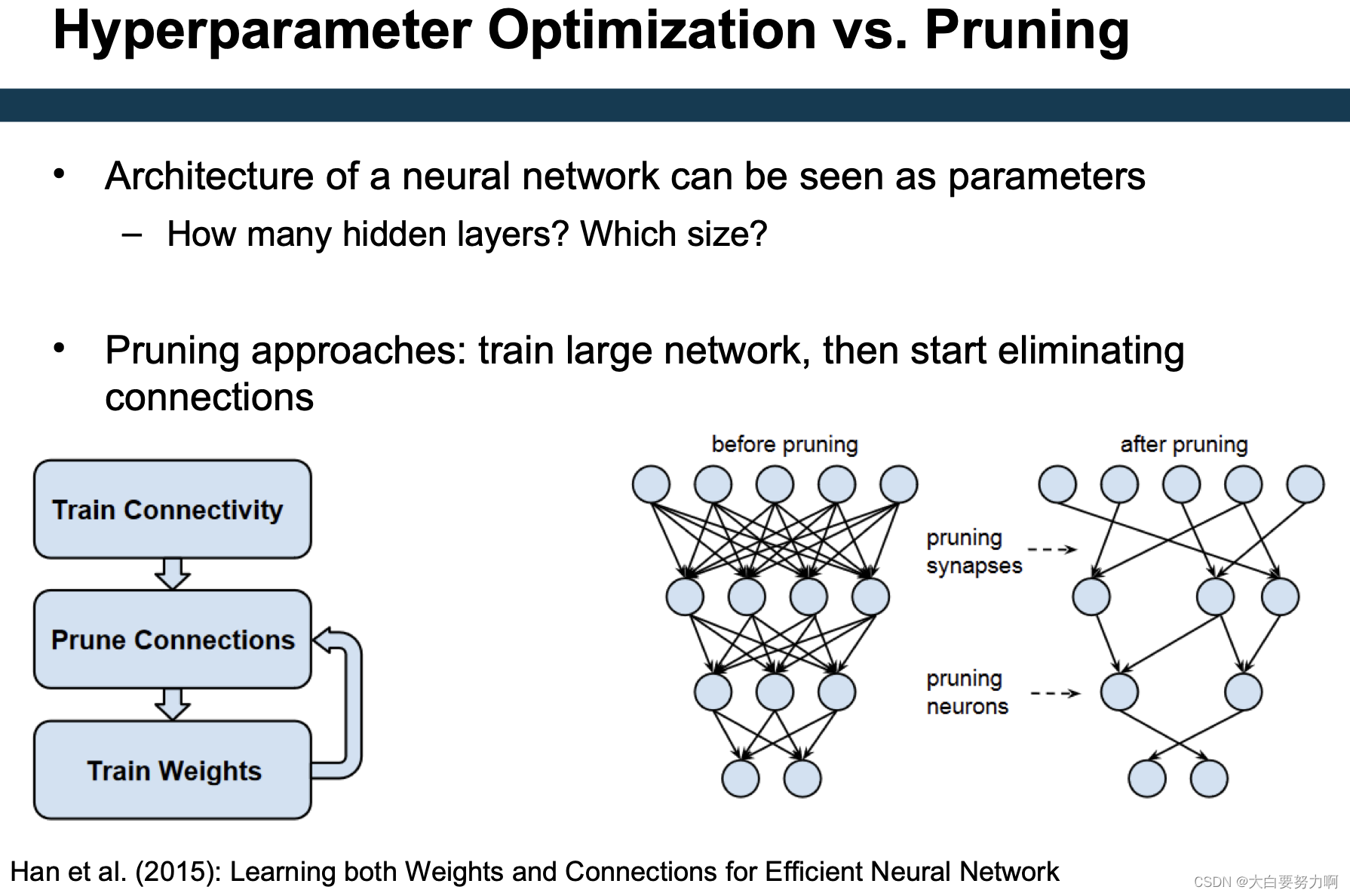
6. Optimization & Hyperparameter Tuning
Why Hyperparameter Tuning?
Many learning algorithms for classification, regression, … Many of those have hyperparameters: k and distance function for k nearest neighbors, splitting and pruning options in decision tree learning, …
But what is their effect?
Hard to tell in general and rules of thumb are rare.
Parameters vs. Hyperparameters
Parameters are learned during training
Typical examples: Coefficients in (linear) regression, Weights in neural networks, …
Training: Find set of of parameters so that objective function is minimized/maximized (on a holdout set)
Hyperparameters are fixed before training
Typical examples: Network layout and learning rate in neural networks, k in kNN, …
Training: Find set of of parameters so that objective function is minimized/maximized (on a holdout set), given a previously fixed set of hyperparameters
Hyperparameter Tuning – a Naive Approach
- run classification/regression algorithm
- look at the results (e.g., accuracy, RMSE, …)
- choose different parameter settings, go to 1
Questions: when to stop? how to select the next parameter setting to test?
