哈希桶源代码
我们将由下列的哈希桶来模拟封装STL库中的unordered_map和unordered_set
注意:为了实现封装unordered_map和unordered_set,我们需要对下列源码进行优化。
//哈希桶
namespace hashbucket
{
template<class K,class V>
struct HashNode
{
HashNode* _next;
pair<K, V> _kv;
HashNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
:_kv(kv)
,_next(nullptr)
{}
};
template<class K,class V>
class HashTables
{
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
public:
//构造函数
HashTables()
{
_tables.resize(10);
}
//析构函数
~HashTables()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
}
//插入函数
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first))
{
return false;
}
//负载因子
if (_n == _tables.size())//因子到1开始扩容
{
//开新表
vector<Node*> newtables;
newtables.resize(_tables.size() * 2, nullptr);
//遍历旧表
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;//记录下一个的地址
size_t hash = cur->_kv.first % newtables.size();//计算哈希值
//头插
cur->_next = newtables[i];
newtables[i] = cur;
//更新下一个位置
cur = next;
}
//将表置空
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
//交换新旧表
_tables.swap(newtables);
}
size_t hash = kv.first % _tables.size();//计算哈希值
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);//创建结点
//头插
newnode->_next = _tables[hash];
_tables[hash] = newnode;
++_n;
return true;
}
//查找函数
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
size_t hash = key % _tables.size();//计算哈希值
Node* cur = _tables[hash];//寻找位置
while (cur)//cur不为空则继续寻找
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)//相同则找到
{
return cur;//返回找到的地址
}
//不相同则判断下一个
cur = cur->_next;
}
//出循环还没找到则返回空
return NULL;
}
//删除函数
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
size_t hash = key % _tables.size();//计算哈希值
Node* prev = nullptr;//记录前地址
Node* cur = _tables[hash];//记录当前地址
while (cur)//不为空则继续寻找
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)//相同则找到
{
if (prev == nullptr)//如果为头删
{
_tables[hash] = cur->_next;//将下一个结点地址放到指针数组上
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;//将前一个结点连接后一个地址
}
delete cur;//删除找到的结点
return true;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
//出循环还没找到则删除失败
return false;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;
size_t _n = 0;
};
}哈希桶的模板参数
这是原始模板:
template<class K, class V>
class HashTables这是优化后的模板:
template<class K, class T,class KeyofT>
class HashTables可以看到,这将V变为T,然后多出了KeyofT,这是什么意思呢?
(V->T请看下面,KeyofT请看仿函数阶段)
class V ---> class T
首先最基本的:set是K模型,map是KV模型
在set容器中,T是对应着key:
template<class K>
class unordered_set
{
public:
//...
private:
hashbucket::HashTables<K, K, SetKeyofT> _ht;
};在map容器中,T是对应着key和value组成的键值对:
template<class K,class V>
class unordered_map
{
public:
//...
