文章目录
- C++001-对比编程语言C++和python
- 编程语言发展史
- 计算机 ENIAC
- 机器语言:
- 汇编语言:
- 高级语言:
- 机器汇编高级语言对比
- C语言与汇编
- 不同高级语言的应用场景
- C++和python语法对比
- Print Hello World
- Print Hello 10 times
- Create a procedure
- Check if list contains a value
- Return two values
- Join a list of strings
- Depth-first traversal in a graph
- Read one line from the standard input
- C++和python案例对比
- 在一个文件中找到给定单词出现的位置并统计出现次数。
- 统计文本中每个单词出现的频率
- python版本
- C++版本
C++001-对比编程语言C++和python
编程语言发展史
计算机 ENIAC
计算机是一种电器, 所以计算机只能识别两种状态, 一种是通电一种是断电。 最初ENIAC的程序是由很多开关和连接电线来完成的。但是这样导致改动一次程序要花很长时间(需要人工重新设置很多开关的状态和连接线)

机器语言:
最初的计算机所使用的是由“0”和“1”组成的二进制数,二进制是计算机的语言的基础,而这种只有计算机能懂的二进制语言被我们称为机器语言。
机器语言直接对计算机硬件进行操作,所以在特定型号的计算机上面,运算效率很高的。
机器语言需要用0、1组成的指令序列交由计算机执行,不容易理解,机器语言的使用与普及较为困难。同时机器语言是针对硬件的操作,不同的平台上,程序缺乏移植能力,从而时间成本,人力成本十分昂贵。
机器语言代码:
10111000 00000001 00000000 00000101 00000001 00000000
汇编语言:
助记符:在加法运算的本地代码中加上 add(addition的缩写)等这些缩写称为助记符
汇编语言:使用助记符的编程语言称为汇编语言
汇编器:把汇编源代码转换成本地代码的程序叫作汇编器
汇编:汇编器转换的过程称之为汇编
20世纪50年代初期在机器语言的基础上汇编语言诞生了。
汇编语言用一些简洁的英文字母、 符号串来替代一个特定的指令的二进制串。使用了大量的助记符来代替二进制指令,方便我们人去编写代码。
汇编语言保持了机器语言的优点,具有直接和简捷的特点,可有效地访问、控制计算机的各种硬件设备。;虽然对于机器语言来说这已经很创新了。
但由于是直接控制硬件,且简单的任务也需要很多汇编语言语句,同时,编语言同样也是直接对硬件进行操作,这样依然局限了它的移植性。

汇编语言代码
MOV AX, 1 ADD AX, 1
高级语言:
面向过程语言设计的代表有:C语言,Fortran等一系列语言,而面向对象语言设计的代表则为:java, c++,Python等。
1967年BCPL(Basic Combined Programming Language)由剑桥大学的Matin Richards在同样由剑桥大学开发的CPL语言上改进而来。BCPL最早被用做牛津大学的OS6操作系统上面的开发工具。
1969年前后B语言:1969年前后美国贝尔实验室的电脑科学家肯尼斯·蓝·汤普森(Kenneth Lane Thompson)在丹尼斯·里奇(Dennis MacAlistair Ritchie)的支持下设计出B语言, B语言是贝尔实验室开发的一种通用的程序设计语言,用于书写UNIX。这个名字取自BCPL中的第一个字母。但B语言使用的时间更短。
1972年C语言:1972年同样是贝尔实验室的丹尼斯·里奇 (Dennis Ritchie) 将B语言进一步改进,并且取了BCPL中的第二个字母将其命名为C语言。C语言,对B取长补短,并用之改写了原来用汇编编写的UNIX, (即UNIX第5版),但仅在贝尔实验室使用。C语言具有运算符丰富;数据类型丰富;允许直接访问物理地址,对硬件进行操作;可移植性好等优点。
但C语言在数据的封装性上缺点使得C在数据的安全性上有很大隐患;并且C语言的语法限制不太严格,对变量的类型约束不严格,影响程序的安全性,对数组下标越界不作检查等。
1979年C++:1979年由本贾尼·斯特劳斯特卢普在AT&T贝尔工作室研发了一款叫C++的语言,它是由C语言扩展升级而产生。C++能允许调整应用性能以及影响所有计算机性能,虽然C++相对来说学习难度很大,但是如果我们可以流畅使用的话,会远远超过其他的程序员。
1990 年Python:Python由荷兰数学和计算机科学研究学会的吉多·范罗苏姆 于1990 年代初设计,作为一门叫做ABC语言的替代品。Python开发速度是快,比如Java100行代码python20行就搞定了。但是作为解释型的语言来说,比编译型语言的速度慢很多。