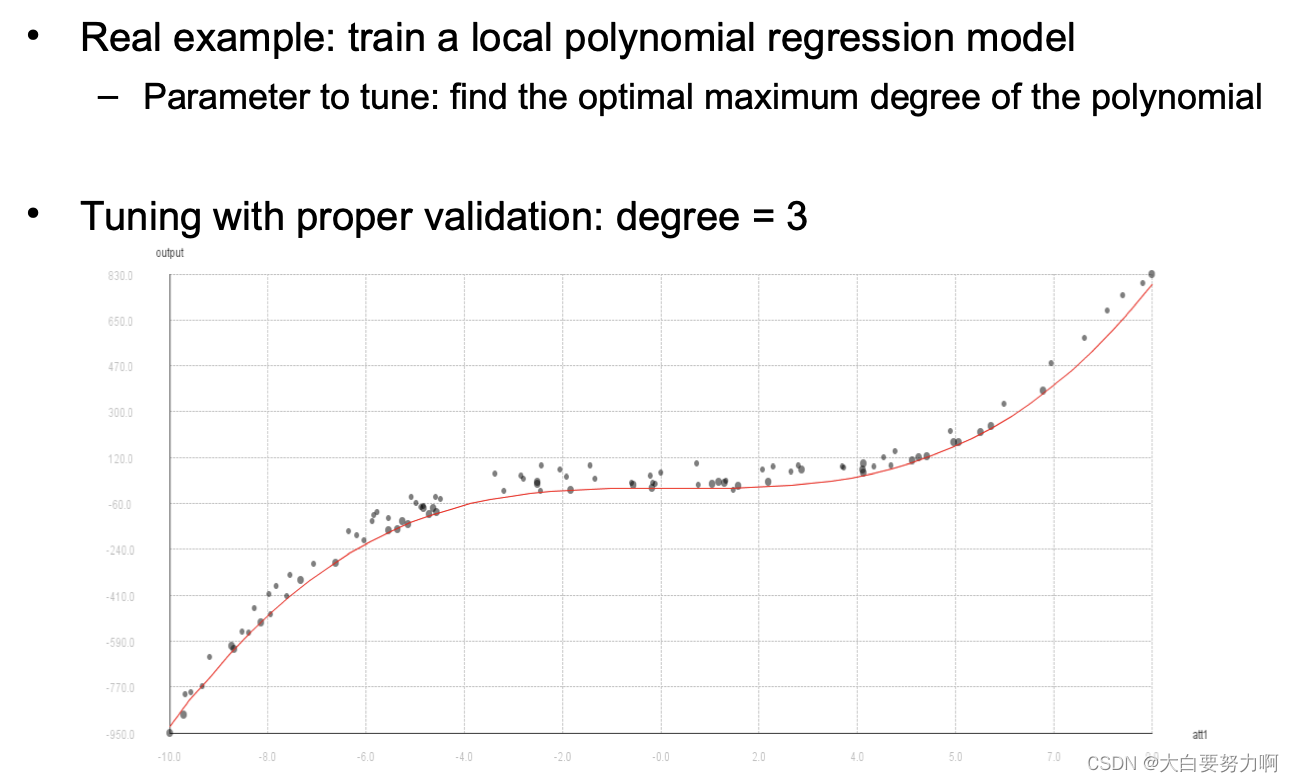
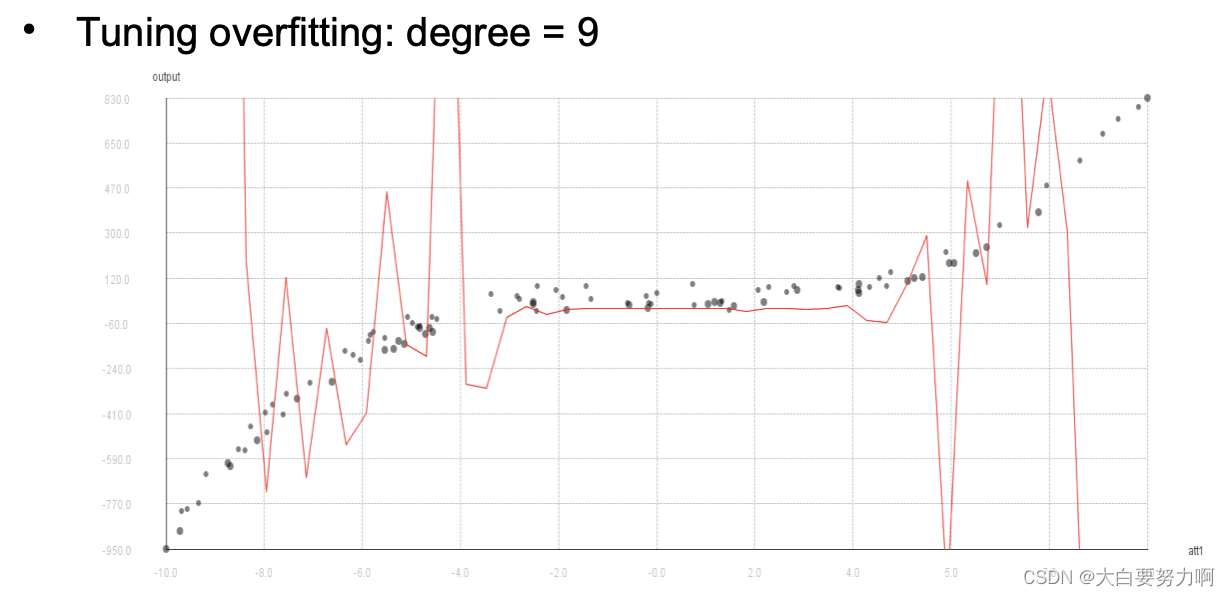
Hyperparameter Tuning – Avoid Overfitting!
Recap overfitting: classifiers may overadapt to training data. The same holds for parameter settings
Possible danger: finding parameters that work well on the training set but not on the test set
Remedy: train / test / validation split

6.1 Hyperparameter Tuning: Brute Force
Try all parameter combinations that exist → we need a better strategy than brute force!
Hyperparameter tuning is an optimization problem
Finding optimal values for N variables
Properties of the problem:
- the underlying model is unknown, i.e., we do not know changing a variable will influence the results
- we can tell how good a solution is when we see it, i.e., by running a classifier with the given parameter set
- but looking at each solution is costly
Related problem: feature subset selection
Given n features, brute force requires 2^n evaluations
e.g. for 20 features, that is already one million → ten million with cross validation
Knapsack problem
given a maximum weight you can carry and a set of items with different weight and monetary value. Pack those items that maximize the monetary value
Problem is NP hard – i.e., deterministic algorithms require an exponential amount of time
Note: feature subset selection for N features requires 2^n evaluations
Many optimization problems are NP hard
Routing problems (Traveling Salesman Problem)
Integer factorization: hard enough to be used for cryptography
Resource use optimization. e.g., minimizing cutoff waste
Chip design - minimizing chip sizes
Properties of Brute Force search
guaranteed to find the best parameter setting, too slow in most practical cases
6.1.1 Grid Search
performs a brute force search with equal-width steps on non-discrete numerical attributes
(e.g., 10,20,30,…,100)
Hyperparameter with a wide range (e.g., 0.0001 to 1,000,000)
with ten equal-width steps, the first step would be 1,000
but what if the optimum is around 0.1?
logarithmic steps may perform better for some parameters
Needed:
solutions that take less time/computation and often find the best parameter setting or find a near-optimal parameter setting
6.2 Hyperparameter Tuning: One After Another
Given n parameters with m degrees of freedom – brute force takes m^n runs of the base classifier
Simple tweak:
- start with default settings
- try all options for the first parameter
2a. fix best setting for first parameter - try all options for the second parameter
3a. fix best setting for second parameter - …
This reduces the runtime to n*m
i.e., no longer exponential – but we may miss the best solution
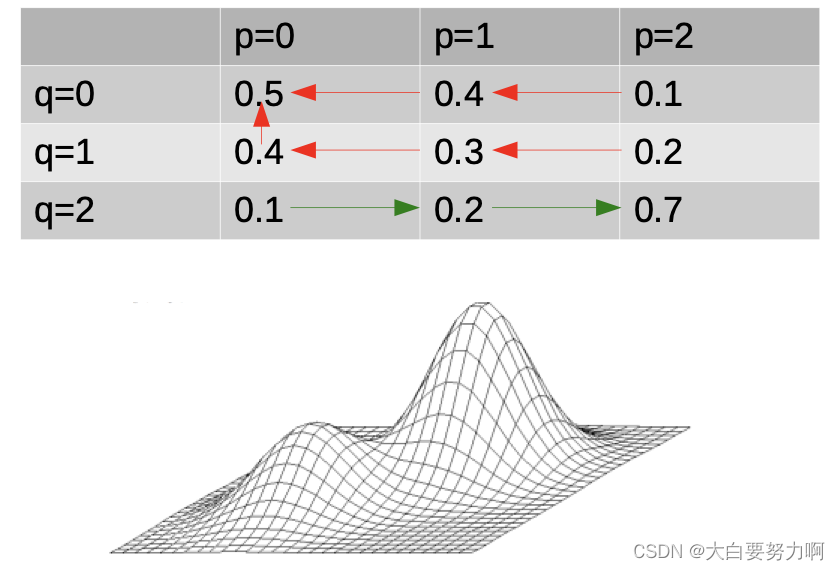
6.2.1 Interaction Effects
Interaction effects make parameter tuning hard. i.e., changing one parameter may change the optimal settings for another one
Example: two parameters p and q, each with values 0,1, and 2 – the table depicts classification accuracy
Example: two parameters p and q, each with values 0,1, and 2. The table depicts classification accuracy. If we try to optimize one parameter by another (first p, then q). We end at p=0,q=0 in six out of nine cases. On average, we investigate 2.3 solutions.
