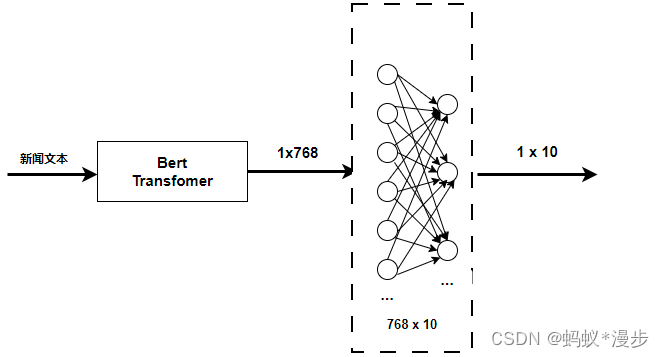
数据可视化案例
相关的技术:scrapy、pandas、pyecharts。
使用豆瓣电影中的数据来进行可视化,网址:豆瓣电影 Top 250 (douban.com)
一、网页数据分析
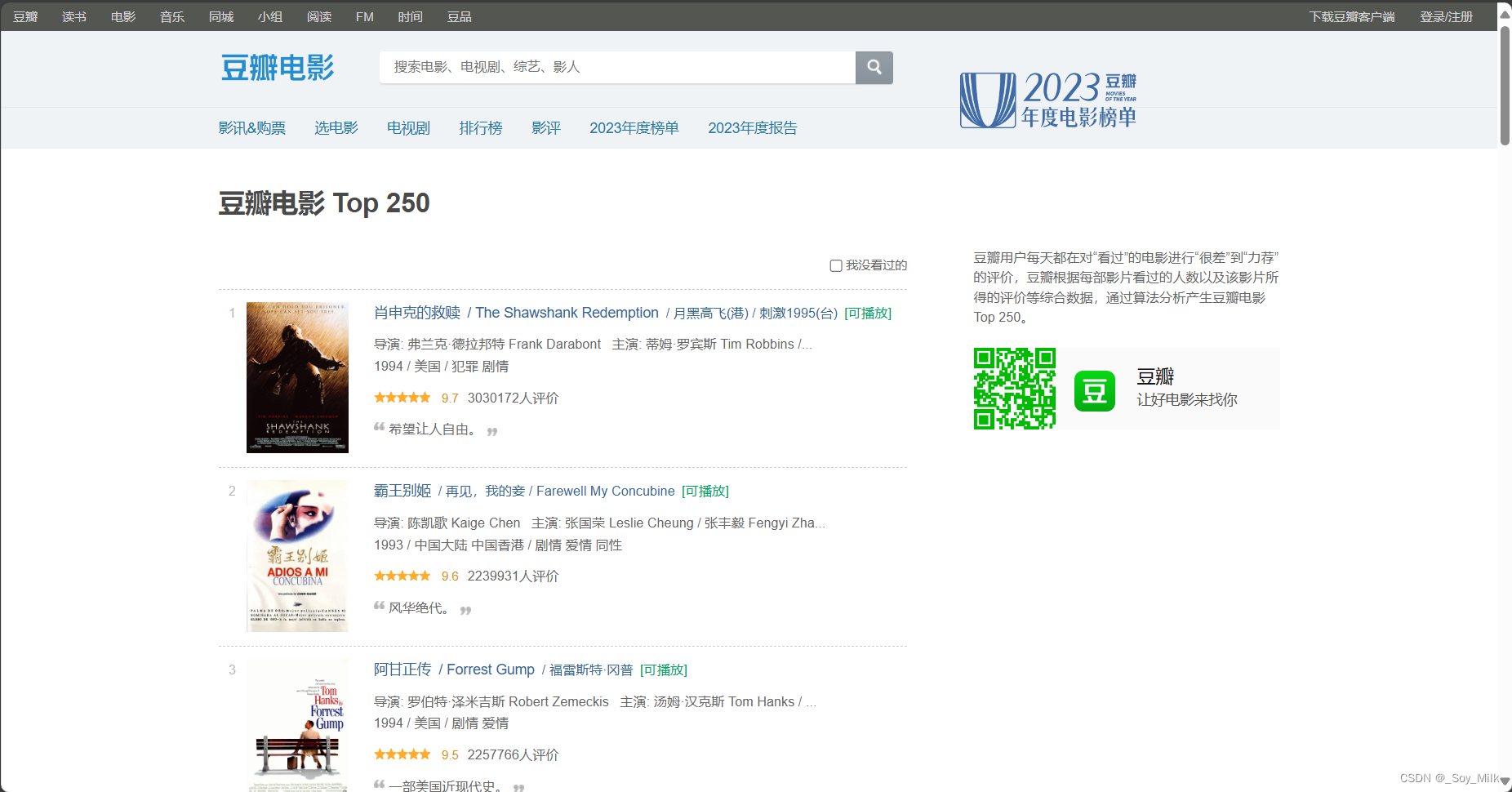
我们需要爬取的是豆瓣电影Top250网页每一页的电影名称、图片链接、导演、年份、国家、电影类型、电影评分这些数据。
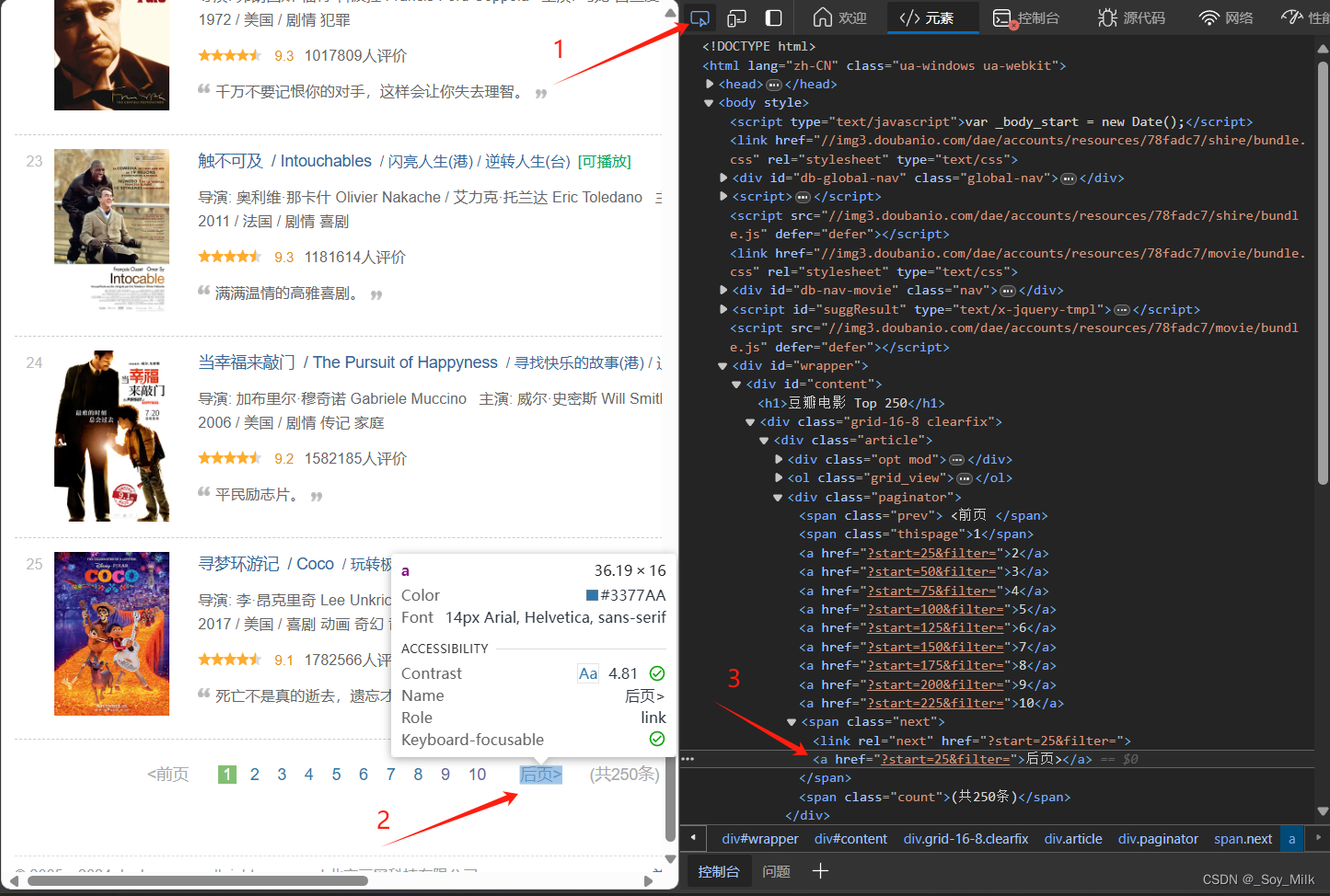
在待爬取的网页中,按下
F12键进入开发者模式,这样可以让我们很方便的找到网页中每一块数据对应的源码。
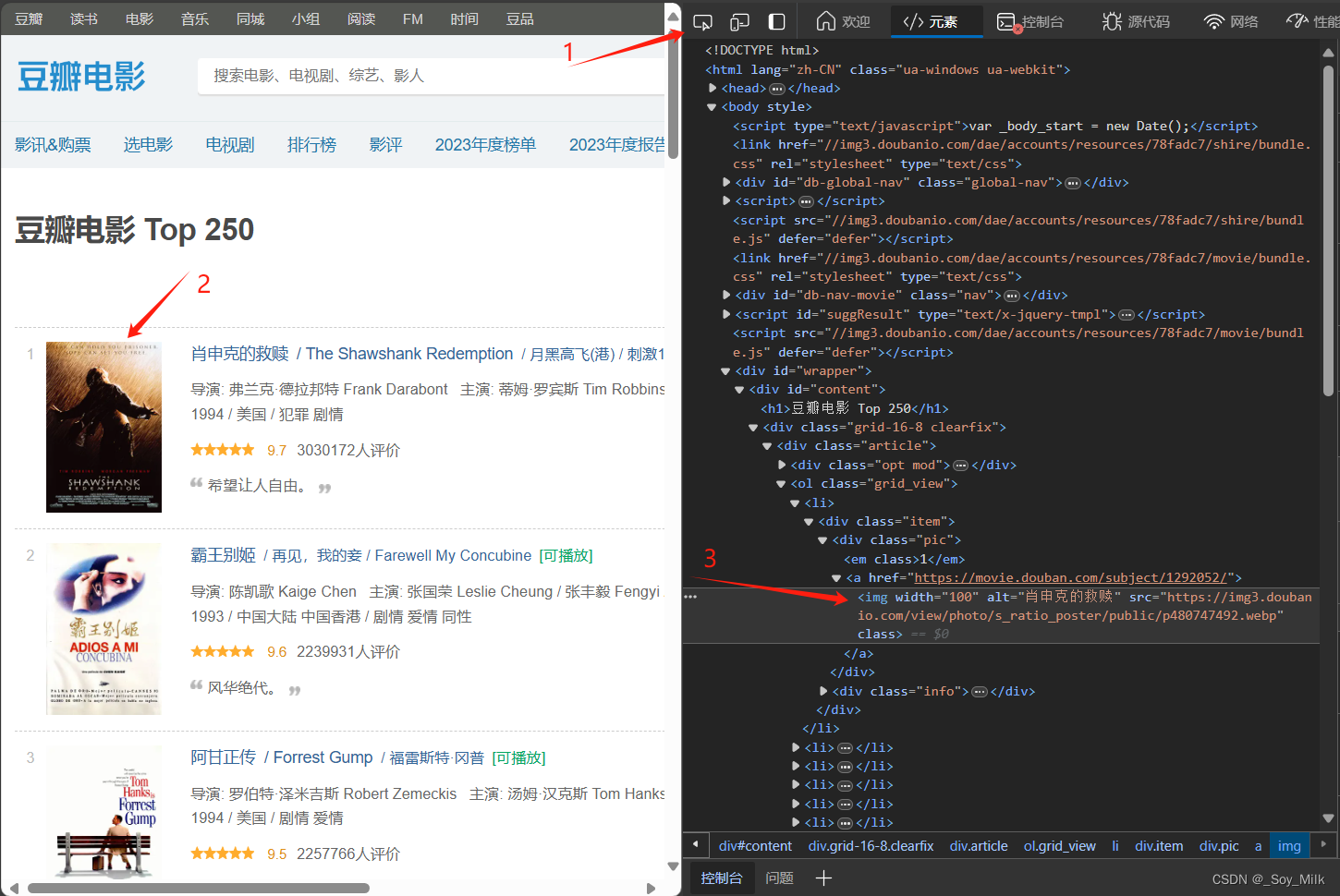
通过以上方式可以让我们很快的找到图片对应的标签,通过观察,我们可以找到每一个图片的链接都存放在<img>标签的src属性下。
同样的,我们可以找到电影名称所在的标签。
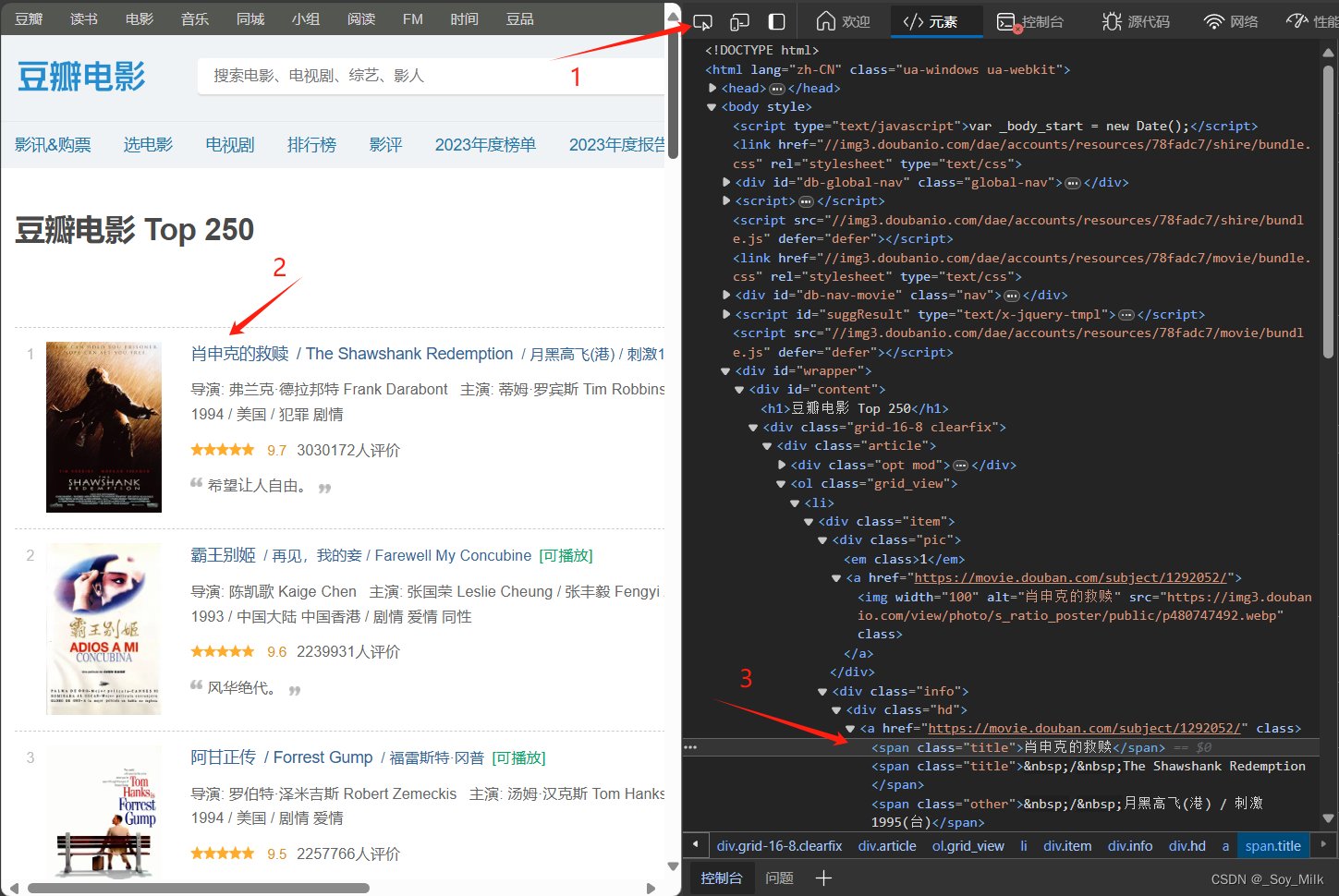
可以知道电影名称所在的位置是<span>标签的值。
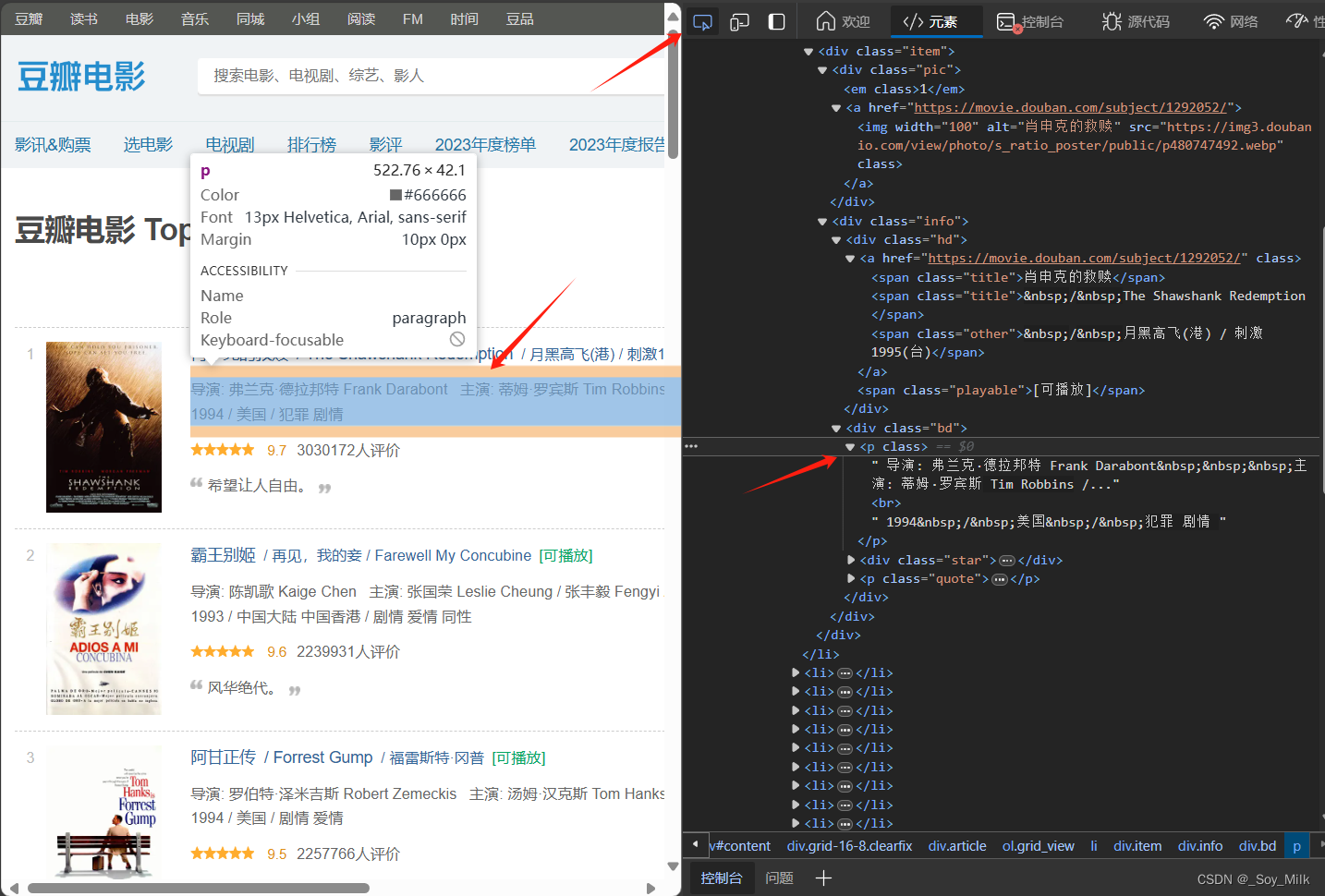
我们可以发现导演、年份、国家类型都在<p>标签下,这种情况我们就需要后期的处理了,先简单的得到<p>标签的数据,然后再通过字符串的分割、选取、剔除等操作可以得到最终我们需要的数据。
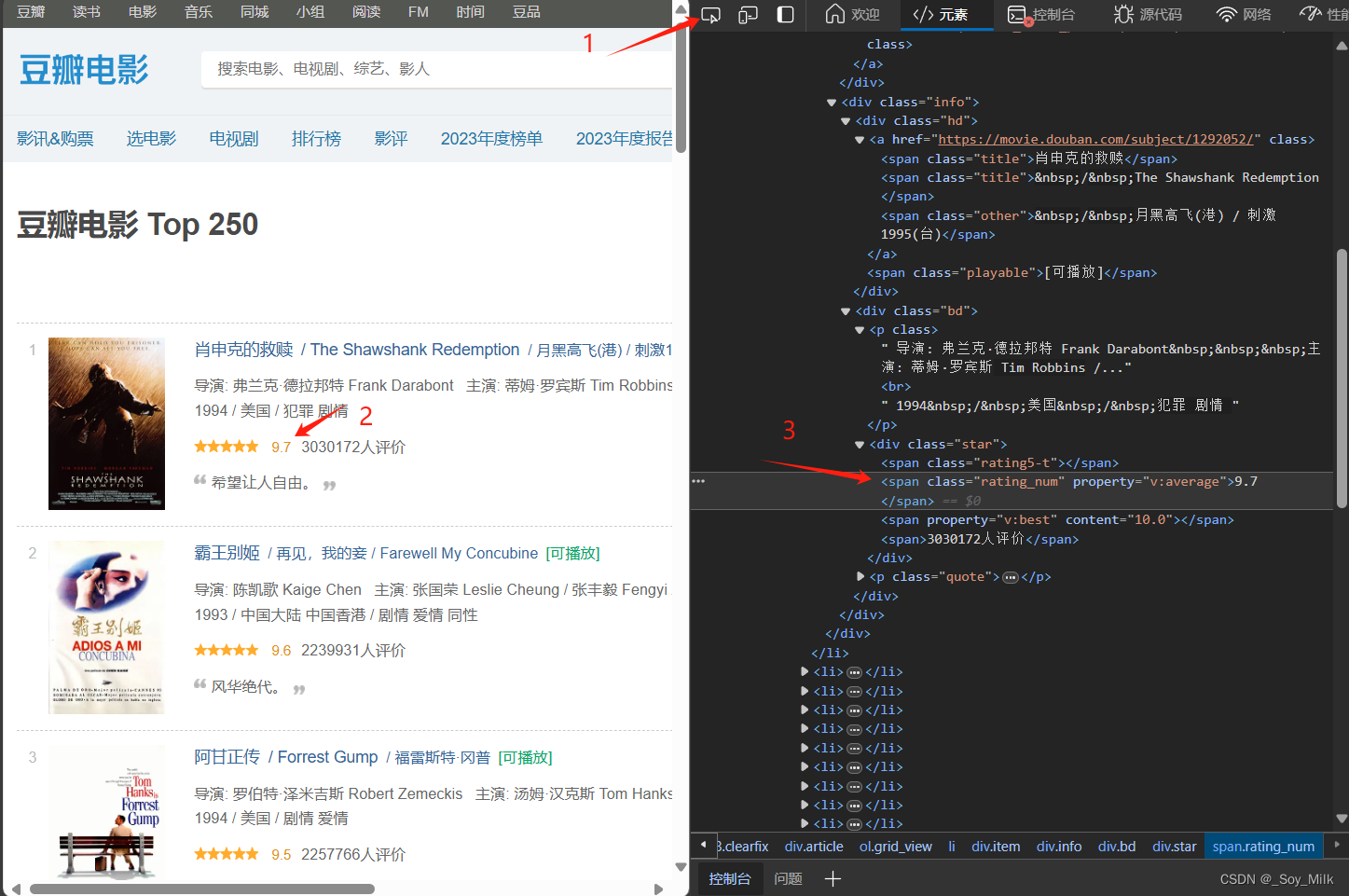
最后一个是评分标签,我们通过同样的方式可以找到评分在<span class="rating_num">标签中,并且是<span class="rating_num">标签的值。
由于我们需要的是每一页的标签,一个简单的可行的思路是找到后页标签对应的标签,这里找到的是<a>标签,<a>标签属性href的值对应的是下一页的网址,如果<a>标签的属性为空时,说明没有下一页了,可以停止爬取了。
通过以上分析,我们开始编写爬虫程序来爬取数据,这里我们使用scrapy爬虫框架来进行爬取数据。
二、数据爬取(获取数据)
1. 安装scrapy库
pip install scrapy -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
2. 初始化scrapy项目
scrapy startproject Douban
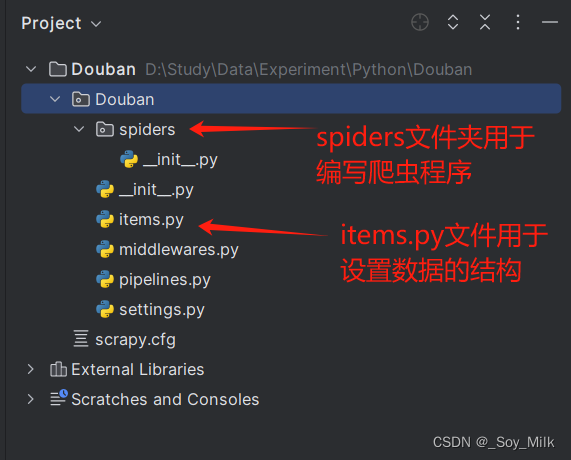
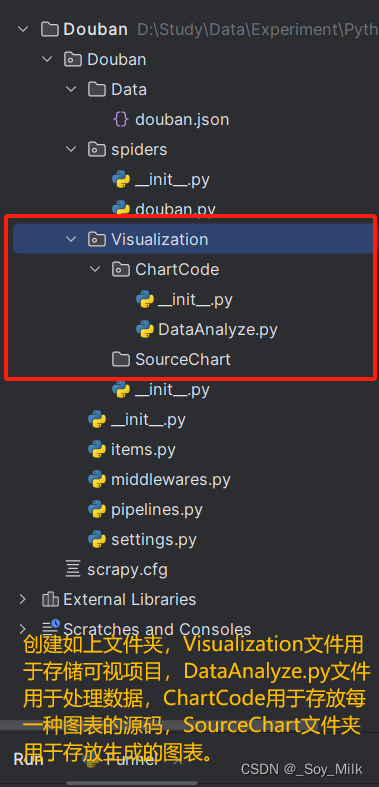
使用PyCharm打开项目,可以观察到项目的整体结构如下:
3. 设置数据结构
items.py文件
