算法拾遗二十五之暴力递归到动态规划三
- 最长回文子串
- 返回象棋从一个位置到另一个位置的方法有多少种
- 返回咖啡机从开始到干净的最短时间
最长回文子串
测试链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-palindromic-subsequence/

子序列:是可以不连续的
子串:必须是连续的
思路一:
给定一个串,并生成一个逆序串,这个逆序串和原串的最长公共子序列就是最长回文子序列。
str1(“ab12c3d43efg21”)
str2逆序串(12gfe34d3c21ba)
最长公共子序列为:1234321就是原串的最长回文子序列
参见上一节的解法(样本对应模型:特别在意考虑样本的结尾如何)
思路二:
定义一个函数f(str,L,R),返回在str的L到R上最长回文子序列是多长
(范围尝试模型:特别在意考虑样本的开头和结尾共同结合的可能性如何)
此种暴力递归超时:
public static int longestPalindromeSubseq3(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
return f3(s.toCharArray(), 0, s.length() - 1);
}
//str[L...R]最长回文子序列长度返回
public static int f3(char[] str, int L, int R) {
//讨论basecase,只有一个字符的情况,只有它自己返回1
if (L == R) {
return 1;
}
//讨论剩余两个字符的情况
if (L == R - 1) {
return str[L] == str[R] ? 2 : 1;
}
//普遍情况(讨论最长回文可能性)
//1、情况一回文既不以L开头也不以R结尾
int p1 = f3(str, L + 1, R - 1);
//2、以L开头不以R结尾
int p2 = f3(str, L, R - 1);
//3、不以L开头以R结尾
int p3 = f3(str, L + 1, R);
//4、以L开头并且以R结尾[L和R字符包含在回文里面所以加2]
int p4 = str[L] == str[R] ? (2 + f3(str, L + 1, R - 1)) : 0;
return Math.max(Math.max(p1, p2), Math.max(p3, p4));
}
下面改dp:
给定如下字符,建立如下图表格
