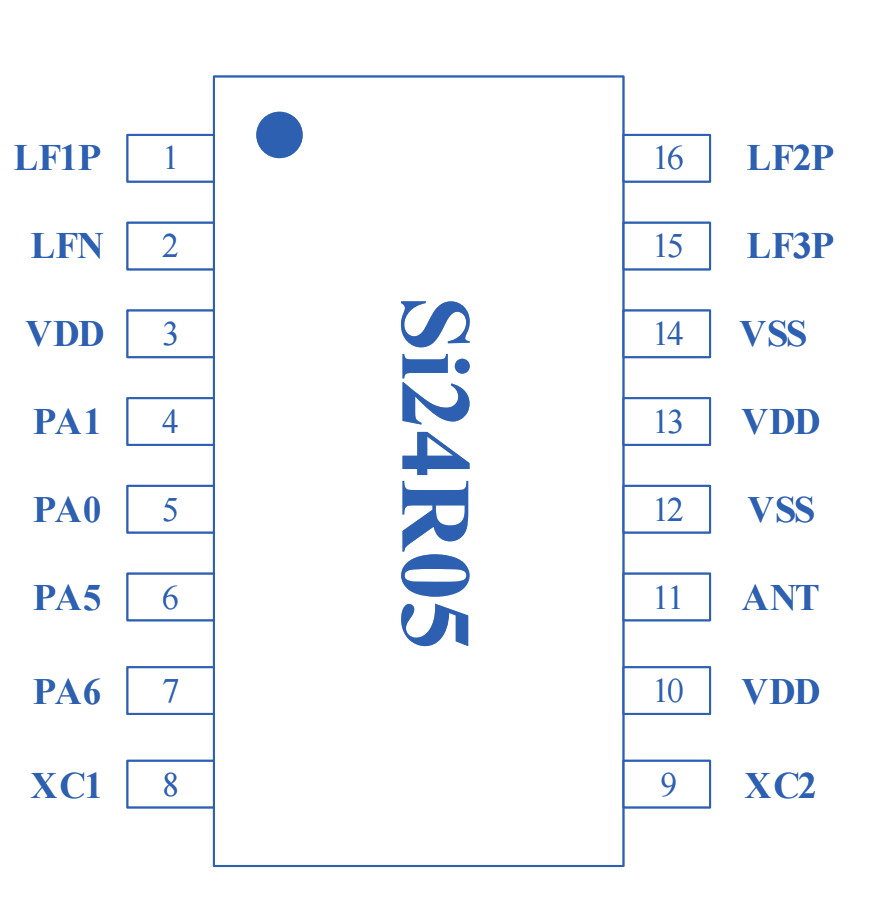
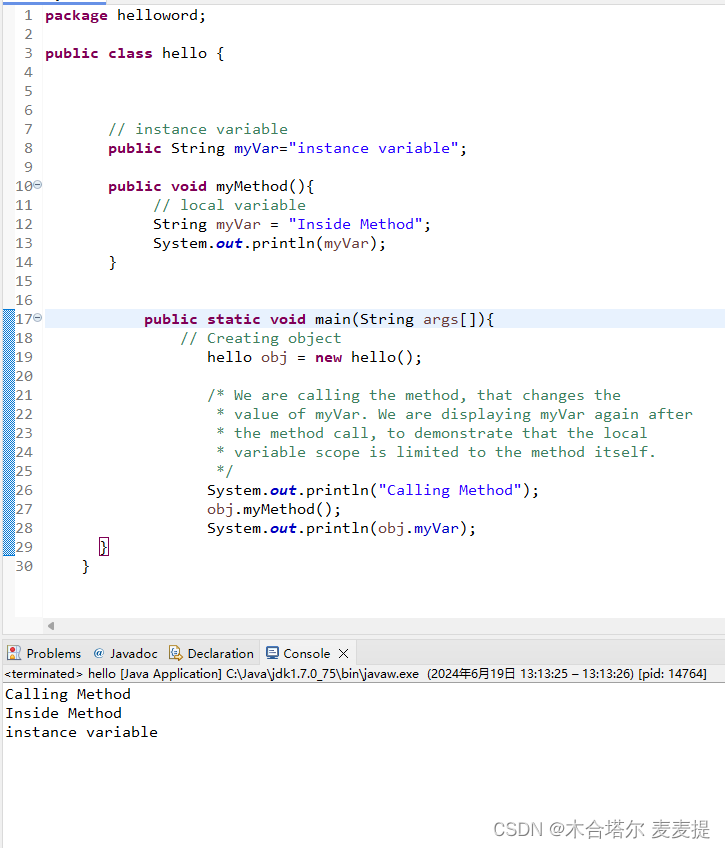
6.6 Git的分支状态存储
有时,当我们在项目的一部分上已经工作一段时间后,所有东西都进入了混乱的状态,而这时想要切换到另一个分支做一点别的事情,则必须将当前工作空间所做的操作提交到版本库,否则Git不允许切换分支。
当前的操作还不足以生成一次版本快照,此时我们就可以使用git stash命令,将当前工作状态存储起来,然后再切换到其他分支工作,最终工作完毕后切回当前分支,从Git存储中取出之前的工作内容。
6.6.1 git stash命令
git stash命令能够将当前工作目录中尚未提交的所有更改(包括暂存区和未暂存的修改)临时存储到stash堆栈中,从而让用户在不影响当前工作进度的前提下,轻松切换到其他分支处理问题、合并代码或恢复到干净的工作状态。
git stash命令的语法如下表所示。
| 命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| git stath | 将当前工作空间的状态保存 |
| git stash list | 查看当前Git中存储的所有状态 |
| git stash apply {stashName} | 根据存储名称读取Git存储 |
| git stash drop {stashName} | 根据存储名称删除Git存储 |
| git stash save “日志信息” | 将当前工作空间的状态保存并指定一个日志信息 |
| git stash pop | 读取stash堆栈中的第一个存储,并将该存储从stash堆栈中移除 |
| git stash show [-p] {stashName} | 查看指定存储与未建立存储时的差异 -p:显示详细差异 |
| git stash branch {branchName} [stashName] | 创建并切换到一个新分支来读取指定的存储 stashName:存储的名称,默认情况下读取stash堆栈中栈顶的存储 |
6.6.2 Git存储的基本使用
接下来我们通过案例来演示一下git stash命令的应用场景和使用方法。
- 搭建测试环境
(1)初始化项目环境。
rm -rf ./* .git
git init
echo '111-master' >> aaa.txt
git add ./
git commit -m '111-master' ./
git checkout -b b1
echo '111-b1' >> aaa.txt
git commit -m '111-b1' ./
echo '222-b1' >> aaa.txt
git commit -m '222-b1' ./
git log --oneline --graph --all
* 8d562c8 (HEAD -> b1) 222-b1 # b1的位置
* 8f29a61 111-b1
* 07f58ec (master) 111-master # master的位置
(2)编辑文件,编辑完了后还不想提交,此时接收到了新的"临时任务",想要切换到其他分支继续操作,发现切换失败。
echo '333-b1' >> aaa.txt # 编辑文件
git status # 查看工作空间的状态
On branch b1
Changes not staged for commit: # 有修改操作还未追踪
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: aaa.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
git checkout master # 切换到master失败
error: Your local changes to the following files would be overwritten by checkout:
aaa.txt
Please commit your changes or stash them before you switch branches.
Aborting
- 使用存储状态
(1)使用Git存储将当前状态存储起来。
git stash list # 查看当前Git存储列表,发现列表为空
git stash # 使用Git存储,将当前状态存储起来
warning: LF will be replaced by CRLF in aaa.txt.