(0.5-local optimum, 0.7-globe optimum)
6.3 Hill climbing with variations
6.3.1 Hill-Climbing Search (greedy local search)
“Like climbing Everest in thick fog with amnesia” always search in the direction of the steepest ascend.
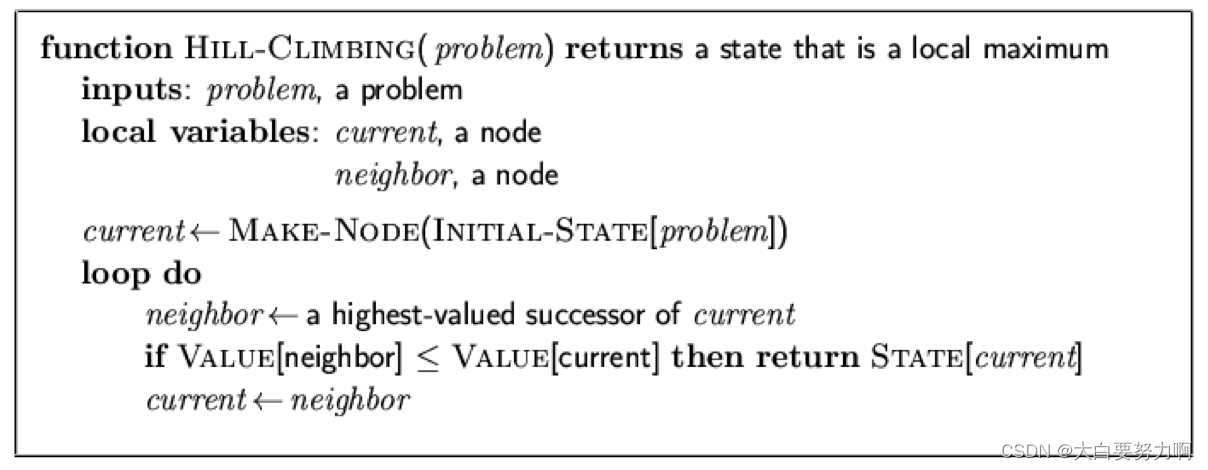
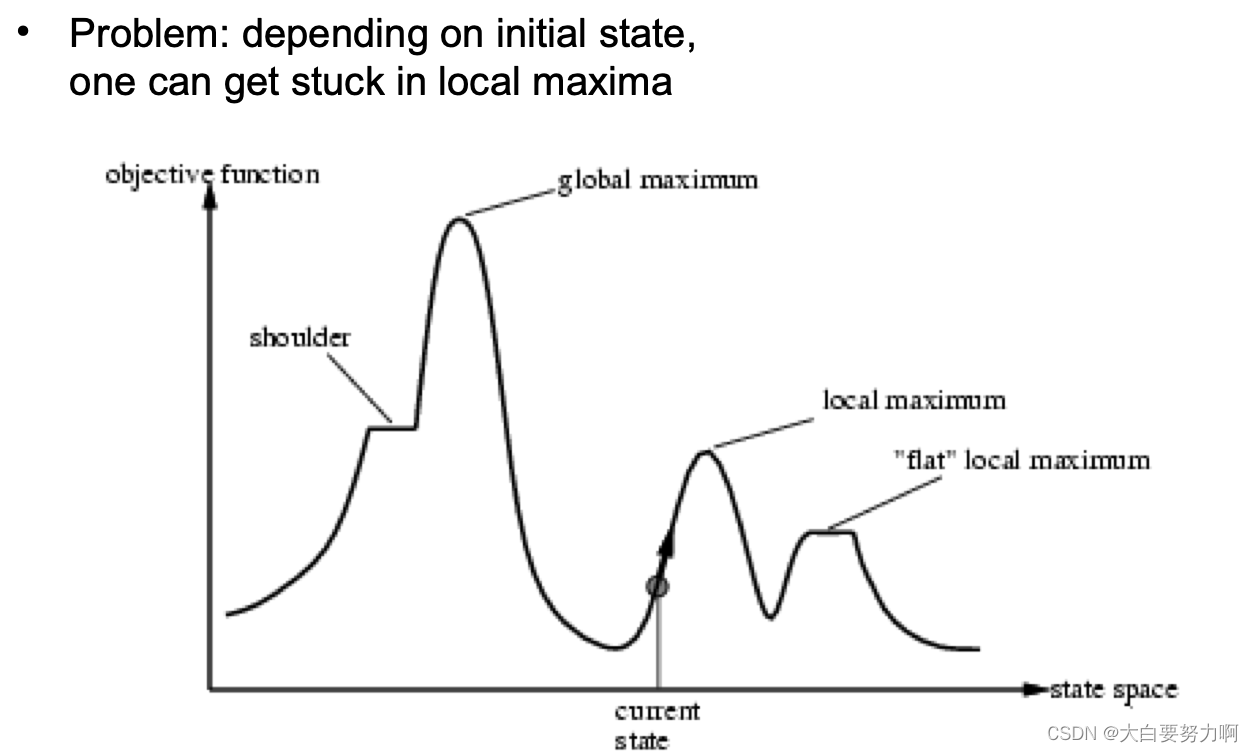

6.3.2 Variations of Hill Climbing Search
- Stochastic hill climbing
random selection among the uphill moves
the selection probability can vary with the steepness of the uphill move - First-choice hill climbing
generating successors randomly until a better one is found, then pick
that one - Random-restart hill climbing
run hill climbing with different seeds
tries to avoid getting stuck in local maxima
6.4 Beam search
Local Beam Search
Keep track of k states rather than just one
Start with k randomly generated states
At each iteration, all the successors of all k states are generated
Select the k best successors from the complete list and repeat
6.5 Random search
Grid Search vs. Random Search
