AIRNet提出了一种较为简易的pipeline,以单一网络结构应对多种任务需求(不同类型,不同程度)。但在效果上看,ALL-In-One是不如One-By-One的,且本文方法的亮点是batch内选择patch进行对比学习。在与sota对比上,仅是Denoise任务精度占优,在Derain与Dehaze任务上,效果不如One-By-One的MPRNet方法。本博客对AIRNet的关键结构实现,loss实现,data_patch实现进行深入分析,并对模型进行推理使用。
其论文的详细可以阅读:https://blog.csdn.net/a486259/article/details/139559389?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
项目地址:https://blog.csdn.net/a486259/article/details/139559389?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
项目依赖:torch、mmcv-full
安装mmcv-full时,需要注意torch所对应的cuda版本,要与系统中的cuda版本一致。
1、模型结构
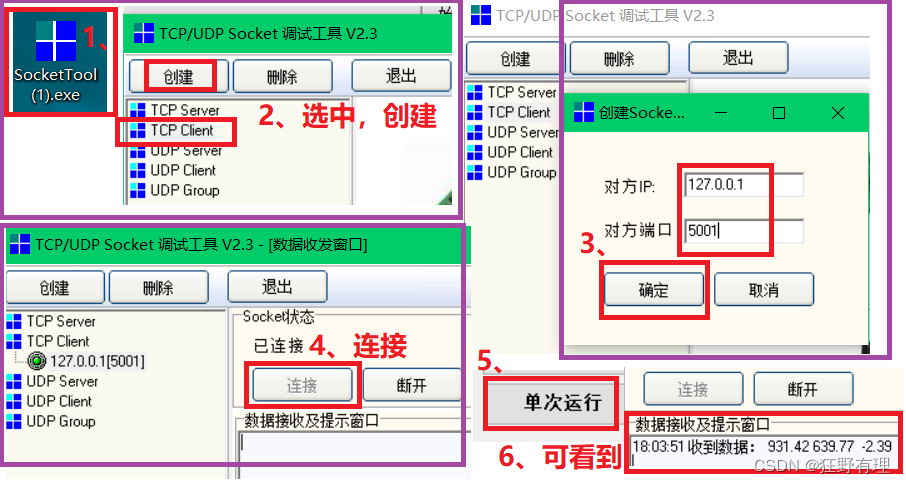
AirNet的网络结构如下所示,输入图像x交由CBDE提取到嵌入空间z,z与x输入到DGRN模块的DGG block中逐步优化,最终输出预测结果。
模型代码在net\model.py
from torch import nn
from net.encoder import CBDE
from net.DGRN import DGRN
class AirNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, opt):
super(AirNet, self).__init__()
# Encoder
self.E = CBDE(opt) #编码特征值
# Restorer
self.R = DGRN(opt) #特征解码
def forward(self, x_query, x_key):
if self.training:
fea, logits, labels, inter = self.E(x_query, x_key)
restored = self.R(x_query, inter)
return restored, logits, labels
else:
fea, inter = self.E(x_query, x_query)
restored = self.R(x_query, inter)
return restored
1.1 CBDE模块
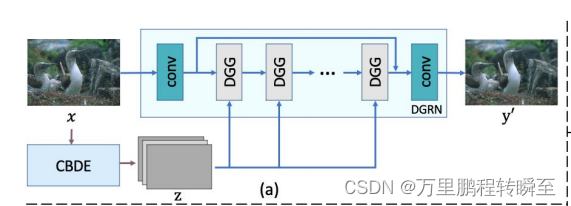
CBDE模块的功能是在模块内进行对比学习,核心是MoCo. Moco论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1911.05722
class CBDE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, opt):
super(CBDE, self).__init__()
dim = 256
# Encoder
self.E = MoCo(base_encoder=ResEncoder, dim=dim, K=opt.batch_size * dim)