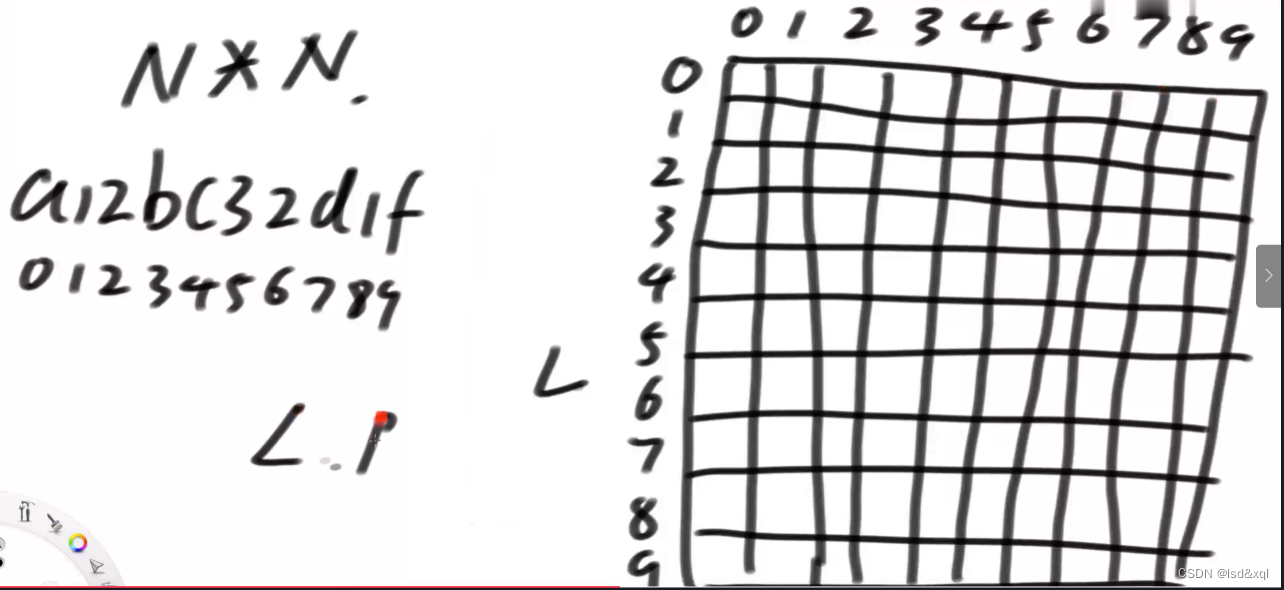
L>R是没用的,正常的范围不会出现L>R的情况
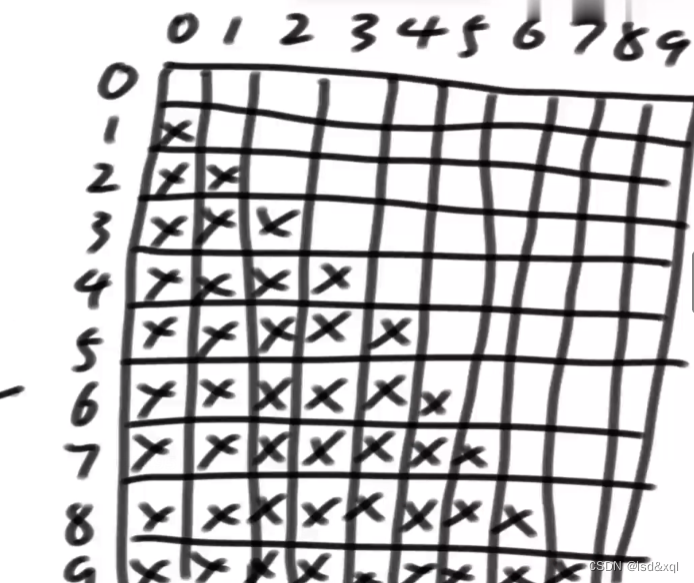
先填入basecase,L==R的时候都是1
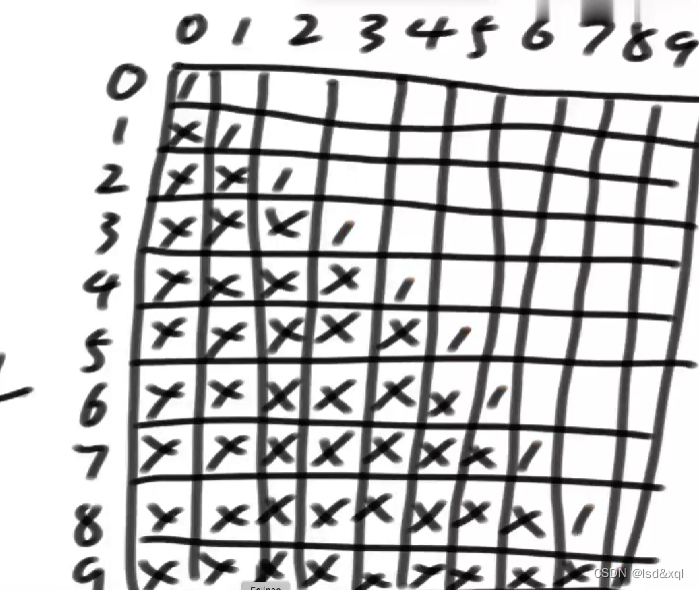
L = R-1的时候,相等就是2,不等就是1
public static int longestPalindromeSubseq4(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
char[] str = s.toCharArray();
int N = str.length;
//L变化范围 0-N-1
//R变化范围 0-N-1;
int[][] dp = new int[N][N];
dp[N - 1][N - 1] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
//两条对角线填完
dp[i][i] = 1;
dp[i][i + 1] = str[i] == str[i + 1] ? 2 : 1;
}
for (int L = N - 3; L >= 0; L--) {
//因为来到第L行,(L,L)及(L,L+1)位置都是被填好了的
//所以R来到L+2位置
for (int R = L + 2; R < N; R++) {
int p1 = dp[L + 1][R - 1];
int p2 = dp[L][R - 1];
int p3 = dp[L + 1][R];
int p4 = str[L] == str[R] ? (2 + dp[L + 1][R - 1]) : 0;
dp[L][R] = Math.max(Math.max(p1, p2), Math.max(p3, p4));
}
}
return dp[0][N - 1];
}
我们可以把p1给省掉:
str[3…15]范围上的最长回文子序列可能性:
1)str[4…14]范围上的最长回文子序列 (左下)
2)str[3…14]范围上的最长回文子序列 (左)
3)str[4…15]范围上的最长回文子序列 (下)
4)在str[3] == str[15]的情况下,2 + str[4…14]
注意看1)范围是[4…14]
注意看2)范围是[3…14]
注意看3)范围是[4…15]
1)范围 在 2)范围 内,发现了吗?
