目录
map::operator[]
[ ]的实现
multimap
习题 前K个高频单词
两个数组的交集
底层结构
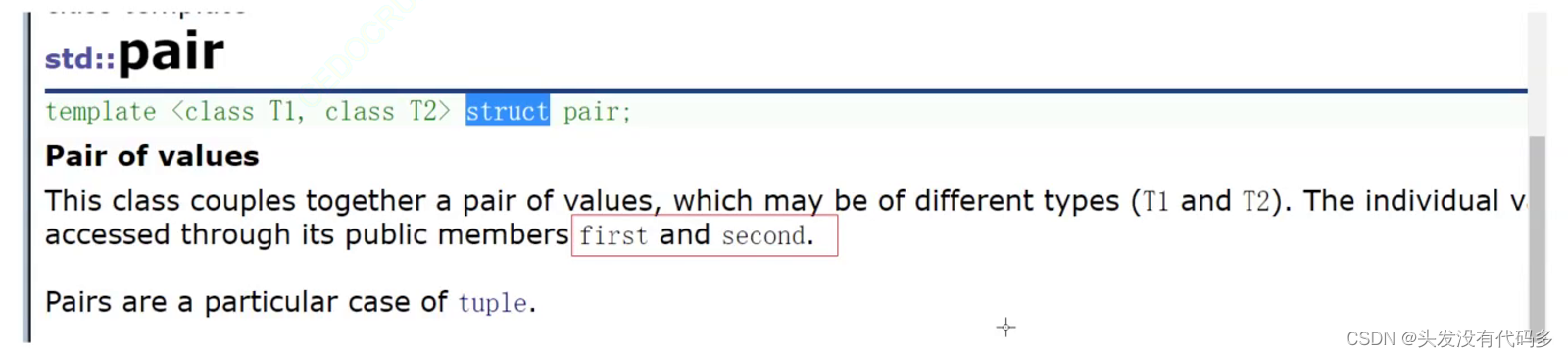
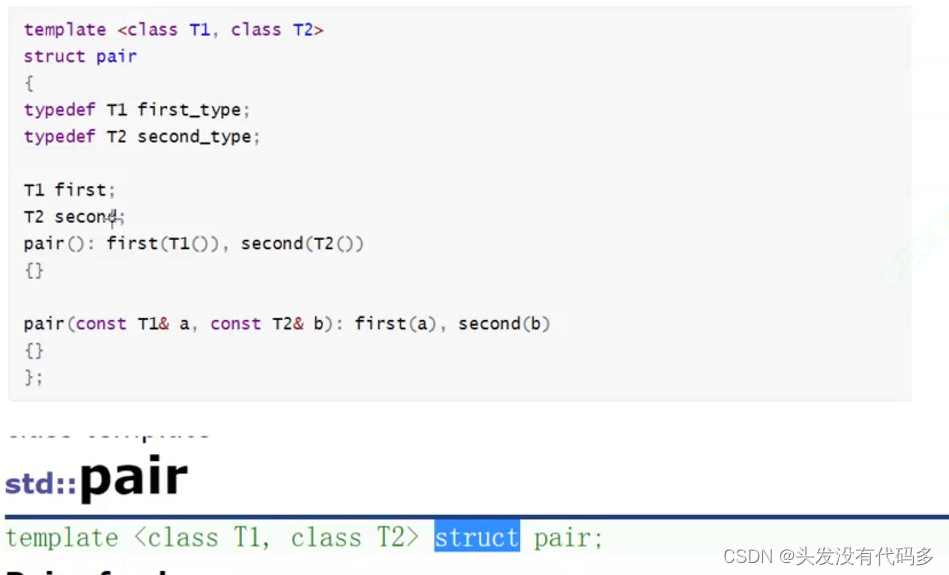
pair有俩个成员一个是first,一个是second
由于pair有俩个模板参数,第一个是first,一个是second
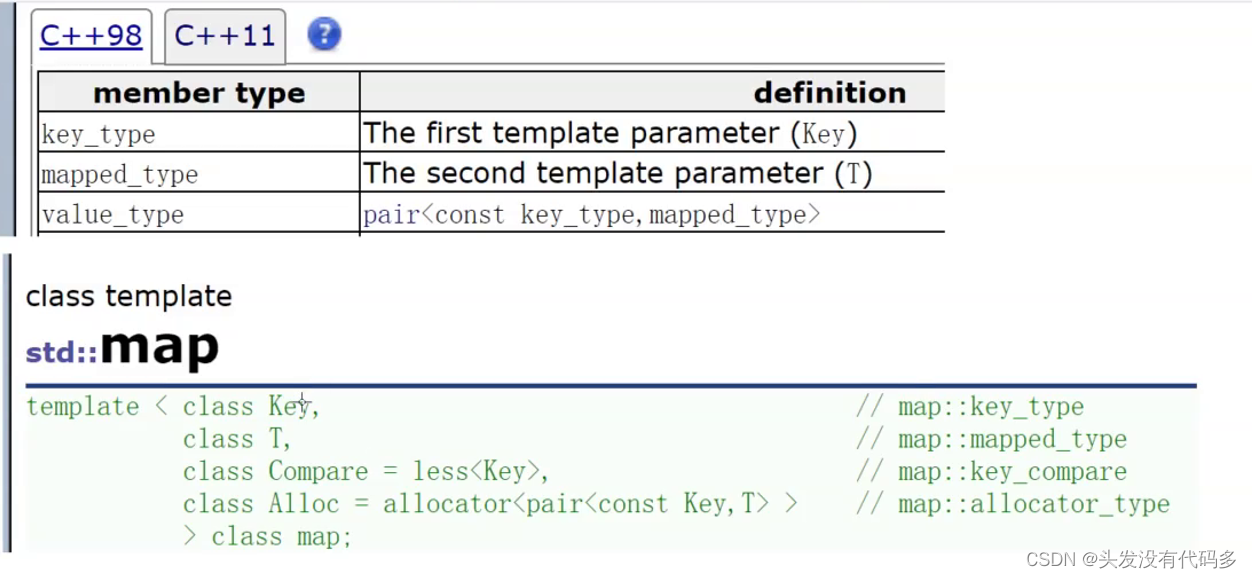
map的insert参数类型是valud_type,value_type就是pair
pair的key_type对应map的第一个模板参数Key,也就是pair的first
mapped_type对应map的第二个模板参数T,也就是pair的second
map<string, int>::iterator it = countMap.find(str);这里的string就是第一个模板参数相当于pair的first,int是第二个模板参数相当于pair的second
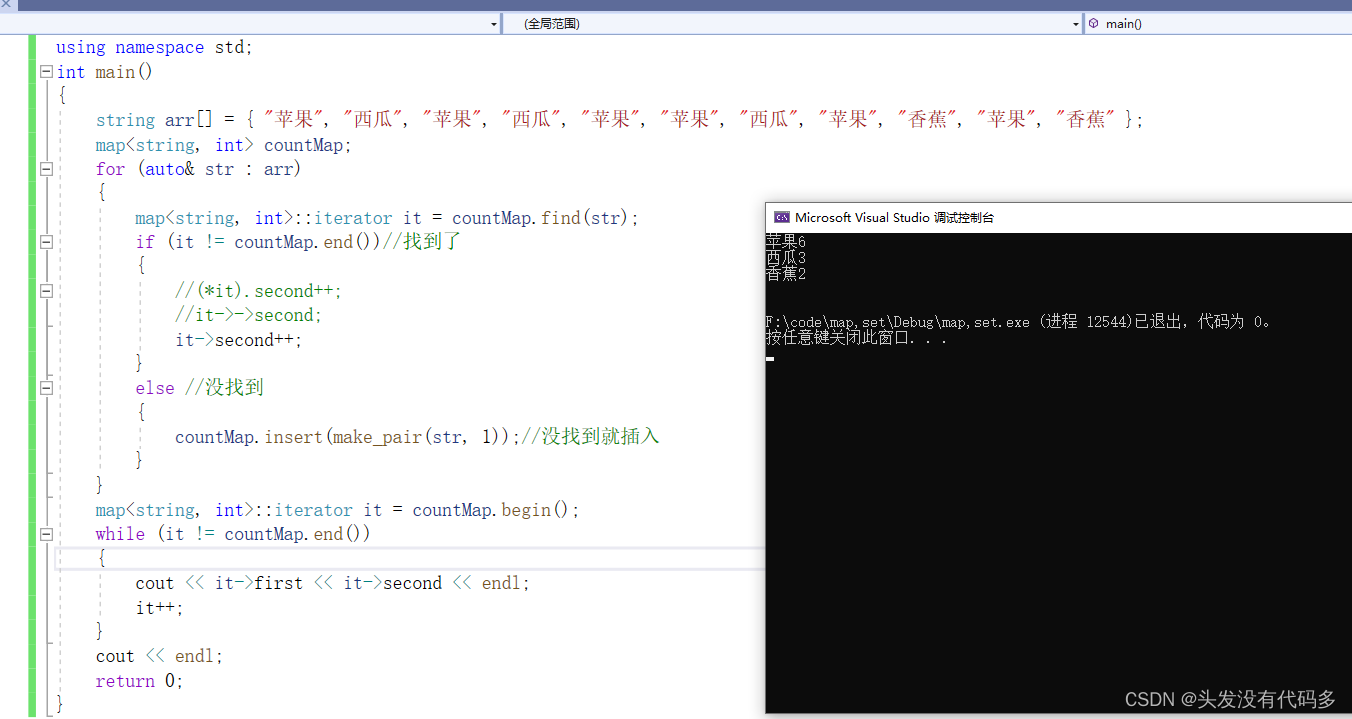
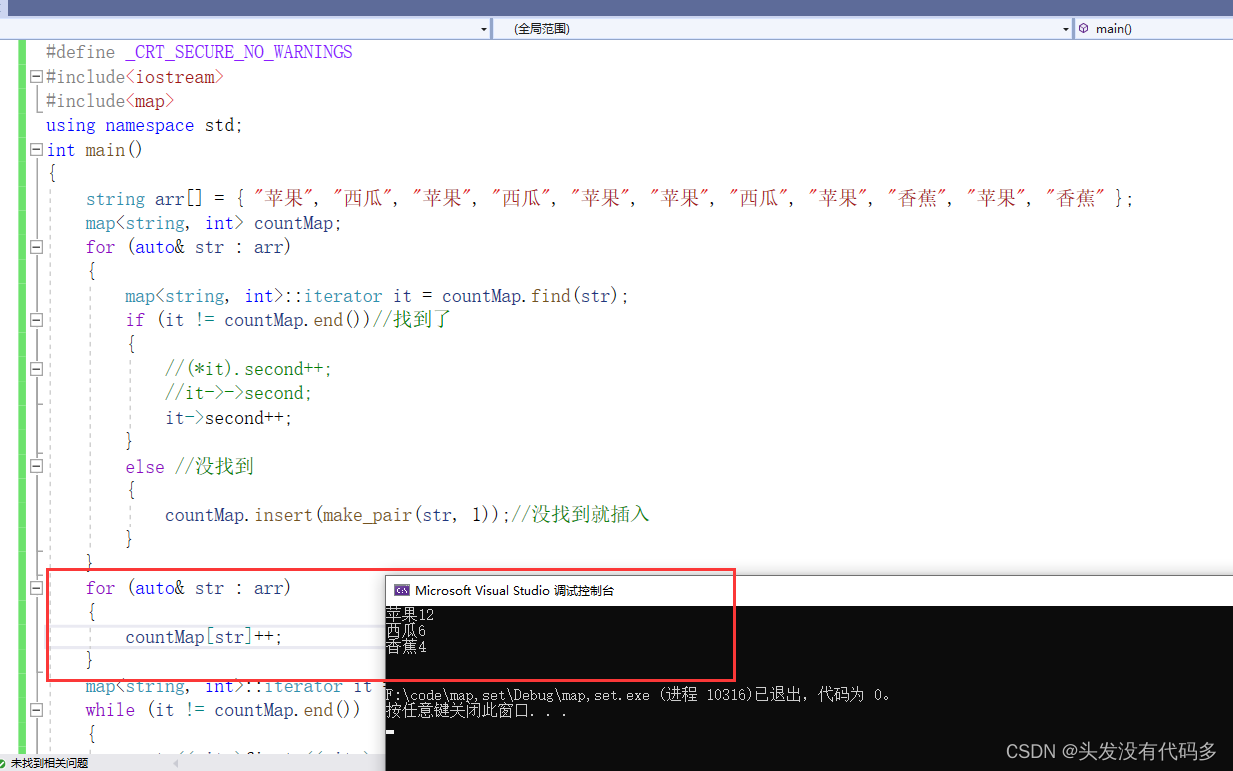
统计出现的次数