private:
hashbucket::HashTables<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyofT> _ht;
};所以模板T实际的类型是取决于上层使用的是K还是pair<K,V>
这一切的一切都是为了让哈希桶能够适配两种不同的容器。
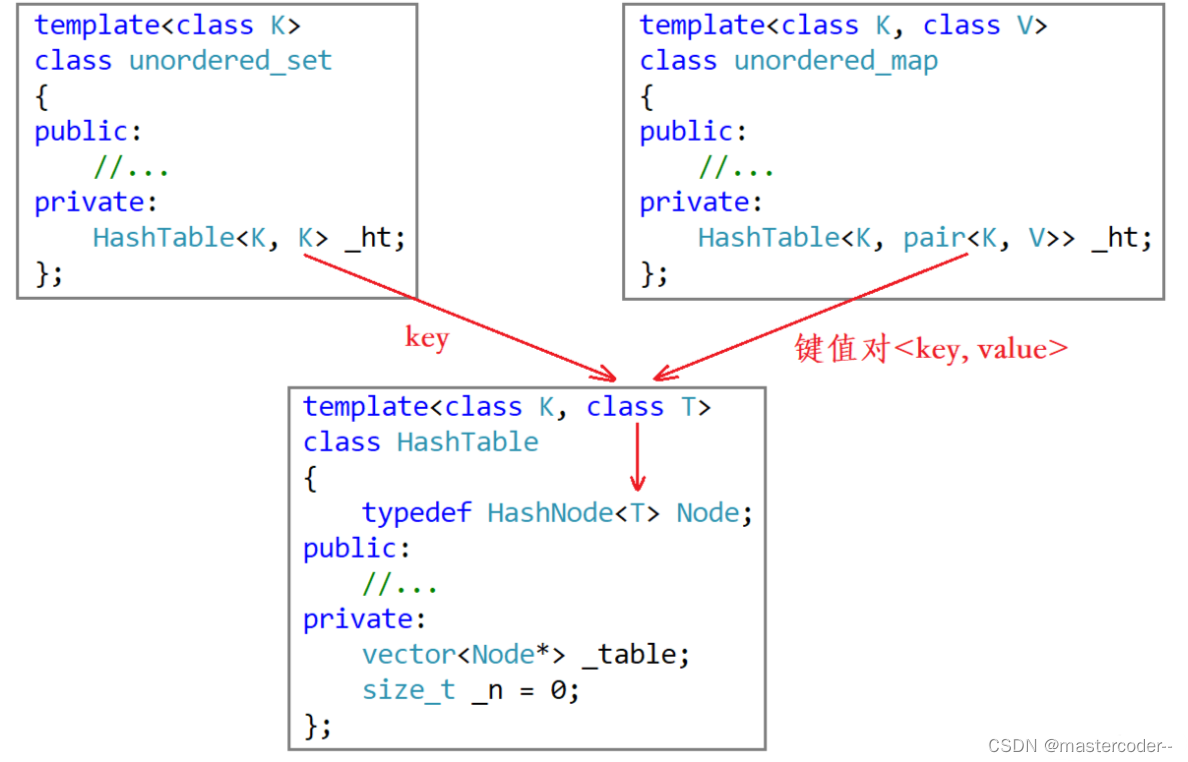
所以,哈希桶的模板参数改变后,那么结点类的模板参数也需要跟着改变了。(看下面标题)
结点类的模板参数实现
优化前:
template<class K,class V>
struct HashNode
{
HashNode* _next;
pair<K, V> _kv;
HashNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
:_kv(kv)
,_next(nullptr)
{}
};优化后:
//结点
template<class T>
struct HashNode
{
HashNode* _next;
T _data;
HashNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
, _next(nullptr)
{}
};可以看到,这里的_data就是原本的kv键值对数据,而T对应set中的key,map中的kv键值对。
那么,class KeyofT呢?这里就要说到仿函数了↓
unordered_map、unordered_set中的仿函数
在unordered_map和unordered_set容器中各自的私有函数分别有着:
![]()
![]()
它们分别传入底层哈希桶时,T传入的可能是key,也可能是key和value的键值对,如果是键值对,那么就需要将键值对的key提取出来再进行比较,那么此时就需要用到仿函数来提取key。
//map容器
struct MapKeyofT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
//set容器
struct SetKeyofT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};可以看到,我们在这个仿函数中重载了operator(), 这个operator()在map中用来提取kv.first,也就是key值,为了能统一map和set,我们在set也重载了operator()。
所以set传入底层哈希桶就是set的仿函数,map传入底层哈希桶就是map的仿函数。
迭代器类的实现
先查看下列代码:
//解决冲突的前置声明
template<class K, class T, class KeyofT>
class HashTables;
//迭代器
template<class K,class T,class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyofT>
struct HTiterator
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;//哈希结点的类型
typedef HTiterator<K, T, Ref, Ptr, KeyofT> Self;//迭代器类型
Node* _node;//结点指针
const HashTables<K, T, KeyofT>* _pht;//迭代器要哈希表,哈希表要迭代器,冲突
//vector<Node*>* _ptb;//直接使用私有类,就不会冲突了
size_t _hash;//用来计算哈希值
};可以看到这里有一个用来解决冲突的前置声明,因为在后续使用迭代器时,我们需要用到哈希表类型,但是这个迭代器类是放在哈希表上面,编译器会往上寻找,找不到,那么就会报错,此时这种情况就是,哈希表需要用到迭代器,迭代器需要用到哈希表,两者冲突了,为了解决这种情况,我们加了个前置声明哈希表,告诉编译器是存在的,往下找就好了。
构造函数
//构造函数
HTiterator(Node* node, HashTables<K, T, KeyofT>* pht, size_t hash)
:_node(node)
, _pht(pht)
, _hash(hash)
{}
//const构造函数
HTiterator(Node* node, const HashTables<K, T, KeyofT>* pht, size_t hash)
:_node(node)
, _pht(pht)
, _hash(hash)
{}*函数重载
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;//对地址的解引用,返回对应数据即可
}->函数重载
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;//返回数据地址的引用
}!=函数重载
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;//判断两个结点的地址是否不同
}==函数重载
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node; //判断两个结点的地址是否相同
}++函数重载
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_next)//如果结点的下一个位置不为空
{
_node = _node->_next;//继续往下走
}
else//如果结点的下一个位置为空
{
//开始重新寻找下一个桶
++_hash;//哈希值++往后寻找
while (_hash < _pht->_tables.size())//当哈希值不超过表的大小的话循环
{
//如果哈希值对应的位置不为空,那么就找到了
if (_pht->_tables[_hash])
{
_node = _pht->_tables[_hash];//更新结点位置
break;//停止循环
}
//如果为空,出了判定条件,那么哈希值继续自增
++_hash;
}
//如果哈希值超过了表的大小,那么说明没有了,让结点置空
if (_hash == _pht->_tables.size())
{
_node = nullptr;
}
}
return *this;
}迭代器函数的实现
typedef HTiterator<K, T, T&, T*, KeyofT> iterator;
typedef HTiterator<K, T, const T&, const T*, KeyofT> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
从表头开始寻找,直到找到第一个不为空的位置,返回该迭代器
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
