- RabbitMQ基础
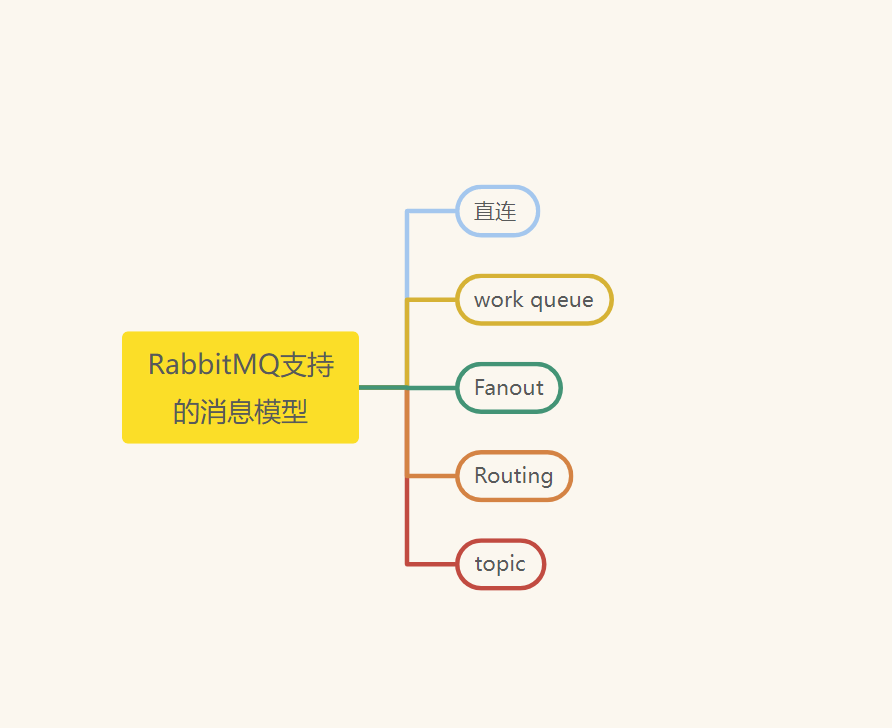
- RabbitMQ支持的消息模型
一、第一种模型(直连)
我们将用Java编写两个程序,发送单个消息的生成者和接收消息并打印出来的消费者。
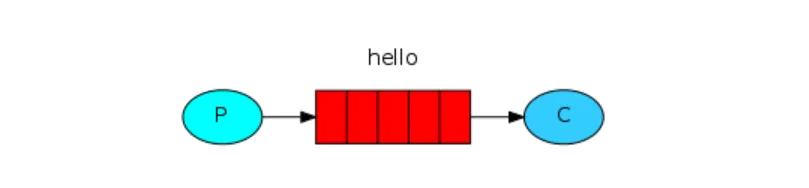
在下图,“P”是生成者,“C”消费者。中间框是一个队列RabbitMQ保留的消息缓冲区 。
首先构建一个Maven项目,然后引入依赖。
<!-- 导入rabbitmq原生依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>amqp-client</artifactId>
<version>5.10.0</version>
</dependency>
定义生产者
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
import com.rabbitmq.client.MessageProperties;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Provider 生产者代码
* @since 2022/12/29
*/
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
// // 1.创建连接工厂
// ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
// // 2.设置连接属性
// connectionFactory.setHost("192.168.137.120");
// connectionFactory.setPort(5672);
// connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("/");
// connectionFactory.setUsername("admin");
// connectionFactory.setPassword("123456");
// connectionFactory.setHandshakeTimeout(60000);
//
// // 3.从连接工厂获得连接
// Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
// 从工具类中获得连接
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
// 4.从连接中获得channel
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 5.声明队列queue存储消息
/**
* 参数s:队列名称 如果队列不存在就自动创建
* 参数b:用来定义队列特性是否要持久化 true 持久化队列 false 不持久化
* 参数b1: exclusive 是否独占队列 true 独占队列 false 不独占
* 参数b2:autoDelete 是否在消费完成后自动删除队列 true 自动删除 false 不自动删除
* 参数5:额外附加参数
*
*/
channel.queueDeclare("hello",true,false,false,null);
// 7.发送消息给中间件
// 参数1:交换机名称 参数2:队列名称 参数3:传递消息的额外设置 参数4:
channel.basicPublish("","hello", MessageProperties.PERSISTENT_TEXT_PLAIN,"hello rabbitmq".getBytes());
System.out.println("消息发送成功");
// // 8.关闭连接
// channel.close();
// connection.close();
RabbitMqUtil.closeConnectionAndChannel(channel,connection);
}
}
执行发送,这个时候可以在web控制台查看到这个队列queue的信息。
定义消费者
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Consumer 消费者
* @since 2022/12/29
*/
public class Consumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
// ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
// connectionFactory.setHost("192.168.137.120");