def forward(self, x_query, x_key):
if self.training:
# degradation-aware represenetion learning
fea, logits, labels, inter = self.E(x_query, x_key)
return fea, logits, labels, inter
else:
# degradation-aware represenetion learning
fea, inter = self.E(x_query, x_query)
return fea, inter
ResEncoder所对应的网络结构如下所示
在AIRNet中的CBDE模块里的MoCo模块的关键代码如下,其在内部自行完成了正负样本的分配,最终输出logits, labels用于计算对比损失的loss。但其所优化的模块实际上是ResEncoder。MoCo模块只是在训练阶段起作用,在推理阶段是不起作用的。
class MoCo(nn.Module):
def forward(self, im_q, im_k):
"""
Input:
im_q: a batch of query images
im_k: a batch of key images
Output:
logits, targets
"""
if self.training:
# compute query features
embedding, q, inter = self.encoder_q(im_q) # queries: NxC
q = nn.functional.normalize(q, dim=1)
# compute key features
with torch.no_grad(): # no gradient to keys
self._momentum_update_key_encoder() # update the key encoder
_, k, _ = self.encoder_k(im_k) # keys: NxC
k = nn.functional.normalize(k, dim=1)
# compute logits
# Einstein sum is more intuitive
# positive logits: Nx1
l_pos = torch.einsum('nc,nc->n', [q, k]).unsqueeze(-1)
# negative logits: NxK
l_neg = torch.einsum('nc,ck->nk', [q, self.queue.clone().detach()])
# logits: Nx(1+K)
logits = torch.cat([l_pos, l_neg], dim=1)
# apply temperature
logits /= self.T
# labels: positive key indicators
labels = torch.zeros(logits.shape[0], dtype=torch.long).cuda()
# dequeue and enqueue
self._dequeue_and_enqueue(k)
return embedding, logits, labels, inter
else:
embedding, _, inter = self.encoder_q(im_q)
