0. 什么是gcc
- GCC 原名为 GNU C语言编译器(GNU C Compiler)
- GCC(GNU Compiler Collection,GNU编译器套件)是由 GNU 开发的编程语言译器。 GNU编译器套件包括C、C++、 Objective-C、 Java、 Ada 和 Go语言前端,也包括了这些语言的库(如 libstdc++,libgcj等)
- GCC 不仅支持 C 的许多“方言”,也可以区别不同的 C 语言标准;可以使用命令行选项来控制编译器在翻译源代码时应该遵循哪个 C 标准。例如,当使用命令行参数
-std=c99启动 GCC 时,编译器支持 C99 标准。 - 安装命令
sudo apt install gcc g++(版本 > 4.8.5) - 查看版本
gcc/g++ -v/--version
1.计算机是如何运行c语言的?
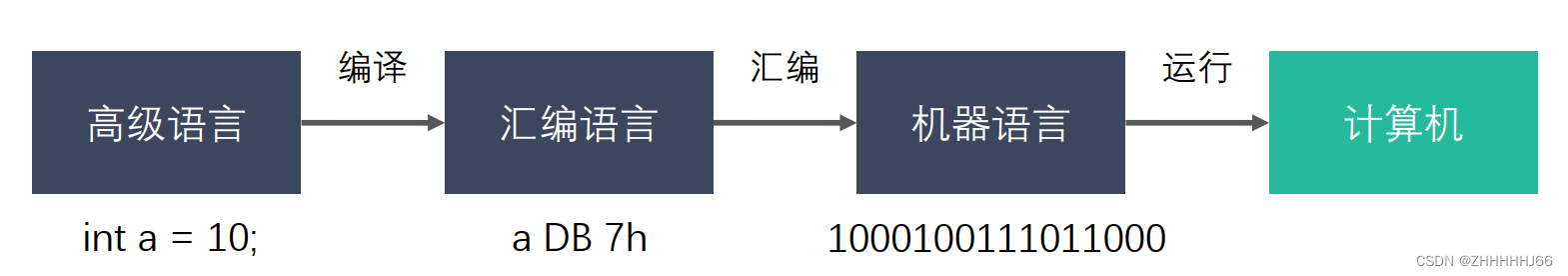
这张图可以很好的解释计算机是如何运行c语言的,将c语言编译后成为汇编语言,再经过汇编为机器语言,最后才得以让计算机运行
2. gcc的工作流程
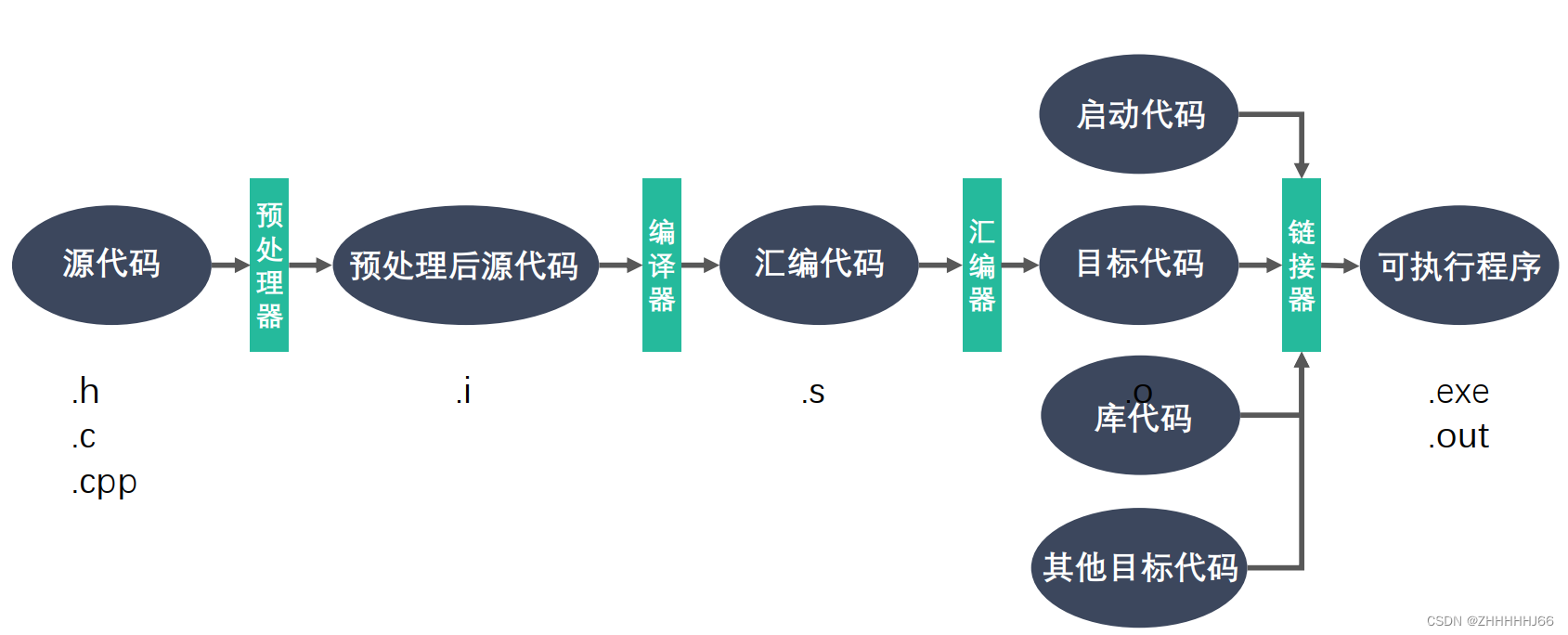
GCC 编译器对程序的编译下图所示,分为 4 个阶段:预处理(预编译)、编译和优化、汇编和链接。GCC 的编译器可以将这 4 个步骤合并成一个。 先介绍一个每个步骤都分别做了写什么事儿:
预处理(
-E):在这个阶段主要做了三件事:展开头文件、宏替换、去掉注释行
- 这个阶段需要 GCC 调用预处理器来完成,最终得到的还是源文件,文本格式
编译(
-S):这个阶段需要 GCC 调用编译器对文件进行编译,最终得到一个汇编文件汇编
-c:这个阶段需要 GCC 调用汇编器对文件进行汇编,最终得到一个二进制文件链接:这个阶段需要 GCC 调用链接器对程序需要调用的库进行链接,最终得到一个可执行的二进制文件
| 文件名后缀 | 说明 | gcc参数 |
|---|---|---|
.c | 源文件 | 无 |
.i | 预处理后的c文件 | -E |
.s | 编译后的得到的汇编语言的源文件 | -S |
.o | 汇编后得到的二进制文件 | -c |
在 Linux 下使用 GCC 编译器编译单个文件十分简单,直接使用 gcc 命令后面加上要编译的 C 语言的源文件,GCC 会自动生成文件名为 a.out 的可执行文件(也可以通过参数 -o 指定生成的文件名),也就是通过一个简单的命令上边提到的 4 个步骤就全部执行完毕了。也可以单步执行
main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#define PI 3.14
int main() {
// printf
printf("Hello, World! PI == %d\n", PI);
return 0;
}
命令:gcc -E main.c -o main.i
main.i
# 1 "main.c"
# 1 "<built-in>"
# 1 "<command-line>"
# 31 "<command-line>"
# 1 "/usr/include/stdc-predef.h" 1 3 4
# 32 "<command-line>" 2
# 1 "main.c"
# 1 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 1 3 4
# 27 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/libc-header-start.h" 1 3 4
# 33 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/libc-header-start.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/features.h" 1 3 4
# 424 "/usr/include/features.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/sys/cdefs.h" 1 3 4
# 427 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/sys/cdefs.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/wordsize.h" 1 3 4
# 428 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/sys/cdefs.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/long-double.h" 1 3 4
# 429 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/sys/cdefs.h" 2 3 4
# 425 "/usr/include/features.h" 2 3 4
# 448 "/usr/include/features.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/gnu/stubs.h" 1 3 4
# 10 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/gnu/stubs.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/gnu/stubs-64.h" 1 3 4
# 11 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/gnu/stubs.h" 2 3 4
# 449 "/usr/include/features.h" 2 3 4
# 34 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/libc-header-start.h" 2 3 4
# 28 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/7/include/stddef.h" 1 3 4
# 216 "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/7/include/stddef.h" 3 4
# 216 "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/7/include/stddef.h" 3 4
typedef long unsigned int size_t;
# 34 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/types.h" 1 3 4
# 27 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/types.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/wordsize.h" 1 3 4
# 28 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/types.h" 2 3 4
typedef unsigned char __u_char;
typedef unsigned short int __u_short;
typedef unsigned int __u_int;
typedef unsigned long int __u_long;
typedef signed char __int8_t;
typedef unsigned char __uint8_t;
typedef signed short int __int16_t;
typedef unsigned short int __uint16_t;
typedef signed int __int32_t;
typedef unsigned int __uint32_t;
typedef signed long int __int64_t;
