文章目录
- Fork之前创建了互斥锁,要警惕死锁问题
- 使用GDB进行调试
- 如何解决该问题?
- 是否还有别的问题?
- 结论
- 参考文献
Fork之前创建了互斥锁,要警惕死锁问题
下面的这段代码会导致子进程出现死锁问题,您看出来了吗?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <string>
using std::string;
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
void* func(void* arg)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
for(int i = 0;i < 10; ++i)
{
sleep(1);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
return NULL;
}
int main(void) {
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, func, NULL);
sleep(5);
int ret = fork();
if (ret == 0) {
printf("before get lock\n");
func(NULL);
printf("after get lock\n");
return 0;
}
else if(ret > 0)
{
pthread_join(tid, 0);
wait(NULL);
}
else
{
printf("fork failed\n");
exit(1);
}
return 0;
}
对上述代码进行编译, 并运行:
[root@localhost test3]# g++ main.cpp -g
[root@localhost test3]# ./a.out
before get lock
我们发现子进程始终没有打印出"after get lock"的日志。
对fork熟悉的朋友们应该知道,在fork之后,由于copy-on-write机制,当子进程尝试修改数据时,会导致父子进程的内存分离,这个过程也将父进程中的互斥锁给拷贝了过来,也包括了互斥锁的状态(锁定,释放)。
在父进程启动时,首先创建了一个线程去执行func函数,为了让该线程在fork之前可以被调度执行,使用了sleep函数让主进程中的主线程让出cpu,从而执行func函数,在func函数中对互斥锁进行了加锁。
5s后,主进程的主线程sleep结束,从而执行fork函数,产生了子进程,子进程也继承了父进程中的互斥锁,也继承了该锁的锁定状态,因此尝试加锁时,就会出现死锁问题。
下面通过GDB调试验证我们的分析。
使用GDB进行调试
如果有同志对GDB还不熟悉,请参考
https://wizardforcel.gitbooks.io/100-gdb-tips/content/index.html
[root@localhost test3]# gdb a.out
首先设置同时调试父子进程
(gdb) set detach-on-fork off
接下来,在fork之前下一个断点,然后进行单步调试。
(gdb) b 26
Breakpoint 1 at 0x401217: file main.cpp, line 26.
(gdb) r
Starting program: /home/work/cpp_proj/test3/a.out
[Thread debugging using libthread_db enabled]
Using host libthread_db library "/lib64/libthread_db.so.1".
[New Thread 0x7ffff7a8c640 (LWP 167076)]
Thread 1 "a.out" hit Breakpoint 1, main () at main.cpp:26
26 int ret = fork();
Missing separate debuginfos, use: dnf debuginfo-install glibc-2.34-40.el9.x86_64 libgcc-11.3.1-2.1.el9.x86_64 libstdc++-11.3.1-2.1.el9.x86_64
(gdb) n
[New inferior 2 (process 167113)]
Reading symbols from /home/work/cpp_proj/test3/a.out...
Reading symbols from /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2...
[Thread debugging using libthread_db enabled]
Using host libthread_db library "/lib64/libthread_db.so.1".
27 if (ret == 0) {
Missing separate debuginfos, use: dnf debuginfo-install glibc-2.34-40.el9.x86_64 libgcc-11.3.1-2.1.el9.x86_64 libstdc++-11.3.1-2.1.el9.x86_64
(gdb) n
33 else if(ret > 0)
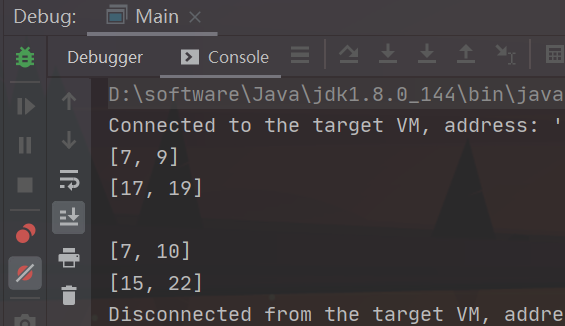
单步到这里,子进程已经创建成功, 我们打开另一个窗口查看一下,确实目前父子进程都已经启动了
[root@localhost ~]# ps aux |grep -v grep|grep a.out
root 166931 0.3 1.4 180844 55780 pts/0 Sl+ 05:29 0:00 gdb a.out
root 167072 0.0 0.0 14020 2220 pts/0 tl 05:29 0:00 /home/work/cpp_proj/test3/a.out
root 167113 0.0 0.0 14020 1588 pts/0 t 05:30 0:00 /home/work/cpp_proj/test3/a.out
这个时候,我们打印一下父进程中mutex的状态, 如下所示:
(gdb) p mutex
$1 = {__data = {__lock = 1, __count = 0, __owner = 167076, __nusers = 1, __kind = 0, __spins = 0, __elision = 0, __list = {__prev = 0x0,
__next = 0x0}}, __size = "\001\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\244\214\002\000\001", '\000' <repeats 26 times>, __align = 1}
因为之前父进程中的线程已经执行了func函数, 因此锁的__lock值为1,即锁定状态,锁的__owner时167076, 说明该锁由父进程所加。
接下来,切换到子进程查看:
单步到执行func函数之前。
(gdb) info inferior
Num Description Connection Executable
* 1 process 167072 1 (native) /home/work/cpp_proj/test3/a.out
2 process 167113 1 (native) /home/work/cpp_proj/test3/a.out
(gdb) inferior 2
[Switching to inferior 2 [process 167113] (/home/work/cpp_proj/test3/a.out)]
[Switching to thread 2.1 (Thread 0x7ffff7a90380 (LWP 167113))]
#0 0x00007ffff7ba98d7 in _Fork () from /lib64/libc.so.6
(gdb) n
Single stepping until exit from function _Fork,
which has no line number information.