The file will have its original line endings in your working directory
Saved working directory and index state WIP on b1: 8d562c8 222-b1
git stash list # 查看当前Git存储列表
stash@{0}: WIP on b1: 8d562c8 222-b1
cat aaa.txt # 使用Git将当前状态存储起来后,文件内容变为了未更改前的内容
111-master
111-b1
222-b1
git status # 再次查看git的状态,发现工作空间正常
On branch b1
nothing to commit, working tree clean
# 查看日志,发现使用Git存储也会产生日志,而且还产生了两个日志
git log --oneline --graph --all
* 082f406 (refs/stash) WIP on b1: 01ca592 222-b1
|\
| * c613227 index on b1: 01ca592 222-b1
|/
* 01ca592 (HEAD -> b1) 222-b1
* 1337456 111-b1
* f828bbd (master) 111-master
(2)当前状态被Git存储了,所以当前的工作空间也是正常的,因此可以切换到其他分支继续操作。
git checkout master # 切换分支到master
Switched to branch 'master'
cat aaa.txt # 查看master分支的内容
111-master
echo "222-master" >> aaa.txt
git commit -m '222-master' ./
git log --oneline --graph --all
* 02e3139 (HEAD -> master) 222-master
| * 36e214a (refs/stash) WIP on b1: 8d562c8 222-b1
| |\
| | * 8ba949c index on b1: 8d562c8 222-b1
| |/
| * 8d562c8 (b1) 222-b1
| * 8f29a61 111-b1
|/
* 07f58ec 111-master
- 读取存储状态
等到"临时任务"处理完后,我们可以切换回b1分支,并将上一次使用Git存储的状态读取出来,示例代码如下:
git checkout b1 # 切换回b1分支
cat aaa.txt # 查看文件内容,依旧是没有编辑前的状态
111-master
111-b1
222-b1
git stash list # 查看Git存储的状态
stash@{0}: WIP on b1: 8d562c8 222-b1
git stash apply stash@{0} # 读取状态
On branch b1
Changes not staged for commit: # 读取成功后回到我们当初的状态(有修改操作还未追踪)
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: aaa.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
cat aaa.txt # 查看文件内容,将文件内容还原回来了
111-master
111-b1
222-b1
333-b1
git commit -m "333-b1" ./
git log --oneline --graph --all
* 1c951a1 (HEAD -> b1) 333-b1
| * 02e3139 (master) 222-master
| | * 36e214a (refs/stash) WIP on b1: 8d562c8 222-b1
| |/|
|/| |
| | * 8ba949c index on b1: 8d562c8 222-b1
| |/
|/|
* | 8d562c8 222-b1
* | 8f29a61 111-b1
|/
* 07f58ec 111-master
- 存储状态的删除
Git存储被读取之后状态并不会被删除,我们可以手动删除存储状态,示例代码如下:
git stash list # 查看Git存储状态,发现依旧存在
stash@{0}: WIP on b1: 8d562c8 222-b1
git stash drop stash@{0} # 手动删除状态
Dropped stash@{0} (36e214a29ab7ac590b1c6089c9d25d4576affae6)
# 查看Git存储的状态,发现没有了
git stash list
# 查看日志,日志也被整理了
git log --oneline --graph --all
* 1c951a1 (HEAD -> b1) 333-b1
* 8d562c8 222-b1
* 8f29a61 111-b1
| * 02e3139 (master) 222-master
|/
* 07f58ec 111-master
6.6.3 Git存储的其他用法
stash堆栈是一个典型的“栈”数据结构,栈的特点是先进先出,因此当stash堆栈中存储了多个状态时那么最先存进去的状态在最底部,最后存储的状态在最顶部,如图所示。