typedef unsigned long int __uint64_t;
typedef long int __quad_t;
typedef unsigned long int __u_quad_t;
typedef long int __intmax_t;
typedef unsigned long int __uintmax_t;
# 130 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/types.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/typesizes.h" 1 3 4
# 131 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/types.h" 2 3 4
typedef unsigned long int __dev_t;
typedef unsigned int __uid_t;
typedef unsigned int __gid_t;
typedef unsigned long int __ino_t;
typedef unsigned long int __ino64_t;
typedef unsigned int __mode_t;
typedef unsigned long int __nlink_t;
typedef long int __off_t;
typedef long int __off64_t;
typedef int __pid_t;
typedef struct { int __val[2]; } __fsid_t;
typedef long int __clock_t;
typedef unsigned long int __rlim_t;
typedef unsigned long int __rlim64_t;
typedef unsigned int __id_t;
typedef long int __time_t;
typedef unsigned int __useconds_t;
typedef long int __suseconds_t;
typedef int __daddr_t;
typedef int __key_t;
typedef int __clockid_t;
typedef void * __timer_t;
typedef long int __blksize_t;
typedef long int __blkcnt_t;
typedef long int __blkcnt64_t;
typedef unsigned long int __fsblkcnt_t;
typedef unsigned long int __fsblkcnt64_t;
typedef unsigned long int __fsfilcnt_t;
typedef unsigned long int __fsfilcnt64_t;
typedef long int __fsword_t;
typedef long int __ssize_t;
typedef long int __syscall_slong_t;
typedef unsigned long int __syscall_ulong_t;
typedef __off64_t __loff_t;
typedef char *__caddr_t;
typedef long int __intptr_t;
typedef unsigned int __socklen_t;
typedef int __sig_atomic_t;
# 36 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/types/__FILE.h" 1 3 4
struct _IO_FILE;
typedef struct _IO_FILE __FILE;
# 37 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/types/FILE.h" 1 3 4
struct _IO_FILE;
typedef struct _IO_FILE FILE;
# 38 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/libio.h" 1 3 4
# 35 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/libio.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/_G_config.h" 1 3 4
# 19 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/_G_config.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/7/include/stddef.h" 1 3 4
# 20 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/_G_config.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/types/__mbstate_t.h" 1 3 4
# 13 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/types/__mbstate_t.h" 3 4
typedef struct
{
int __count;
union
{
unsigned int __wch;
char __wchb[4];
} __value;
} __mbstate_t;
# 22 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/_G_config.h" 2 3 4
typedef struct
{
__off_t __pos;
__mbstate_t __state;
} _G_fpos_t;
typedef struct
{
__off64_t __pos;
__mbstate_t __state;
} _G_fpos64_t;
# 36 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/libio.h" 2 3 4
# 53 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/libio.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/7/include/stdarg.h" 1 3 4
# 40 "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/7/include/stdarg.h" 3 4
typedef __builtin_va_list __gnuc_va_list;
# 54 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/libio.h" 2 3 4
# 149 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/libio.h" 3 4
struct _IO_jump_t; struct _IO_FILE;
typedef void _IO_lock_t;
struct _IO_marker {
struct _IO_marker *_next;
struct _IO_FILE *_sbuf;
int _pos;
# 177 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/libio.h" 3 4
};
enum __codecvt_result
{
__codecvt_ok,
__codecvt_partial,
__codecvt_error,
__codecvt_noconv
};
# 245 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/libio.h" 3 4
struct _IO_FILE {