# Define here the models for your scraped items
#
# See documentation in:
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html
import scrapy
class DoubanItem(scrapy.Item):
imgUrl = scrapy.Field() # 图片链接
name = scrapy.Field() # 电影名称
author = scrapy.Field() # 导演名称
year = scrapy.Field() # 年份
country = scrapy.Field() # 国家
types = scrapy.Field() # 电影类型
score = scrapy.Field() # 电影评分
4. 创建爬虫程序
scrapy genspider douban "movie.douban.com" # douban是爬虫的名称, "movie.douban.com"是要爬取网址的域名
打开爬虫文件,更改带爬取的文件的网址:
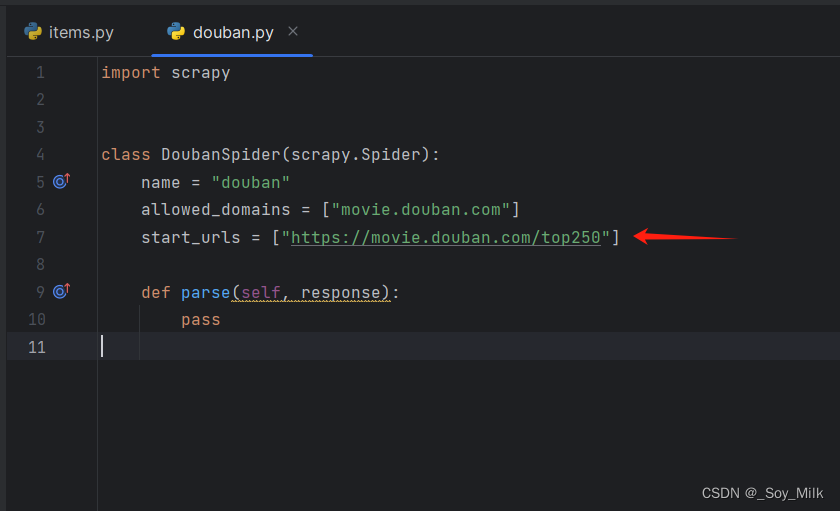
编写爬虫程序douban.py:
import scrapy
from ..items import DoubanItem
class DoubanSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "douban"
allowed_domains = ["movie.douban.com"]
start_urls = ["https://movie.douban.com/top250"]
def parse(self, response):
doubans = response.xpath("//ol[@class='grid_view']/li")
for douban in doubans:
item = DoubanItem()
item['name'] = douban.xpath("div[@class='item']/div[2]/div[1]/a/span/text()").extract_first()
item['imgUrl'] = douban.xpath("div/div[@class='pic']/a/@href").extract_first()
text = douban.xpath("div/div[@class='info']/div[@class='bd']/p/text()").extract()[1]
fs_text = douban.xpath("div/div[@class='info']/div[@class='bd']/p/text()").extract()[0]
