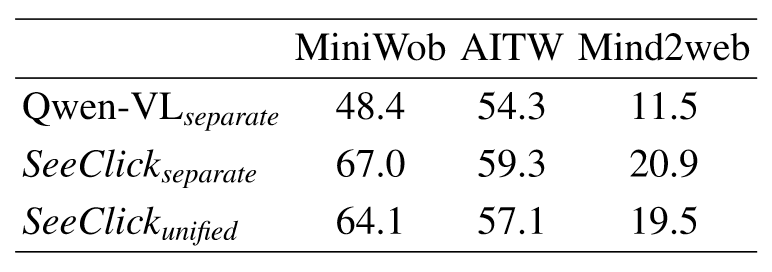
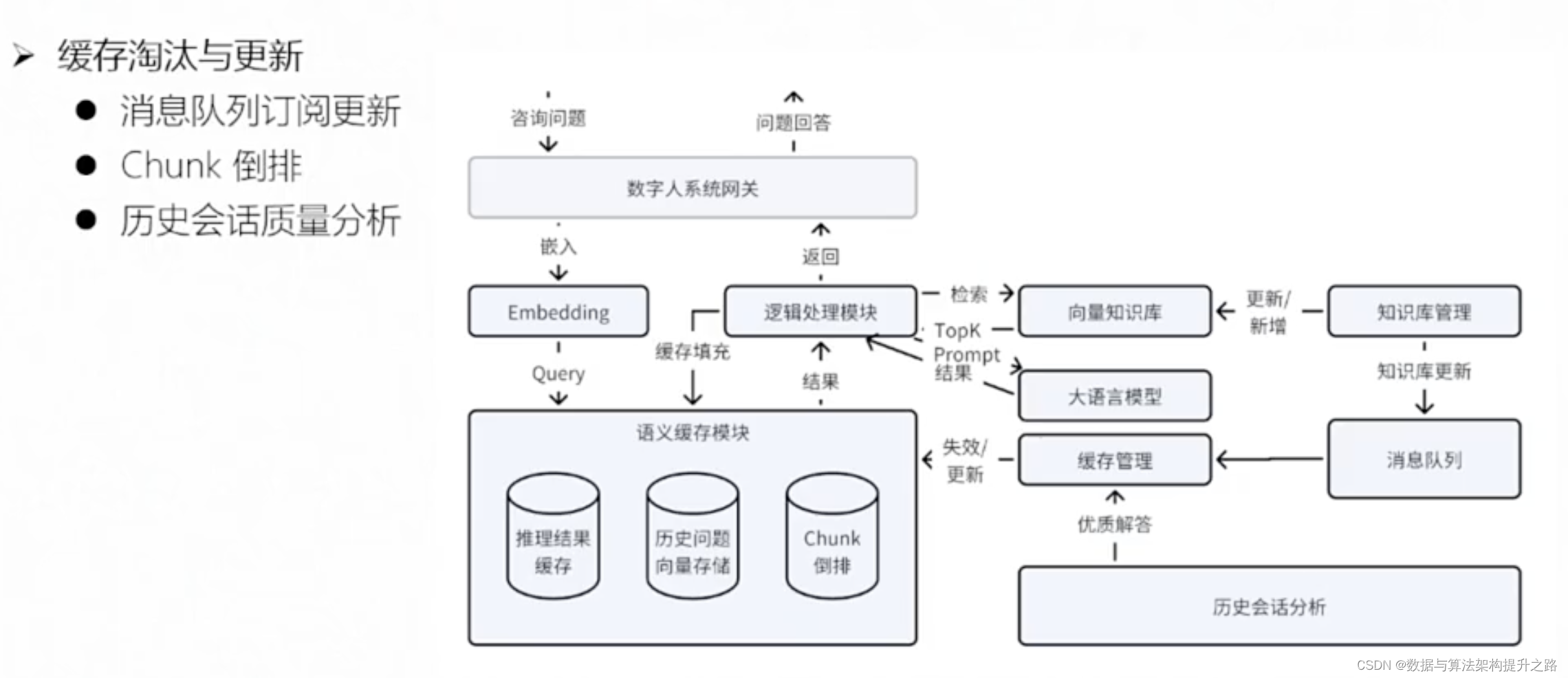
Queue 的定义和结构
队列(Queue) 是只允许在一端进行插入,在另一端进行删除的线性表
队列是一种先进先出(First In First Out)的线性表,简称 FIFO(First IN First OUT), 允许插入的一端称为队尾, 允许删除的一端称为队列头
队列的基本结构如下图所示:

Queue 的抽象数据类型
队列也有线性表的各种操作,不同的是插入元素只能在队列尾,删除元素只能在对列头进行:
队列的抽象结构如下所示:
ADT Queue(队列)
Data:
同线性表, 元素具有相同的类型,相邻的元素具有前驱和后继关系
Operation:
InitQueue(Q*)
DestroyQueue(Q*)
isEmpty(Q*)
isFull(Q*)
dequeue(Q*, *e)
enqueue(Q*, e)
queueSize(Q)
endADT
队列有多种实现方式,比如 静态数组,动态数组,单链表,双链表等
静态数组实现Queue
静态数组实现队列的基本原理:
- 建立一个
MAX_SIZE的数组, 用于存放 Queue 中的元素 - 建立int类型
queue->rear代表队列尾, 每次enqueue一个元素时,queu->rear指向最新的元素位置