#include<iostream> #include<map> using namespace std; int main() { string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" }; map<string, int> countMap; for (auto& str : arr) { map<string, int>::iterator it = countMap.find(str); if (it != countMap.end())//找到了 { //(*it).second++; //it->->second; it->second++; } else //没找到 { countMap.insert(make_pair(str, 1));//没找到就插入 } } map<string, int>::iterator it = countMap.begin(); while (it != countMap.end()) { cout << it->first << it->second << endl; it++; } cout << endl; return 0; }
map::operator[]
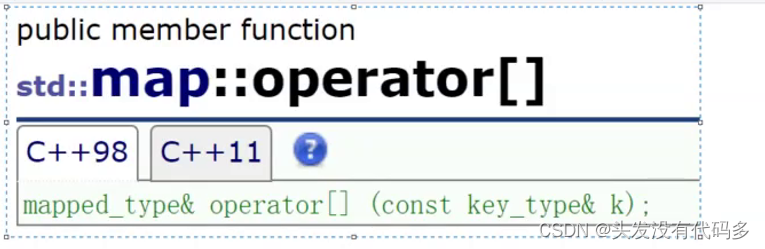
map容器重载了 [] 运算符,只要知道 map 容器中某个键值对的键的值,就可以向获取数组中元素那样,通过键直接获取对应的值。
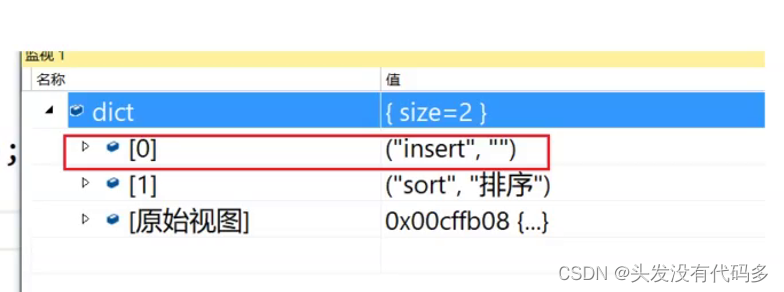
[]的返回值是value的引用,如果k不存在,函数会插入一个新的元素,然后返回。
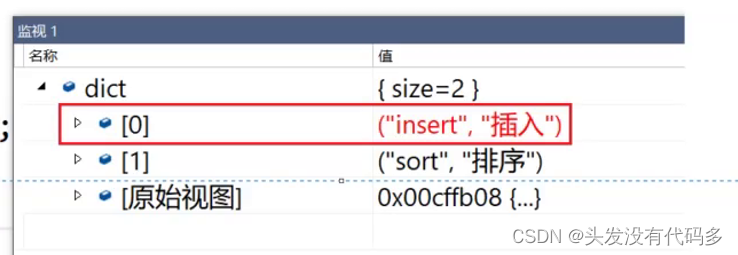
1.map当中有key,返回value的引用(可查找,修改value)
2.map中没有key,会插入一个新元素,新元素是pair(key,V());第一个是key,第二个是value的匿名对象,然后返回value的引用,(可充当插入+修改)
这种插入若str不在countMap中,会插入 pair(str,int());,然后再对返回的次数++
如果str在countMap中,返回value(次数)的引用,次数++
[ ]的实现

insert的返回类型是pair
insert的返回值
1.key已经在map中,返回pair(key_iterator,false)第一个参数是key的迭代器,如果已经存在第二个参数返回false
2.key不在map中,返回pair(new_key_iterator,true);
模拟实现
ret.first是迭代器,first->second是value
multimap
即使重复,multimap仍然会继续插入