item['author'] = fs_text.split(" ")[0].strip().split(" ")[1: -1]
item['score'] = douban.xpath(
"div/div[@class='info']/div[2]/div[@class='star']/span[2]/text()").extract_first()
c_start = text.find("/")
c_end = text.find("/", c_start + 1)
country = text[c_start + 1: c_end]
year = text[: c_start]
types = text[c_end:]
country_analyse = country.split(" ")
country_have = country_analyse[1].split(" ") if len(country_analyse) > 1 else country_analyse[0].split(" ")
item['country'] = country_have if country_have != [""] else ["中国大陆"]
item['year'] = year.split(" ")[0].strip()
item['types'] = types.split(" ")[1].strip().split(" ")
yield item
next_page = response.xpath("/html/body/div[3]/div[1]/div[1]/div[1]/div[2]/span[3]/a/@href").extract_first()
if next_page:
yield response.follow(next_page, self.parse)
配置settings.py文件:
- 首先设置代理
USER_AGENT:
# 第17行
USER_AGENT = "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/109.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
- 设置不服从
ROBOOTS协议:
ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = False # 第20行
5. 运行爬虫程序
scrapy crawl douban -o ./Data/douban.json
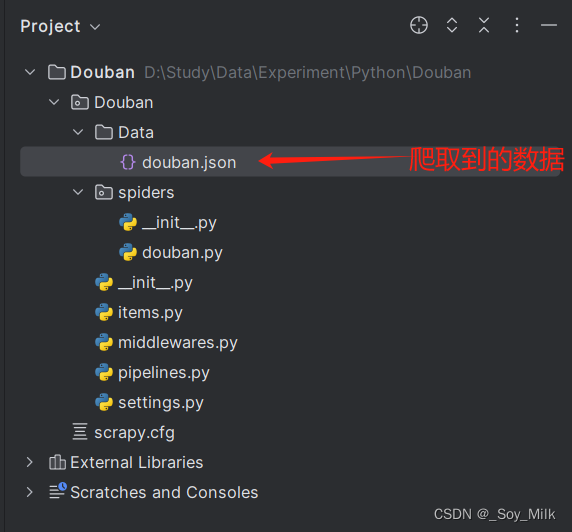
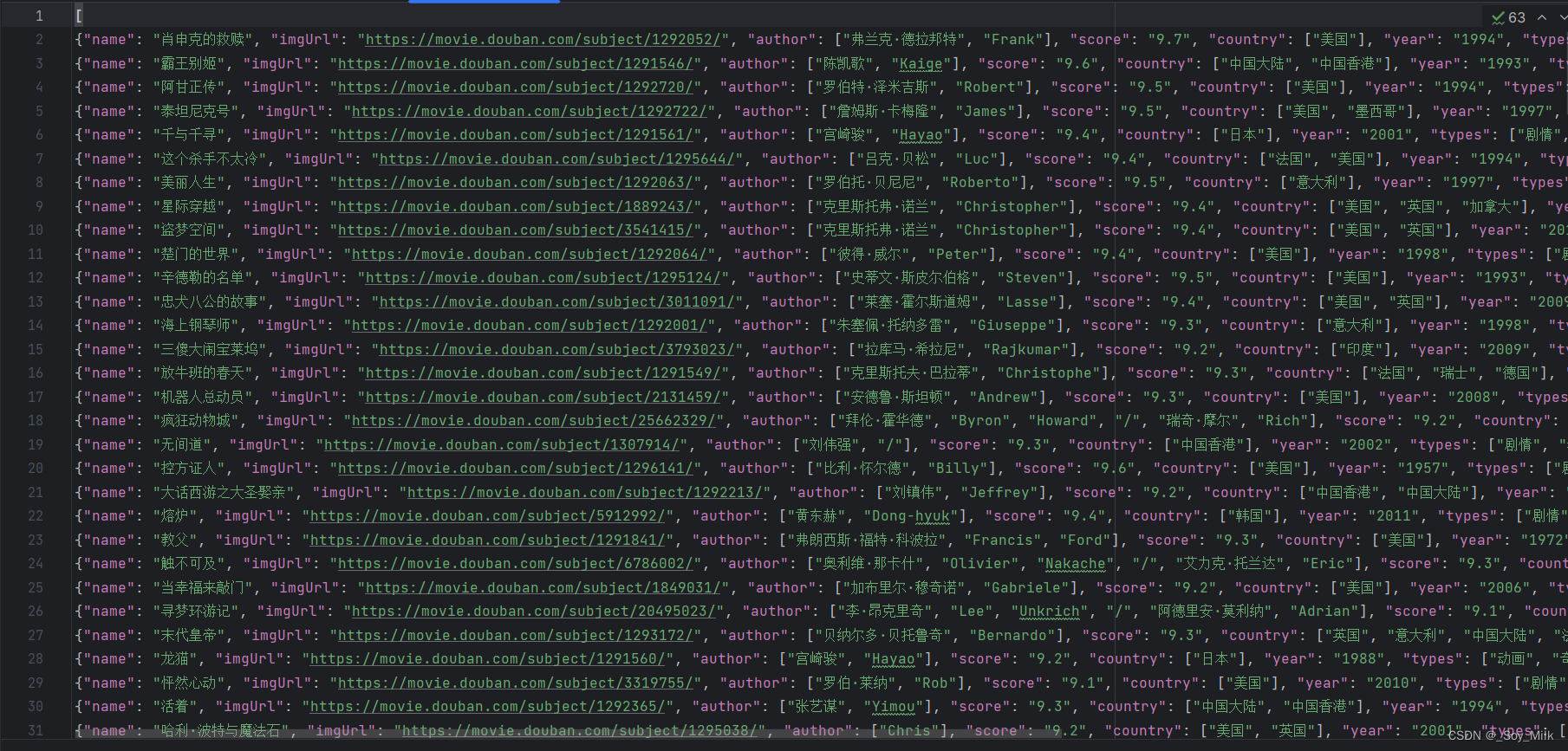
打开douban.json数据可以查看到爬取到的结果:
三、数据处理与可视化