1995年Java:1995年5月23日,Sun Microsystems公司推出Java程序设计语言和Java平台。Java是一门面向对象的编程语言,不仅吸收了C++语言的各种优点,还摒弃了C++里难以理解的多继承、指针等概念,因此Java语言具有功能强大和简单易用两个特征。java程序可独立于特定的硬件基础设施运行,即是可以在任何机器上运行(安装对应的JVM),这样可减少额外的维护成本。但是由于java程序编译成字节码后需要解释成机器码,在JVM解释的过程中需要额外的抽象动作以及消耗更多的内存。
机器汇编高级语言对比

C语言与汇编
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39966065/article/details/104206680
C语言:
int AddNum(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
void MyFunc()
{
int c;
c = AddNum(123, 456);
}
汇编语言:
_TEXT segment dword public use32 'CODE'
_TEXT ends
_DATA segment dword public use32 'DATA'
_DATA ends
_BSS segment dword public use32 'BSS'
_BSS ends
DGROUP group _BSS,_DATA
_TEXT segment dword public use32 'CODE'
_AddNum proc near
;
; int AddNum(int a, int b)
;
push ebp
mov ebp,esp
;
; {
; return a + b;
;
mov eax,dword ptr [ebp+8]
add eax,dword ptr [ebp+12]
;
; }
;
pop ebp
ret
_AddNum endp
_MyFunc proc near
;
; void MyFunc()
;
push ebp
mov ebp,esp
;
; {
; int c;
; c = AddNum(123, 456);
;
push 456
push 123
call _AddNum
add esp,8
;
; }
;
pop ebp
ret
_MyFunc endp
_TEXT ends
end

不同高级语言的应用场景
C语言的应用:写操作系统、linux以及windows等等常见的操作系统的内核和驱动;
C++的应用:常用的软件几乎都是C++写的。可以做游戏服务器、网络攻防、windows企业项目方向,大型3D游戏;
C#的应用:网站、这桌面应用程序、后端接口、Unity等框架等;
Python的应用:领域很多,算法相对比较多。核心的就业方向是web以及数据挖掘、机器学习方向;
Java的应用:安卓应用开发、视频游戏开发、桌面GUI、软件开发等;

C++和python语法对比
Print Hello World
python代码
print("Hello World")
C++代码
std::cout << "Hello World" << std::endl;
Print Hello 10 times
python代码
for _ in range(10):
print("Hello")
# print("Hello\n"*10)
C++代码
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
cout << "Hello\n";
Create a procedure
python代码
def finish(name):
print(f'My job here is done. Goodbye {name}')
C++代码
void finish(char* name){
cout << "My job here is done. Goodbye " << name << "\n";
}
Check if list contains a value
python代码
x in list
C++代码
bool Contains(const std::vector<int> &list, int x)
{
return std::find(list.begin(), list.end(), x) != list.end();
}
Return two values
Implement a function search which looks for item x in a 2D matrix m.
Return indices i, j of the matching cell.