int _flags;
char* _IO_read_ptr;
char* _IO_read_end;
char* _IO_read_base;
char* _IO_write_base;
char* _IO_write_ptr;
char* _IO_write_end;
char* _IO_buf_base;
char* _IO_buf_end;
char *_IO_save_base;
char *_IO_backup_base;
char *_IO_save_end;
struct _IO_marker *_markers;
struct _IO_FILE *_chain;
int _fileno;
int _flags2;
__off_t _old_offset;
unsigned short _cur_column;
signed char _vtable_offset;
char _shortbuf[1];
_IO_lock_t *_lock;
# 293 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/libio.h" 3 4
__off64_t _offset;
void *__pad1;
void *__pad2;
void *__pad3;
void *__pad4;
size_t __pad5;
int _mode;
char _unused2[15 * sizeof (int) - 4 * sizeof (void *) - sizeof (size_t)];
};
typedef struct _IO_FILE _IO_FILE;
struct _IO_FILE_plus;
extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stdin_;
extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stdout_;
extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stderr_;
# 337 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/libio.h" 3 4
typedef __ssize_t __io_read_fn (void *__cookie, char *__buf, size_t __nbytes);
typedef __ssize_t __io_write_fn (void *__cookie, const char *__buf,
size_t __n);
typedef int __io_seek_fn (void *__cookie, __off64_t *__pos, int __w);
typedef int __io_close_fn (void *__cookie);
# 389 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/libio.h" 3 4
extern int __underflow (_IO_FILE *);
extern int __uflow (_IO_FILE *);
extern int __overflow (_IO_FILE *, int);
# 433 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/libio.h" 3 4
extern int _IO_getc (_IO_FILE *__fp);
extern int _IO_putc (int __c, _IO_FILE *__fp);
extern int _IO_feof (_IO_FILE *__fp) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int _IO_ferror (_IO_FILE *__fp) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int _IO_peekc_locked (_IO_FILE *__fp);
extern void _IO_flockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern void _IO_funlockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int _IO_ftrylockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# 462 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/libio.h" 3 4
extern int _IO_vfscanf (_IO_FILE * __restrict, const char * __restrict,
__gnuc_va_list, int *__restrict);
extern int _IO_vfprintf (_IO_FILE *__restrict, const char *__restrict,
__gnuc_va_list);
extern __ssize_t _IO_padn (_IO_FILE *, int, __ssize_t);
extern size_t _IO_sgetn (_IO_FILE *, void *, size_t);
extern __off64_t _IO_seekoff (_IO_FILE *, __off64_t, int, int);
extern __off64_t _IO_seekpos (_IO_FILE *, __off64_t, int);
extern void _IO_free_backup_area (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# 42 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
typedef __gnuc_va_list va_list;
# 57 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
typedef __off_t off_t;
# 71 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
typedef __ssize_t ssize_t;
typedef _G_fpos_t fpos_t;
# 131 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/stdio_lim.h" 1 3 4
# 132 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
extern struct _IO_FILE *stdin;
extern struct _IO_FILE *stdout;
extern struct _IO_FILE *stderr;
extern int remove (const char *__filename) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int rename (const char *__old, const char *__new) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int renameat (int __oldfd, const char *__old, int __newfd,
const char *__new) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern FILE *tmpfile (void) ;