数据处理部分,我们使用Pandas库来对数据进行处理,可视化部分,我们使用pyecharts库来进行数据可视化。
pyecharts参考网站:pyecharts
创建目录结构:
数据处理:
编写DataAnalyze.py文件
import json
import pandas as pd
path = '../Data/douban.json'
with open(path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
global data
data = json.load(file)
def YearNumTop_5() -> tuple:
'''
:return: 发布电影次数最多的前五名年份以及电影次数
'''
years = []
for movie in data:
years.append(movie['year'][:4])
# 统计数据出现的次数
y = pd.Series(years)
y_count = y.value_counts() # value_counts函数会统计次数并且进行自动的排序,降序
y_count = y_count.head(5)
# print(y_count)
x_list = y_count.index.tolist() # 将索引转换为列表
y_list = y_count.values.tolist() # 将值转换为列表
# print(x_list, y_list)
return (x_list, y_list)
def TpyeNum() -> tuple:
'''
:return: 电影类型及类型出现的次数
'''
types = []
for type in data:
types.extend(type['types'])
# print(types)
tp = pd.Series(types)
tp = tp.value_counts()[1: -2]
tp_label = tp.index.tolist() # tolist用于将pandas中的Series或DataFrame转换为列表对象
tp_count = tp.values.tolist()
# print(tp_label, tp_count)
return (tp_label, tp_count)
def YearMovies() -> tuple:
'''
:return: 年份,以及每一年的电影
'''
name = []
year = []
tree_dict = {}
for movie in data:
name.append(movie["name"])
year.append(movie['year'])
for n, y in zip(name, year):
# print(z)
# print(n, y)
if tree_dict.get(y) is None:
tree_dict[y] = [n] # 如果键不存在,初始化为列表
else:
tree_dict[y].append(n)
# 我们只取得前5年的数据
keys_sliced = list(tree_dict.keys())[0: 5]
tree_part = {key: tree_dict[key] for key in keys_sliced}
# print(keys_sliced, tree_part)
return (keys_sliced, tree_part)
def CountryNum() -> tuple:
'''
:return: 返回国家以及每个国家的电影数量
'''
country = []
for movie in data:
country.extend(movie['country'])
# print(country)
cou = pd.Series(country)
cou_sort = cou.value_counts()
country_ans = cou_sort.index.tolist()
count_ans = cou_sort.values.tolist()
# print(country_ans, count_ans)
return (country_ans, count_ans)
if __name__ == '__main__':
CountryNum()
可视化:
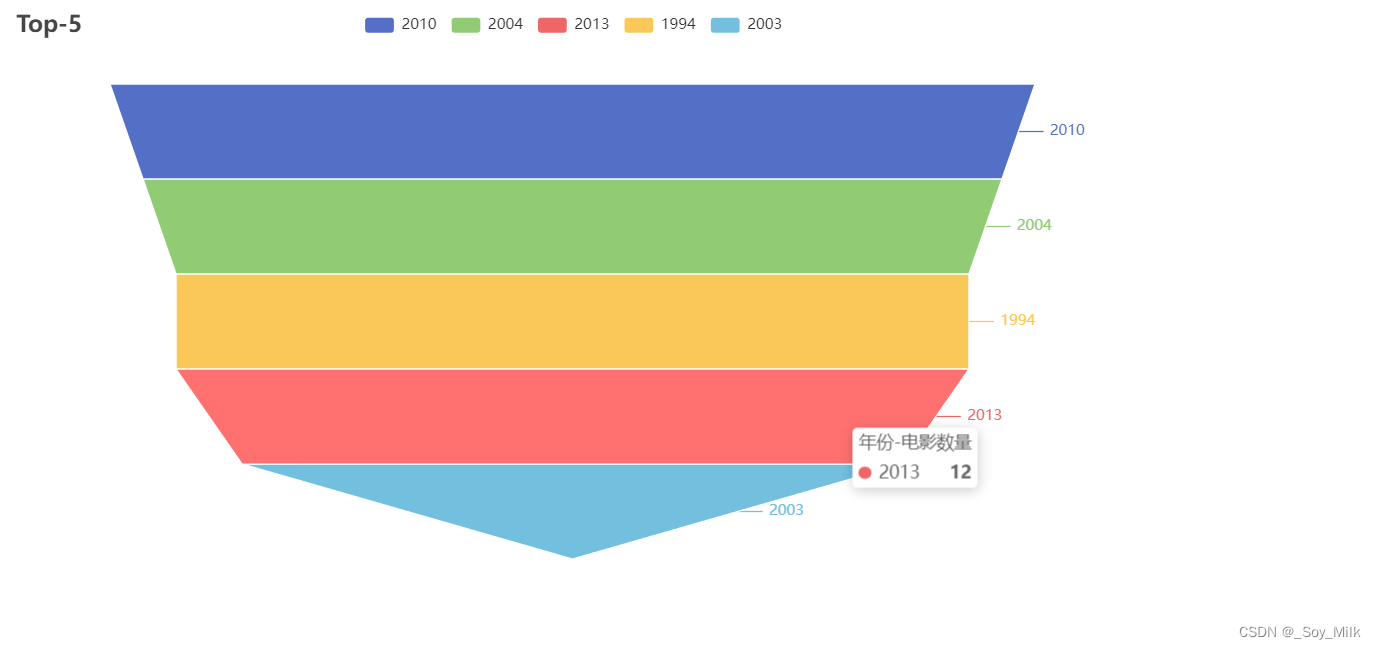
1. 锥形图
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Funnel
from DataAnalyze import YearNumTop_5
data = YearNumTop_5()
funnel_table = (
Funnel()
.add("年份-电影数量", [list(z) for z in zip(data[0], data[1])])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Top-5"))
.render("../SourceChart/Funnel.html")
)
2. 词云图
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import WordCloud
from pyecharts.globals import SymbolType
from DataAnalyze import TypeNum
label, count = TypeNum()
words = [(l, c) for l, c in zip(label, count)] # 使用列表生成式,生成元素为元组的列表
