1.外观数列
38. 外观数列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
「外观数列」是一个数位字符串序列,由递归公式定义:
countAndSay(1) = "1"countAndSay(n)是countAndSay(n-1)的行程长度编码。
//考虑递归和迭代两种思想

amazing!!!
//同一个数字出现的次数我们考虑通过栈来进行分析
方法一:遍历生成

class Solution {
public String countAndSay(int n) {
String str="1";
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
StringBuffer stringBuffer=new StringBuffer();
int start=0;
int pos=0;
//11
//
while(pos<str.length()){
int m=0;
while(pos<str.length()&&str.charAt(pos)==str.charAt(start)){
pos++;
m++;
}
stringBuffer.append(Integer.toString(m)).append(str.charAt(start));
start=pos;
}
str=stringBuffer.toString();
}
return str;
}
}2.组合总和
给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组
candidates和一个目标整数target,找出candidates中可以使数字和为目标数target的 所有 不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。
candidates中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。对于给定的输入,保证和为
target的不同组合数少于150个。

//我们主要找的数字应该小于target
//如果大于target直接是不成立的
//我们首先把数组从大到小进行排序
//如果可以整除的话,我们就可以重复这些数字
//第一个数字还没有结束,此时我们的target变为target-第一个数字
//如果不能整除的话,我们把target-第一个数字
//循环结束的条件是target-相应的数字<0
//如果等于0的话我们就可以把我们所试验的值直接添加到数组中。
class Solution1 { public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { List<List<Integer>> list=new ArrayList<>(); Arrays.sort(candidates);//从小到大进行排序 int tmp=target; for(int i=0;i<candidates.length;i++){ target=tmp; if(candidates[i]>target){ break; } int j=0; while(target<0&&j<candidates.length-1){ List<Integer> list1=new ArrayList<>(); if(target%candidates[j]==0){ for(j=0;j<(target/candidates[j]);j++){ list1.add(candidates[j]); } list.add(list1); }else { list1.add(candidates[j]); target=target-candidates[j]; j++; if(target==0){ list.add(list1); } } } } return list; } }经过思考,我想我们是不是应该用递归
1,2,3,4,5
如果是可以整出我们就直接添加
如果不可以整除我们把target-目标值
//未完成
//卡壳了
class Solution2 { public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { List<List<Integer>> list=new ArrayList<>(); Arrays.sort(candidates);//从小到大进行排序 for(int i=0;i<candidates.length;i++){ list.add(getTarget(candidates,target,i)); } return list; } public List<Integer> getTarget(int[] candidates,int target,int index){ int tmp=target; for(int i=0;i<candidates.length;i++){ target=tmp; if(candidates[i]>target){ break; } int j=0; while(target<0&&j<candidates.length-1){ List<Integer> list1=new ArrayList<>(); if(target%candidates[j]==0){ for(j=0;j<(target/candidates[j]);j++){ list1.add(candidates[j]); } list.add(list1); }else { list1.add(candidates[j]); target=target-candidates[j]; j++; if(target==0){ list.add(list1); } } } } } } }