All the examples discussed so far use fixed grids
Challenges: some hyperparameters are pretty sensitive
e.g., 0.02 is a good value, but 0 and 0.05 are not – others have little influence
but it is hard to know upfront which
grid search may easily miss best parameters but random search often yields better results
6.6 Genetic Programming
Genetic Algorithms is inspired by evolution:
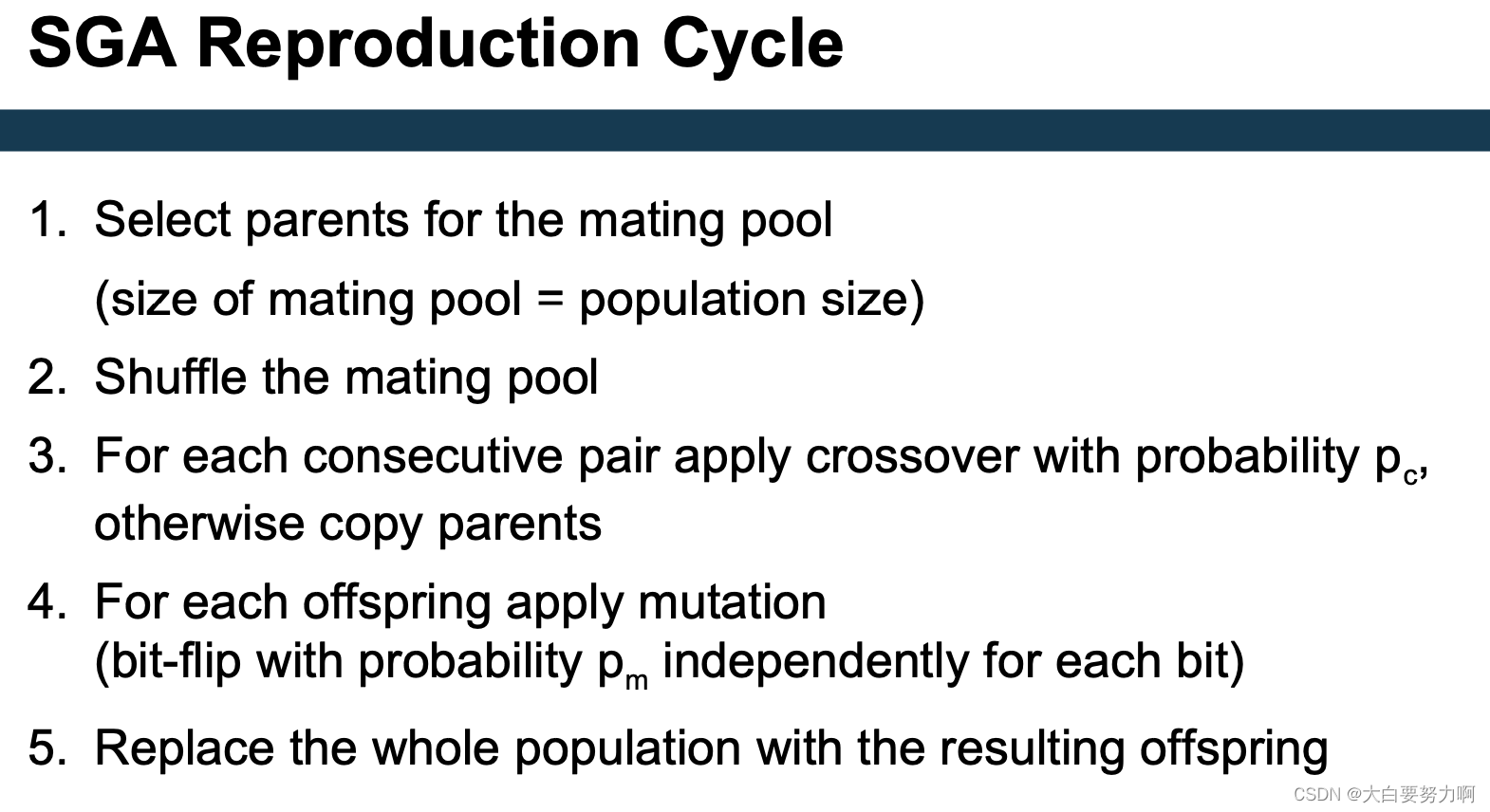
use a population of individuals (solutions) -> create new individuals by crossover -> introduce random mutations -> from each generation, keep only the best solutions (“survival of the fittest”)
Standard Genetic Algorithm (SGA)
6.6.1 SGA
Basic ingredients:
- individuals: the solutions
hyperparameter tuning: a hyperparameter setting - a fitness function
hyperparameter tuning: performance of a hyperparameter setting (i.e., run learner with those parameters) - acrossover method
hyperparameter tuning: create a new setting from two others - amutation method
hyperparameter tuning: change one parameter - survivor selection