1)范围 在 3)范围 内,发现了吗?
一个内部小范围的回文子序列长度,可能比包含它的大范围的回文子序列长度,更长?
不可能。
动态规划都一定可以用递归改出来,但不是所有递归都能改动态规划的
public static int longestPalindromeSubseq4(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
char[] str = s.toCharArray();
int N = str.length;
//L变化范围 0-N-1
//R变化范围 0-N-1;
int[][] dp = new int[N][N];
dp[N - 1][N - 1] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
//两条对角线填完
dp[i][i] = 1;
dp[i][i + 1] = str[i] == str[i + 1] ? 2 : 1;
}
for (int L = N - 3; L >= 0; L--) {
//因为来到第L行,(L,L)及(L,L+1)位置都是被填好了的
//所以R来到L+2位置
for (int R = L + 2; R < N; R++) {
dp[L][R] = Math.max(dp[L][R-1],dp[L+1][R]);
if(str[L] == str[R]) {
dp[L][R] = Math.max(dp[L][R],2+dp[L+1][R+1]);
}
}
}
return dp[0][N - 1];
}
返回象棋从一个位置到另一个位置的方法有多少种

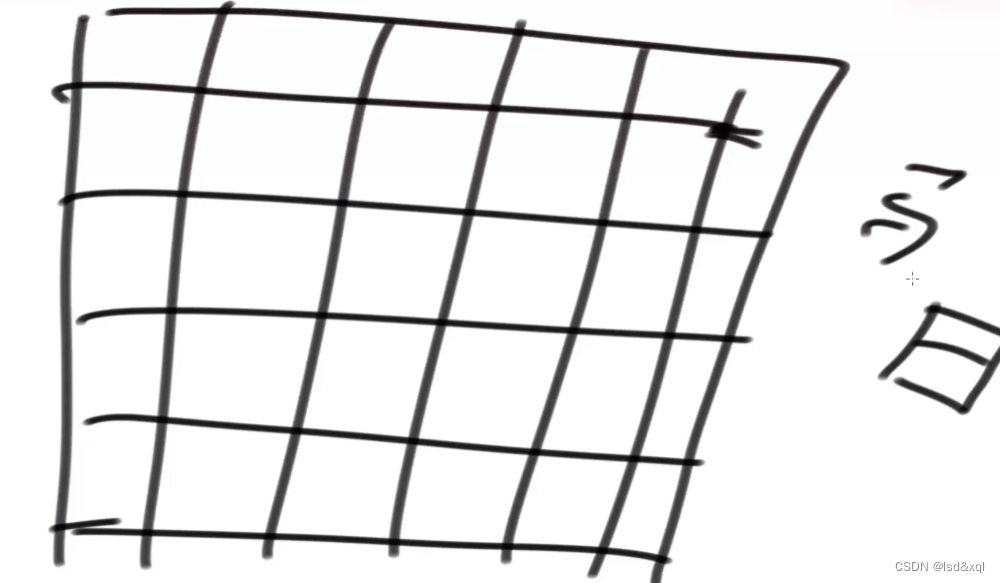
马走日字格,并且永远从(0,0)位置出发,且棋盘大小为9*10,然后到达a,b位置,必须走k步。
一个🐎在(x,y)位置存在八种跳法:
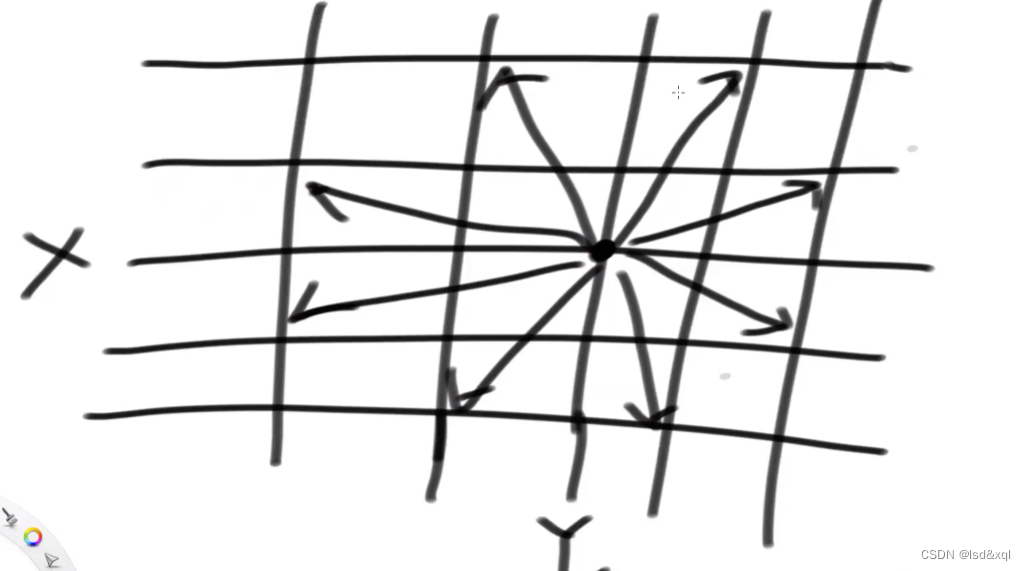
暴力递归:复杂度O(8的k次方)
//当前来到的位置是x,y
//还剩下rest步需要跳
//跳完rest步,正好跳到a,b的方法数是多少?
//可变参数为x,y,rest【三维动态规划,设计三个可变参数】
public static int jump1(int a,int b,int k) {
return process1(0,0,k,a,b);
}
public static int process1(int x,int y,int rest,int a,int b) {
//棋盘越界处理(无效值) 10*9
if(x<0 || x>9 || y <0 || y> 8) {
return 0;
}
if(rest == 0) {
return (x==a && y == b) ? 1 : 0;
}
//x,y的总数应该是八个方向蹦收集到的返回数的总和
int ways = process1(x+2,y+1,rest-1,a,b);
ways += process1(x+1,y+2,rest-1,a,b);
ways += process1(x-1,y+2,rest-1,a,b);
ways += process1(x-2,y+1,rest-1,a,b);
ways += process1(x-2,y-1,rest-1,a,b);
ways += process1(x-1,y-2,rest-1,a,b);
ways += process1(x+1,y-2,rest-1,a,b);
ways += process1(x+2,y-1,rest-1,a,b);
return ways;
}
动态规划:(复杂度O(k))
public static int dp1(int a, int b, int k) {
//k范围为0-k所以准备k+1个
int[][][] dp = new int[10][9][k + 1];
// if(rest == 0) {
// return (x==a && y == b) ? 1 : 0;
// }
//此basecase能够搞定这个三维数组的第0层
//由暴力递归得到每一层的东西都依赖其下层,而不存在同层依赖
//有了第0层可以推出所有的第一层,有了第一层可以推出所有的第一层,以此类推
//第0层只有x等于a,y等于b的才为1其他都为0
dp[a][b][0] = 1;
for (int rest = 1; rest <= k; rest++) {
for (int x = 0; x < 10; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < 9; y++) {