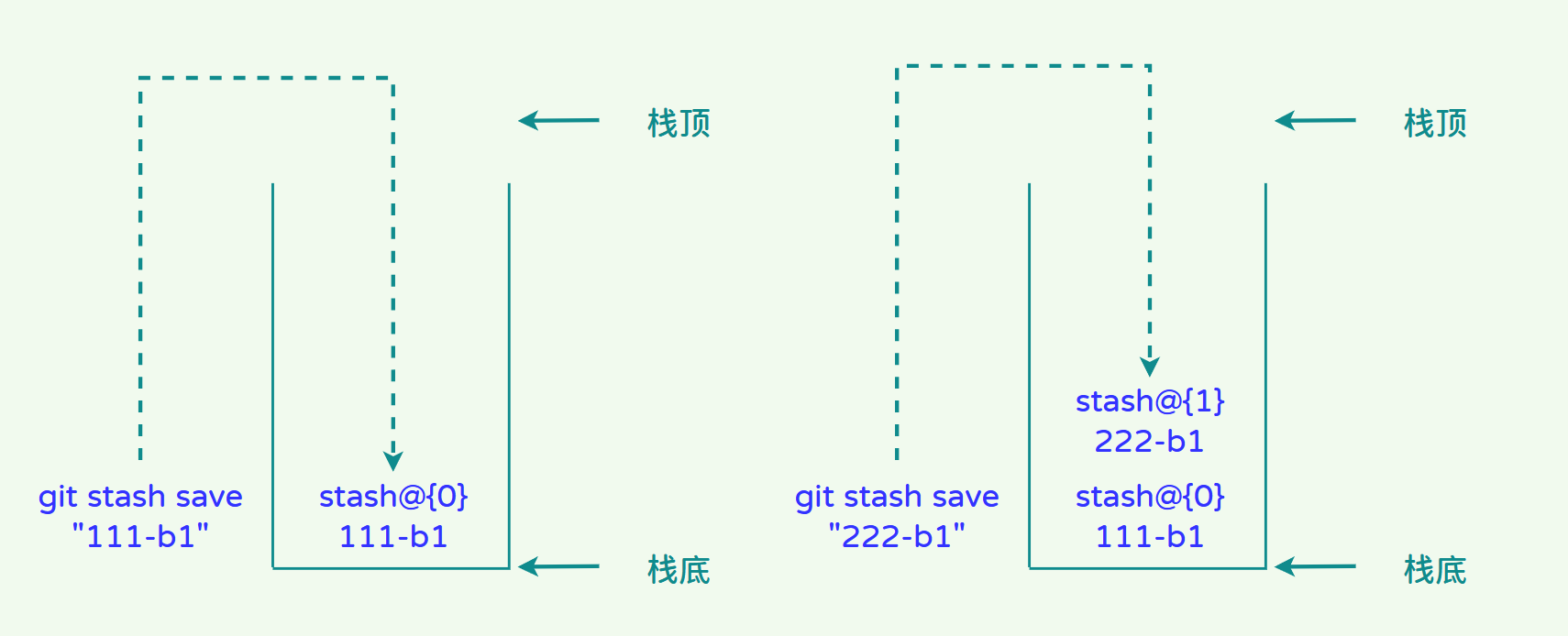
接下来我们来学习一下Git存储关于查看存储状态、弹栈存储状态、基于存储创建分支等用法。为了方便测试,我们建立一个新的测试仓库来测试。
- 搭建测试环境
(1)建立测试仓库。
rm -rf ./* .git
git init
echo '111-master' >> aaa.txt
git add ./
git commit -m '111-master' ./
git checkout -b b1
echo '111-b1' >> aaa.txt
git commit -m '111-b1' ./
(2)使用状态存储,存储两个状态。
echo "222-b1" >> aaa.txt # 编辑文件
git stash save "222-b1" # 使用存储状态
git stash list # 查看所有的存储状态
stash@{0}: On b1: 222-b1
git stash apply stash@{0} # 应用存储状态
git stash list # 应用了存储状态之后存储状态依然存在于stash堆栈中
stash@{0}: On b1: 222-b1
cat aaa.txt # 工作空间的内容也变回来了
111-master
111-b1
222-b1
git commit -m '222-b1' ./ # 提交
git log --oneline --graph --all
* 8fd2fee (HEAD -> b1) 222-b1
| * 5af855e (refs/stash) On b1: 222-b1
|/|
| * a30270e index on b1: 627154a 111-b1
|/
* 627154a 111-b1
* 0398907 (master) 111-master
echo "333-b1" >> aaa.txt # 编辑文件
git stash save "333-b1" # 使用存储状态
git stash list # 查看stash堆栈中所有的存储状态
stash@{0}: On b1: 333-b1
stash@{1}: On b1: 222-b1
- 查看存储状态
stash是一个栈的数据结构,因此我们先存储进来的状态是在最底部,最顶部为最近一次存储进来的状态。
git stash show stash@{0} # 查看stash@{0}存储状态
aaa.txt | 1 +
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) # 做了插入一行的操作
git stash show stash@{1} # 查看stash@{1}存储状态
aaa.txt | 1 +
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) # 做了插入一行的操作
git stash show -p stash@{0} # 查看stash@{0}存储状态的详细信息
diff --git a/aaa.txt b/aaa.txt
index 0dd56f7..b1f5002 100644
--- a/aaa.txt
+++ b/aaa.txt
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
111-master
111-b1
222-b1
+333-b1 # 相比较没有使用存储状态之前新增了这一行
git stash show -p stash@{1} # 查看stash@{1}存储状态的详细信息
diff --git a/aaa.txt b/aaa.txt
index cd728b7..0dd56f7 100644
--- a/aaa.txt
+++ b/aaa.txt
@@ -1,2 +1,3 @@
111-master
111-b1
+222-b1 # 相比较没有使用存储状态之前新增了这一行
- 弹栈stash
使用git stash apply命令只是读取指定的状态,该状态并没有从stash堆栈中删除。如果想要使用状态后将其删除可以使用git stash pop命令。git stash pop命令总是读取stash堆栈顶部的状态,然后将其移除,示例代码如下:
git status # 查看当前存储状态
On branch b1
nothing to commit, working tree clean
cat aaa.txt # 当前工作空间的内容
111-master
111-b1
222-b1
git stash pop # 使用弹栈stash,读取栈顶的存储状态并移除
On branch b1
Changes not staged for commit: # 工作空间的状态变为了使用存储状态前的
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: aaa.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
Dropped refs/stash@{0} (33a16b3dce96cff4456ca0bd593d425572ecb19c)
cat aaa.txt # 工作空间恢复了
111-master
111-b1
222-b1
333-b1
