欢迎回到C# WPF入门学习系列的第六篇。在前面的文章中,我们探讨了按钮(Button)的事件处理。今天,我们将继续学习另一个常用的WPF控件——TextBox。本文将介绍 TextBox 的常见属性和事件,并通过示例代码展示如何在实际应用中使用这些功能。
一、TextBox的基础知识
TextBox 是WPF中一个重要的输入控件,允许用户在应用程序中输入和编辑文本。它常用于表单、搜索框和任何需要文本输入的场景。
TextBox的基本定义
我们先来看看一个简单的 TextBox 定义:
<Window
x:Class="WpfApp.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="MainWindow" Height="350" Width="525">
<Grid>
<TextBox x:Name="myTextBox" Width="200" Height="30"
HorizontalAlignment="Center"
VerticalAlignment="Center"
Text="Hello, World!" />
</Grid>
</Window>在这个示例中,我们定义了一个 TextBox 控件,其默认文本为“Hello, World!”。
二、TextBox的常见属性
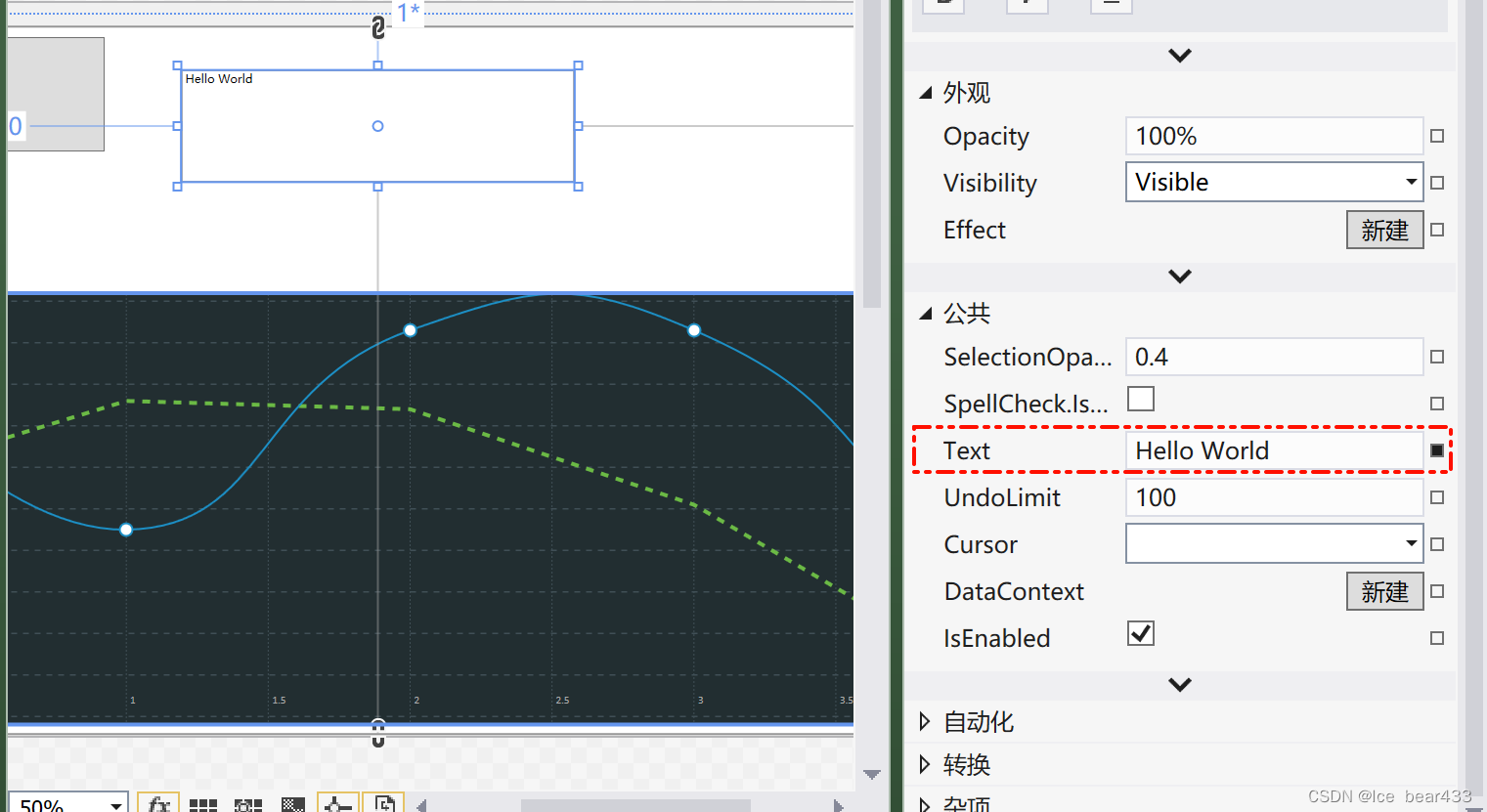
1. Text
Text 属性用于获取或设置 TextBox 中的文本内容。在上面的示例中,Text="Hello, World!" 设置了 TextBox 的初始文本。
2. Width 和 Height
Width 和 Height 属性用于设置 TextBox 的宽度和高度。例如:
<TextBox Width="200" Height="30" />3. HorizontalAlignment 和 VerticalAlignment
HorizontalAlignment 和 VerticalAlignment 属性用于设置 TextBox 在父容器中的水平和垂直对齐方式。例如:
<TextBox HorizontalAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center" />4. MaxLength
MaxLength 属性用于设置 TextBox 中允许输入的最大字符数。例如:
<TextBox MaxLength="100" />
5. IsReadOnly
IsReadOnly 属性用于设置 TextBox 是否为只读。例如:
<TextBox IsReadOnly="True" />示例
下面是一个包含以上常见属性的完整示例:
<TextBox
x:Name="myTextBox" Width="200" Height="30"
HorizontalAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center"
Text="Hello, World!"
MaxLength="100"
IsReadOnly="False"
/>三、TextBox的常见事件
TextBox 支持多种事件,用于处理用户输入和交互。我们来看看一些常见的事件及其用法。
1. TextChanged
TextChanged 事件在 TextBox 的文本内容发生变化时触发。我们可以在后台代码中处理这个事件:
<TextBox
x:Name="myTextBox" Width="200" Height="30"
HorizontalAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center"
TextChanged="MyTextBox_TextChanged"
/>后台代码
private void MyTextBox_TextChanged(object sender, TextChangedEventArgs e) {