// connectionFactory.setPort(5672);
// connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("/");
// connectionFactory.setUsername("admin");
// connectionFactory.setPassword("123456");
// connectionFactory.setHandshakeTimeout(60000);
//
// // 创建连接
// Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
// 从工具类中获得连接
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
// 创建信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 消费者成功消费时的回调
DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag,message) ->{
System.out.println(new String(message.getBody()));
};
// 消费者取消消费时的回调
CancelCallback callback = consumerTag ->{
System.out.println("消费者取消消费接口的回调");
};
// 参数1:消费队列的名称
// 参数2:消息的自动确认机制(已获得消息就通知MQ消息已被消费)true 打开 false 关闭
// 参数3:
channel.basicConsume("hello",true,deliverCallback,callback);
// channel.close();
// connection.close();
}
}
工具类的包装
package com.duan.rabbitmq.utils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description RabbitMqUtil
* @since 2023/1/2
*/
public class RabbitMqUtil {
// 定义提供连接对象的方法
public static Connection getConnection(){
try{
// 1.创建连接工厂
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
// 2.设置连接属性
connectionFactory.setHost("192.168.137.120");
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("/");
connectionFactory.setUsername("admin");
connectionFactory.setPassword("123456");
connectionFactory.setHandshakeTimeout(60000);
return connectionFactory.newConnection();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
// 关闭连接通道和关闭连接的工具方法
public static void closeConnectionAndChannel(Channel channel,Connection connection){
try{
if(channel !=null){
channel.close();
}
if(connection != null){
connection.close();
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
报连接超时错误
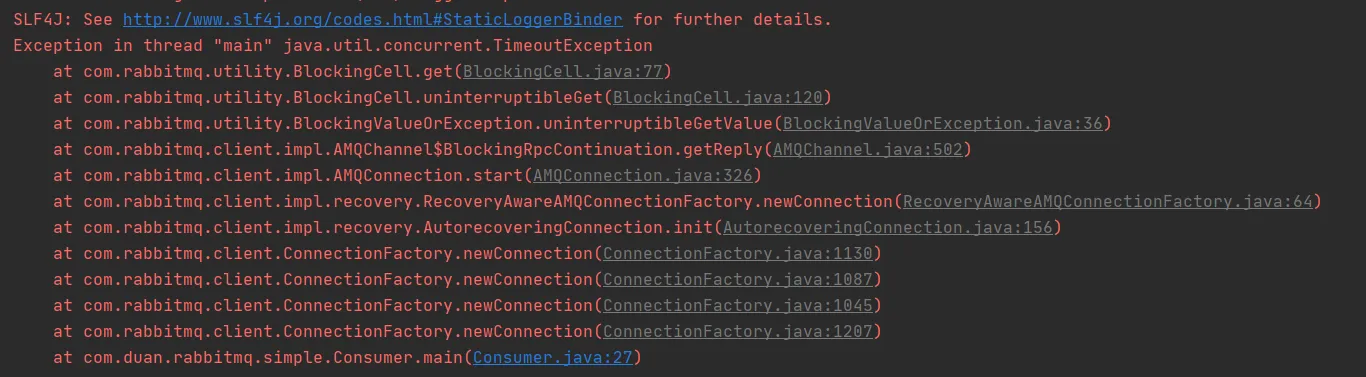
**解决方案:**原因是连接超时,加超时时间。
maevn项目设置超时时间:factory.setHandshakeTimeout\(60000\)
二、第二种模型(work quene)
work queues被称为任务队列(Task queues)。当消息处理比较耗时的时候,可能生产消息的速度会远远大于消息的消费速度。长此以往,消息就会堆积越来越多,无法及时处理。此时就可以使用work 模型: 让多个消费者绑定到一个队列,共同消费队列中的消息。 队列中的消息一旦消费,就会消失,因此任务是不会被重复执行的。