仍然是回溯法 (需要了解回溯法)
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> ans=new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> combine=new ArrayList<>();
dfs(candidates,target,ans,combine,0);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(int[] candidates, int target, List<List<Integer>> ans, List<Integer> combine, int idx) {
if(idx==candidates.length){
return;
}
if(target==0){
ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(combine));
return;
}
//直接跳过
dfs(candidates,target,ans,combine,idx+1);
//选择当前数
if(target-candidates[idx]>=0){
combine.add(candidates[idx]);
dfs(candidates, target - candidates[idx], ans, combine, idx);
combine.remove(combine.size() - 1);
}
}
}3.组合总和2(暂时不看)
40. 组合总和 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
方法一:回溯+剪枝
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
int len = candidates.length;
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (len == 0) {
return res;
}
// 关键步骤
Arrays.sort(candidates);
Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque<>(len);
dfs(candidates, len, 0, target, path, res);
return res;
}
/**
* @param candidates 候选数组
* @param len 冗余变量
* @param begin 从候选数组的 begin 位置开始搜索
* @param target 表示剩余,这个值一开始等于 target,基于题目中说明的"所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数"这个条件
* @param path 从根结点到叶子结点的路径
* @param res
*/
private void dfs(int[] candidates, int len, int begin, int target, Deque<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) {
if (target == 0) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = begin; i < len; i++) {
// 大剪枝:减去 candidates[i] 小于 0,减去后面的 candidates[i + 1]、candidates[i + 2] 肯定也小于 0,因此用 break
if (target - candidates[i] < 0) {
break;
}
// 小剪枝:同一层相同数值的结点,从第 2 个开始,候选数更少,结果一定发生重复,因此跳过,用 continue
if (i > begin && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
path.addLast(candidates[i]);
// 调试语句 ①
// System.out.println("递归之前 => " + path + ",剩余 = " + (target - candidates[i]));
// 因为元素不可以重复使用,这里递归传递下去的是 i + 1 而不是 i
dfs(candidates, len, i + 1, target - candidates[i], path, res);
path.removeLast();
// 调试语句 ②
// System.out.println("递归之后 => " + path + ",剩余 = " + (target - candidates[i]));
