第一题
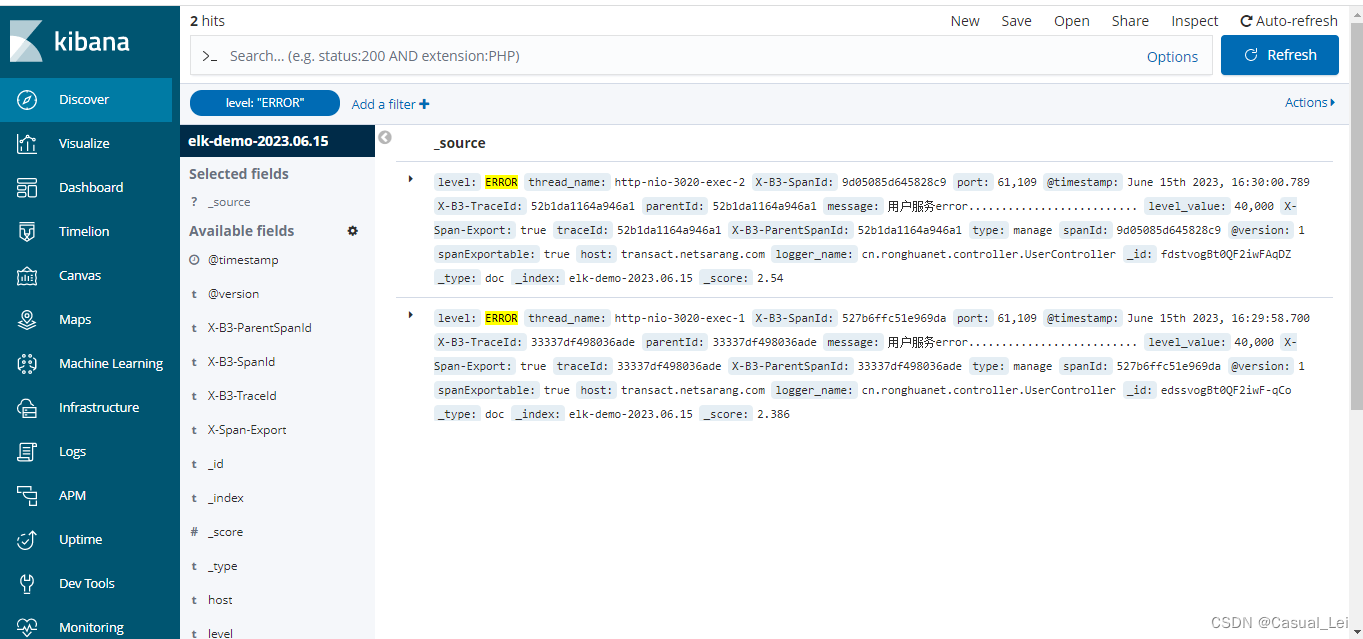
207. 课程表
步骤一:
通过下图的课程数组,首先画出DAG图(有向无环图)
步骤二:
其次我们按照DAG图,来构建该图的拓扑排序,等有效的点都按照规则排完序后,观察是否有剩下的点的入度不为0;
步骤三:
使用数组的结构来存放每一个点的入度;
我们通过创建队列来存储拓扑排序,首先遍历所有的点,将入度为0的点入队列,这时候进行这个点的bfs,即扫描其他的点。如果被扫描的点和该点有连接,则被扫描的点的入度减去一,同时此时被扫描的点的如度为零的话,就将这个点添加到队列中,进行下一个点的扫描;
重复上述步骤,直到完成所有队列中的点的bfs,此时判断是否存在一个点的入度不为0来返回数值;
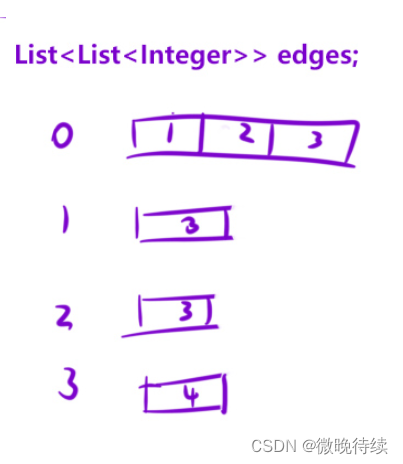
建图的概念:
方法一:hash表;如下图所示,使用邻接表来存储图的构造,我们采用hash表来完成这一邻接表的结构;下图第一行表示,0节点后面并列连着1,2,3;
所以edges表示两个节点之间的连接; key里面存放的是每一个点,valueb表示该节点所连接的点的集合;
方法二:
链表嵌套链表;
edges.get(0),表示0号节点;
edges.get(0).get(3),表示0号节点和3号节点之间的连接;
至此,代码如下:
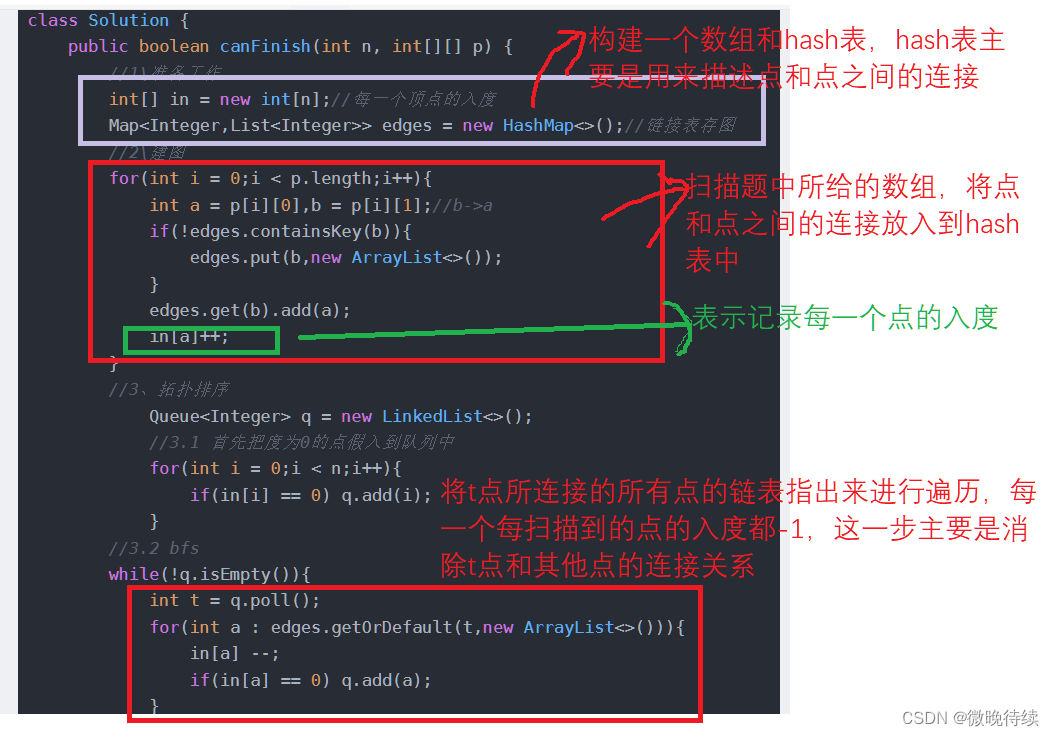
class Solution { public boolean canFinish(int n, int[][] p) { //1\准备工作 int[] in = new int[n];//每一个顶点的入度 Map<Integer,List<Integer>> edges = new HashMap<>();//链接表存图 //2\建图 for(int i = 0;i < p.length;i++){ int a = p[i][0],b = p[i][1];//b->a if(!edges.containsKey(b)){ edges.put(b,new ArrayList<>()); } edges.get(b).add(a); in[a]++; } //3、拓扑排序 Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>(); //3.1 首先把度为0的点假入到队列中 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){ if(in[i] == 0) q.add(i); } //3.2 bfs while(!q.isEmpty()){ int t = q.poll(); for(int a : edges.getOrDefault(t,new ArrayList<>())){ in[a] --; if(in[a] == 0) q.add(a); } } //4\判断是都有环 for(int x : in){ if(x != 0) return false; } return true; } }代码详解:
第二题
210. 课程表 II
题解如上题故事,这次我们采用链表嵌套链表的方式来创建图,即完成点与点之间的连接,至此,代码如下:
class Solution { public int[] findOrder(int n, int[][] p) { //1、准备工作 List<List<Integer>> edges = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i = 0;i < n; i++){ edges.add(new ArrayList<>()); } int[] in = new int[n]; //2、建图 for(int i = 0; i<p.length;i++){ int a = p[i][0], b = p[i][1];//b->a