RotateRect.h
#include <vector>
/**
* @brief 计算点集最小旋转外接矩形
*/
class RotateRect {
public:
enum { CALIPERS_MAXHEIGHT = 0, CALIPERS_MINAREARECT = 1, CALIPERS_MAXDIST = 2 };
struct Point {
float x, y;
};
using Points = std::vector<Point>;
struct Sizef {
float width, height;
};
struct Rect {
float left, top, right, bottom;
};
explicit RotateRect(const Points& pts);
const Point& center() const;
const Sizef& size() const;
float angle() const;
public:
void update();
Points toPoints() const;
Rect getOutLine() const;
private:
double crossProduct(const Point& A, const Point& B, const Point& C) const;
double calculateDistance(const Point& A, const Point& B) const;
Points convexHull() const;
/* we will use usual cartesian coordinates */
void rotatingCalipers(const Point* pts, int n, int mode, float* out) const;
private:
const Points& m_inputs;
Point m_center;
//! returns width and height of the rectangle
Sizef m_size;
//! returns the rotation angle. When the angle is 0, 90, 180, 270 etc., the rectangle becomes an up-right rectangle.
float m_angle;
};RotateRect.cpp
#include "RotateRect.h"
#include <cmath>
#include <assert.h>
#ifndef CV_PI
#define CV_PI 3.1415926535897932384626433832795
#endif
RotateRect::RotateRect(const RotateRect::Points& pts) : m_inputs(pts), m_angle(0), m_size{ 0, 0 }, m_center{ 0, 0 } {}
/*
* @brief 计算BA与CA之间面积
* @param [in] A 点
* @param [in] B 点
* @param [in] C 点
* @return
BA x CA > 0, C在B的逆时针方向,B在C右边
BA x CA < 0, C在B的顺时针方向,B在C左边
BA x CA = 0, C和B共线,可能正方向,也可能反方向
*/
double RotateRect::crossProduct(const RotateRect::Point& A, const RotateRect::Point& B, const RotateRect::Point& C) const {
return (B.x - A.x) * (C.y - A.y) - (C.x - A.x) * (B.y - A.y);
}
/*
* @brief 找到x方向最小点为起始点,查找所有点最右边点,到起始点结束
* @return 所有凸包点,逆时针方向
*/
RotateRect::Points RotateRect::convexHull() const {
const auto& points = m_inputs;
int n = points.size();
if (n <= 3) {
return points;
}
std::vector<Point> hull;
int l = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (points[i].x < points[l].x) {
l = i;
}
}
int p = l, q;
do {
hull.push_back(points[p]);
q = (p + 1) % n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (crossProduct(points[p], points[i], points[q]) > 0) {
q = i;
}
}
p = q;
} while (p != l);
return hull;
}
double RotateRect::calculateDistance(const RotateRect::Point& A, const RotateRect::Point& B) const {
return std::sqrt(std::pow(B.x - A.x, 2) + std::pow(B.y - A.y, 2));
}
void rotate90CCW(const RotateRect::Point& in, RotateRect::Point& out)
{
out.x = -in.y;
out.y = in.x;
}
void rotate90CW(const RotateRect::Point& in, RotateRect::Point& out)
{
out.x = in.y;
out.y = -in.x;
}
void rotate180(const RotateRect::Point& in, RotateRect::Point& out)
{
out.x = -in.x;
out.y = -in.y;