0x00007ffff7ba96fa in fork () from /lib64/libc.so.6
(gdb) n
Single stepping until exit from function fork,
which has no line number information.
main () at main.cpp:27
27 if (ret == 0) {
(gdb) n
28 printf("before get lock\n");
(gdb) n
before get lock
29 func(NULL);
这个时候,我们查看一下子进程中mutex的状态, 可以发现__lock的值为1,说明目前该互斥锁已经被加锁。而且可以看到__owner也属于父进程。
(gdb) p mutex
$2 = {__data = {__lock = 1, __count = 0, __owner = 167076, __nusers = 1, __kind = 0, __spins = 0, __elision = 0, __list = {__prev = 0x0,
__next = 0x0}}, __size = "\001\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\244\214\002\000\001", '\000' <repeats 26 times>, __align = 1}
(gdb)
到此,我们就验证了我们的分析, 确实时由于锁的状态的继承,导致了子进程的死锁。
如何解决该问题?
使用pthread_atfork函数在fork子进程之前清理一下锁的状态。
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_atfork(void (*prepare)(void), void (*parent)(void),
void (*child)(void));
https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man3/pthread_atfork.3.html
pthread_atfork()在fork()之前调用,当调用fork时,内部创建子进程前在父进程中会调用prepare,内部创建子进程成功后,父进程会调用parent ,子进程会调用child。
修改之后,代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <string>
using std::string;
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
void* func(void* arg)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
for(int i = 0;i < 10; ++i)
{
sleep(1);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
return NULL;
}
void clean()
{
if(pthread_mutex_trylock(&mutex) != 0)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
int main(void) {
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, func, NULL);
sleep(5);
pthread_atfork(NULL, NULL, clean);
int ret = fork();
if (ret == 0) {
printf("before get lock\n");
func(NULL);
printf("after get lock\n");
return 0;
}
else if(ret > 0)
{
pthread_join(tid, 0);
wait(NULL);
}
else
{
printf("fork failed\n");
exit(1);
}
return 0;
}
重新编译并运行,死锁问题解决了。
[root@localhost test3]# ./a.out
before get lock
after get lock
是否还有别的问题?
同样的代码,只是本此将锁增加了"可重入"的属性。我们再看看执行结果。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <string>
using std::string;
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_mutexattr_t mta;
void* func(void* arg)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
for(int i = 0;i < 10; ++i)
{
sleep(1);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
return NULL;
}
void clean()
{
if(pthread_mutex_trylock(&mutex) != 0)
{
int ret = pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
printf("ret = %d\n", ret);
}
}
int main(void) {
//增加可重入的属性
pthread_mutexattr_init(&mta);
pthread_mutexattr_settype(&mta, PTHREAD_MUTEX_RECURSIVE);
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, &mta);
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, func, NULL);
sleep(5);
pthread_atfork(NULL, NULL, clean);
int ret = fork();
if (ret == 0) {
printf("before get lock\n");
func(NULL);
printf("after get lock\n");
return 0;
}
else if(ret > 0)
{
pthread_join(tid, 0);
wait(NULL);
}
else
{
printf("fork failed\n");
exit(1);
}
return 0;
}
执行结果如下:
[root@localhost test3]# ./a.out
ret = 1
before get lock
此时发现再次发生了死锁。
原因在于可重入锁解锁必须是相同的线程。子进程中的主线程并非加锁线程,因此无法解锁。
查看glibc中的相关实现:
https://github.com/lattera/glibc/blob/master/nptl/pthread_mutex_unlock.c
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-udad9xLR-1674974041614)(null)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d329495e36114ddfa9bfc79f973b2745.png)
可以看到可重入锁解锁时,确实会有owner的检查。并且会返回EPERM的errno, EPERM=1, 这与我们打印出来的ret=1是相一致的。
结论
- fork函数执行后,子进程会继承来自父进程中的锁和锁的状态
- 可重入锁解锁会检查owner, 非owner不能解锁。
- 在fork之前如果有创建互斥锁, 一定需要小心其状态。
参考文献
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/343845048