return embedding, inter
1.2 DGRN模块
DGRN模块的实现代码如下所示,可以看到核心是DGG模块,其不断迭代优化输入图像。
class DGRN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, opt, conv=default_conv):
super(DGRN, self).__init__()
self.n_groups = 5
n_blocks = 5
n_feats = 64
kernel_size = 3
# head module
modules_head = [conv(3, n_feats, kernel_size)]
self.head = nn.Sequential(*modules_head)
# body
modules_body = [
DGG(default_conv, n_feats, kernel_size, n_blocks) \
for _ in range(self.n_groups)
]
modules_body.append(conv(n_feats, n_feats, kernel_size))
self.body = nn.Sequential(*modules_body)
# tail
modules_tail = [conv(n_feats, 3, kernel_size)]
self.tail = nn.Sequential(*modules_tail)
def forward(self, x, inter):
# head
x = self.head(x)
# body
res = x
for i in range(self.n_groups):
res = self.body[i](res, inter)
res = self.body[-1](res)
res = res + x
# tail
x = self.tail(res)
return x
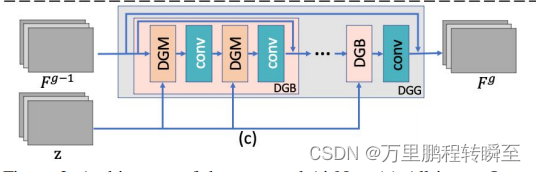
DGG模块的结构示意如下所示
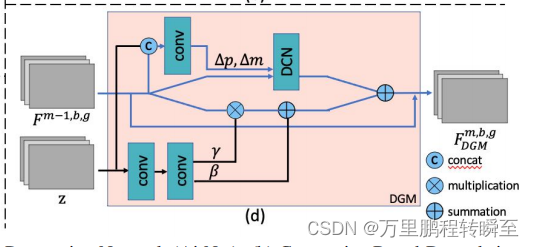
DGG代码实现如下所示,DGG模块内嵌DGB模块,DGB模块内嵌DGM模块,DGM模块内嵌SFT_layer模块与DCN_layer(可变性卷积)
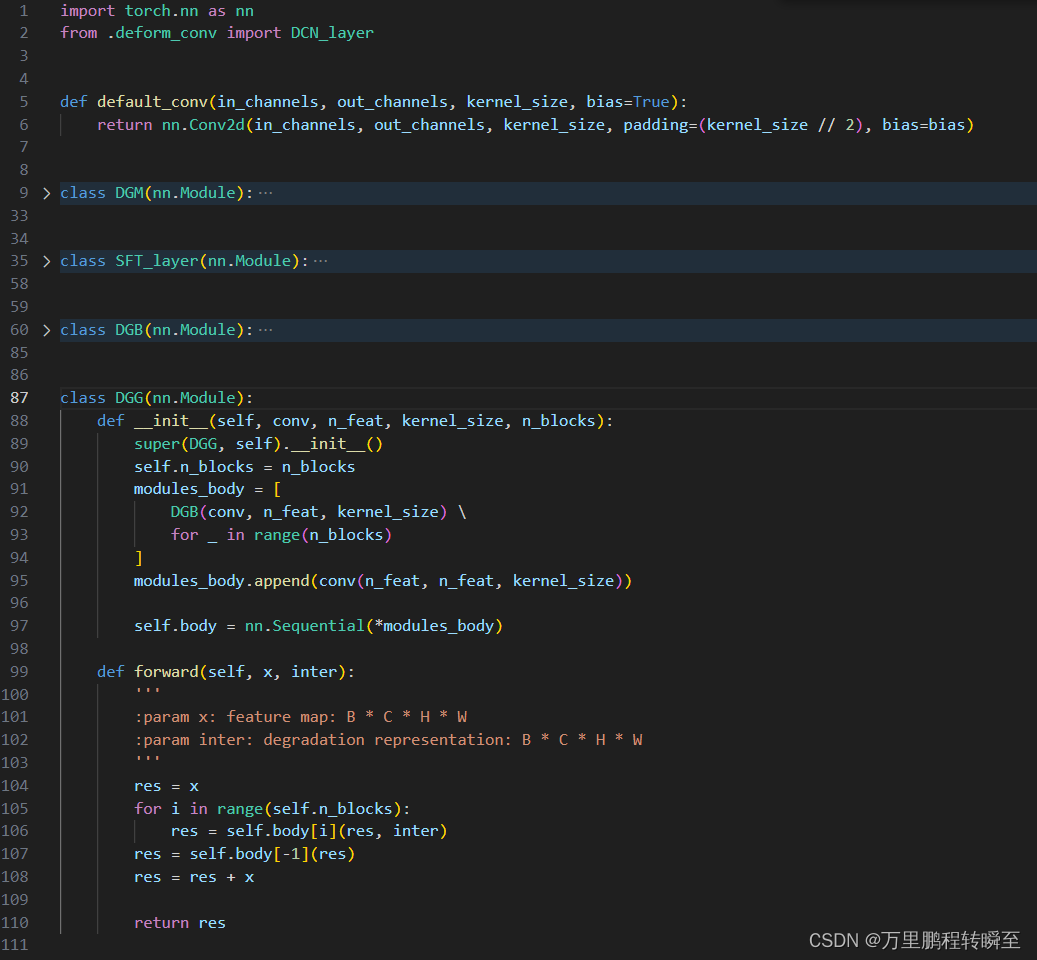
2、loss实现
AIRNet中提到的loss如下所示,其中Lrec是L1 loss,Lcl是Moco模块实现的对比损失。
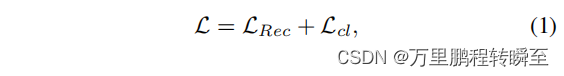
AIRNet的loss实现代码在train.py中,CE loss是针对CBDE(Moco模块)的输出进行计算,l1 loss是针对修复图像与清晰图片。
# Network Construction
net = AirNet(opt).cuda()
net.train()
# Optimizer and Loss
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=opt.lr)
CE = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda()
l1 = nn.L1Loss().cuda()
# Start training
print('Start training...')