// 根据如下递归调用推倒
// int ways = process1(x+2,y+1,rest-1,a,b);
// ways += process1(x+1,y+2,rest-1,a,b);
// ways += process1(x-1,y+2,rest-1,a,b);
// ways += process1(x-2,y+1,rest-1,a,b);
// ways += process1(x-2,y-1,rest-1,a,b);
// ways += process1(x-1,y-2,rest-1,a,b);
// ways += process1(x+1,y-2,rest-1,a,b);
// ways += process1(x+2,y-1,rest-1,a,b);
int ways = pick1(dp, x + 2, y + 1, rest - 1);
ways += pick1(dp, x + 1, y + 2, rest - 1);
ways += pick1(dp, x - 1, y + 2, rest - 1);
ways += pick1(dp, x - 2, y + 1, rest - 1);
ways += pick1(dp, x - 2, y - 1, rest - 1);
ways += pick1(dp, x - 1, y - 2, rest - 1);
ways += pick1(dp, x + 1, y - 2, rest - 1);
ways += pick1(dp, x + 2, y - 1, rest - 1);
dp[x][y][rest] = ways;
}
}
}
//主函数调0,0,k
return dp[0][0][k];
}
public static int pick1(int[][][] dp, int x, int y, int rest) {
if (x < 0 || x > 9 || y < 0 || y > 8) {
return 0;
}
return dp[x][y][rest];
}
返回咖啡机从开始到干净的最短时间

纯暴力解法:
// 验证的方法
// 彻底的暴力
// 很慢但是绝对正确
public static int right(int[] arr, int n, int a, int b) {
int[] times = new int[arr.length];
int[] drink = new int[n];
return forceMake(arr, times, 0, drink, n, a, b);
}
// 每个人暴力尝试用每一个咖啡机给自己做咖啡
public static int forceMake(int[] arr, int[] times, int kth, int[] drink, int n, int a, int b) {
if (kth == n) {
int[] drinkSorted = Arrays.copyOf(drink, kth);
Arrays.sort(drinkSorted);
return forceWash(drinkSorted, a, b, 0, 0, 0);
}
int time = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int work = arr[i];
int pre = times[i];
drink[kth] = pre + work;
times[i] = pre + work;
time = Math.min(time, forceMake(arr, times, kth + 1, drink, n, a, b));
drink[kth] = 0;
times[i] = pre;
}
return time;
}
public static int forceWash(int[] drinks, int a, int b, int index, int washLine, int time) {
if (index == drinks.length) {
return time;
}
// 选择一:当前index号咖啡杯,选择用洗咖啡机刷干净
int wash = Math.max(drinks[index], washLine) + a;
int ans1 = forceWash(drinks, a, b, index + 1, wash, Math.max(wash, time));