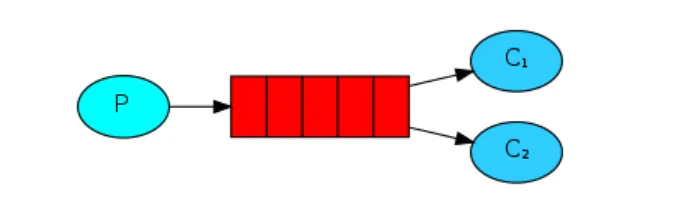
- P:生产者
- C1:消费者1
- C2:消费者2
定义生成者
package com.duan.rabbitmq.work;
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Producer
* @since 2023/3/24
*/
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
/**
* 声明队列queue存储信息
* 参数1: 队列名称
* 参数2: 用来定义队列是否要持久化
* 参数3: exclusion 是否是独占队列
* 参数4: autoDelete 是否再消费完成后自动删除队列
* 参数5: 额外附加参数
*/
channel.queueDeclare("work",true,false,false,null);
for(int i = 0; i<10; i++){
// 参数1:交换机名称 参数2:队列名称 参数3:消息传递的额外设置
channel.basicPublish("","work",null,(i+"work").getBytes());
}
RabbitMqUtil.closeConnectionAndChannel(channel,connection);
}
}
定义消费者1
package com.duan.rabbitmq.work;
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Consumer1
* @since 2023/3/24
*/
public class Consumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
// 创建信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 消费者消费成功时的回调
channel.queueDeclare("work",true,false,false,null);
channel.basicConsume("work",true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException{
System.out.println("消费者1: "+new String(body));
}
});
RabbitMqUtil.closeConnectionAndChannel(channel,connection);
}
}
定义消费者2
package com.duan.rabbitmq.work;
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Consumer1
* @since 2023/3/24
*/
public class Consumer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
// 创建信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 消费者消费成功时的回调
channel.queueDeclare("work",true,false,false,null);
channel.basicConsume("work",true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException{
try{
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("消费者2: "+new String(body));
}
});
RabbitMqUtil.closeConnectionAndChannel(channel,connection);
}
}
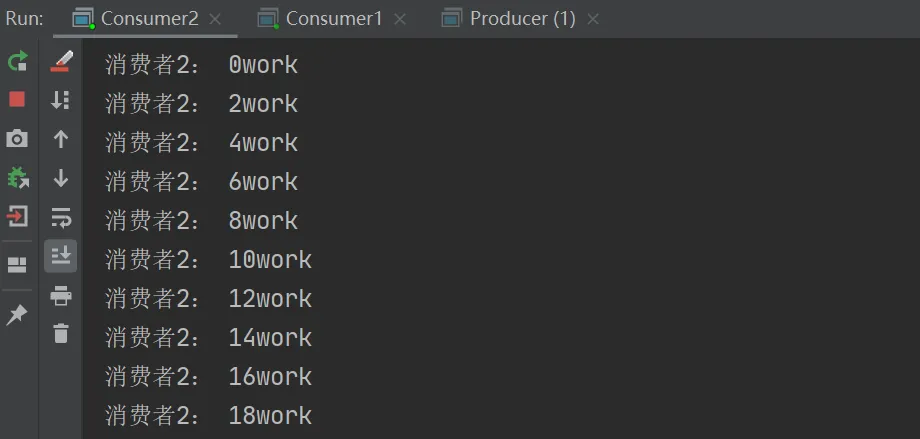
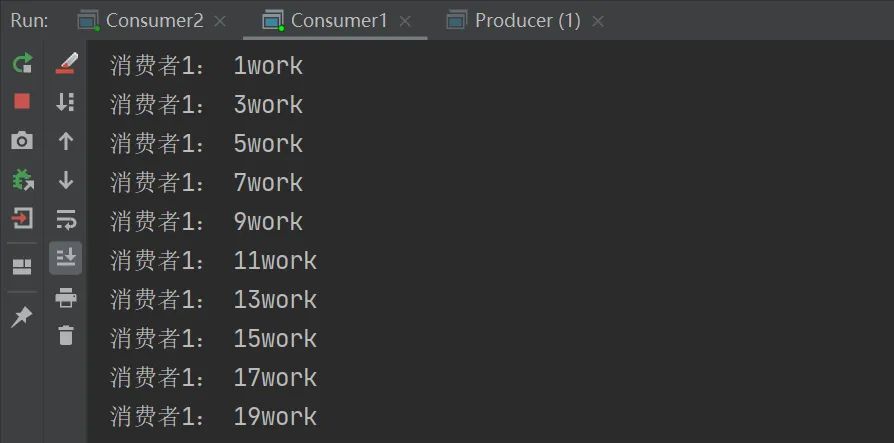
rabbitMQ讲按照顺序将每个消息发给下一个使用者,每个消费者都会收到相同数量的消息。
测试结果
消息确认机制
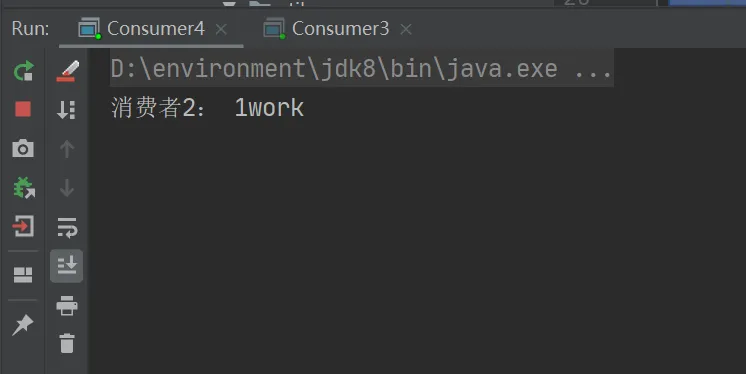
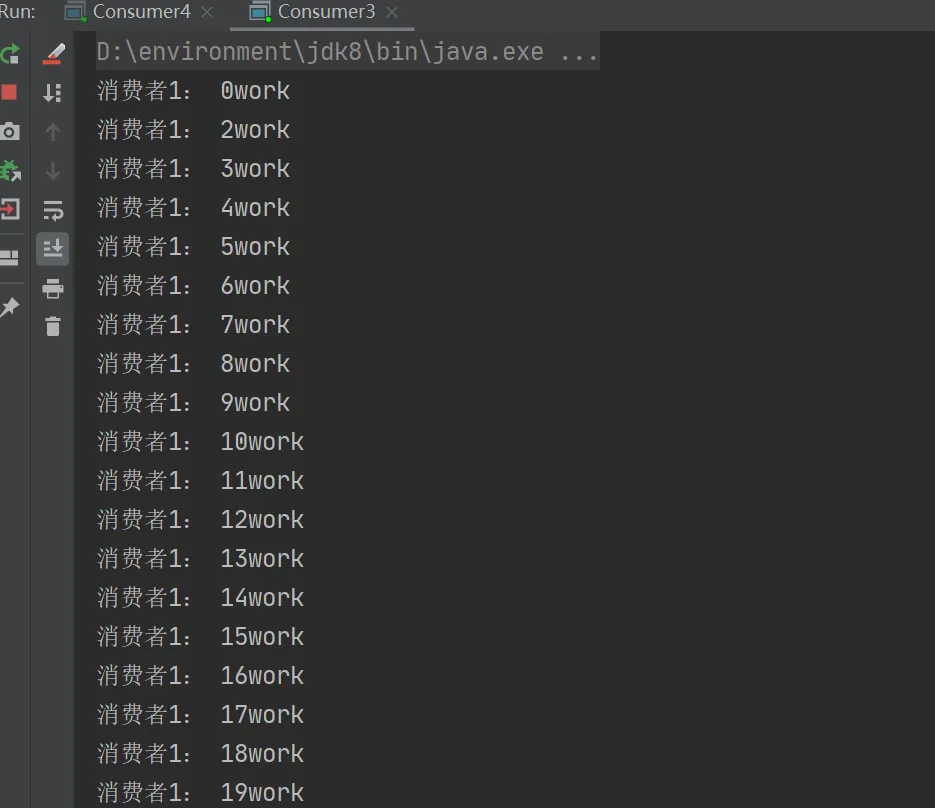
前面看到的是所有的消费者均分消息,会有一个问题,如果一个消费者宕机了,会出现消息丢失现场,希望当出现消费者宕机时,消息被另一个消费者消费,也就是多劳多得生产者代码。
package com.duan.rabbitmq.work;
