文章目录
- 一、前言
- 二、分析报错原因
- 三、如何解决
- 四、具体步骤
你是否曾遇到这样的困境:在本地使用file://协议直接打开HTML文件时,由于现代浏览器的安全限制,无法跨源请求(CORS)本地资源?尤其是当你试图通过
<script type="module">标签导入本地JS模块时,浏览器会将其视为跨源请求,但file://协议并不支持CORS,导致你的代码无法正常运行。
现在,有一个简单而高效的解决方案!通过搭建一个本地服务器,你可以轻松地在本地环境中测试HTML和JS代码,无需担心CORS问题。在本文中,我将教你如何使用Node.js快速搭建一个本地服务器,让你的开发工作更加顺畅。无需复杂的配置,只需简单几步,即可实现本地文件的快速访问与调试。快来跟随我,一起解决这个令人头疼的CORS限制吧!
一、前言
闲来无事,我写了一个防抖函数,想测试它的可行性。于是,我就在本地创建了一个debounce.js文件。
function debounce(fn, delay = 500) {
let timer = null;
return function () {
if (timer) {
clearTimeout(timer);
}
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, arguments);
timer = null;
}, delay);
};
}
export { debounce };
顺带,我就写了一个简单的test.html文件,想着校验一些自己写的函数对不对。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>测试事件防抖</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" id="input1" />
<script type="module">
import { debounce } from "./debounce.js";
function handleInput(e) {
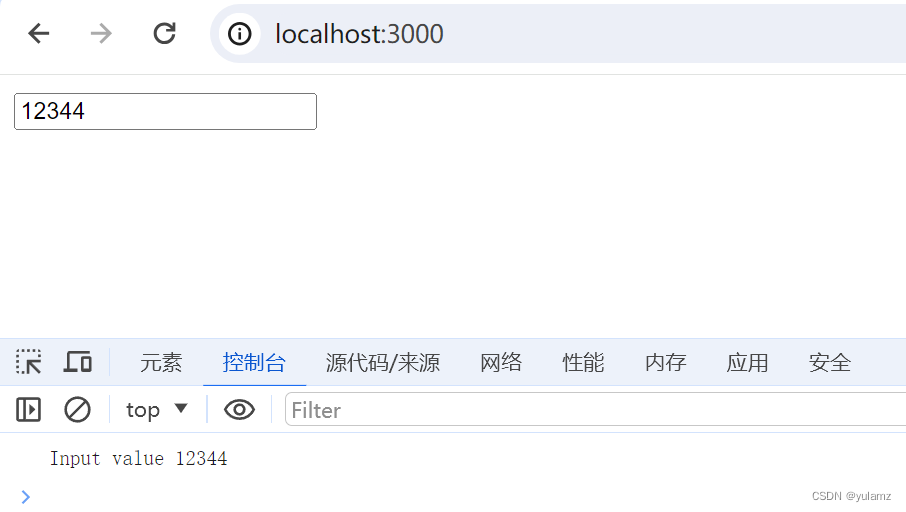
console.log("Input value", e.target.value);
}
input1.addEventListener("keyup", debounce(handleInput));
</script>
</body>
</html>
接着,就在浏览器直接打开了这个html文件。此时,控制台会报错:Access to script at 'file:///d%3A/code/a-exercise/%E7%BC%96%E7%A8%8B%E9%A2%98/%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0%E8%8A%82%E6%B5%81%E9%98%B2%E6%8A%96/debounce.js' from origin 'null' has been blocked by CORS policy: Cross origin requests are only supported for protocol schemes: http, data, isolated-app, chrome-extension, chrome, https, chrome-untrusted.