if (_tables[i])
{
return iterator(_tables[i], this, i);
}
}
//如果没找到那么就直接返回空,调用end()即可
return end();
}
iterator end()
{
//返回nullptr
return iterator(nullptr, this, -1);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
if (_tables[i])
{
return const_iterator(_tables[i], this, i);
}
}
return end();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr, this, -1);
}优化之后的哈希桶代码
//哈希桶
namespace hashbucket
{
//结点
template<class T>
struct HashNode
{
HashNode* _next;
T _data;
HashNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
, _next(nullptr)
{}
};
//解决冲突的前置声明
template<class K, class T, class KeyofT>
class HashTables;
//迭代器
template<class K,class T,class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyofT>
struct HTiterator
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef HTiterator<K, T, Ref, Ptr, KeyofT> Self;
Node* _node;
const HashTables<K, T, KeyofT>* _pht;//迭代器要哈希表,哈希表要迭代器,冲突
//vector<Node*>* _ptb;//直接使用私有类,就不会冲突了
size_t _hash;
HTiterator(Node* node,HashTables<K,T,KeyofT>* pht,size_t hash)
:_node(node)
,_pht(pht)
,_hash(hash)
{}
HTiterator(Node* node, const HashTables<K, T, KeyofT>* pht, size_t hash)
:_node(node)
, _pht(pht)
, _hash(hash)
{}
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_next)
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else
{
++_hash;
while (_hash < _pht->_tables.size())
{
if (_pht->_tables[_hash])
{
_node = _pht->_tables[_hash];
break;
}
++_hash;
}
if (_hash == _pht->_tables.size())
{
_node = nullptr;
}
}
return *this;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};
//哈希表
template<class K, class T,class KeyofT>
class HashTables
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
//友元函数,让外部类能访问私有成员
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyofT>
friend struct HTiterator;
public:
typedef HTiterator<K, T, T&, T*, KeyofT> iterator;
typedef HTiterator<K, T, const T&, const T*, KeyofT> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
if (_tables[i])
{
return iterator(_tables[i], this, i);
}
}
return end();
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this, -1);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
if (_tables[i])
{
return const_iterator(_tables[i], this, i);
}
}
return end();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr, this, -1);
}
//构造函数
HashTables()
{
_tables.resize(10);
}
//析构函数
~HashTables()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
}
//插入函数
pair<iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
KeyofT kot;
iterator it = Find(kot(data));
if (it != end())
{
return make_pair(it,false);
}
//负载因子
if (_n == _tables.size())//因子到1开始扩容
{
//开新表
vector<Node*> newtables;
newtables.resize(_tables.size() * 2, nullptr);
//遍历旧表
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;//记录下一个的地址
size_t hash = kot(cur->_data) % newtables.size();//计算哈希值
//头插
cur->_next = newtables[i];
newtables[i] = cur;
//更新下一个位置
cur = next;
}
//将表置空
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
//交换新旧表
_tables.swap(newtables);
}
size_t hash = kot(data) % _tables.size();//计算哈希值