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Producer
* @since 2023/3/24
*/
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
/**
* 声明队列queue存储信息
* 参数1: 队列名称
* 参数2: 用来定义队列是否要持久化
* 参数3: exclusion 是否是独占队列
* 参数4: autoDelete 是否再消费完成后自动删除队列
* 参数5: 额外附加参数
*/
channel.queueDeclare("work",true,false,false,null);
for(int i = 0; i<20; i++){
// 参数1:交换机名称 参数2:队列名称 参数3:消息传递的额外设置
channel.basicPublish("","work",null,(i+"work").getBytes());
}
RabbitMqUtil.closeConnectionAndChannel(channel,connection);
}
}
生成者1
package com.duan.rabbitmq.work;
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Consumer3
* @since 2023/11/27
*/
public class Consumer3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
// 创建信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.basicQos(1); // 每次只消费一个消息
// 消费者消费成功时的回调
channel.queueDeclare("work",true,false,false,null);
channel.basicConsume("work",false,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException{
System.out.println("消费者1: "+new String(body));
// 手动确认,参数1:消息标识 参数2:每次确认1个
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(),false);
}
});
}
}
生成者2
package com.duan.rabbitmq.work;
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Consumer4
* @since 2023/11/27
*/
public class Consumer4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
// 创建信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.basicQos(1); // 每次消费一个消息
// 消费者消费成功时的回调
channel.queueDeclare("work",true,false,false,null);
channel.basicConsume("work",false,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException{
try{
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("消费者2: "+new String(body));
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(),false);
}
});
}
}
测试结果
三、第三种模型(Fanout)
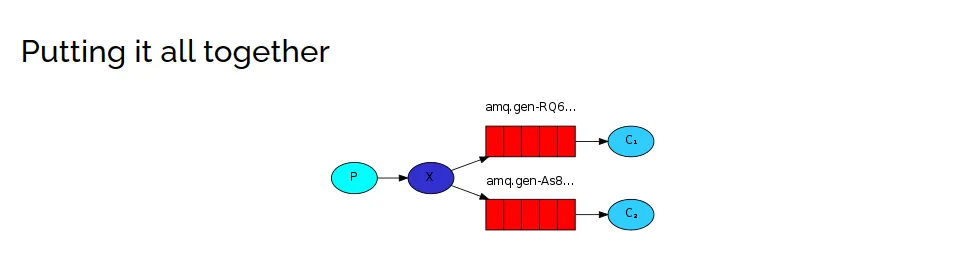
广播模式下:发送消息流程是可以有多个消费者每个消费者都有自己的队列(queue)每个队列都要绑定交换机(exchange)生成者发送消息,只能发送到交换机,交换机决定把消息发给哪个队列,生成者无法决定交换机把消息发给绑定过的所有队列,队列的消费者都能拿到消息,一条消息可以被多个消费者消费。
生产者
package com.duan.rabbitmq.fanout;
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Provider
* @since 2023/11/28
*/
public class Provider {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 获取连接对象