}
}
}4.字符串相乘
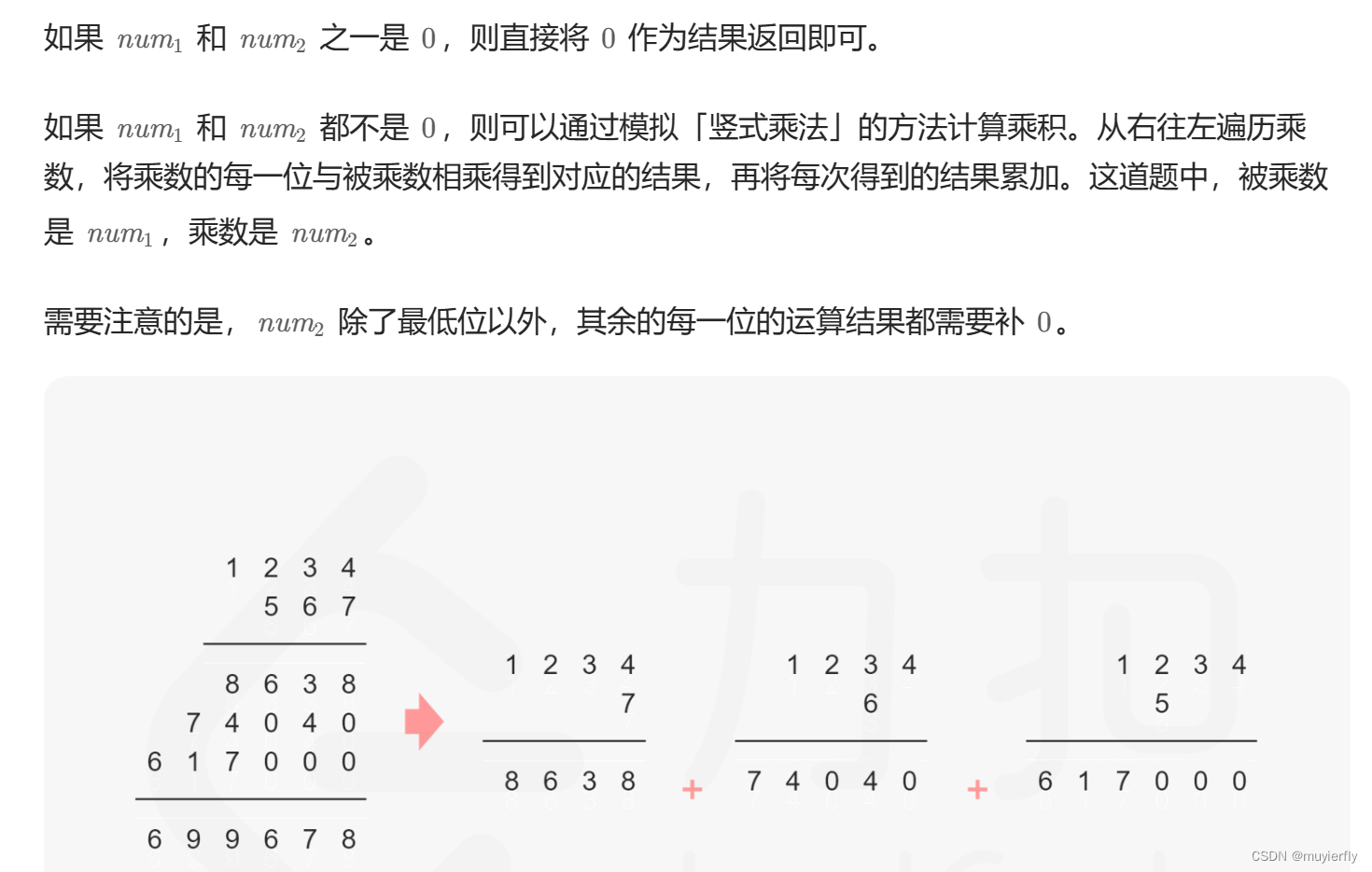
43. 字符串相乘 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定两个以字符串形式表示的非负整数
num1和num2,返回num1和num2的乘积,它们的乘积也表示为字符串形式。注意:不能使用任何内置的 BigInteger 库或直接将输入转换为整数。
失败,溢出了
class Solution {
public static String multiply(String num1, String num2) {
int sumnum1=0;
int sumnum2=0;
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<num1.length();i++){
count=num1.charAt(i)-'0';
int step1=num1.length()-i;
int m=(int)Math.pow(10,step1-1);
sumnum1=m*count+sumnum1;
}
for(int j=0;j<num2.length();j++){
count=num2.charAt(j)-'0';
int step2=num2.length()-j;
int m=(int)Math.pow(10,step2-1);
sumnum2=count*m+sumnum2;
}
long intsum=sumnum1*sumnum2;
return intsum+"";
}
}方法一:做加法
class Solution {
public String multiply(String num1, String num2) {
if (num1.equals("0") || num2.equals("0")) {
return "0";
}
String ans = "0";
int m = num1.length(), n = num2.length();
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
StringBuffer curr = new StringBuffer();
int add = 0;
for (int j = n - 1; j > i; j--) {
curr.append(0);
}
int y = num2.charAt(i) - '0';
for (int j = m - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
int x = num1.charAt(j) - '0';
int product = x * y + add;
curr.append(product % 10);
add = product / 10;
}
if (add != 0) {
curr.append(add % 10);
}
ans = addStrings(ans, curr.reverse().toString());
}
return ans;
}
public String addStrings(String num1, String num2) {
int i = num1.length() - 1, j = num2.length() - 1, add = 0;
StringBuffer ans = new StringBuffer();
while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 || add != 0) {
int x = i >= 0 ? num1.charAt(i) - '0' : 0;
int y = j >= 0 ? num2.charAt(j) - '0' : 0;
int result = x + y + add;
ans.append(result % 10);
add = result / 10;
i--;
j--;
}
ans.reverse();
return ans.toString();
}
}

5.跳跃游戏2(暂时不看)
45. 跳跃游戏 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个长度为
n的 0 索引整数数组nums。初始位置为nums[0]。每个元素
nums[i]表示从索引i向前跳转的最大长度。换句话说,如果你在nums[i]处,你可以跳转到任意nums[i + j]处:
0 <= j <= nums[i]i + j < n返回到达
nums[n - 1]的最小跳跃次数。生成的测试用例可以到达nums[n - 1]。
贪心算法
解题思路
这道题是典型的贪心算法,通过局部最优解得到全局最优解。以下两种方法都是使用贪心算法实现,只是贪心的策略不同。





![【YOLOv8改进[注意力]】使用CascadedGroupAttention(2023)注意力改进c2f + 含全部代码和详细修改方式 + 手撕结构图](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/0b1ba0c314a44dafbbe0971e7041faf0.png)