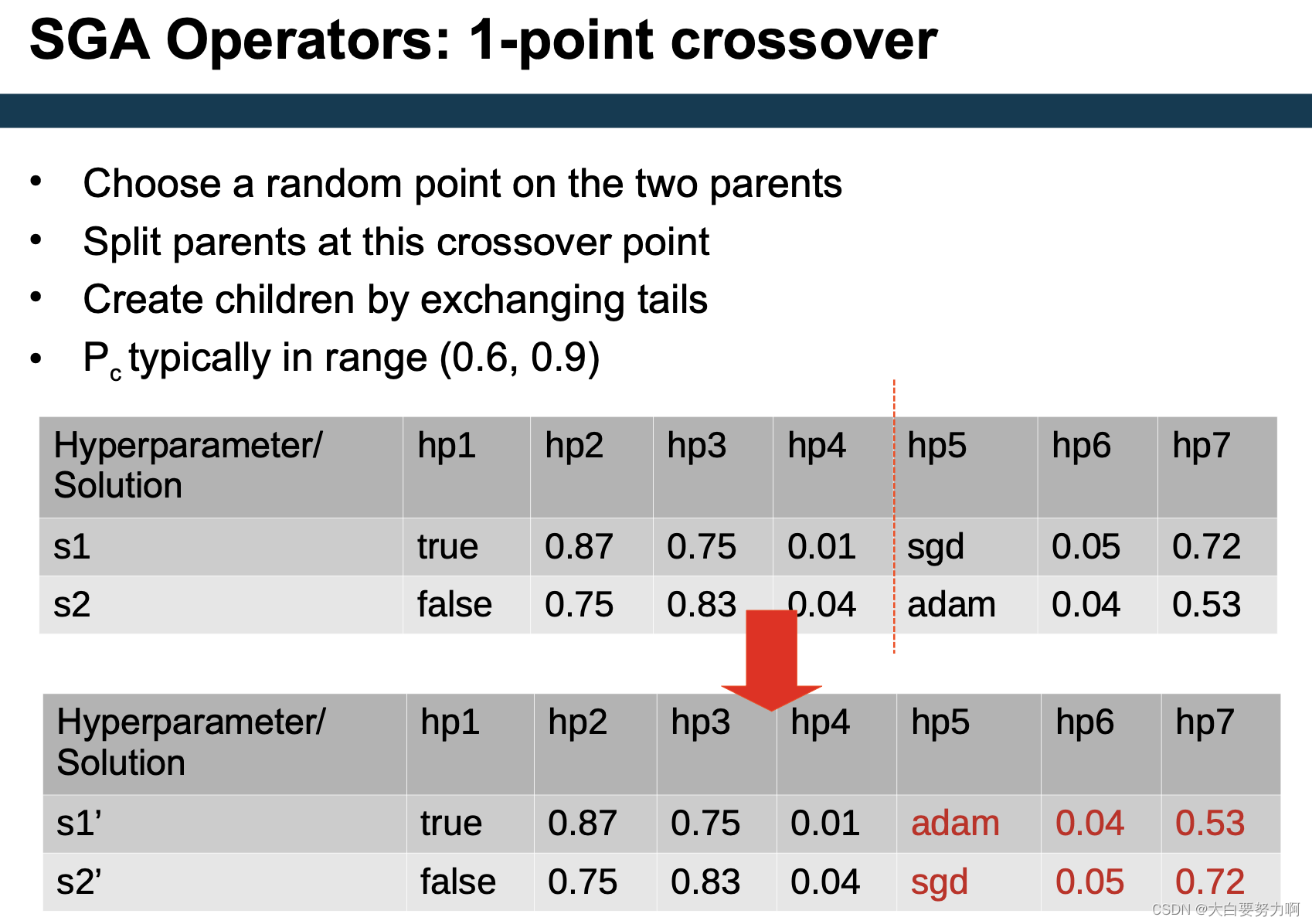
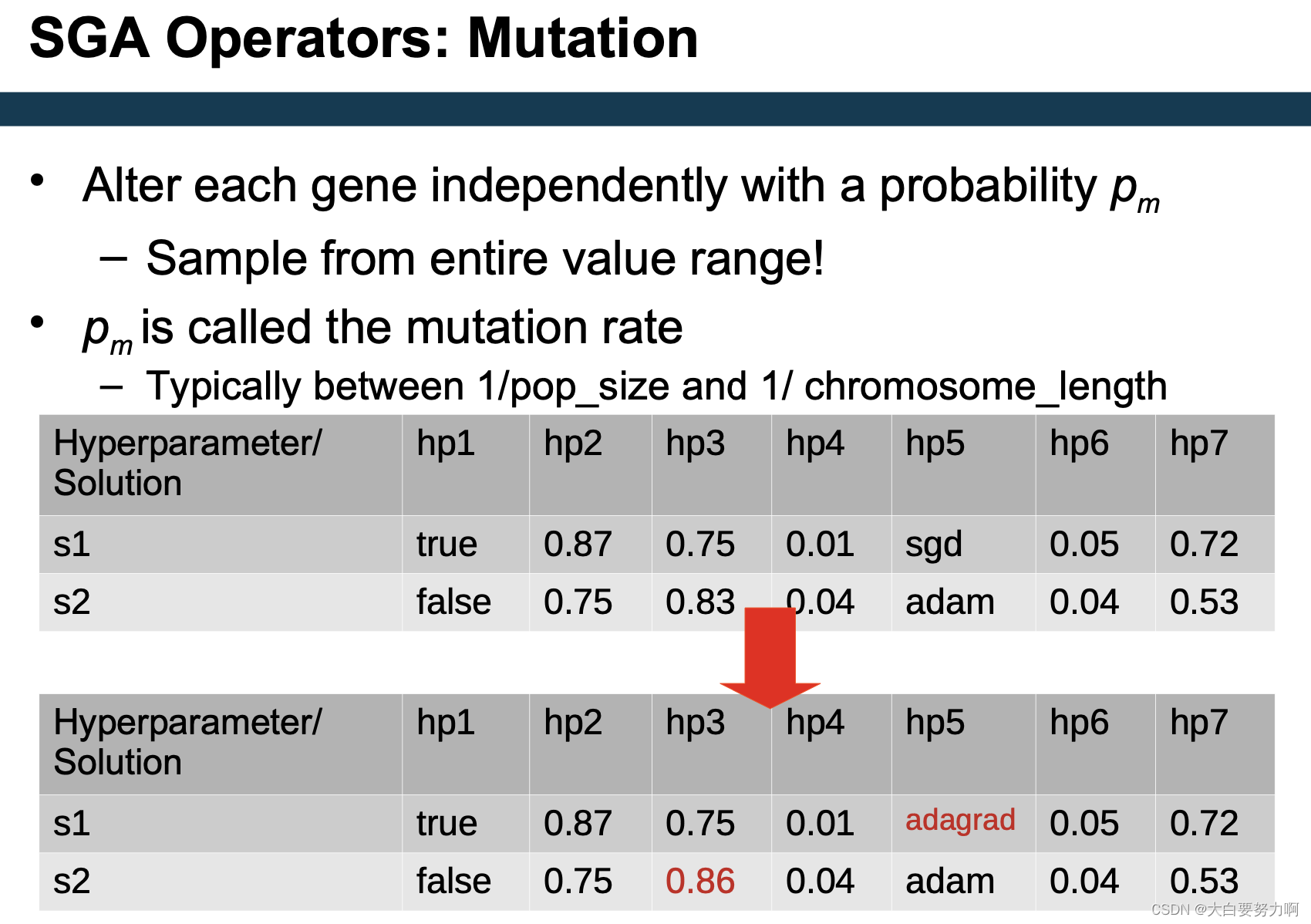
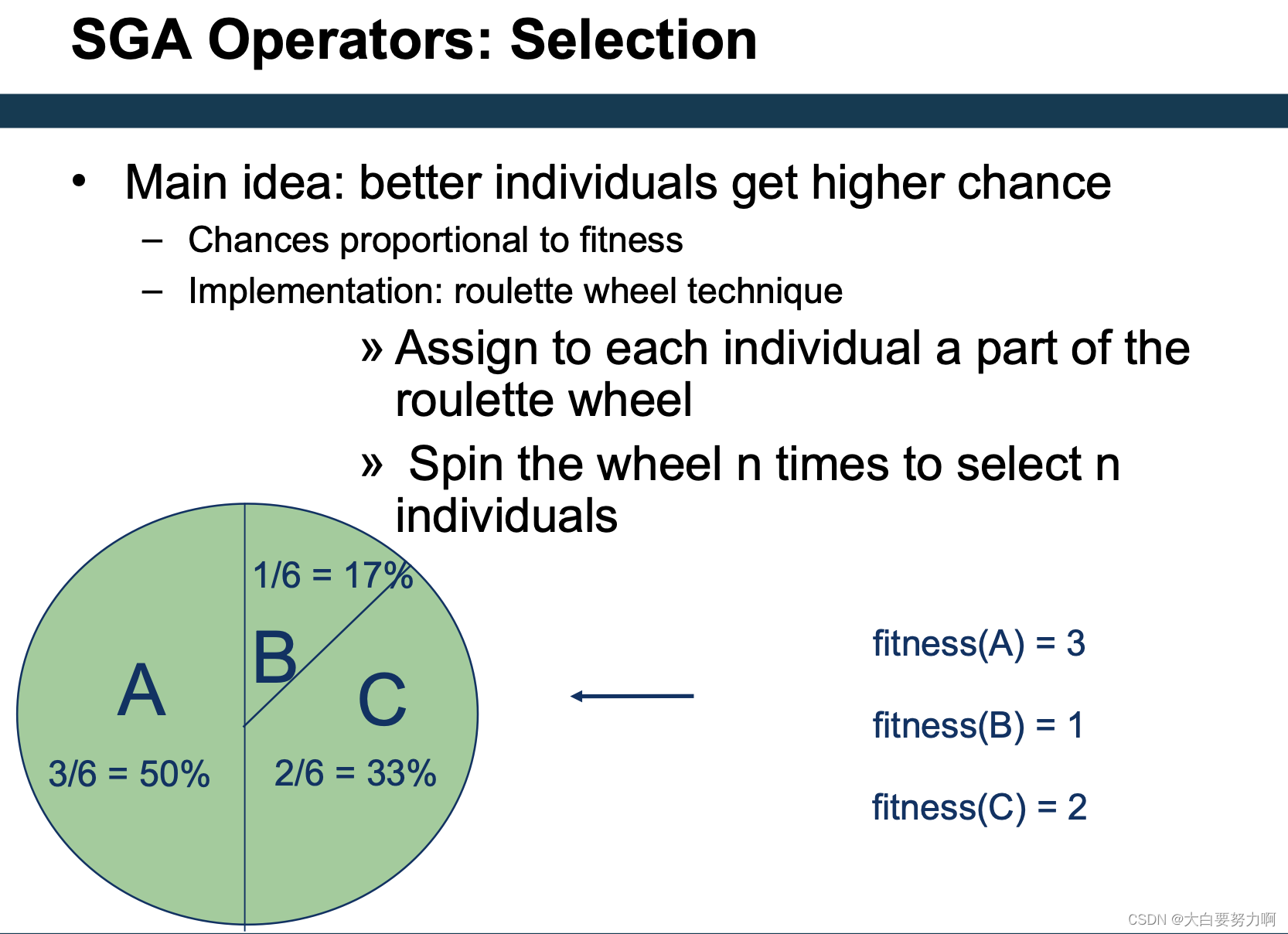
Crossover OR Mutation?
Decade long debate: which one is better / necessary …
Answer (at least, rather wide agreement): it depends on the problem, but
in general, it is good to have both – both have another role
mutation-only-EA is possible, crossover-only-EA would not work
Exploration: Discovering promising areas in the search space, i.e. gaining information on the problem
Exploitation: Optimising within a promising area, i.e. using information
There is co-operation AND competition between them
Crossover is explorative, it makes a big jump to an area
somewhere “in between” two (parent) areas
Mutation is exploitative, it creates random small diversions, thereby staying near (in the area of) the parent
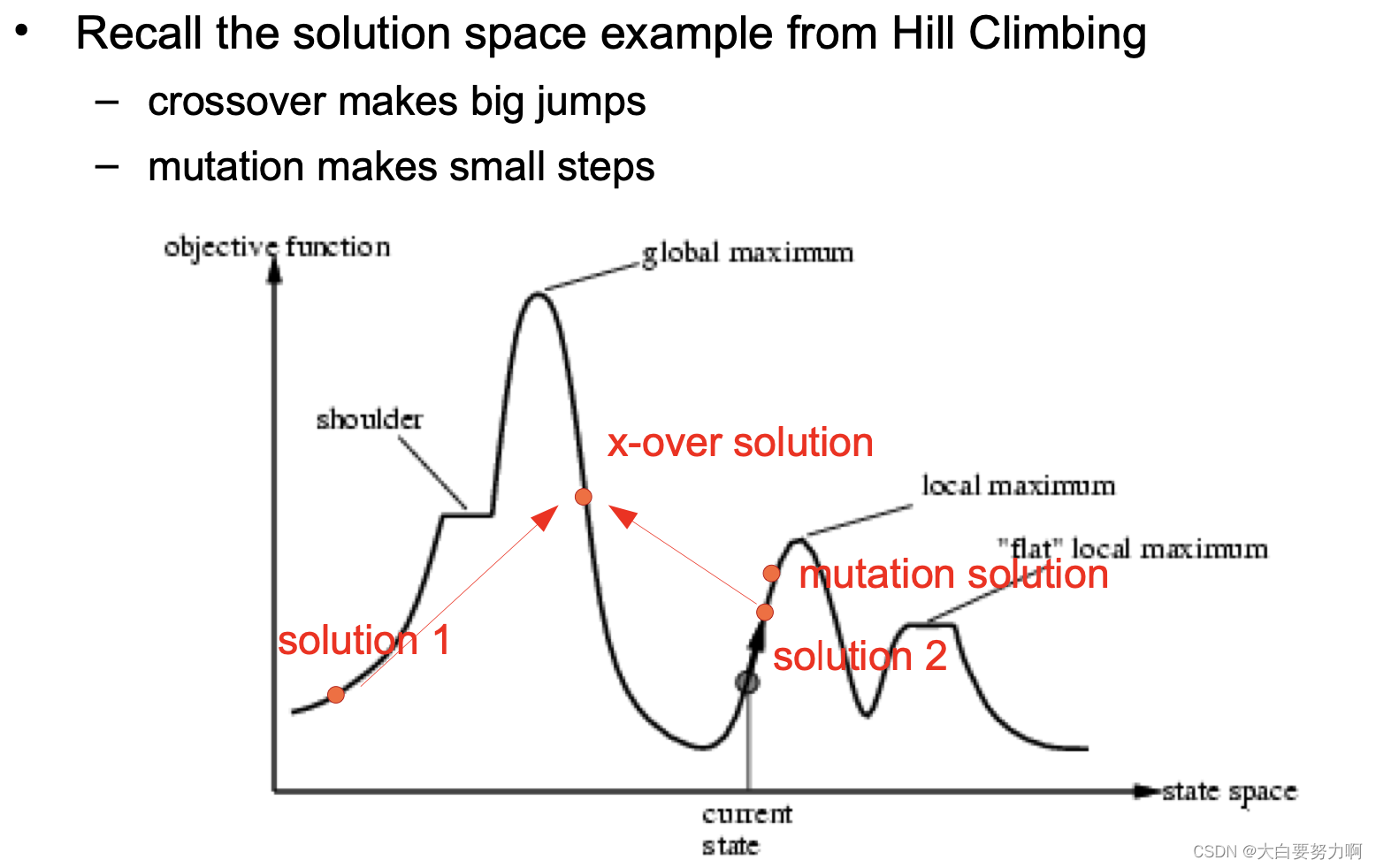
Only crossover can combine information from two parents
Remember: sample from entire value range
Only mutation can introduce new information (alleles)
To hit the optimum you often need a ‘lucky’ mutation
6.6.2 Genetic Feature Subset Selection
Feature Subset Selection can also be solved by Genetic Programming
Individuals: feature subsets
Representation: binary – 1 = feature is included; – 0 = feature is not included
Fitness: classification performance
Crossover: combine selections of two subsets
Mutation: flip bits
6.6.3 Selecting a Learner by Meta Learning
So far, we have looked at finding good parameters for a learner – the learner was always fixed
A similar problem is selecting a learner for the task at hand
Again, we could go with search. Another approach is meta learning
Meta Learning i.e., learning about learning
Goal: learn how well a learner will perform on a given dataset features: dataset characteristics, learning algorithm
prediction target: accuracy, RMSE, …
Also known as AutoML
Basic idea: train a regression model
- data points: individual datasets plus ML approach
- target: expected accuracy/RMSE etc.