git stash list # 查看存储状态,只剩一个了
stash@{0}: On b1: 222-b1
git commit -m '333-b1' ./
[b1 d202b34] 333-b1
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
- 基于存储状态创建分支
示例代码:
git log --oneline --all --graph
* d202b34 (HEAD -> b1) 333-b1
* 8fd2fee 222-b1
| * 5af855e (refs/stash) On b1: 222-b1
|/|
| * a30270e index on b1: 627154a 111-b1
|/
* 627154a 111-b1
* 0398907 (master) 111-master
git stash list # 只有一个分支状态
stash@{0}: On b1: 222-b1
# 将stash顶部的状态弹出,基于该状态创建一个分支,并切换到该分支
git stash branch test stash@{0}
Switched to a new branch 'test'
On branch test
Changes not staged for commit: # test分支
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: aaa.txt
cat aaa.txt
111-master
111-b1
222-b1
git stash list # 已经没有了任何的状态
git log --oneline --all --graph
* d202b34 (b1) 333-b1
* 8fd2fee 222-b1
* 627154a (HEAD -> test) 111-b1 # 已经切换test分支了
* 0398907 (master) 111-master
6.6.4 Git存储与暂存区
我们之前测试的操作都是未添加到暂存区的操作然后使用git stash将其存储起来,实际上,就算是某个操作已经添加到暂存区了也可以使用Git存储将其存储起来,然后工作空间变为“noting to commit”状态。
需要注意的是,使用git stash命令将当前状态存储起来后虽然可以将当前工作空间的暂存区变为“noting to commit”状态,但是后期将该存储读取出来后,暂存区并不会回到之前的状态。
我们通过一个实际案例来演示一遍。
(1)创建一个新的测试仓库。
git log --oneline --all
38124a1 (HEAD -> master, b1) 111
(2)编辑操作,然后将操作添加到暂存区,最后使用git stash命令将当前状态存储起来。
echo "222" >> aaa.txt # 编辑文件
git add ./ # 添加到暂存区
git status # 查看当前工作空间的状态
On branch master
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
modified: aaa.txt
git ls-files -s # 查看暂存区的内容
100644 a30a52a3be2c12cbc448a5c9be960577d13f4755 0 aaa.txt
# 查看该Blob对象的内容
git cat-file -p a30a52a3be2c12cbc448a5c9be960577d13f4755
111
222
git stash save 'master-222' # 使用Git状态存储,将当前状态存储起来
git status # 查看当前工作空间的状态
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean
git ls-files -s
100644 58c9bdf9d017fcd178dc8c073cbfcbb7ff240d6c 0 aaa.txt
# 查看暂存区的内容,发现暂存区的内容回到了没有编辑前的状态
git cat-file -p 58c9bdf9d017fcd178dc8c073cbfcbb7ff240d6c
111
(3)读取状态,然后查看暂存区的内容,发现并没有回到使用git stash命令前的状态。
git stash pop # 获取顶部的存储状态
# 工作空间变为了"Changes not staged for commit"而不是"Changes to be committed"
# 意味着没有该操作没有添加到暂存区
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: aaa.txt
cat aaa.txt # 查看工作空间的状态(已经回到了使用git stash命令之前的状态)
111
222
git ls-files -s # 查看暂存区的内容
100644 58c9bdf9d017fcd178dc8c073cbfcbb7ff240d6c 0 aaa.txt
# 查看该文件的内容,发现并没有回到使用git stash命令前的状态
git cat-file -p 58c9bdf9d017fcd178dc8c073cbfcbb7ff240d6c
111
6.6.5 Git存储的原理