}
/* return true if first vector is to the right (clockwise) of the second */
bool firstVecIsRight(const RotateRect::Point& vec1, const RotateRect::Point& vec2)
{
RotateRect::Point tmp;
rotate90CW(vec1, tmp);
return tmp.x * vec2.x + tmp.y * vec2.y < 0;
}
/*
* @brief 计算凸包点的最小旋转矩形
*/
/* we will use usual cartesian coordinates */
void RotateRect::rotatingCalipers(const RotateRect::Point* points, int n, int mode, float* out) const
{
using Point = RotateRect::Point;
float minarea = FLT_MAX;
float max_dist = 0;
char buffer[32] = {};
int i, k;
std::vector<float> abuf(n * 3);
float* inv_vect_length = abuf.data();
Point* vect = (Point*)(inv_vect_length + n);
int left = 0, bottom = 0, right = 0, top = 0;
int seq[4] = { -1, -1, -1, -1 };
Point rot_vect[4];
/* rotating calipers sides will always have coordinates
(a,b) (-b,a) (-a,-b) (b, -a)
*/
/* this is a first base vector (a,b) initialized by (1,0) */
float orientation = 0;
float base_a;
float base_b = 0;
float left_x, right_x, top_y, bottom_y;
Point pt0 = points[0];
left_x = right_x = pt0.x;
top_y = bottom_y = pt0.y;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
double dx, dy;
if (pt0.x < left_x)
left_x = pt0.x, left = i;
if (pt0.x > right_x)
right_x = pt0.x, right = i;
if (pt0.y > top_y)
top_y = pt0.y, top = i;
if (pt0.y < bottom_y)
bottom_y = pt0.y, bottom = i;
Point pt = points[(i + 1) & (i + 1 < n ? -1 : 0)];
dx = pt.x - pt0.x;
dy = pt.y - pt0.y;
vect[i].x = (float)dx;
vect[i].y = (float)dy;
inv_vect_length[i] = (float)(1. / std::sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy));
pt0 = pt;
}
// find convex hull orientation
{
double ax = vect[n - 1].x;
double ay = vect[n - 1].y;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
double bx = vect[i].x;
double by = vect[i].y;
double convexity = ax * by - ay * bx;
if (convexity != 0)
{
orientation = (convexity > 0) ? 1.f : (-1.f);
break;
}
ax = bx;
ay = by;
}
assert(orientation != 0);
}
base_a = orientation;
/*****************************************************************************************/
/* init calipers position */
seq[0] = bottom;
seq[1] = right;
seq[2] = top;
seq[3] = left;
/*****************************************************************************************/
/* Main loop - evaluate angles and rotate calipers */
/* all of edges will be checked while rotating calipers by 90 degrees */
for (k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
/* number of calipers edges, that has minimal angle with edge */
int main_element = 0;
/* choose minimum angle between calipers side and polygon edge by dot product sign */
rot_vect[0] = vect[seq[0]];
rotate90CW(vect[seq[1]], rot_vect[1]);
rotate180(vect[seq[2]], rot_vect[2]);