MessageBox.Show($"Text changed: {myTextBox.Text}");
}2. GotFocus 和 LostFocus
GotFocus 事件在 TextBox 获得焦点时触发,LostFocus 事件在 TextBox 失去焦点时触发。
XAML代码
<TextBox
x:Name="myTextBox" Width="200" Height="30"
HorizontalAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center"
GotFocus="MyTextBox_GotFocus" LostFocus="MyTextBox_LostFocus"
/>后台代码
private void MyTextBox_GotFocus(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) {
myTextBox.Background = new SolidColorBrush(Colors.LightYellow);
}
private void MyTextBox_LostFocus(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) {
myTextBox.Background = new SolidColorBrush(Colors.White);
}3. KeyDown 和 KeyUp
KeyDown 事件在用户按下键盘键时触发,KeyUp 事件在用户释放键盘键时触发。
XAML代码
<TextBox
x:Name="myTextBox" Width="200" Height="30"
HorizontalAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center"
KeyDown="MyTextBox_KeyDown" KeyUp="MyTextBox_KeyUp"
/>后台代码
private void MyTextBox_KeyDown(object sender, KeyEventArgs e) {
if (e.Key == Key.Enter) { MessageBox.Show("Enter key pressed!");
}
}
private void MyTextBox_KeyUp(object sender, KeyEventArgs e) {
// 处理键盘释放事件
}4. PreviewTextInput
PreviewTextInput 事件在文本输入之前触发,通常用于自定义输入验证。
XAML代码
<TextBox
x:Name="myTextBox" Width="200" Height="30"
HorizontalAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center" PreviewTextInput="MyTextBox_PreviewTextInput"
/>后台代码
private void MyTextBox_PreviewTextInput(object sender, TextCompositionEventArgs e) {
// 只允许输入数字 e.Handled = !IsTextAllowed(e.Text);
}
private static bool IsTextAllowed(string text) {
return text.All(char.IsDigit);
}四、总结
在本篇博客中,我们详细介绍了 WPF 中 TextBox 控件的常见属性和事件。通过这些示例代码,你可以了解如何设置 TextBox 的外观和行为,并且能够处理用户的输入和交互。这些知识对于创建丰富和互动的用户界面至关重要。