- 使用Git存储
在使用git stash命令后,Git直接将当前工作空间的更改添加到暂存区,然后提交。中途生成了Blob对象、Tree对象、Commit对象等三类对象,用于存储在执行stash命令之前对工作空间的修改。
其中Commit对象会生成2次,第1次指向原来的Tree对象,即没有执行stash之前的Tree对象。第2次指向新的Tree对象,即执行了stash命令之后的Tree对象。之后再将暂存区改回原来的样子(执行git stash命令之前的样子)。在这个过程中,Blob对象生成了1个,Tree对象生成了1个,Commit对象生成了2个。
由于当前工作空间的操作均已提交,因此当前工作空间的状态自然为nothing to commit状态,然后就可以切换到其他分支了。
当使用git stash命令以后,会产生两个Commit对象,其还会在.git/refs/目录创建一个名为stash的文件,该文件保存着最新Commit对象的hash值(执行git stash命令后生成的那个新Commit对象),如下图所示。
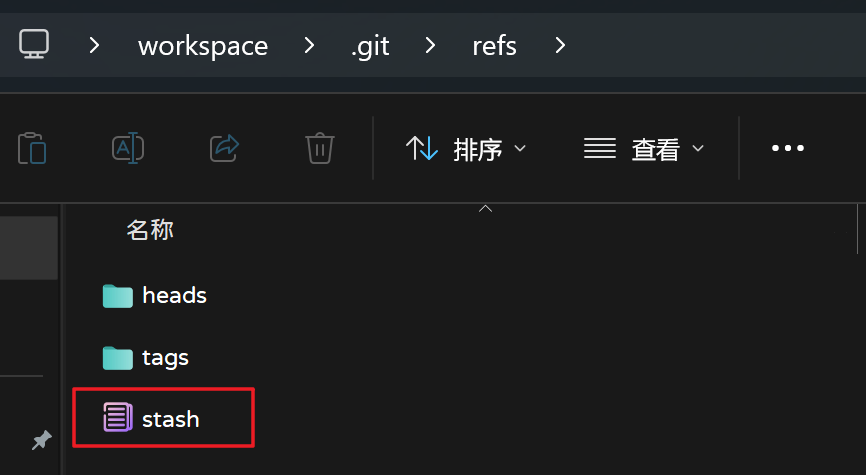
- 读取Git存储状态的原理
当使用git stash apply {stashName}或git stash pop命令读取Git存储状态时,其底层其实就是读取到stash文件中的Commit对象,通过该Commit对象找到执行git stash命令后生成的Blob对象,读取该Blob对象的内容写入当前工作空间,达到还原工作空间的目的。
- 删除Git存储状态的原理
整理Git提交日志(在Git日志中查询不到了),然后将git/refs/stash文件删除掉。
下面我们通过代码来实际演示一下git stash命令的工作原理。
(1)创建一个初始仓库
rm -rf ./* .git
git init
echo '111' >> aaa.txt
git add ./
git commit -m "111" ./
git checkout -b b1
find .git/objects/ -type f # 查看所有的Git对象
.git/objects/58/c9bdf9d017fcd178dc8c073cbfcbb7ff240d6c # Blob对象
.git/objects/7d/811c6d8fa7794fc7a0a2371a4cf197e8cfb47d # Commit对象
.git/objects/8f/96f2f60c766a6a6b78591e06e6c1529c0ad9af # Tree对象
git ls-files -s # 查看当前暂存区
100644 58c9bdf9d017fcd178dc8c073cbfcbb7ff240d6c 0 aaa.txt
git log --oneline --all --graph # 查看提交日志
* 7d811c6 (HEAD -> b1, master) 111
(2)使用存储状态的原理
编辑文件,使用stash命令观察效果,示例代码如下:
echo "222" >> aaa.txt
git status
On branch b1
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: aaa.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
git stash # 使用Git存储
git ls-files -s
100644 58c9bdf9d017fcd178dc8c073cbfcbb7ff240d6c 0 aaa.txt
git cat-file -p 58c9bdf9 # 暂存区没有变化
111
find .git/objects/ -type f
.git/objects/58/c9bdf9d017fcd178dc8c073cbfcbb7ff240d6c # Blob对象.v1
.git/objects/70/3a3923a3f4d516543ba3e6e9182467f31b328c # Tree对象.v2
.git/objects/7d/811c6d8fa7794fc7a0a2371a4cf197e8cfb47d # Commit对象.v1
.git/objects/8f/96f2f60c766a6a6b78591e06e6c1529c0ad9af # Tree对象.v1
.git/objects/99/11efb0f75f3280b2e8581bd83724e9a7a10528 # Commit对象.v2
.git/objects/a3/0a52a3be2c12cbc448a5c9be960577d13f4755 # Blob对象.v2
.git/objects/b3/e1f5cd5d92a906cff3dfc4816d6e22c72afffe # Commit对象.v3
cat .git/refs/stash # 查看stash文件,保存的是最新Commit对象(v3)的hash值
b3e1f5cd5d92a906cff3dfc4816d6e22c72afffe
git cat-file -p a30a52a # 查看Blob对象.v2
111
222
git cat-file -p 703a3923a3f4d516543ba3e6e9182467f31b328c # 查看Tree对象.v2