# 173 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern char *tmpnam (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern char *tmpnam_r (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
# 190 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern char *tempnam (const char *__dir, const char *__pfx)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) __attribute__ ((__malloc__)) ;
extern int fclose (FILE *__stream);
extern int fflush (FILE *__stream);
# 213 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fflush_unlocked (FILE *__stream);
# 232 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern FILE *fopen (const char *__restrict __filename,
const char *__restrict __modes) ;
extern FILE *freopen (const char *__restrict __filename,
const char *__restrict __modes,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
# 265 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern FILE *fdopen (int __fd, const char *__modes) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
# 278 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern FILE *fmemopen (void *__s, size_t __len, const char *__modes)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern FILE *open_memstream (char **__bufloc, size_t *__sizeloc) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern void setbuf (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int setvbuf (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf,
int __modes, size_t __n) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern void setbuffer (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf,
size_t __size) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern void setlinebuf (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int fprintf (FILE *__restrict __stream,
const char *__restrict __format, ...);
extern int printf (const char *__restrict __format, ...);
extern int sprintf (char *__restrict __s,
const char *__restrict __format, ...) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern int vfprintf (FILE *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format,
__gnuc_va_list __arg);
extern int vprintf (const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg);
extern int vsprintf (char *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format,
__gnuc_va_list __arg) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern int snprintf (char *__restrict __s, size_t __maxlen,
const char *__restrict __format, ...)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, 3, 4)));
extern int vsnprintf (char *__restrict __s, size_t __maxlen,
const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, 3, 0)));
# 365 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int vdprintf (int __fd, const char *__restrict __fmt,
__gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, 2, 0)));
extern int dprintf (int __fd, const char *__restrict __fmt, ...)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, 2, 3)));
extern int fscanf (FILE *__restrict __stream,
const char *__restrict __format, ...) ;
extern int scanf (const char *__restrict __format, ...) ;
extern int sscanf (const char *__restrict __s,
const char *__restrict __format, ...) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# 395 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fscanf (FILE *__restrict __stream, const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_fscanf")
;
extern int scanf (const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_scanf")
;
extern int sscanf (const char *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_sscanf") __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__))
;