rotate90CCW(vect[seq[3]], rot_vect[3]);
for (i = 1; i < 4; i++)
{
if (firstVecIsRight(rot_vect[i], rot_vect[main_element]))
main_element = i;
}
/*rotate calipers*/
{
//get next base
int pindex = seq[main_element];
float lead_x = vect[pindex].x * inv_vect_length[pindex];
float lead_y = vect[pindex].y * inv_vect_length[pindex];
switch (main_element)
{
case 0:
base_a = lead_x;
base_b = lead_y;
break;
case 1:
base_a = lead_y;
base_b = -lead_x;
break;
case 2:
base_a = -lead_x;
base_b = -lead_y;
break;
case 3:
base_a = -lead_y;
base_b = lead_x;
break;
default:
assert("main_element should be 0, 1, 2 or 3" && false);
}
}
/* change base point of main edge */
seq[main_element] += 1;
seq[main_element] = (seq[main_element] == n) ? 0 : seq[main_element];
switch (mode)
{
case RotateRect::CALIPERS_MAXHEIGHT:
{
/* now main element lies on edge aligned to calipers side */
/* find opposite element i.e. transform */
/* 0->2, 1->3, 2->0, 3->1 */
int opposite_el = main_element ^ 2;
float dx = points[seq[opposite_el]].x - points[seq[main_element]].x;
float dy = points[seq[opposite_el]].y - points[seq[main_element]].y;
float dist;
if (main_element & 1)
dist = (float)fabs(dx * base_a + dy * base_b);
else
dist = (float)fabs(dx * (-base_b) + dy * base_a);
if (dist > max_dist)
max_dist = dist;
}
break;
case RotateRect::CALIPERS_MINAREARECT:
/* find area of rectangle */
{
float height;
float area;
/* find vector left-right */
float dx = points[seq[1]].x - points[seq[3]].x;
float dy = points[seq[1]].y - points[seq[3]].y;
/* dotproduct */
float width = dx * base_a + dy * base_b;
/* find vector left-right */
dx = points[seq[2]].x - points[seq[0]].x;
dy = points[seq[2]].y - points[seq[0]].y;
/* dotproduct */
height = -dx * base_b + dy * base_a;
area = width * height;
if (area <= minarea)
{
float* buf = (float*)buffer;
minarea = area;
/* leftist point */
((int*)buf)[0] = seq[3];
buf[1] = base_a;
buf[2] = width;
buf[3] = base_b;
buf[4] = height;
/* bottom point */
((int*)buf)[5] = seq[0];
buf[6] = area;
}
}
break;
} /*switch */
} /* for */
switch (mode)
{
case RotateRect::CALIPERS_MINAREARECT:
{
float* buf = (float*)buffer;
float A1 = buf[1];
float B1 = buf[3];
float A2 = -buf[3];
float B2 = buf[1];
float C1 = A1 * points[((int*)buf)[0]].x + points[((int*)buf)[0]].y * B1;
float C2 = A2 * points[((int*)buf)[5]].x + points[((int*)buf)[5]].y * B2;
float idet = 1.f / (A1 * B2 - A2 * B1);
float px = (C1 * B2 - C2 * B1) * idet;
float py = (A1 * C2 - A2 * C1) * idet;
out[0] = px;
out[1] = py;
out[2] = A1 * buf[2];
out[3] = B1 * buf[2];
out[4] = A2 * buf[4];
out[5] = B2 * buf[4];
}
break;
case RotateRect::CALIPERS_MAXHEIGHT:
{
out[0] = max_dist;
}
break;
}
}
void RotateRect::update()
{
using Point = RotateRect::Point;