wordCloud = (
WordCloud()
.add("电影类型", words, word_size_range=[20, 100], shape=SymbolType.DIAMOND)
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Movie Type Distribution"))
.render("../SourceChart/WordCloud.html")
)

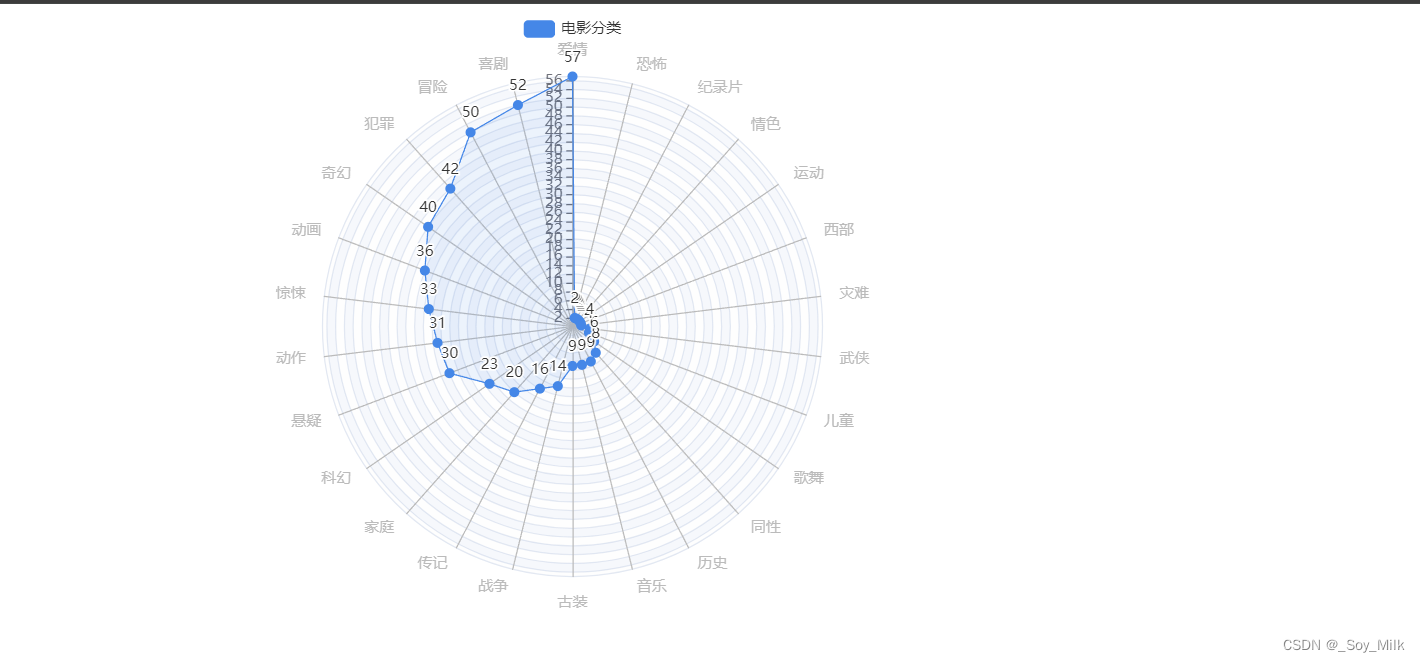
3. 雷达图
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Radar
from DataAnalyze import TypeNum
types = TypeNum()
data = [{"value": types[1], "name": "电影类型"}]
# 设置雷达图的取值范围,最大为57,最小为0
max = 57
min = 0
c_schema = [
{"name": name, "max": max, "min": min} for name in types[0]
]
radar = (
Radar()
.set_colors(["#4587E7"])
.add_schema(
schema=c_schema,
shape="circle",
center=["50%", "50%"],
radius="80%",
angleaxis_opts=opts.AngleAxisOpts(
min_=0,
max_=360,
is_clockwise=False,
interval=5,
axistick_opts=opts.AxisTickOpts(is_show=False),
axislabel_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False),
axisline_opts=opts.AxisLineOpts(is_show=False),
splitline_opts=opts.SplitLineOpts(is_show=False),
),
radiusaxis_opts=opts.RadiusAxisOpts(
min_=min,
max_=max,
interval=2,
splitarea_opts=opts.SplitAreaOpts(
is_show=True, areastyle_opts=opts.AreaStyleOpts(opacity=1)
),
),
polar_opts=opts.PolarOpts(),
splitarea_opt=opts.SplitAreaOpts(is_show=False),