// 选择二:当前index号咖啡杯,选择自然挥发
int dry = drinks[index] + b;
int ans2 = forceWash(drinks, a, b, index + 1, washLine, Math.max(dry, time));
return Math.min(ans1, ans2);
}
// 以下为贪心+优良暴力
public static class Machine {
//当前时间点
public int timePoint;
//工作时间
public int workTime;
public Machine(int t, int w) {
timePoint = t;
workTime = w;
}
}
public static class MachineComparator implements Comparator<Machine> {
@Override
public int compare(Machine o1, Machine o2) {
return (o1.timePoint + o1.workTime) - (o2.timePoint + o2.workTime);
}
}
// 优良一点的暴力尝试的方法
public static int minTime1(int[] arr, int n, int a, int b) {
PriorityQueue<Machine> heap = new PriorityQueue<Machine>(new MachineComparator());
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
heap.add(new Machine(0, arr[i]));
}
int[] drinks = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Machine cur = heap.poll();
cur.timePoint += cur.workTime;
drinks[i] = cur.timePoint;
heap.add(cur);
}
return bestTime(drinks, a, b, 0, 0);
}
// drinks 所有杯子可以开始洗的时间
// wash 单杯洗干净的时间(串行)
// air 挥发干净的时间(并行)
// free 洗的机器什么时候可用
// drinks[index.....]都变干净,最早的结束时间(返回)
public static int bestTime(int[] drinks, int wash, int air, int index, int free) {
if (index == drinks.length) {
return 0;
}
// index号杯子 决定洗
int selfClean1 = Math.max(drinks[index], free) + wash;
int restClean1 = bestTime(drinks, wash, air, index + 1, selfClean1);
int p1 = Math.max(selfClean1, restClean1);
// index号杯子 决定挥发
int selfClean2 = drinks[index] + air;
int restClean2 = bestTime(drinks, wash, air, index + 1, free);
int p2 = Math.max(selfClean2, restClean2);
return Math.min(p1, p2);
}
改动态规划发现free的变化范围很飘忽不定,这个时候就需要人为去想限制把
这个free估计出来(所有杯子都去洗的时间)
// 贪心+优良尝试改成动态规划
public static int minTime2(int[] arr, int n, int a, int b) {
PriorityQueue<Machine> heap = new PriorityQueue<Machine>(new MachineComparator());
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
heap.add(new Machine(0, arr[i]));
}
int[] drinks = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Machine cur = heap.poll();