std::vector<Point> hull;
Point out[3];
hull = convexHull();
int n = hull.size();
const Point* hpoints = &hull[0];
if (n > 2)
{
rotatingCalipers(hpoints, n, RotateRect::CALIPERS_MINAREARECT, (float*)out);
m_center.x = out[0].x + (out[1].x + out[2].x) * 0.5f;
m_center.y = out[0].y + (out[1].y + out[2].y) * 0.5f;
m_size.width = (float)std::sqrt((double)out[1].x * out[1].x + (double)out[1].y * out[1].y);
m_size.height = (float)std::sqrt((double)out[2].x * out[2].x + (double)out[2].y * out[2].y);
m_angle = (float)atan2((double)out[1].y, (double)out[1].x);
}
else if (n == 2)
{
m_center.x = (hpoints[0].x + hpoints[1].x) * 0.5f;
m_center.y = (hpoints[0].y + hpoints[1].y) * 0.5f;
double dx = hpoints[1].x - hpoints[0].x;
double dy = hpoints[1].y - hpoints[0].y;
m_size.width = (float)std::sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
m_size.height = 0;
m_angle = (float)atan2(dy, dx);
}
else
{
if (n == 1)
m_center = hpoints[0];
}
m_angle = (float)(m_angle * 180 / CV_PI);
}
RotateRect::Points RotateRect::toPoints() const
{
RotateRect::Points pt(4);
double _angle = m_angle * CV_PI / 180.;
float b = (float)cos(_angle) * 0.5f;
float a = (float)sin(_angle) * 0.5f;
pt[0].x = m_center.x - a * m_size.height - b * m_size.width;
pt[0].y = m_center.y + b * m_size.height - a * m_size.width;
pt[1].x = m_center.x + a * m_size.height - b * m_size.width;
pt[1].y = m_center.y - b * m_size.height - a * m_size.width;
pt[2].x = 2 * m_center.x - pt[0].x;
pt[2].y = 2 * m_center.y - pt[0].y;
pt[3].x = 2 * m_center.x - pt[1].x;
pt[3].y = 2 * m_center.y - pt[1].y;
return pt;
}
const RotateRect::Point& RotateRect::center() const {
return m_center;
}
const RotateRect::Sizef& RotateRect::size() const {
return m_size;
}
float RotateRect::angle() const {
return m_angle;
}
RotateRect::Rect RotateRect::getOutLine() const {
if (m_inputs.empty())
return { 0, 0, 0, 0 };
using Number = std::numeric_limits<float>;
RotateRect::Rect rect{ Number::max(), Number::max(), Number::min(), Number::min() };
for (const auto& point : m_inputs) {
if (point.x < rect.left)
rect.left = point.x;
if (point.x > rect.right)
rect.right = point.x;
if (point.y < rect.top)
rect.top = point.y;
if (point.y > rect.bottom)
rect.bottom = point.y;
}
return rect;
}main.cpp
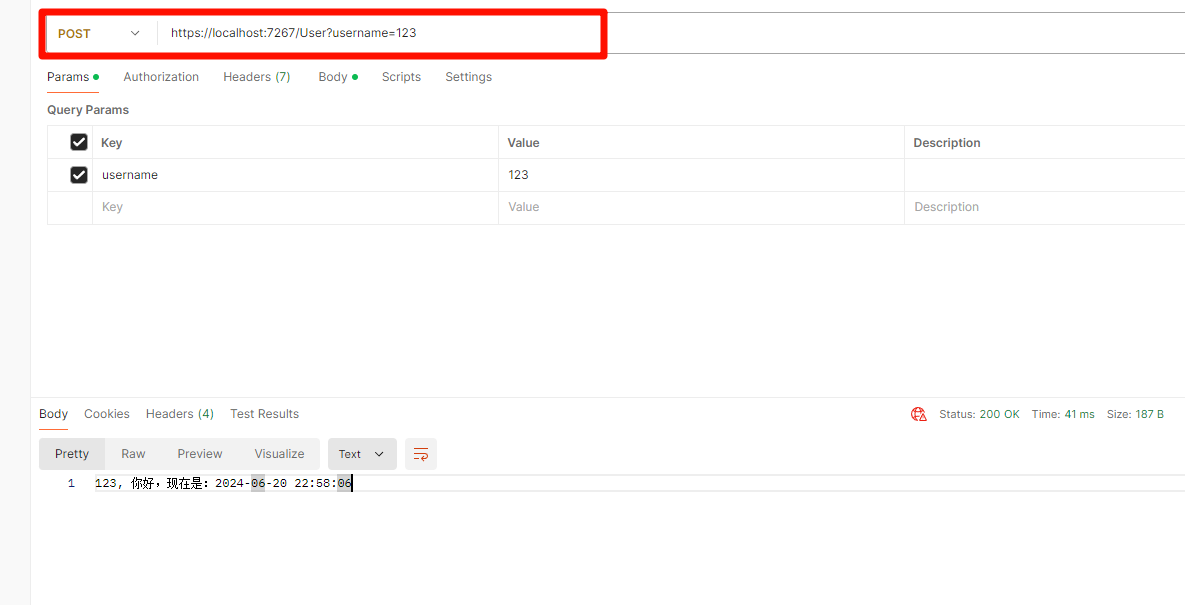
RotateRect::Points myPoints = { {233, 86}, {322, 106}, {214, 154}, {307, 176}, {286, 209}, {331, 183}, {346, 319}, {392, 294}, {356, 346}, {419, 311}, {419, 311}, {778, 1031}, {840, 995} };
RotateRect myRotateRect(myPoints);
myRotateRect.update();
创作不易,小小的支持一下吧!








![[Vulnhub] Sleepy JDWP+Tomcat+Reverse+Reverse-enginnering](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/b490c94cf3e2dffdd472ea0e61537e30.jpeg)