Think of the most idiomatic way in the language to return the two values at the same time.
python代码
def search(m, x):
for idx, item in enumerate(m):
if x in item:
return idx, item.index(x)
C++代码
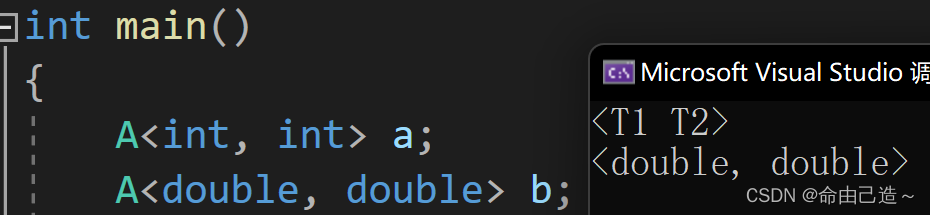
template<typename T, size_t len_x, size_t len_y>
std::pair<size_t, size_t> search (const T (&m)[len_x][len_y], const T &x) {
for(size_t pos_x = 0; pos_x < len_x; ++pos_x) {
for(size_t pos_y = 0; pos_y < len_y; ++pos_y) {
if(m[pos_x][pos_y] == x) {
return std::pair<size_t, size_t>(pos_x, pos_y);
}
}
}
// return an invalid value if not found
return std::pair<size_t, size_t>(len_x, len_y);
}
Join a list of strings
Concatenate elements of string list x joined by the separator ", " to create a single string y.
python代码
y = ', '.join(x)
C++代码
std::vector<std::string> x;
std::string y;
const char* const delim = ", ";
switch (x.size())
{
case 0: y = ""; break;
case 1: y = x[0]; break;
default:
std::ostringstream os;
std::copy(x.begin(), x.end() - 1,
std::ostream_iterator<std::string>(os, delim));
os << *x.rbegin();
y = os.str();
}
Depth-first traversal in a graph
Call th function f on every vertex accessible from the vertex v, in depth-first prefix order
python代码
def depth_first(start, f):
seen = set()
stack = [start]
while stack:
vertex = stack.pop()
f(vertex)
seen.add(vertex)
stack.extend(
v for v in vertex.adjacent if v not in seen
)
C++代码
void dfs(Node& root, std::function<void(Node*)> f) {
std::stack<Node*> queue;
queue.push(&root);
std::unordered_set<const Node*> visited;
while (!queue.empty()) {
Node* const node = queue.top();
queue.pop();
f(node);
visited.insert(node);
for (Node* const neighbor : node->neighbors) {
if (visited.find(neighbor) == visited.end()) {
queue.push(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
Read one line from the standard input
python代码
line = sys.stdin.readline()
C++代码
int main() {
for (std::string line; std::getline(std::cin, line);) {
std::cout << line << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
C++和python案例对比
在一个文件中找到给定单词出现的位置并统计出现次数。
python实现
if __name__=='__main__':
file_name = input('Input the file you want to find in:')
try:
in_file = open(file_name,'r')
lines = in_file.readlines()
tag_tok = ''
while tag_tok.upper() != 'Q':
tag_tok = input('Input the Word you want to find(Q for quit):')
if tag_tok.upper() != 'Q':
count = 0
line_no = 0
for line in lines:
line_no = line_no + 1
inline_cnt = line.count(tag_tok)
count = count + inline_cnt
if inline_cnt > 0:
print('Find %s %d time(s) in line :%d'%(tag_tok,inline_cnt,line_no))
print(line)
print('---------------------------------')
print('Total fount %s %d time(s)'%(tag_tok, count))
except:
print("Can't open file %s"%(file_name))
输出为:
Input the file you want to find in:requirements.txt
Input the Word you want to find(Q for quit):ali
Find ali 1 time(s) in line :4
python-alipay-sdk # >= 3.0.4,
---------------------------------
Total fount ali 1 time(s)
Input the Word you want to find(Q for quit):a
Find a 1 time(s) in line :1
cryptography==38.0.4
---------------------------------
Total fount a 1 time(s)
Find a 5 time(s) in line :2
Django # >= 3.2, # Replace "X.Y" as appropriate
---------------------------------
Total fount a 6 time(s)
Find a 2 time(s) in line :4
