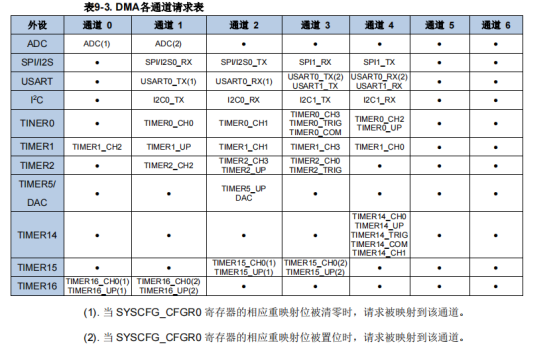
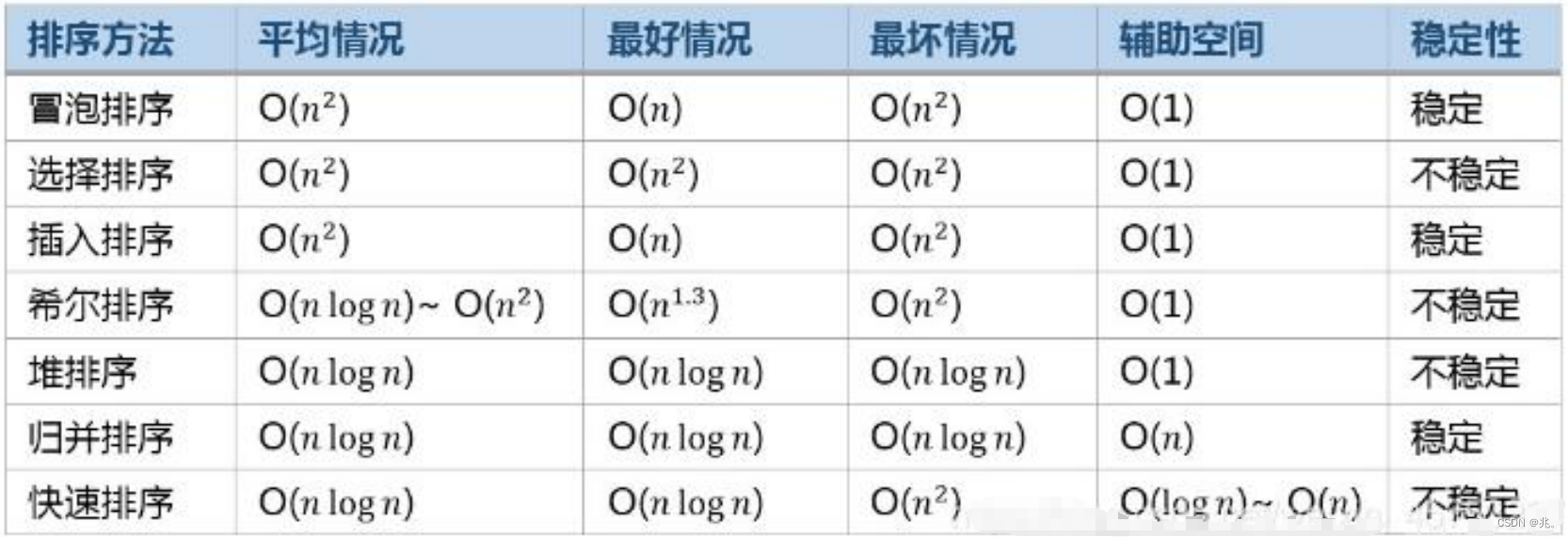
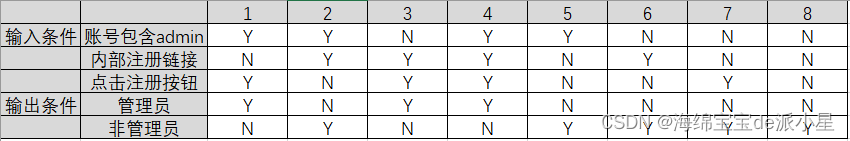
二维:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
pic_names = ["pic1", "pic2", "pic3", "pic4", "pic5", "pic6", "pic7", "pic8", "pic9", "pic10"]
# 生成随机的数据
def generate_pareto_front(num_points=100):
x = np.random.rand(num_points)
y = np.random.rand(num_points)
return x, y
# 创建图形
fig, axs = plt.subplots(3, 4, figsize=(20, 15))
# 遍历基准函数并绘制
for i, name in enumerate(pic_names):
if i < 8: # 前8个图
ax = axs[i // 4, i % 4]
else: # 最后两个图
ax = axs[2, i - 8 + 1] # 移动到第三行的第2和第3个位置
# 生成并绘制随机数据
x, y = generate_pareto_front()
ax.scatter(x, y, c='b', marker='o')
ax.set_title(name.upper())
ax.set_xlabel("f1")
ax.set_ylabel("f2")
# 删除空白子图
fig.delaxes(axs[2, 0])
fig.delaxes(axs[2, 3])
# 调整布局
plt.tight_layout()
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.3, hspace=0.3)
# 添加统一图例
handles, labels = axs[0, 0].get_legend_handles_labels()
fig.legend(handles, labels, loc='center left', bbox_to_anchor=(0.8, 0.2), ncol=1,prop={'size': 18})
# 显示图形
plt.show()

三维:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
pic_names = ["pic1", "pic2", "pic3", "pic4", "pic5", "pic6", "pic7", "pic8", "pic9", "pic10"]
# 生成随机的帕累托前沿数据
def generate_pareto_front(num_points=100):
x = np.random.rand(num_points)
y = np.random.rand(num_points)
z = np.random.rand(num_points)
return x, y, z
# 创建图形
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 15))
gs = fig.add_gridspec(3, 4)
# 遍历基准函数并绘制
for i, name in enumerate(pic_names):
if i < 8: # 前两行的8个图像
ax = fig.add_subplot(gs[i // 4, i % 4], projection='3d')
elif i == 8: # 第9个图,居中显示
ax = fig.add_subplot(gs[2, 1], projection='3d')
else: # 第10个图,居中显示
ax = fig.add_subplot(gs[2, 2], projection='3d')
# 生成并绘制随机数据
x, y, z = generate_pareto_front()
ax.scatter(x, y, z, c='b', marker='o')
ax.set_title(problem_name.upper())
ax.set_xlabel("f1")
ax.set_ylabel("f2")
ax.set_zlabel("f3")
# 设置视角
ax.view_init(elev=20, azim=20)
# 删除空白子图
fig.delaxes(fig.add_subplot(gs[2, 0]))
fig.delaxes(fig.add_subplot(gs[2, 3]))
# 调整布局
plt.tight_layout()
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.3, hspace=0.3)
# 显示图形
plt.show()