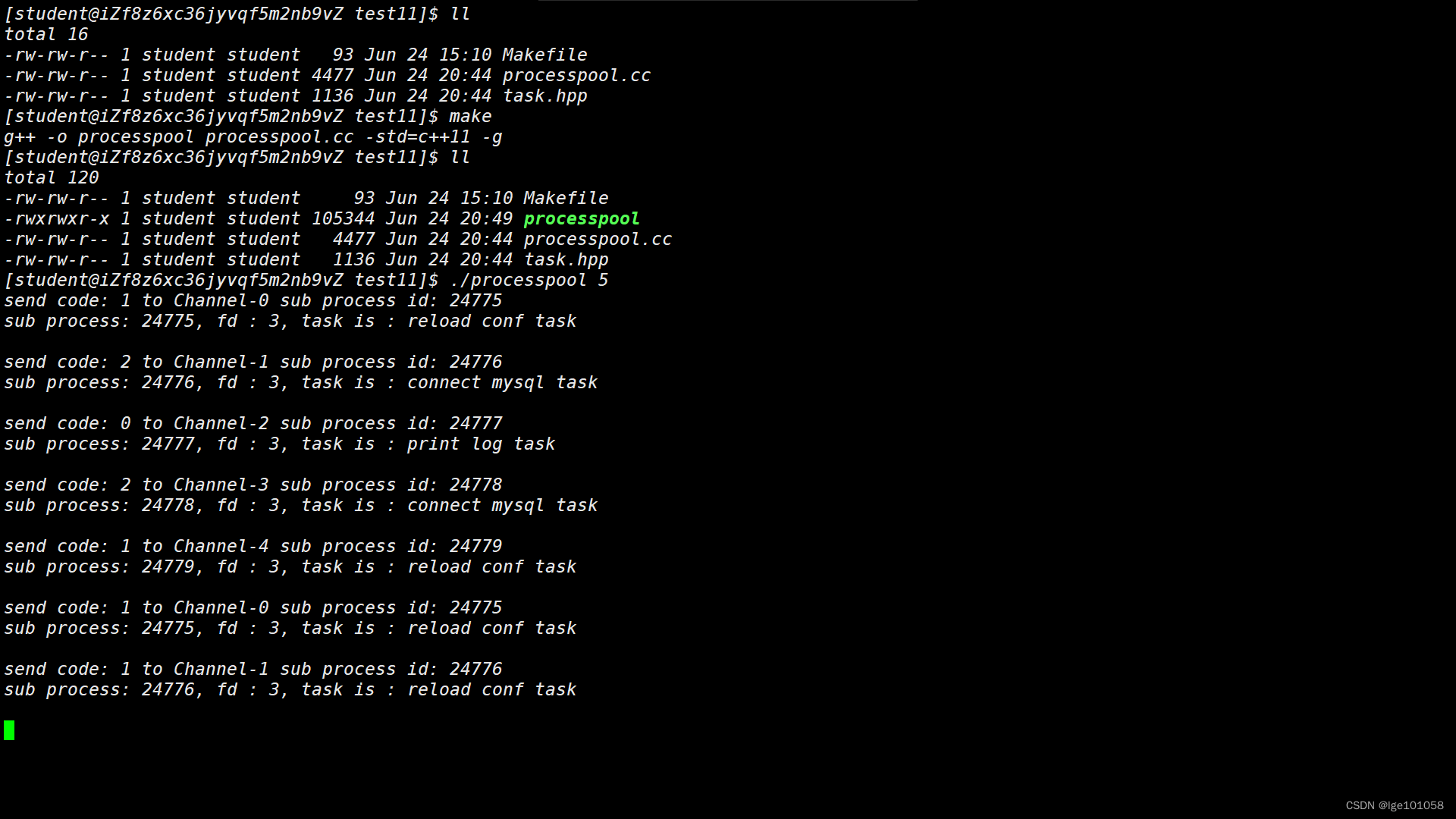
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 2)
{
Usage(argv[0]);
return UsageError;
}
int num_processes = std::stoi(argv[1]);
if (num_processes < 1 || num_processes > 5)
return ArgError;
srand((unsigned)time(nullptr));
// 创建进程池对象
ProcessPool* pp = new ProcessPool(num_processes);
// 创建子进程和信道
pp->CreateProcess(worker);
// 控制子进程执行指定数量的任务
CtrlProcessPool(pp, 10);
// 让所有的子进程退出
pp->KillAll();
// 回收子进程资源
pp->WaitAll();
return 0;
}





![适用于 Windows 11 的 5 大数据恢复软件 [免费和付费]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/7d514dfaf1bb7c2c5d07e90c2167093f.jpeg)