splitline_opt=opts.SplitLineOpts(is_show=False),
)
.add(
series_name="电影分类",
data=data,
areastyle_opts=opts.AreaStyleOpts(opacity=0.1),
linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts(width=1),
)
.render("../SourceChart/Radar.html")
)
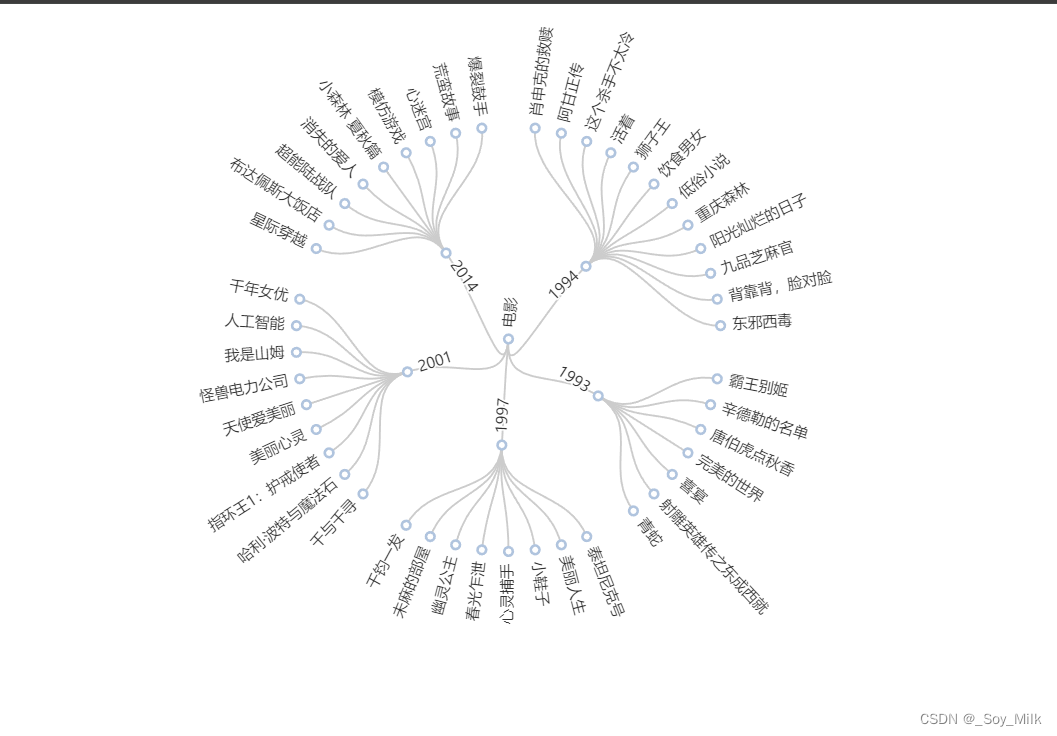
4. 树图
import pyecharts.options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Tree
from DataAnalyze import YearMovies
year, movie_data = YearMovies()
# 构造类似于递归字典的数据类型
for y in year:
movie_data[y] = [{"name": value, "children": 1} for value in movie_data[y]]
data = [{'name': y, 'children': movie_data[y]} for y in year]
data = {'name': "电影", 'children': data}
tree = (
Tree()
.add(
series_name="",
data=[data],
pos_top="18%",
pos_bottom="14%",
layout="radial",
symbol="emptyCircle",
symbol_size=7,
)
.set_global_opts(
tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts(trigger="item", trigger_on="mousemove")
)
.render("../SourceChart/Tree.html")
)
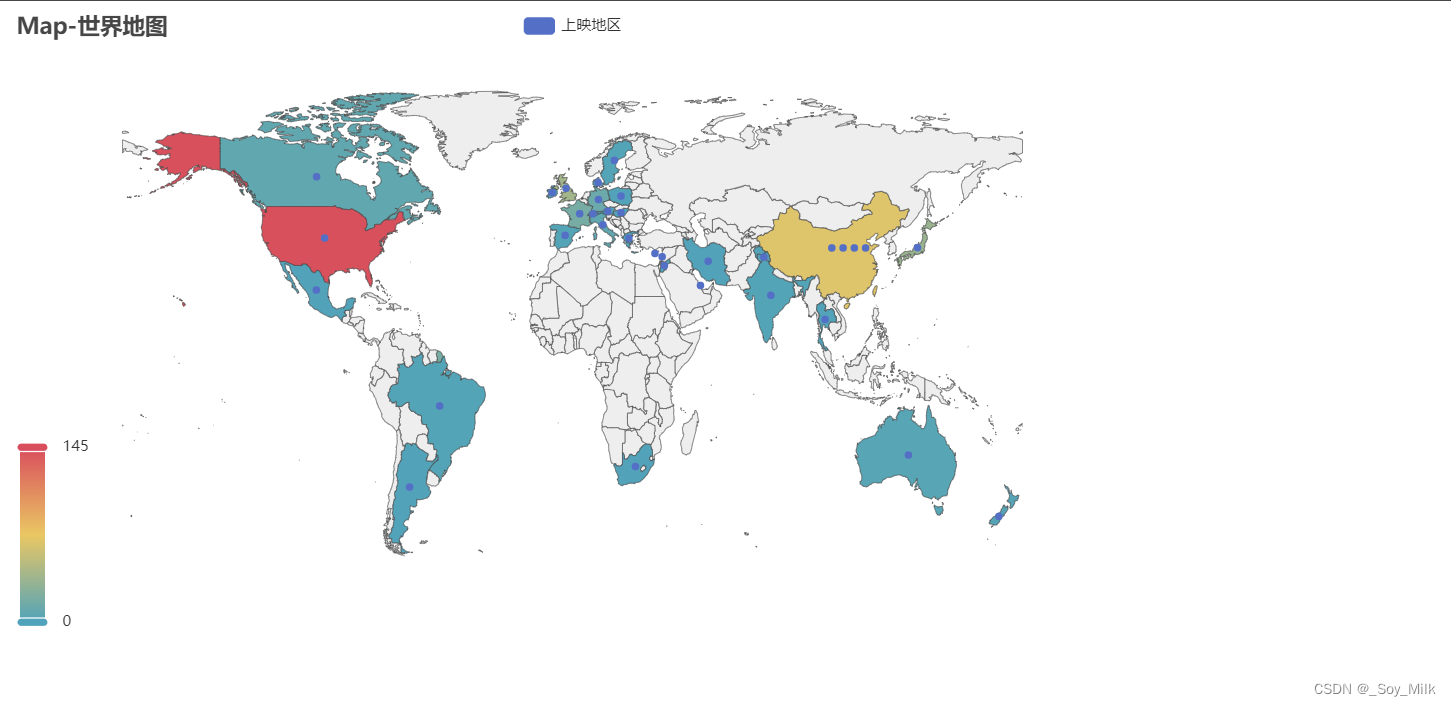
5. 地图
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Map
from DataAnalyze import CountryNum
from translate import Translator
# 实例话翻译类:从中文翻译为英文
translator = Translator(from_lang="Chinese", to_lang="English")
data = CountryNum()