100644 blob a30a52a3be2c12cbc448a5c9be960577d13f4755 aaa.txt
git cat-file -p 9911efb0f75f3280b2e8581bd83724e9a7a10528 # 查看Commit对象.v2
tree 8f96f2f60c766a6a6b78591e06e6c1529c0ad9af # 包裹的是原来的Tree对象(v1版本)
parent 7d811c6d8fa7794fc7a0a2371a4cf197e8cfb47d # 父提交对象是Commit对象.v1
author xiaohui <xiaohui@aliyun.com> 1697278938 +0800
committer xiaohui <xiaohui@aliyun.com> 1697278938 +0800
index on b1: 7d811c6 111
git cat-file -p b3e1f5cd5d92a906cff3dfc4816d6e22c72afffe # 查看Commit对象.v3
tree 703a3923a3f4d516543ba3e6e9182467f31b328c # 包裹的是新的Tree对象(v2)
parent 7d811c6d8fa7794fc7a0a2371a4cf197e8cfb47d # 指向Commit对象.v1
parent 9911efb0f75f3280b2e8581bd83724e9a7a10528 # 指向Commit对象.v2
author xiaohui <xiaohui@aliyun.com> 1697278938 +0800
committer xiaohui <xiaohui@aliyun.com> 1697278938 +0800
WIP on b1: 7d811c6 111
git log --oneline --all --graph # 查看日志,发现生成了两个Commit对象
* b3e1f5c (refs/stash) WIP on b1: 7d811c6 111 # Commit对象.v3
|\
| * 9911efb index on b1: 7d811c6 111 # Commit对象.v2
|/
* 7d811c6 (HEAD -> b1, master) 111 # HEAD指针还是指向b1
(3)读取存储状态的原理
执行如下代码观察效果:
git checkout master # 由于当前是Git的工作空间状态为"所有操作均已提交",因此可以切换到master分支
git checkout b1 # 重新切换到b1分支
git stash apply stash@{0} # 读取Git存储
On branch b1
cat aaa.txt # 实质上就是把Blob.v2的内容读取到工作空间中来
111
222
git status
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: aaa.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a") # 工作空间状态恢复成原来的状态了
(4)删除存储状态的原理
执行如下代码观察效果:
git stash list # 查看所有Git存储
stash@{0}: WIP on b1: 7d811c6 111
git stash drop stash@{0} # 删除Git存储状态
Dropped stash@{0} (b3e1f5cd5d92a906cff3dfc4816d6e22c72afffe)
ll .git/refs/ # 发现stash文件已经被删除
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 1 Adminstrator 197121 0 Oct 14 18:22 heads/
drwxr-xr-x 1 Adminstrator 197121 0 Oct 14 18:20 tags/
git log --oneline --all --graph # 查看提交日志
* 7d811c6 (HEAD -> b1, master) 111
find .git/objects/ -type f # 查看所有Git对象
.git/objects/58/c9bdf9d017fcd178dc8c073cbfcbb7ff240d6c # Blob对象.v1
.git/objects/70/3a3923a3f4d516543ba3e6e9182467f31b328c # Tree对象.v2
.git/objects/7d/811c6d8fa7794fc7a0a2371a4cf197e8cfb47d # Commit对象.v1
.git/objects/8f/96f2f60c766a6a6b78591e06e6c1529c0ad9af # Tree对象.v1
.git/objects/99/11efb0f75f3280b2e8581bd83724e9a7a10528 # Commit对象.v2
.git/objects/a3/0a52a3be2c12cbc448a5c9be960577d13f4755 # Blob对象.v2
.git/objects/b3/e1f5cd5d92a906cff3dfc4816d6e22c72afffe # Commit对象.v3