# 420 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int vfscanf (FILE *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format,
__gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 2, 0))) ;
extern int vscanf (const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 1, 0))) ;
extern int vsscanf (const char *__restrict __s,
const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 2, 0)));
# 443 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int vfscanf (FILE *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vfscanf")
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 2, 0))) ;
extern int vscanf (const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vscanf")
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 1, 0))) ;
extern int vsscanf (const char *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vsscanf") __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__))
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 2, 0)));
# 477 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fgetc (FILE *__stream);
extern int getc (FILE *__stream);
extern int getchar (void);
# 495 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int getc_unlocked (FILE *__stream);
extern int getchar_unlocked (void);
# 506 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fgetc_unlocked (FILE *__stream);
# 517 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fputc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putchar (int __c);
# 537 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fputc_unlocked (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putc_unlocked (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putchar_unlocked (int __c);
extern int getw (FILE *__stream);
extern int putw (int __w, FILE *__stream);
extern char *fgets (char *__restrict __s, int __n, FILE *__restrict __stream)
;
# 603 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern __ssize_t __getdelim (char **__restrict __lineptr,
size_t *__restrict __n, int __delimiter,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern __ssize_t getdelim (char **__restrict __lineptr,
size_t *__restrict __n, int __delimiter,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern __ssize_t getline (char **__restrict __lineptr,
size_t *__restrict __n,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern int fputs (const char *__restrict __s, FILE *__restrict __stream);
extern int puts (const char *__s);
extern int ungetc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern size_t fread (void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern size_t fwrite (const void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __s);
# 673 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern size_t fread_unlocked (void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern size_t fwrite_unlocked (const void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream);
extern int fseek (FILE *__stream, long int __off, int __whence);
extern long int ftell (FILE *__stream) ;
extern void rewind (FILE *__stream);
# 707 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fseeko (FILE *__stream, __off_t __off, int __whence);
extern __off_t ftello (FILE *__stream) ;
# 731 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fgetpos (FILE *__restrict __stream, fpos_t *__restrict __pos);
extern int fsetpos (FILE *__stream, const fpos_t *__pos);