for epoch in range(opt.epochs):
for ([clean_name, de_id], degrad_patch_1, degrad_patch_2, clean_patch_1, clean_patch_2) in tqdm(trainloader):
degrad_patch_1, degrad_patch_2 = degrad_patch_1.cuda(), degrad_patch_2.cuda()
clean_patch_1, clean_patch_2 = clean_patch_1.cuda(), clean_patch_2.cuda()
optimizer.zero_grad()
if epoch < opt.epochs_encoder:
_, output, target, _ = net.E(x_query=degrad_patch_1, x_key=degrad_patch_2)
contrast_loss = CE(output, target)
loss = contrast_loss
else:
restored, output, target = net(x_query=degrad_patch_1, x_key=degrad_patch_2)
contrast_loss = CE(output, target)
l1_loss = l1(restored, clean_patch_1)
loss = l1_loss + 0.1 * contrast_loss
# backward
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
这里可以看出来,AIRNet首先是训练CBDE模块,最后才训练CBDE模块+DGRN模块。
3、TrainDataset
TrainDataset的实现代码在utils\dataset_utils.py中,首先找到__getitem__函数进行分析。以下代码为关键部分,删除了大部分在逻辑上重复的部分。TrainDataset一共支持5种数据类型,‘denoise_15’: 0, ‘denoise_25’: 1, ‘denoise_50’: 2,是不需要图像对的(在代码里面自动对图像添加噪声);‘derain’: 3, ‘dehaze’: 4是需要图像对进行训练的。
class TrainDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, args):
super(TrainDataset, self).__init__()
self.args = args
self.rs_ids = []
self.hazy_ids = []
self.D = Degradation(args)
self.de_temp = 0
self.de_type = self.args.de_type
self.de_dict = {'denoise_15': 0, 'denoise_25': 1, 'denoise_50': 2, 'derain': 3, 'dehaze': 4}
self._init_ids()
self.crop_transform = Compose([
ToPILImage(),
RandomCrop(args.patch_size),
])
self.toTensor = ToTensor()
def __getitem__(self, _):
de_id = self.de_dict[self.de_type[self.de_temp]]
if de_id < 3:
if de_id == 0:
clean_id = self.s15_ids[self.s15_counter]
self.s15_counter = (self.s15_counter + 1) % self.num_clean
if self.s15_counter == 0:
random.shuffle(self.s15_ids)
# clean_id = random.randint(0, len(self.clean_ids) - 1)
clean_img = crop_img(np.array(Image.open(clean_id).convert('RGB')), base=16)
clean_patch_1, clean_patch_2 = self.crop_transform(clean_img), self.crop_transform(clean_img)
clean_patch_1, clean_patch_2 = np.array(clean_patch_1), np.array(clean_patch_2)
# clean_name = self.clean_ids[clean_id].split("/")[-1].split('.')[0]
clean_name = clean_id.split("/")[-1].split('.')[0]