Examples for features: number of instances/attributes, fraction of nominal/numerical attributes, min/max/average entropy of attributes, skewness of classes, …
Recap: search heuristics are good for problems where finding an optimal solution is difficult, evaluating a solution candidate is easy, the search space of possible solutions is large
Possible solution: genetic programming
We have encountered such problems quite frequently
Example: learning an optimal decision tree from data
6.6.4 Genetic Decision Tree Learning
Population: candidate decision trees (initialization: e.g., trained on small subsets of data)
Create new decision trees by means of crossover & mutation
Fitness function: e.g., accuracy
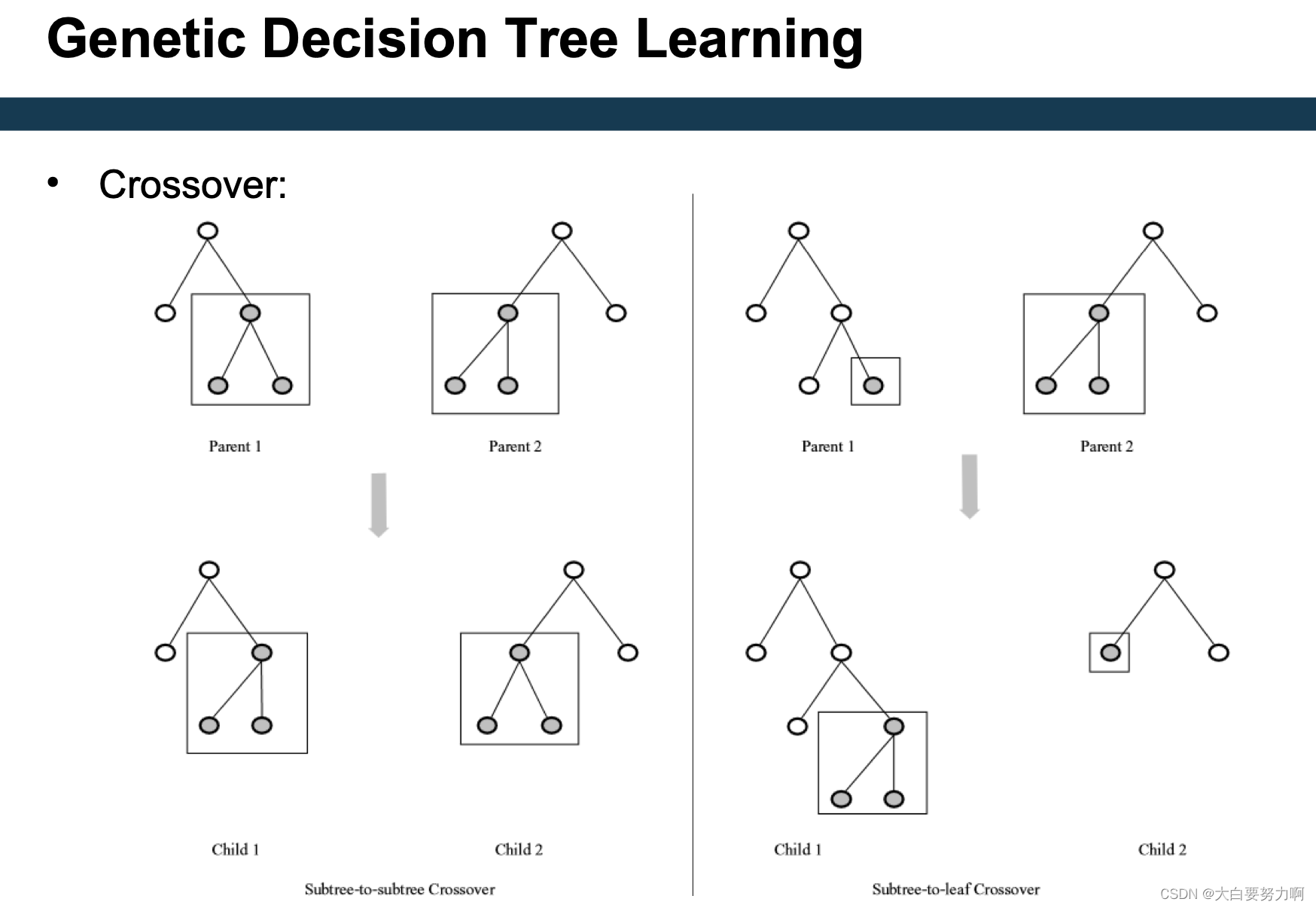
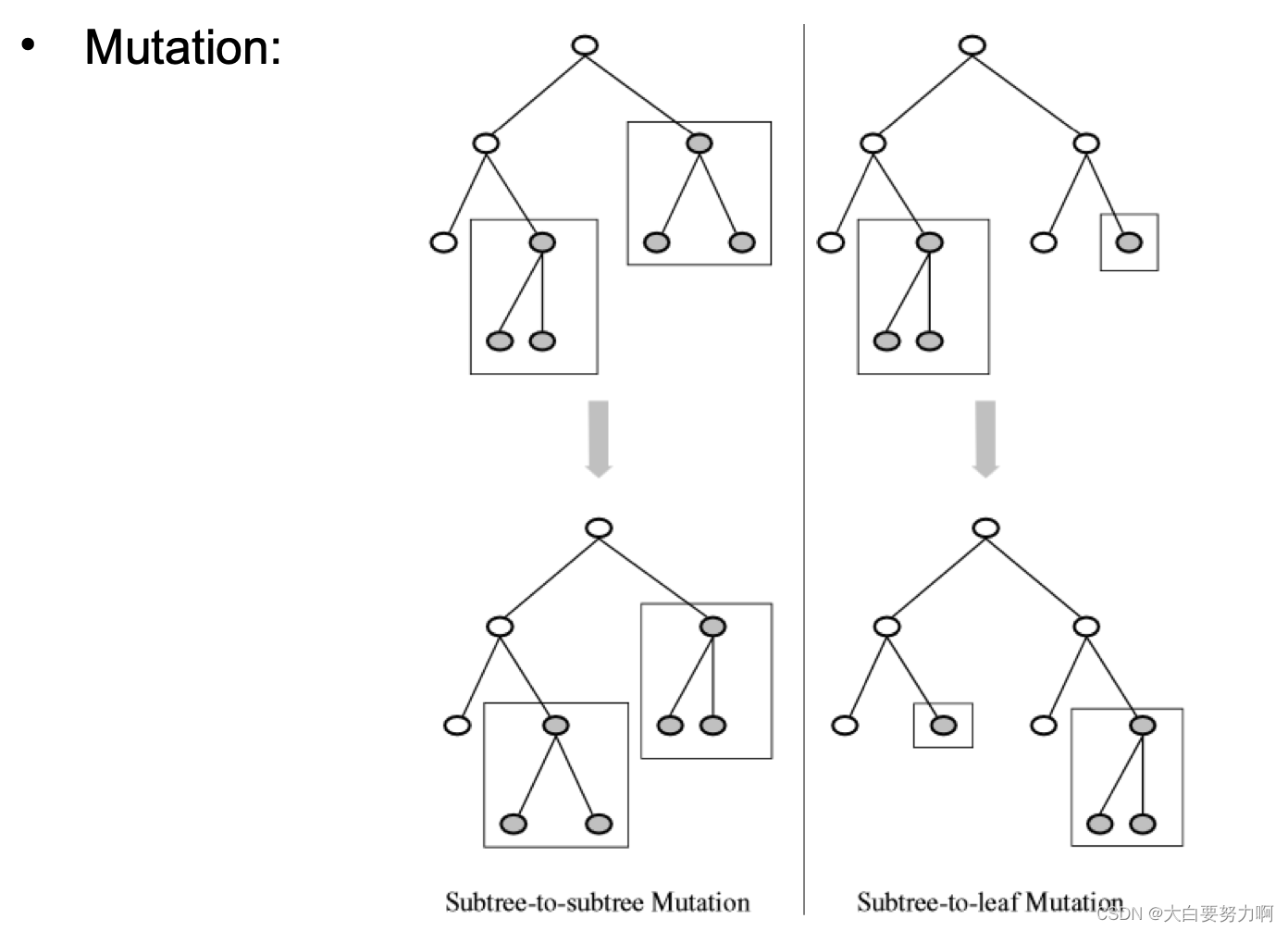
swap can happen in different level, just randomly

6.6.5 Combination of GP with other Learning Methods
Rule Learning (“Learning Classifier Systems”)
Population: set of rule sets (!)
Crossover: combining rules from two sets
Mutation: changing a rule
Artificial Neural Networks
Easiest solution: fixed network layout
The network is then represented as an ordered set (vector) of weights
