LeetCode链表相关解法
- 1.移除链表元素
- [203. 移除链表元素](https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/)
- 不设置头节点
- 设置虚拟头节点
- 2.设计链表
- [707. 设计链表](https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-linked-list/)
- 3.反转链表
- [206. 反转链表](https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/)
- 思路
- 代码
- 4.两两交换链表节点
- [24. 两两交换链表中的节点](https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/)
- 5.删除链表的倒数第N个节点
- [19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点](https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/)
- 思路
- 代码
- 6.链表相交
- [面试题 02.07. 链表相交](https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/)
- 双指针法
- 思路
- 哈希法
- 7.环形链表II
- [142. 环形链表 II](https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/)
- 哈希法
- 双指针法
LeetCode一般提供的链表节点结构如下
public class ListNode {
// 结点的值
int val;
// 下一个结点
ListNode next;
// 节点的构造函数(无参)
public ListNode() {
}
// 节点的构造函数(有一个参数)
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
// 节点的构造函数(有两个参数)
public ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
1.移除链表元素
203. 移除链表元素
不设置头节点
需要先进行删除,保证第一位不是目标元素
然后再进行后面的遍历
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
//处理第一位,注意是while
while(head != null && head.val == val){
head = head.next;
}
if(head == null){
return head;
}
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode current = head.next;
while(current != null){
if(current.val == val){
current = current.next;
pre.next = current;
}else{
current = current.next;
pre = pre.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
设置虚拟头节点
设置一个虚拟头节点,方便操作
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head == null){
return head;
}
//添加一个虚拟头节点
ListNode VirtualHead = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode pred = VirtualHead;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val == val){
cur = cur.next;
pred.next = cur;
}else{
cur = cur.next;
pred = pred.next;
}
}
return VirtualHead.next;
}
}
2.设计链表
707. 设计链表
先找前驱节点
class LinkedNode {
int val;
LinkedNode next;
public LinkedNode(){}
public LinkedNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
class MyLinkedList {
//size存储链表元素的个数
int size;
//虚拟头结点
ListNode head;
//初始化链表
public MyLinkedList() {
size = 0;
head = new ListNode(-1);
}
public int get(int index) {
//如果index非法,返回-1
if (index < 0 || index > size-1) {
return -1;
}
int curIndex = 0;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while(cur != null){