clean_patch_1, clean_patch_2 = random_augmentation(clean_patch_1, clean_patch_2)
degrad_patch_1, degrad_patch_2 = self.D.degrade(clean_patch_1, clean_patch_2, de_id)
clean_patch_1, clean_patch_2 = self.toTensor(clean_patch_1), self.toTensor(clean_patch_2)
degrad_patch_1, degrad_patch_2 = self.toTensor(degrad_patch_1), self.toTensor(degrad_patch_2)
self.de_temp = (self.de_temp + 1) % len(self.de_type)
if self.de_temp == 0:
random.shuffle(self.de_type)
return [clean_name, de_id], degrad_patch_1, degrad_patch_2, clean_patch_1, clean_patch_2
可以看出TrainDataset返回的数据有:degrad_patch_1, degrad_patch_2, clean_patch_1, clean_patch_2。
3.1 clean_patch分析
通过以下代码可以看出 clean_patch_1, clean_patch_2是来自于同一个图片,然后基于crop_transform变化,变成了2个对象
clean_img = crop_img(np.array(Image.open(clean_id).convert('RGB')), base=16)
clean_patch_1, clean_patch_2 = self.crop_transform(clean_img), self.crop_transform(clean_img)
# clean_name = self.clean_ids[clean_id].split("/")[-1].split('.')[0]
clean_name = clean_id.split("/")[-1].split('.')[0]
clean_patch_1, clean_patch_2 = random_augmentation(clean_patch_1, clean_patch_2)
crop_transform的定义如下,可见是随机进行crop
crop_transform = Compose([
ToPILImage(),
RandomCrop(args.patch_size),
])
random_augmentation的实现代码如下,可以看到只是随机对图像进行翻转或旋转,其目的是尽可能使随机crop得到clean_patch_1, clean_patch_2差异更大,避免裁剪出高度相似的patch。
def random_augmentation(*args):
out = []
flag_aug = random.randint(1, 7)
for data in args:
out.append(data_augmentation(data, flag_aug).copy())
return out
def data_augmentation(image, mode):
if mode == 0:
# original
out = image.numpy()
elif mode == 1:
# flip up and down
out = np.flipud(image)
elif mode == 2:
# rotate counterwise 90 degree
out = np.rot90(image)
elif mode == 3:
# rotate 90 degree and flip up and down
out = np.rot90(image)
out = np.flipud(out)
elif mode == 4:
# rotate 180 degree
out = np.rot90(image, k=2)
elif mode == 5:
# rotate 180 degree and flip
out = np.rot90(image, k=2)
out = np.flipud(out)
elif mode == 6:
# rotate 270 degree
out = np.rot90(image, k=3)
elif mode == 7:
# rotate 270 degree and flip
out = np.rot90(image, k=3)
out = np.flipud(out)
else:
raise Exception('Invalid choice of image transformation')