# 对每一个数据进行翻译
for idx, cou in enumerate(data[0]):
if cou == "美国":
data[0][idx] = "United States"
continue
if cou == "英国":
data[0][idx] = "United Kingdom"
continue
if cou in ["中国大陆", "中国香港", "中国台湾", "1964(中国大陆)"]:
cou = "中国"
target = translator.translate(f'{cou}')
data[0][idx] = target
if idx % 5 == 0:
print(target)
map_table = (
Map()
.add("上映地区", [list(z) for z in zip(data[0], data[1])], "world")
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False))
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Map-世界地图"),
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(max_=145),
)
.render("../SourceChart/Map.html")
)
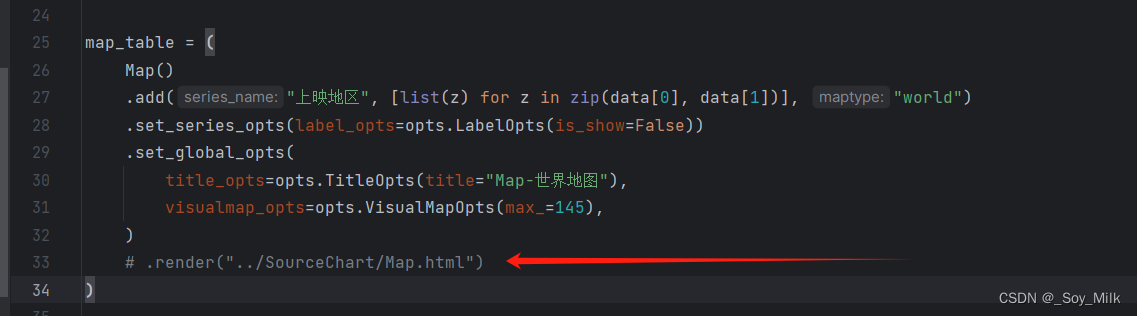
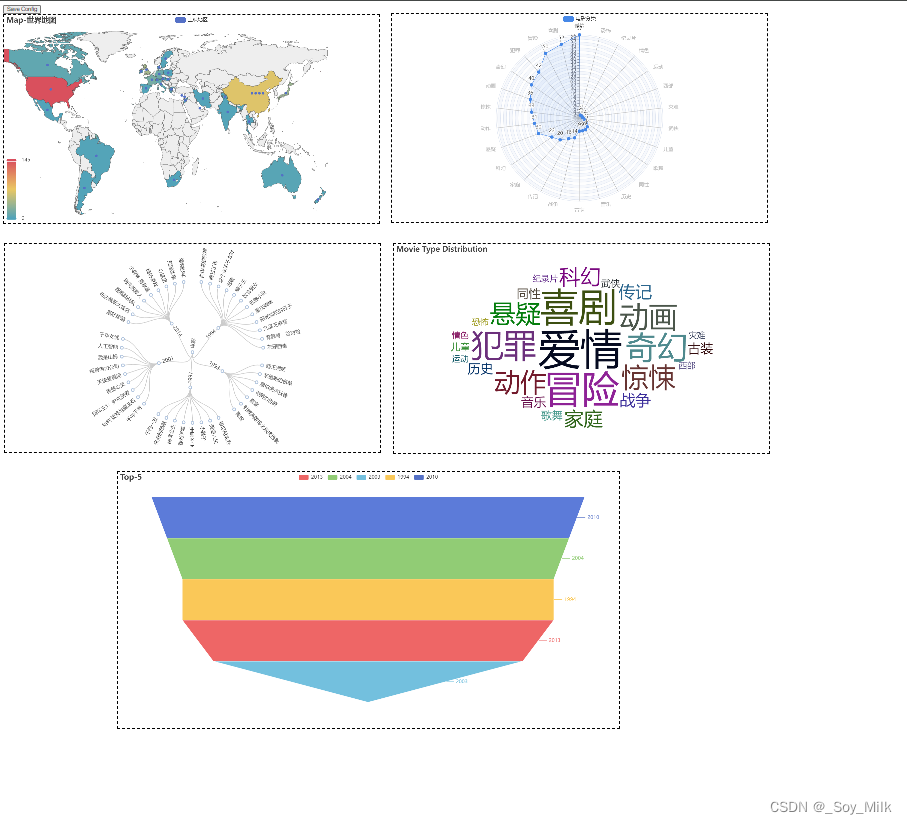
5. 将所有图汇总到一张网页上
如果要把所有图表汇总到一个网页上,那么需要将每一个绘制图的./render给注释掉,类似与下面这样,否则会将图表识别为字符串类型的数据。
Summary.py
from pyecharts.charts import Page
from Funnel import funnel_table
from Map import map_table
from Radar import radar
from Tree import tree
from WordCloud import wordCloud
# 初始化网页
page = Page(layout=Page.DraggablePageLayout)
page.add(map_table) # 添加地图
page.add(radar) # 添加雷达图
page.add(tree) # 添加树图
page.add(wordCloud) # 添加词云图
page.add(funnel_table) # 添加漏斗图
page.render("../SourceChart/Summary.html")
声明:本项目只用于学习,禁止用于任何非法的行为。—— 2024.6.16