e.g., [0.8, 0.2, 0.5, 0.1, 0.1, 0.2]
Crossover and mutation are straight forward
Variant: AutoMLP - Searches for best combination of hidden layers and learning rate
6.7 Hyperparameter learning
Hyperparameter tuning as a learning problem: Given a set of hyperparameters H, predict performance p of model. The prediction model is referred to as a surrogate model or oracle
Rationale:
Training and evaluating an actual model is costly
Learning and predicting with the surrogate model is fast
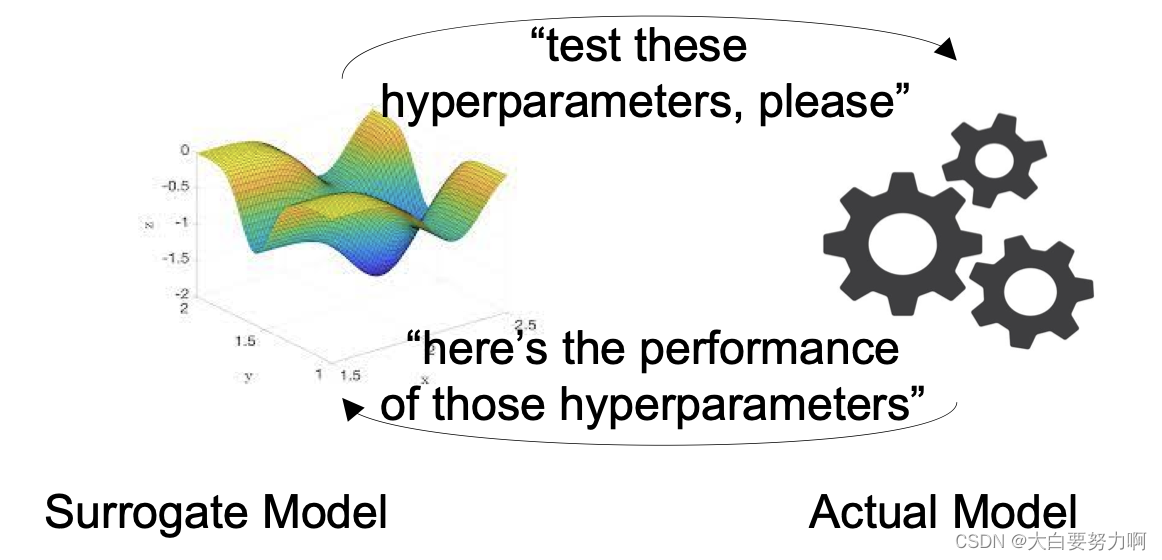
Note:
we want to use not too many runs of the actual model, i.e., the surrogate model will have few training points - use a simple model.
Most well-known: bayesian optimization
Summary: Grid Search, Random Search, Learning hyperparameters / bayesian optimization
Grid search
Inefficient
Fixed grid sizes may miss good parameters (Smaller grid sizes would be even less efficient!)
Random search
Often finds good solutions in less time
Learning hyperparameters / bayesian optimization
Sucessively tests hyperparameters close to local optima
Similar to hill climbing
Difference: explicit surrogate model
6.8 Summary