if(curIndex == index){
return cur.val;
}
cur = cur.next;
curIndex++;
}
return -1;
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
addAtIndex(0, val);
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
addAtIndex(size, val);
}
// 在第 index 个节点之前插入一个新节点,例如index为0,那么新插入的节点为链表的新头节点。
// 如果 index 等于链表的长度,则说明是新插入的节点为链表的尾结点
// 如果 index 大于链表的长度,则返回空
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if(index >= size-1){
return;
}
if (index < 0) {
index = 0;
}
//找到要插入节点的前驱
ListNode pre = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);
newNode.next = pre.next;
pre.next = newNode;
size++;
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size-1) {
return;
}
if (index == 0) {
head = head.next;
return;
}
ListNode pre = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index ; i++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
pre.next = pre.next.next;
size--;
}
}
/**
* Your MyLinkedList object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyLinkedList obj = new MyLinkedList();
* int param_1 = obj.get(index);
* obj.addAtHead(val);
* obj.addAtTail(val);
* obj.addAtIndex(index,val);
* obj.deleteAtIndex(index);
*/
3.反转链表
206. 反转链表
思路
利用双指针,将所有的节点的next进行反转
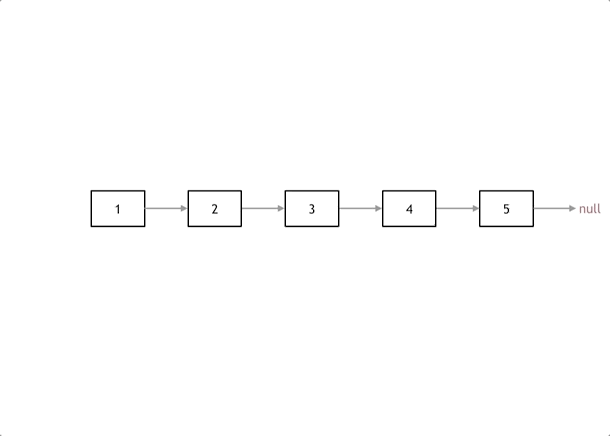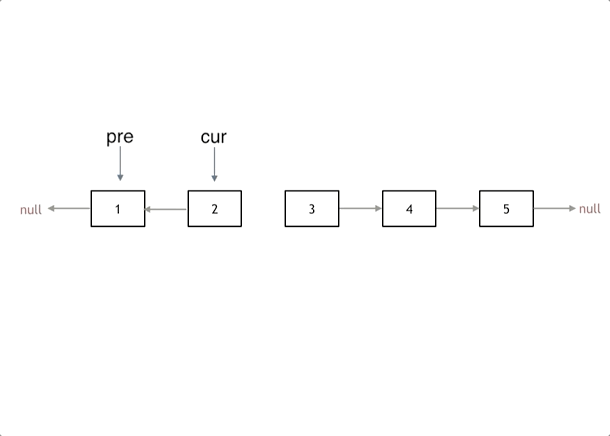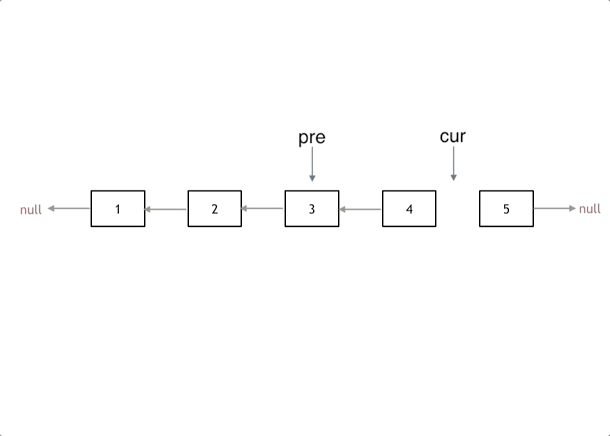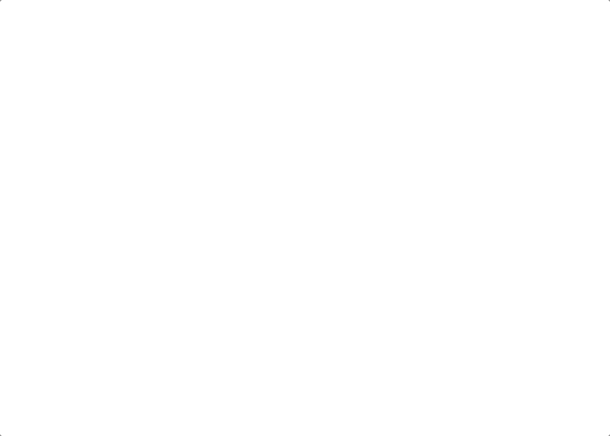
注意点
- 开始的时候pre为null
- 结束条件为cur == null
- 当前节点的next已经被修改了,cur如何到下一个节点? 使用temp临时指针
代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pred = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pred;
pred = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pred;
}
}
4.两两交换链表节点
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
模拟题,A->B->C->D顺序如下
- 后一个节点B的指针指向前一个节点A
- A指向B的下一个节点C
- 之前的节点连接到B
注意点如下:
- 开始时进行判断.如果节点个数小于2直接返回
- 初始化时,pred和cur都为head,在进入循环后cur再为pred.next,避免空指针
- 结束条件为剩下的节点不足两个
- B节点指向A后,不知道C在哪了,所以需要一个临时指针temp指向C
- B节点到了链表头部后,需要一个连接指针link来把头节点来指向B
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode virtualHead = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode pred = head;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode link = virtualHead; //记录之前连接到哪个节点了
while(pred != null && pred.next != null){
//在这里才真正赋值,因为pred!=null可用保证不会空指针
cur = pred.next;
//更改连线
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pred;
pred.next = temp;
link.next = cur;
//移动
link = pred;
pred = pred.next;