python-alipay-sdk # >= 3.0.4,
---------------------------------
Total fount a 8 time(s)
Find a 2 time(s) in line :5
django-cors-headers # >= 3.11.0,
---------------------------------
Total fount a 10 time(s)
Find a 1 time(s) in line :6
django-crispy-forms # >= 1.14.0,
---------------------------------
Total fount a 11 time(s)
Find a 1 time(s) in line :7
django-filter # >= 21.1,
---------------------------------
Total fount a 12 time(s)
Find a 1 time(s) in line :8
coreapi # >= 2.3.3,
---------------------------------
Total fount a 13 time(s)
Find a 2 time(s) in line :9
djangorestframework # >= 3.13.1,
---------------------------------
Total fount a 15 time(s)
Find a 1 time(s) in line :11
django-simpleui
---------------------------------
Total fount a 16 time(s)
Find a 1 time(s) in line :12
#cryptography==38.0.4
---------------------------------
Total fount a 17 time(s)
Input the Word you want to find(Q for quit):Q
统计文本中每个单词出现的频率
python版本
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/Ethereal_tl/article/details/127943817
import string
def word_frequency(txt):
"""接收去除标点、符号的字符串,统计并返回每个单词出现的次数
返回值为字典类型,单词为键,对应出现的次数为值"""
word_list = txt.split()
d = {} # 定义一个空字典
for word in word_list:
if word in d:
d[word] += 1
else:
d[word] = 1
return d
def top_ten_words(frequency, cnt):
"""接收词频字典,输出出现次数最多的cnt个单词及其出现次数"""
dic=sorted(frequency.items(),key=lambda x:x[1],reverse=True)
for i in range(cnt):
print(dic[i][0],dic[i][1])
def read_file(file):
"""接收文件名为参数,将文件中的内容读为字符串,
只保留文件中的英文字母和西文符号,过滤掉中文
所有字符转为小写,
将其中所有标点、符号替换为空格,返回字符串"""
with open(file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as novel:
txt = novel.read()
english_only_txt = ''.join(x for x in txt if ord(x) < 256)
english_only_txt = english_only_txt.lower()
for character in string.punctuation:
english_only_txt = english_only_txt.replace(character, ' ')
return english_only_txt
if __name__ == '__main__':
filename = 'requirements.txt' # 文件名
content = read_file(filename) # 调用函数返回字典类型的数据
frequency_result = word_frequency(content) # 统计词频
n = int(input("请输入返回的top n值"))
top_ten_words(frequency_result, n)
C++版本
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
#include<iterator>
#include<cctype>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
unordered_map<string, int> strMap; //保存的结果
/***从字符串流中依次读入单词记录出现频率***/
void countWord(stringstream &ss)
{
//依次读入单词
string strTmp;
while (ss >> strTmp)
{
unordered_map<string, int>::iterator it = strMap.find(strTmp);
if (it == strMap.end())
{
strMap.insert(unordered_map<string, int>::value_type(strTmp, 1));
}
else
strMap[strTmp]++;
}
}
int main()
{
//读入文档
string strFile, tmp;
fstream file("E:\\vscode\\happy-shop-demo-bak\\requirements.txt");
while(getline(file, tmp)) //!file.eof()
{
strFile.append(tmp);
tmp.clear();
}
//去除符号
for (int i = 0; i<strFile.length(); i++)
{
if (ispunct(strFile[i]))
strFile[i] = ' ';
}
//统计字符
stringstream ss(strFile);
//stringstream ss("django");
countWord(ss);
//打印结果
unordered_map<string,int>::const_iterator it;
for (it = strMap.begin(); it != strMap.end(); ++it)
cout << it->first << "=" << it->second << endl;
cout << endl;
return 0;
}



![为什么 Go 不支持 []T 转换为 []interface](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/53fc9d125f199fe3ddd1cf862fce5cd0.png)