习题 前K个高频单词
692. 前K个高频单词 - 力扣(LeetCode)
优先级队列
这里认为是在建大堆
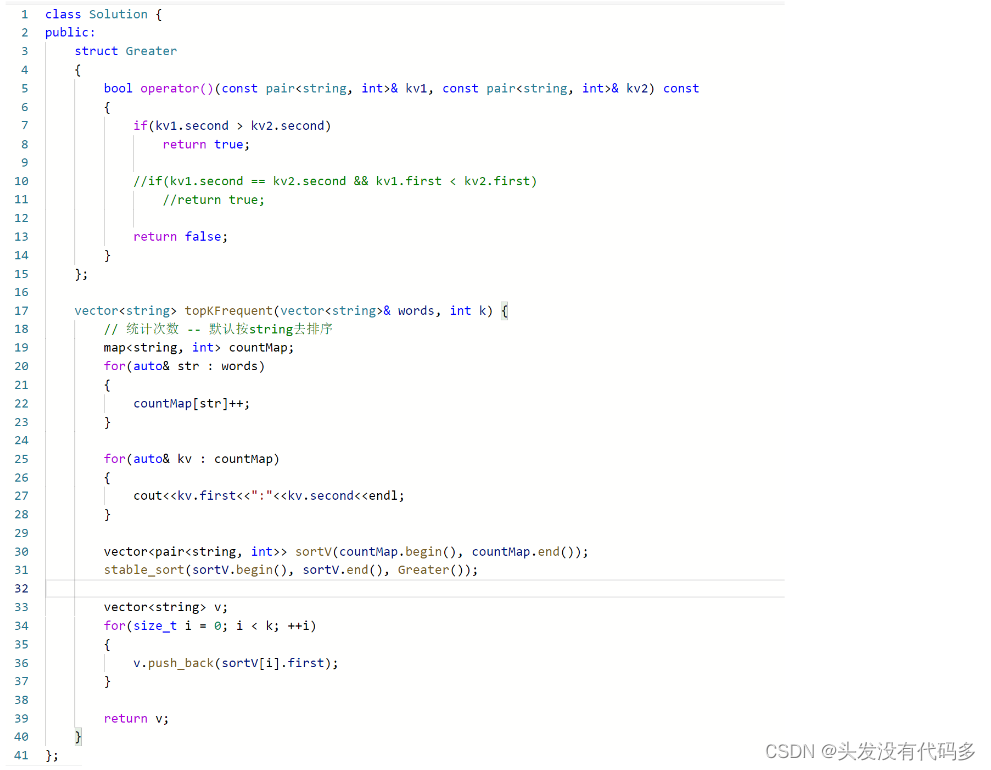
class Solution { public: struct Less//构造大堆 { bool operator()(const pair<string,int>& kv1,const pair<string,int>& kv2 )const { if(kv1.second<kv2.second)//先比较出现的次数多少 return true; if(kv1.second==kv2.second&&kv1.first>kv2.first)//出现次数一样,比较字典序大小,大的在前面 return true; return false; } }; vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k) { map<string,int> countMap; for(auto &str:words) { countMap[str]++; }//统计出现的个数 typedef priority_queue<pair<string,int>, vector<pair<string,int>>,Less> maxHeap; maxHeap