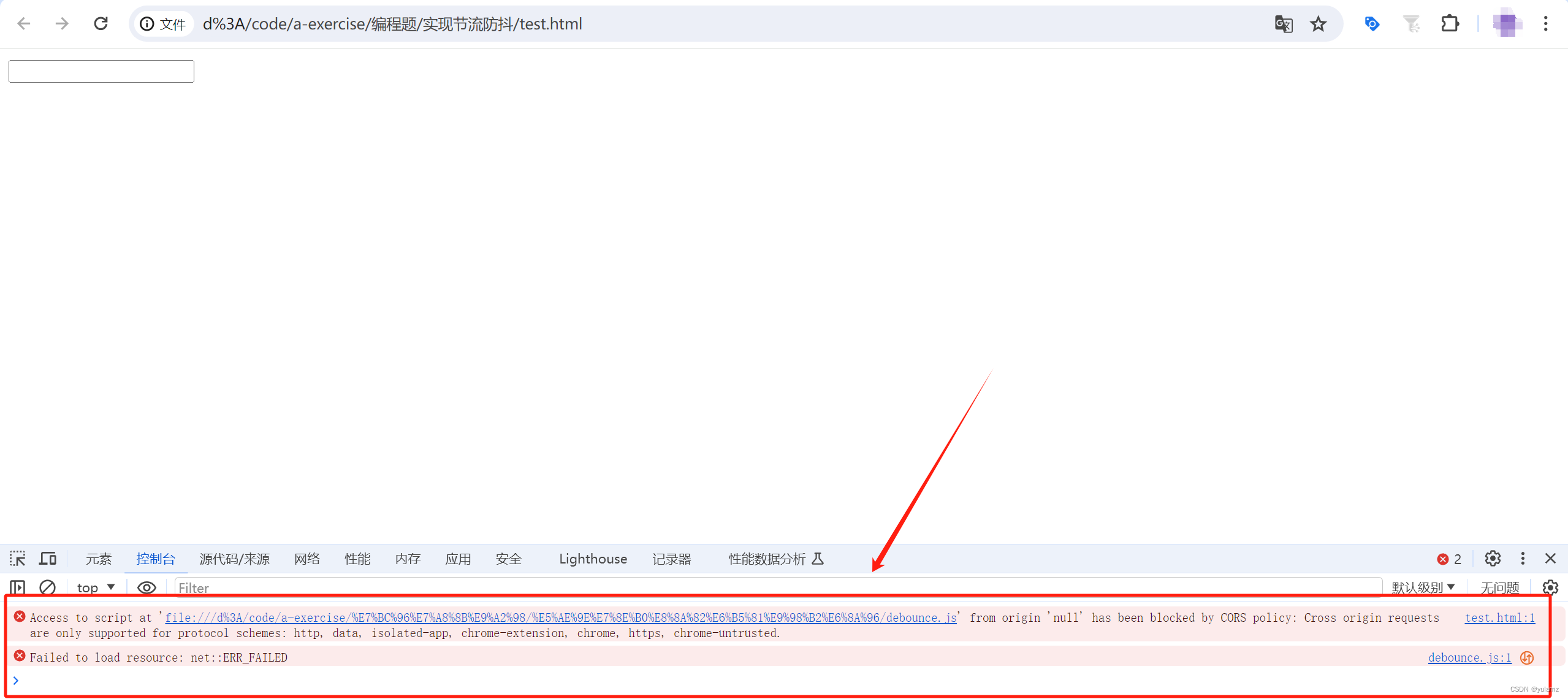
二、分析报错原因
简单翻译了一下这段报错,简单来说就是通过file://协议直接打开HTML文件,而现代浏览器出于安全考虑,对于通过file://协议访问的资源,不允许跨源请求(CORS)。
因此,当我们试图通过<script type="module"> 标签导入本地 js 模块时,浏览器会尝试作为跨源请求来处理,但file://协议不支持这种跨源资源共享。
三、如何解决
为了解决这个问题,建议使用本地服务器来提供你的文件,这样你就可以在本地环境中测试你的HTML和JavaScript代码,而不会遇到CORS问题。
四、具体步骤
在同一个文件夹下,创建一个server.js文件,文件内容如下:
// 这是一个简单的Node.js HTTP服务器,它使用http模块来创建服务器,fs模块来读取文件以及path模块来处理文件路径
// 1.引入模块
const http = require("http");
const fs = require("fs");
const path = require("path");
// 2.设置服务器参数 -- 服务器将在本地IP地址(127.0.0.1)的3000端口上运行
const hostname = "127.0.0.1";
const port = 3000;
// 3.创建HTTP服务器
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
// 3.1处理请求 -- 确定读取的文件路径
let filePath = req.url === "/" ? "./test.html" : `.${req.url}`;
const absPath = path.resolve(__dirname, filePath);
// 3.2读取文件并发送响应 -- 使用fs.readFile异步读取文件
fs.readFile(absPath, (err, data) => {
// 3.2.1异常处理
if (err) {
res.writeHead(404);
res.end(`File ${filePath} not found!`);
return;
}
// 3.2.2确定文件的MIME类型并发送响应
const contentType = getContentType(filePath);
res.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": contentType });
res.end(data, "utf-8");
});
});
/**
* 根据文件的扩展名确定MIME类型
* @param {*} filePath
* @returns
*/
function getContentType(filePath) {
const fileExtension = path.extname(filePath).toLowerCase();
const map = {
".html": "text/html",
".js": "text/javascript",
".css": "text/css",
// 可拓展更多文件类型
};
return map[fileExtension] || "text/plain";
}
// 4.启动服务器
server.listen(port, hostname, () => {
console.log(`Server running at http://${hostname}:${port}/`);
});
注意:http://127.0.0.1:3000/ 中的 127.0.0.1 是一个特殊的 IP 地址,称为“本地回环地址”或“localhost”。这个 IP 地址是保留给每个计算机或网络设备的,用于指代设备自身。换句话说,当你在计算机上访问 127.0.0.1 时,你实际上是在访问那台计算机本身,而不是网络上的任何其他设备。
最后,在当前文件夹上运行node server.js命令就可以啦。

至此,我们就完美解决了file协议访问资源时产生的跨域问题,让你在本地也能轻松调试文件~







![[Qt]Qt框架解析:从入门到精通,探索平台开发的无限可能](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/79321df2706d4575a45facd17923ce86.png)