- 建立
queue->front代表队列头, 每次dequeue一个元素,从queue->front位置处取出数据,并且最后其指向下一个元素位置

- 当
queue->rear和queue->front相等时,queue->front和queue->rear都重新设置为 0,此时队列为空,表示重新开始存储数据

参考代码如下:
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct {
int data[MAX_SIZE];
int front;
// queue 尾端的索引
int rear;
}Queue;
void Queueinit(Queue* queue) {
queue->front = -1;
queue->rear = -1;
}
int isEmpty(Queue* queue) {
return (queue->front == -1 && queue->rear == -1);
};
int isFull(Queue* queue) {
// queue->rear == MAX_SIZE - 1 queue->front = 0
//return (queue->rear + 1)%MAX_SIZE == queue->front;
if((queue->rear + 1 - queue->front) == MAX_SIZE) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
};
void enqueue(Queue* queue,int item) {
if(isFull(queue)) {
fprintf(stderr,"queue is full. \n");
return;
}
//printf("queue front is %d rear is %d \n",queue->front,queue->rear);
if(isEmpty(queue)) {
queue->rear = 0;
queue->front = 0;
} else {
queue->rear = (queue->rear+1)%MAX_SIZE;
}
queue->data[queue->rear] = item;
}
int dequeue(Queue* queue) {
if(isEmpty(queue)) {
fprintf(stderr,"queue is empty. \n");
return -1;
}
int item = queue->data[queue->front];
// with no element
if(queue->front == queue->rear) {
printf("queue has no element backup to empty\n");
queue->front = -1;
queue->rear = -1;
} else {
queue->front = (queue->front +1)%MAX_SIZE;
}
return item;
}
int peek(Queue* queue) {
if(isEmpty(queue)) {
fprintf(stderr,"queue is empty. \n");
return -1;
}
return queue->data[queue->front];
}
int testbasicQueueStaticArray(int agrc, char *argv[]) {
{
Queue testqueue = {
.front = -1,
.rear = -1,
};
Queueinit(&testqueue);
for(int i = 0; i < 2000; i++) {
enqueue(&testqueue,200+i);
dequeue(&testqueue);
}
enqueue(&testqueue,1001);
enqueue(&testqueue,1002);
enqueue(&testqueue,1003);
printf("dequeue item:%d \n", dequeue(&testqueue));
printf("dequeue item:%d \n", dequeue(&testqueue));
printf("dequeue item:%d \n", dequeue(&testqueue));
printf("dequeue item:%d \n", dequeue(&testqueue));
printf("peek queue element: %d queue size:%d\n", peek(&testqueue),QueueSize(&testqueue));
}
}
单链表实现Queue
单链表实现Queue的基本原理:
-
建立一个单链表,包含指向队列头的指针
queue->front和指向队列尾的指针queue->rear -
当
enqueue时,首先为新元素分配空间,然后插入到单链表的尾部,用queue->rear指向它

-
当
dequeue时,首先返回queue->front指向的节点内容,然后free掉queue->front节点,queue->front指向顺序的后一个节点

参考代码如下:
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
typedef struct {
struct node *front;
struct node *rear;
}Queue;
static int empty(Queue* queue){
return (queue->front == NULL);
}
static void initQueue(Queue* queue) {
queue->front = queue->rear = NULL;
}
static void push(Queue* queue, int value) {
struct node *pnode;
pnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(pnode == NULL) {
printf("malloc node failed!.\n");
exit(1);
}
pnode->data = value;
pnode->next = NULL;
if(empty(queue)) {
queue->front = pnode;
queue->rear = pnode;
} else {
queue->rear->next= pnode;
queue->rear = pnode;
}
}
static int pop(Queue* queue) {
if (empty(queue))
{
printf("Queue Underflow. Unable to remove.\n");
exit(1);
}
int item;
struct node *p = queue->front;
item = queue->front->data;
queue->front = queue->front->next;
if (queue->front == NULL) /* Queue contained only one node */
queue->rear = NULL;
free(p);
return item;
}
static int peek(Queue* queue) {
if (empty(queue))
{
printf("Queue Underflow. Unable to remove.\n");
exit(1);
}
return queue->front->data;
}
static int queueSize(Queue* queue){
struct node *p = queue->front;
int count = 0;
if(empty(queue)){
return 0;
}
do {
p = p->next;
count++;
}while(p != NULL);
return count;
}
int testbasicQueueImplsingleLinkedList(int agrc, char *argv[]) {
{
Queue testqueue;
int qsize = 0;
initQueue(&testqueue);
push(&testqueue, 10);
printf("queue size: %d. \n", queueSize(&testqueue));
push(&testqueue, 101);
push(&testqueue, 102);
push(&testqueue, 103);
push(&testqueue, 104);
printf("queue size: %d. \n", queueSize(&testqueue));
printf("pop value: %d queue size: %d. \n", pop(&testqueue), qsize);
qsize = queueSize(&testqueue);
printf("pop value: %d queue size: %d. \n", pop(&testqueue), qsize);
qsize = queueSize(&testqueue);
printf("pop value: %d queue size: %d. \n", pop(&testqueue), qsize);
qsize = queueSize(&testqueue);
printf("pop value: %d queue size: %d. \n", pop(&testqueue), qsize);
printf("queue size: %d. \n", queueSize(&testqueue));
printf("peek value: %d \n", peek(&testqueue));
printf("queue size: %d. \n", queueSize(&testqueue));
}
return 1;
}