}
return virtualHead.next;
}
}
5.删除链表的倒数第N个节点
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
思路
删除一个节点需要知道这个节点的上一个节点
我们可用定义两个快慢指针
- 快指针先走N步
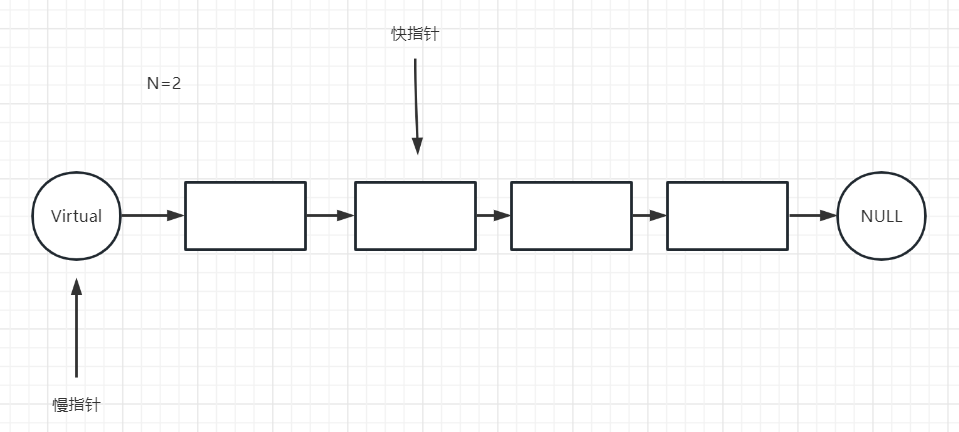
- 然后快慢指针一起走,直到快指针的下一个为null
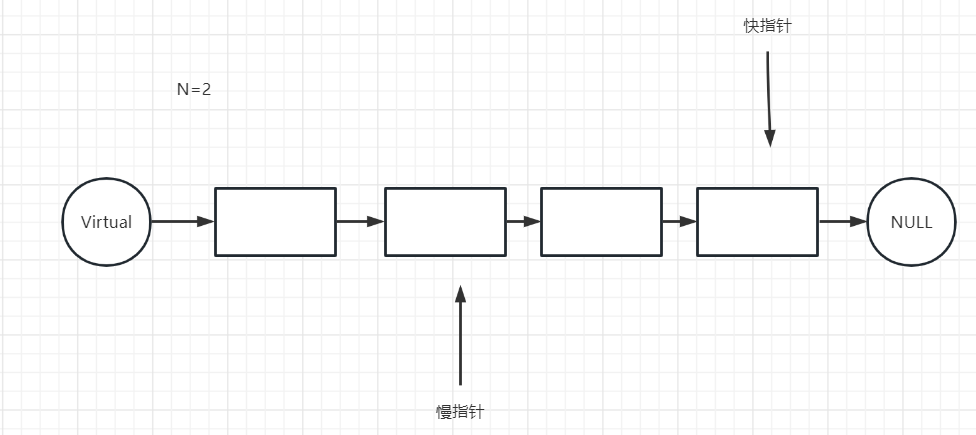
- 这时候慢指针删除下一个节点
代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode virtualHead = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode fast = virtualHead;
ListNode slow = virtualHead;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
fast = fast.next;
}
while(fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//删除节点
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return virtualHead.next;
}
}
6.链表相交
面试题 02.07. 链表相交
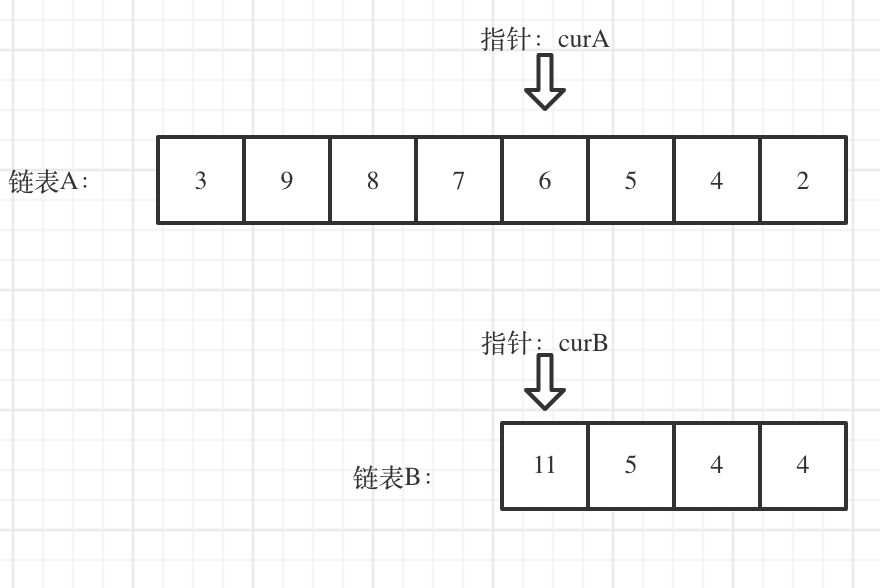
双指针法
思路
-
先各自获得链表的长度A B
-
假如A长,A链表从A-B的地方开始和B一起遍历
-
依次比较指针是否相等
计算一下两个链表的长度,让长链表先走,等两个链表长度一样的时候再一起走,结点相等直接返回,没有相交返回null
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
//获取长度
while(curA != null){
lenA++;
curA = curA.next;
}
while(curB != null){
lenB++;
curB = curB.next;
}
//让长的为headA,短的为headB
if(lenA < lenB){
int temp = lenA;
lenA = lenB;
lenB = temp;
ListNode tempNode = headA;
headA = headB;
headB = tempNode;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
int gap = lenA - lenB;
//长的走到和短的相同的地方
for(int i = 0; i < gap; i++){
curA = curA.next;
}
while(curA != null){
if(curA == curB){
return curA;
}
curA = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
哈希法
先把其中一个链表的节点都放入HashSet,然后放入另一个链表的节点,如果有包含的话,就说明是同个节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
HashSet set = new HashSet();
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
while(curA != null){
set.add(curA);
curA = curA.next;
}
while(curB != null){
if(set.contains(curB)){
return curB;
}
curB = curB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
7.环形链表II
142. 环形链表 II
哈希法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
HashSet set = new HashSet();
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(set.contains(cur)){
return cur;
}
set.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
}
双指针法
https://programmercarl.com/0142.%E7%8E%AF%E5%BD%A2%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8II.html#_142-%E7%8E%AF%E5%BD%A2%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8ii






![[Android Studio]Android Studio Logcat日志样式设置](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/24b696d76d374a9992017e1625389592.gif)