edges.get(b).add(a); in[a]++; } //3、拓扑排序 Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>(); for(int i = 0; i<n;i++){ if(in[i] == 0) q.add(i); } int[] ret = new int[n]; int idex = 0; while(!q.isEmpty()){ int t = q.poll(); ret[idex++] = t; for(int a : edges.get(t)){ in[a]--; if(in[a] == 0) q.add(a); } } //4、判断 if(idex == n) return ret; else return new int[0]; } }
第三题
LCR 114. 火星词典
至此,代码如下:
class Solution { Map<Character,Set<Character>> edges = new HashMap<>();//邻接表 Map<Character,Integer> in = new HashMap<>();//统计入度hash表 boolean check;//主要是防止边界即一个为空一个不为空 public String alienOrder(String[] words) { //1\初始化入度信息(哈希表)+建图 for(String s :words){ for(int i = 0; i< s.length();i++){ char ch = s.charAt(i); in.put(ch,0); } } int n = words.length; for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){ for(int j = i+1;j < n;j++){ add(words[i] , words[j]); if(check == true) return ""; } } //2、拓扑排序 Queue<Character> q = new LinkedList<>(); for(char ch : in.keySet()){ if(in.get(ch) == 0) q.add(ch); } StringBuffer ret = new StringBuffer(); while(!q.isEmpty()){ char t = q.poll(); ret.append(t); if(!edges.containsKey(t)) continue; for(char ch : edges.get(t)){ in.put(ch,in.get(ch) - 1); if(in.get(ch) == 0) q.add(ch); } } //3、判断 for(char ch : in.keySet()){ if(in.get(ch) != 0) return ""; } return ret.toString(); } public void add(String s1,String s2){ int n = Math.min(s1.length(),s2.length()); int i = 0; for( ; i < n; i++){ char c1 = s1.charAt(i);char c2 = s2.charAt(i); if(c1 != c2){ //c1 -> c2 if(!edges.containsKey(c1)){ edges.put(c1,new HashSet<>()); } if(!edges.get(c1).contains(c2)){ edges.get(c1).add(c2); in.put(c2,in.get(c2) +1); } break; } } if(i == s2.length() && i < s1.length()) check = true; } }
ps:本次的内容就到这里结束了,如果对你有所帮助的话,就请一键三连哦!!!