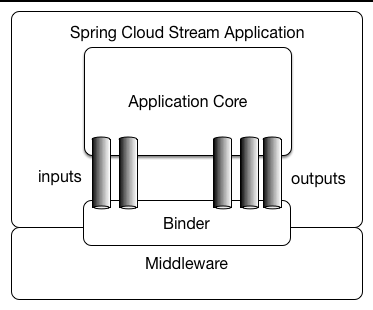
张量,即多维数组,是现代机器学习框架的支柱。操纵这些张量可能会变得冗长且难以阅读,尤其是在处理高维数据时。Einops 使用简洁的符号简化了这些操作。
Einops (Einstein-Inspired Notation for operations),受爱因斯坦运算符号启发的张量操作库,已成为AI工程师无缝操控张量以产生AI的必备工具。这是我编写的简单教程,旨在帮助没有 Einops 经验的人创建复杂而实用的神经网络。
NSDT工具推荐: Three.js AI纹理开发包 - YOLO合成数据生成器 - GLTF/GLB在线编辑 - 3D模型格式在线转换 - 可编程3D场景编辑器 - REVIT导出3D模型插件 - 3D模型语义搜索引擎 - Three.js虚拟轴心开发包 - 3D模型在线减面 - STL模型在线切割
在开始之前,让我们先使用 pip 安装 Einops:
pip install einops1、Einops的3个基本操作
Einops 围绕三个核心操作:重排、规约和重复。让我们通过示例深入探讨每个操作。
1.1 重排
重排(rearrange)让你可以通过一个容易看懂的操作符改变张量的维度和形状。
import torch
from einops import rearrange
# Create a 4D tensor of shape (batch, channels, height, width)
tensor = torch.rand(10, 3, 32, 32) # Example: a batch of 10 RGB images 32x32
# Rearrange to (batch, height, width, channels) for image processing libraries that expect this format
rearranged = rearrange(tensor, 'b c h w -> b h w c')上面的操作将通道 c移至最后一个维度,这是 matplotlib 等库中图像处理的常见要求。
1.2 规约
规约(reduce) 对张量的指定维度(如总和、平均值或最大值)应用规约操作,从而简化张量聚合任务。
from einops import reduce
# Reduce the tensor's channel dimension by taking the mean, resulting in a grayscale image
grayscale = reduce(tensor, 'b c h w -> b h w', 'mean')此操作通过对通道 c 进行平均,将我们的 RGB 图像转换为灰度图像。
1.3 重复
重复(repeat)沿任意维度复制张量,从而轻松实现数据增强或张量扩展。
from einops import repeat
# Repeat each image in the batch 4 times along a new dimension
repeated = repeat(tensor, 'b c h w -> (repeat b) c h w', repeat=4)上面的操作通过重复每个图像来增加数据集的大小,这对于数据增强非常有用。
2、Einops的高级模式
Einops 以其直观处理复杂重塑模式的能力而出名。
2.1 拆分和合并通道
将 RGB 通道拆分为单独的张量,对其进行处理,然后合并回去。
# Split channels
red, green, blue = rearrange(tensor, 'b (c rgb) h w -> rgb b c h w', rgb=3)
# Example processing (identity here)
processed_red, processed_green, processed_blue = red, green, blue
# Merge channels back
merged = rearrange([processed_red, processed_green, processed_blue], 'rgb b c h w -> b (rgb c) h w')2.2 展平和反展平
展平完全连接层的空间维度,然后反展平。
# Flatten spatial dimensions
flattened = rearrange(tensor, 'b c h w -> b (c h w)')
# Example neural network operation
# output = model(flattened)
# Unflatten back to spatial dimensions (assuming output has shape b, features)
# unflattened = rearrange(output, 'b (c h w) -> b c h w', c=3, h=32, w=32)2.3 批量图像裁剪
批量裁剪图像中心。
# Assuming tensor is batch of images b, c, h, w
crop_size = 24
start = (32 - crop_size) // 2
cropped = rearrange(tensor, 'b c (h crop) (w crop) -> b c h w', crop=crop_size, h=start, w=start)上面的操作从批次中的每个 32x32 图像中提取居中的 24x24 裁剪图像。
3、高级用例:实现注意力机制
注意力机制,尤其是自注意力(self attention),已成为现代深度学习架构(如 Transformers)的基石。让我们看看 Einops 如何简化自注意力机制的实现。
自注意力允许模型衡量输入数据不同部分的重要性。它是使用从输入数据中得出的查询 (Q)、键 (K) 和值 (V) 来计算的。
3.1 示例:简化的自注意力
为简单起见,我们将演示自注意力的基本版本。请注意,实际实现(如 Transformers 中的实现)包括掩码和缩放等其他步骤。
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from einops import rearrange
def simplified_self_attention(q, k, v):
"""
A simplified self-attention mechanism.
Args:
q, k, v (torch.Tensor): Queries, Keys, and Values. Shape: [batch_size, num_tokens, feature_dim]
Returns:
torch.Tensor: The result of the attention mechanism.
"""
# Compute the dot product between queries and keys
scores = torch.matmul(q, k.transpose(-2, -1))
# Apply softmax to get probabilities
attn_weights = F.softmax(scores, dim=-1)
# Multiply by values
output = torch.matmul(attn_weights, v)
return output
# Example tensors representing queries, keys, and values
batch_size, num_tokens, feature_dim = 10, 16, 64
q = torch.rand(batch_size, num_tokens, feature_dim)
k = torch.rand(batch_size, num_tokens, feature_dim)
v = torch.rand(batch_size, num_tokens, feature_dim)
# Apply self-attention
attention_output = simplified_self_attention(q, k, v)
print("Output shape:", attention_output.shape)在此示例中,为简单起见,使用 torch.matmul 来计算点积。Einops 在这些操作之前或之后重新排列张量时特别有用,可确保它们在矩阵乘法等操作中正确对齐。
3.2 进一步利用 Einops
除了基本的重排、规约和重复之外,Einops 还可用于更复杂的张量操作,这在多头注意力中经常遇到,其中将特征维度拆分为多个“头”可以简洁地表达:
def multi_head_self_attention(q, k, v, num_heads=8):
"""
Multi-head self-attention using Einops for splitting and merging heads.
"""
batch_size, num_tokens, feature_dim = q.shape
head_dim = feature_dim // num_heads
# Split into multiple heads
q, k, v = [
rearrange(x, 'b t (h d) -> b h t d', h=num_heads)
for x in (q, k, v)
]
# Apply self-attention to each head
output = simplified_self_attention(q, k, v)
# Merge the heads back
output = rearrange(output, 'b h t d -> b t (h d)')
return output
# Apply multi-head self-attention
multi_head_attention_output = multi_head_self_attention(q, k, v)
print("Multi-head output shape:", multi_head_attention_output.shape)此示例展示了 Einops 在轻松处理复杂张量重塑任务方面的强大功能,使您的代码更具可读性和可维护性。
4、结束语
Einops 是一种多功能且功能强大的张量操作工具,可以显著简化深度学习模型中复杂操作的实现。通过掌握 Einops,你将能够编写更简洁、可读和高效的张量操作代码,从而提升你的深度学习项目。无论是实现复杂的神经网络架构(如 Transformers)还是执行基本的张量重塑任务,Einops 都能满足你的需求。
原文链接:Einops 张量操作入门 - BimAnt