cur.timePoint += cur.workTime;
drinks[i] = cur.timePoint;
heap.add(cur);
}
return bestTimeDp(drinks, a, b);
}
public static int bestTimeDp(int[] drinks, int wash, int air) {
int N = drinks.length;
int maxFree = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < drinks.length; i++) {
maxFree = Math.max(maxFree, drinks[i]) + wash;
}
int[][] dp = new int[N + 1][maxFree + 1];
for (int index = N - 1; index >= 0; index--) {
for (int free = 0; free <= maxFree; free++) {
int selfClean1 = Math.max(drinks[index], free) + wash;
if (selfClean1 > maxFree) {
break; // 因为后面的也都不用填了
}
// index号杯子 决定洗
int restClean1 = dp[index + 1][selfClean1];
int p1 = Math.max(selfClean1, restClean1);
// index号杯子 决定挥发
int selfClean2 = drinks[index] + air;
int restClean2 = dp[index + 1][free];
int p2 = Math.max(selfClean2, restClean2);
dp[index][free] = Math.min(p1, p2);
}
}
return dp[0][0];
}
对数器代码:
// for test
public static int[] randomArray(int len, int max) {
int[] arr = new int[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * max) + 1;
}
return arr;
}
// for test
public static void printArray(int[] arr) {
System.out.print("arr : ");
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[j] + ", ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int len = 10;
int max = 10;
int testTime = 10;
System.out.println("测试开始");
for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {
int[] arr = randomArray(len, max);
int n = (int) (Math.random() * 7) + 1;
int a = (int) (Math.random() * 7) + 1;
int b = (int) (Math.random() * 10) + 1;
int ans1 = right(arr, n, a, b);
int ans2 = minTime1(arr, n, a, b);
int ans3 = minTime2(arr, n, a, b);
if (ans1 != ans2 || ans2 != ans3) {
printArray(arr);
System.out.println("n : " + n);
System.out.println("a : " + a);
System.out.println("b : " + b);
System.out.println(ans1 + " , " + ans2 + " , " + ans3);
System.out.println("===============");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("测试结束");
}