mh(countMap.begin(),countMap.end()); vector<string> v; while(k--) { v.push_back(mh.top().first); mh.pop(); } return v; } };这里如果用sort排序会非常的麻烦
用stable_sort
这里不能用map,map会去重
class Solution { public: vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k) { map<string,int> countMap; for(auto &str:words) { countMap[str]++; }//统计出现的个数 multimap<int,string,greater<int>> sortMap; for(auto& kv:countMap) { sortMap.insert(make_pair(kv.second,kv.first)); } vector<string> v; multimap<int,string,greater<int>>::iterator it=sortMap.begin(); for(size_t i=0;i<k;++i) { v.push_back(it->second); ++it; } return v; } };
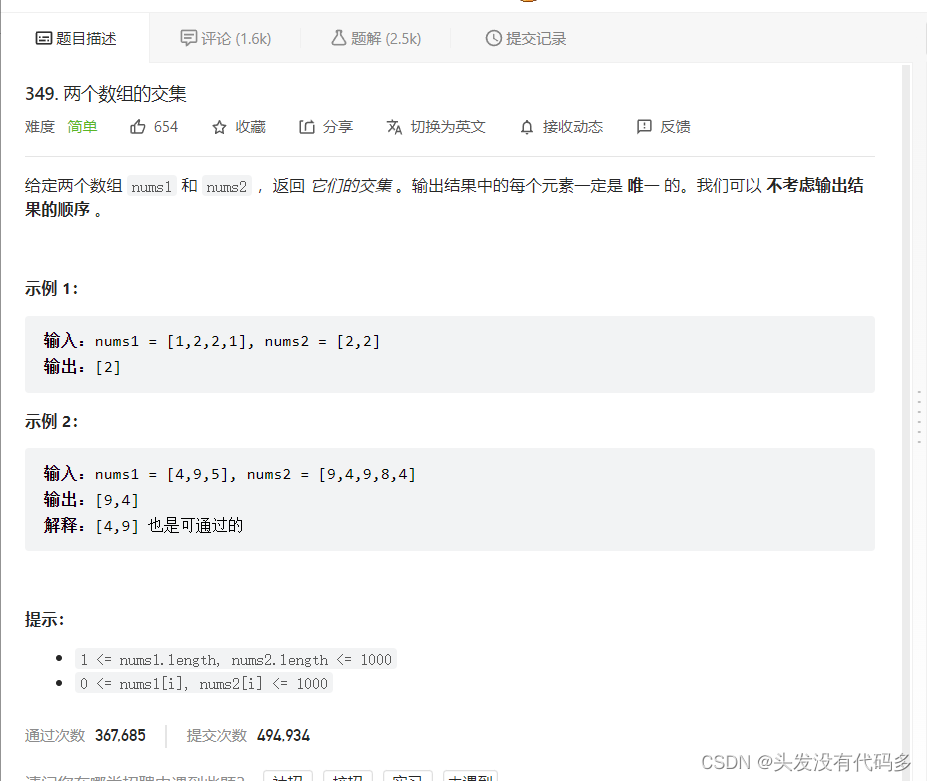
两个数组的交集
class Solution { public: vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) { set s1(nums1.begin(),nums1.end()); set s2(nums2.begin(),nums2.end()); vector<int> v; auto it1=s1.begin(); auto it2=s2.begin(); while(it1!=s1.end()&&it2!=s2.end()) { if(*it1<*it2) it1++; else if(*it2<*it1) it2++; else { v.push_back(*it1); it1++; it2++; } } return v; } };349. 两个数组的交集 - 力扣(LeetCode)
底层结构
这几个容器有个共同点是:其底层都是按照二叉搜索树来实现的,但是二叉搜索树有其自身的缺陷,假如往树中插入的元素有序或者接近有序,二叉搜索树就会退化成单支树,时间复杂度会退化成O(N),因此map、set等关联式容器的底层结构是对二叉树进行了平衡处理,即采用平衡树来实现。