# 757 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern void clearerr (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int feof (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern int ferror (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern void clearerr_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int feof_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern int ferror_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern void perror (const char *__s);
# 1 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/sys_errlist.h" 1 3 4
# 26 "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/sys_errlist.h" 3 4
extern int sys_nerr;
extern const char *const sys_errlist[];
# 782 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
extern int fileno (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern int fileno_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
# 800 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern FILE *popen (const char *__command, const char *__modes) ;
extern int pclose (FILE *__stream);
extern char *ctermid (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# 840 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern void flockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int ftrylockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern void funlockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# 868 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
# 2 "main.c" 2
# 5 "main.c"
int main() {
printf("Hello, World! PI == %d\n", 3.14);
return 0;
}
可以发现
.i文件会将头文件展开,将我们所定义的宏替换成设定的值,并且会去掉我们写得注释
命令:gcc -S main.c -o main.s
main.s
.file "main.c"
.text
.section .rodata
.LC1:
.string "Hello, World! PI == %f\n"
.text
.globl main
.type main, @function
main:
.LFB0:
.cfi_startproc
pushq %rbp
.cfi_def_cfa_offset 16
.cfi_offset 6, -16
movq %rsp, %rbp
.cfi_def_cfa_register 6
subq $16, %rsp
movq .LC0(%rip), %rax
movq %rax, -8(%rbp)
movsd -8(%rbp), %xmm0
leaq .LC1(%rip), %rdi
movl $1, %eax
call printf@PLT
movl $0, %eax
leave
.cfi_def_cfa 7, 8
ret
.cfi_endproc
.LFE0:
.size main, .-main
.section .rodata
.align 8
.LC0:
.long 1374389535
.long 1074339512
.ident "GCC: (Ubuntu 7.5.0-3ubuntu1~18.04) 7.5.0"
.section .note.GNU-stack,"",@progbits
这一步转化为相应的汇编代码
main.o
一个二进制文件
3. gcc和g++的区别
-
gcc 和 g++都是GNU(组织)的一个编译器。
-
误区一
-
gcc 只能编译 c 代码, g++ 只能编译 c++ 代码。两者都可以,请注意:后缀为 .c 的, gcc 把它当作是 C 程序,而 g++ 当作是 c++ 程序后缀为 .cpp 的,两者都会认为是 C++ 程序, C++ 的语法规则更加严谨一些
-
编译阶段, g++ 会调用 gcc,对于 C++ 代码,两者是等价的,但是因为 gcc命令不能自动和 C++ 程序使用的库联接,所以通常用 g++ 来完成链接,为了统一起见,干脆编译/链接统统用 g++ 了,这就给人一种错觉,好像 cpp 程序只能用g++似的
-
-
误区二 :gcc 不会定义 __cplusplus 宏,而 g++ 会
- 实际上,这个宏只是标志着编译器将会把代码按 C 还是 C++ 语法来解释
- 如上所述,如果后缀为 .c,并且采用 gcc 编译器,则该宏就是未定义的,否则,就是已定义
-
误区三:编译只能用 gcc,链接只能用 g++
- 严格来说,这句话不算错误,但是它混淆了概念,应该这样说:编译可以用gcc/g++,而链接可以用 g++ 或者 gcc -lstdc++。
- gcc 命令不能自动和C++程序使用的库联接,所以通常使用 g++ 来完成联接。但在编译阶段, g++ 会自动调用 gcc,二者等价
4. gcc常用参数
| gcc 编译选项 | 选项的意义 |
|---|---|
| -E | 预处理指定的源文件,不进行编译 |
| -S | 编译指定的源文件,但是不进行汇编 |
| -c | 编译、汇编指定的源文件,但是不进行链接 |
| -o [file1] [file2] / [file2] -o [file1] | 将文件 file2 编译成文件 file1 |
| -I directory (大写的 i) | 指定 include 包含文件的搜索目录 |
| -g | 在编译的时候,生成调试信息,该程序可以被调试器调试 |
| -D | 在程序编译的时候,指定一个宏 |
| -w | 不生成任何警告信息,不建议使用,有些时候警告就是错误 |
| -Wall | 生成所有警告信息 |
| -On | n 的取值范围:0~3。编译器的优化选项的 4 个级别,-O0 表示没有优化,-O1 为缺省值,-O3 优化级别最高 |
| -l | 在程序编译的时候,指定使用的库 |
| -fPIC/fpic | 生成与位置无关的代码 |
| -shared | 生成共享目标文件。通常用在建立共享库时 |
| std | 指定 C 方言,如:-std=c99,gcc 默认的方言是 GNU C |
5. 多文件编译例子
main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "my_strlen.h"
int main() {
char* str1 = "junhaozhendeshuai!!!!";
printf("字符串长度为:%d", my_strlen(str1));
return 0;
}
my_strlen.h
//
// Created by xrgeek on 2023/1/27.
//
#ifndef CODE_MY_STRLEN_H
#define CODE_MY_STRLEN_H
unsigned int my_strlen(char* str);
#endif //CODE_MY_STRLEN_H
my_strlen.c
//
// Created by xrgeek on 2023/1/27.
//
unsigned int my_strlen(char* str)
{
int count = 0;
while (*str++ != '\0')
{
count++;
}
return count;
}
gcc my_strlen.c main.c -o main
./main