return out
3.2 degrad_patch分析
degrad_patch来自于clean_patch,可以看到是通过D.degrade进行转换的。
degrad_patch_1, degrad_patch_2 = self.D.degrade(clean_patch_1, clean_patch_2, de_id)
D.degrade相关的代码如下,可以看到只是对图像添加噪声。难怪AIRNet在图像去噪上效果最好。
class Degradation(object):
def __init__(self, args):
super(Degradation, self).__init__()
self.args = args
self.toTensor = ToTensor()
self.crop_transform = Compose([
ToPILImage(),
RandomCrop(args.patch_size),
])
def _add_gaussian_noise(self, clean_patch, sigma):
# noise = torch.randn(*(clean_patch.shape))
# clean_patch = self.toTensor(clean_patch)
noise = np.random.randn(*clean_patch.shape)
noisy_patch = np.clip(clean_patch + noise * sigma, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
# noisy_patch = torch.clamp(clean_patch + noise * sigma, 0, 255).type(torch.int32)
return noisy_patch, clean_patch
def _degrade_by_type(self, clean_patch, degrade_type):
if degrade_type == 0:
# denoise sigma=15
degraded_patch, clean_patch = self._add_gaussian_noise(clean_patch, sigma=15)
elif degrade_type == 1:
# denoise sigma=25
degraded_patch, clean_patch = self._add_gaussian_noise(clean_patch, sigma=25)
elif degrade_type == 2:
# denoise sigma=50
degraded_patch, clean_patch = self._add_gaussian_noise(clean_patch, sigma=50)
return degraded_patch, clean_patch
def degrade(self, clean_patch_1, clean_patch_2, degrade_type=None):
if degrade_type == None:
degrade_type = random.randint(0, 3)
else:
degrade_type = degrade_type
degrad_patch_1, _ = self._degrade_by_type(clean_patch_1, degrade_type)
degrad_patch_2, _ = self._degrade_by_type(clean_patch_2, degrade_type)
return degrad_patch_1, degrad_patch_2
4、推理演示
项目中默认包含了All.pth,要单独任务的模型可以到预训练模型下载地址: Google Drive and Baidu Netdisk (password: cr7d). 下载模型放到 ckpt/ 目录下
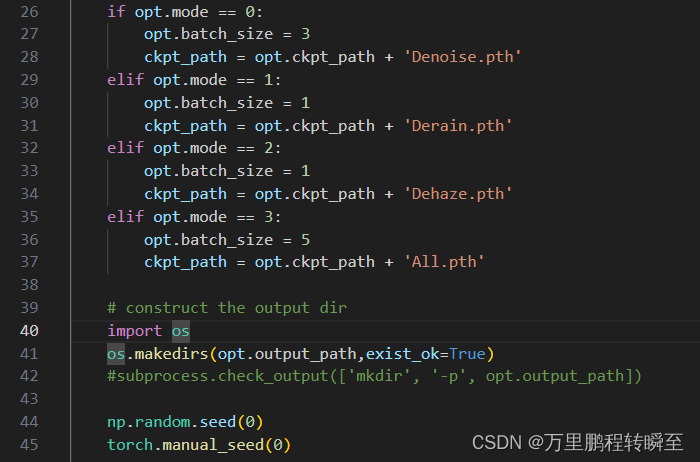
打开demo.py,将 subprocess.check_output(['mkdir', '-p', opt.output_path]) 替换为os.makedirs(opt.output_path,exist_ok=True),避免在window上报错,具体修改如下所示
demo.py默认从test\demo目录下读取图片进行测试,可见原始图像如下
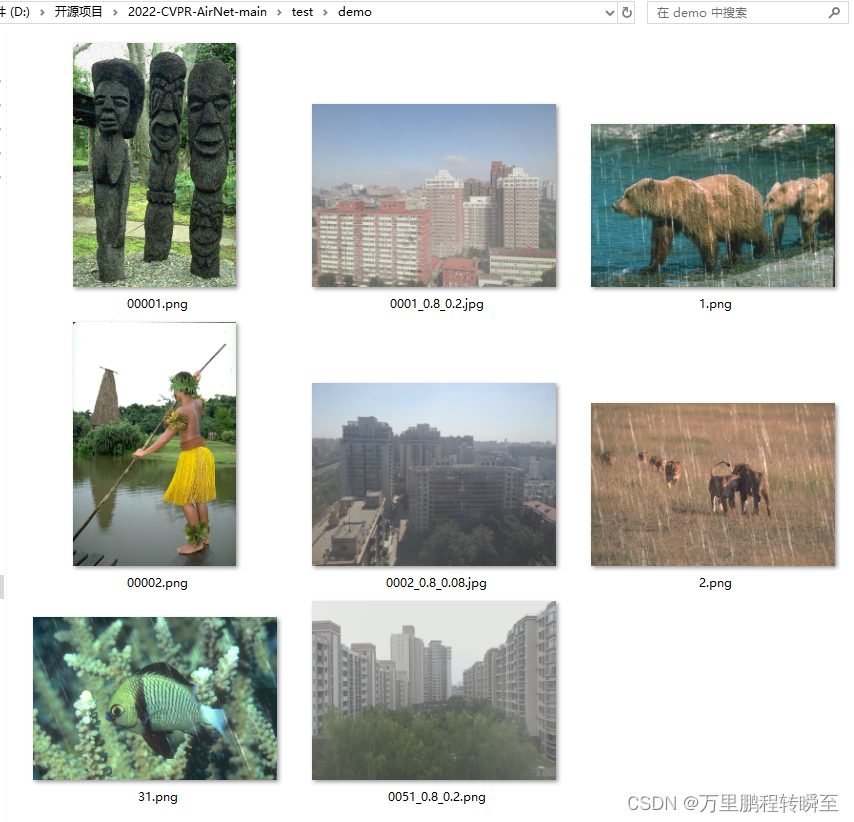
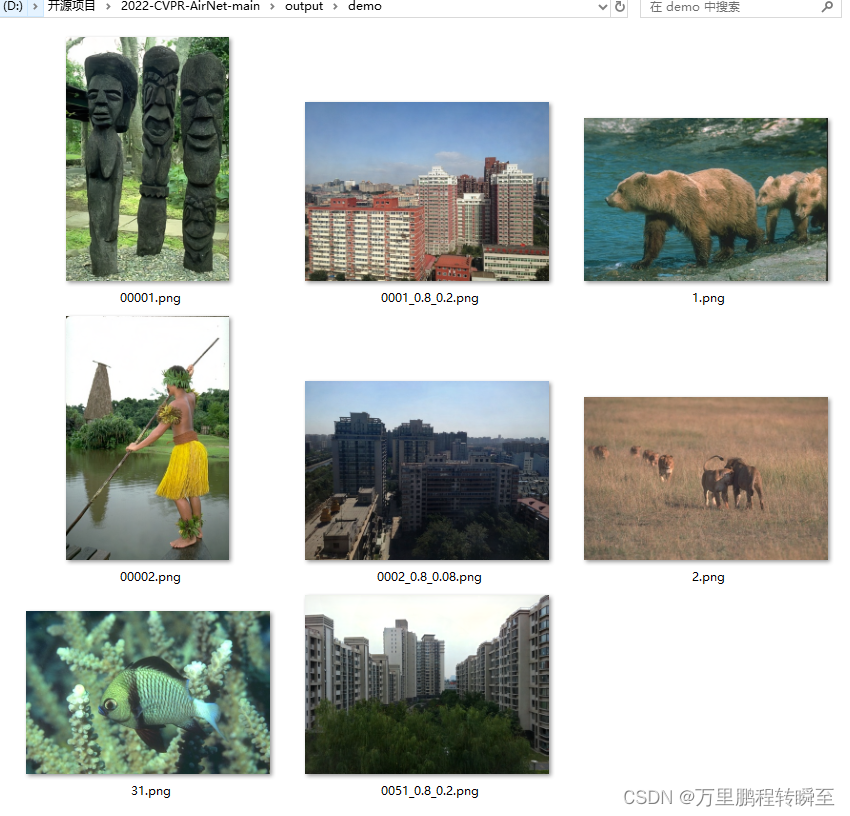
代码运行后的输出结果默认保存在 output\demo目录下,可见对于去雨,去雾,去噪声效果都比较好。
模型推理时间如下所示,可以看到对一张320, 480的图片,要0.54s