Node* newnode = new Node(data);//创建结点
//头插
newnode->_next = _tables[hash];
_tables[hash] = newnode;
++_n;
return make_pair(iterator(newnode,this,hash), true);
}
//查找函数
iterator Find(const K& key)
{
KeyofT kot;
size_t hash = key % _tables.size();//计算哈希值
Node* cur = _tables[hash];//寻找位置
while (cur)//cur不为空则继续寻找
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == key)//相同则找到
{
return iterator(cur,this,hash);//返回找到的地址
}
//不相同则判断下一个
cur = cur->_next;
}
//出循环还没找到则返回空
return end();
}
//删除函数
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
KeyofT kot;
size_t hash = key % _tables.size();//计算哈希值
Node* prev = nullptr;//记录前地址
Node* cur = _tables[hash];//记录当前地址
while (cur)//不为空则继续寻找
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == key)//相同则找到
{
if (prev == nullptr)//如果为头删
{
_tables[hash] = cur->_next;//将下一个结点地址放到指针数组上
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;//将前一个结点连接后一个地址
}
delete cur;//删除找到的结点
return true;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
//出循环还没找到则删除失败
return false;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;
size_t _n = 0;
};
}
用哈希桶封装unordered_map的代码
#pragma once
#include"hashtable.h"
namespace bear
{
template<class K,class V>
class unordered_map
{
struct MapKeyofT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename hashbucket::HashTables<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyofT>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename hashbucket::HashTables<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyofT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _ht.begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _ht.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
return _ht.Insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _ht.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
V& operator[](const K& key) const
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _ht.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
iterator Find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
private:
hashbucket::HashTables<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyofT> _ht;
};
}用哈希桶封装unordered_set的代码
#pragma once
#include"hashtable.h"
namespace bear
{
template<class K>
class unordered_set
{
struct SetKeyofT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename hashbucket::HashTables<K, K, SetKeyofT>::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename hashbucket::HashTables<K, K, SetKeyofT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
//iterator begin()
//{
// return _ht.begin();
//}
//iterator end()
//{
// return _ht.end();
//}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _ht.begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _ht.end();
}
pair<const_iterator,bool> Insert(const K& key)
{
auto ret = _ht.Insert(key);
return pair<const_iterator, bool>(const_iterator(ret.first._node,ret.first._pht,ret.first._hash),ret.second);
}
iterator Find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
private:
hashbucket::HashTables<K, K, SetKeyofT> _ht;
};
}