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 将通道声明交换机 参数1:交换机名称 参数2:交换机类型
channel.exchangeDeclare("logs","fanout");
// 发送消息
channel.basicPublish("logs","",null,"fanout type message".getBytes());
// 释放资源
RabbitMqUtil.closeConnectionAndChannel(channel,connection);
}
}
消费者1
package com.duan.rabbitmq.fanout;
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Customer1
* @since 2023/11/28
*/
public class Customer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 获得连接对象
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 通道绑定交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare("logs","fanout");
// 绑定临时队列
String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
// 绑定交换机和队列
channel.queueBind(queue,"logs","");
// 消费消息
channel.basicConsume(queue,true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者1: "+new String(body));
}
});
}
}
消费者2
package com.duan.rabbitmq.fanout;
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Customer1
* @since 2023/11/28
*/
public class Customer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 获得连接对象
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 通道绑定交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare("logs","fanout");
// 绑定临时队列
String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
// 绑定交换机和队列
channel.queueBind(queue,"logs","");
// 消费消息
channel.basicConsume(queue,true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者2: "+new String(body));
}
});
}
}
消费者3
package com.duan.rabbitmq.fanout;
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Customer1
* @since 2023/11/28
*/
public class Customer3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 获得连接对象
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 通道绑定交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare("logs","fanout");
// 绑定临时队列
String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
// 绑定交换机和队列
channel.queueBind(queue,"logs","");
// 消费消息
channel.basicConsume(queue,true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者3: "+new String(body));
}
});
}
}
测试结果


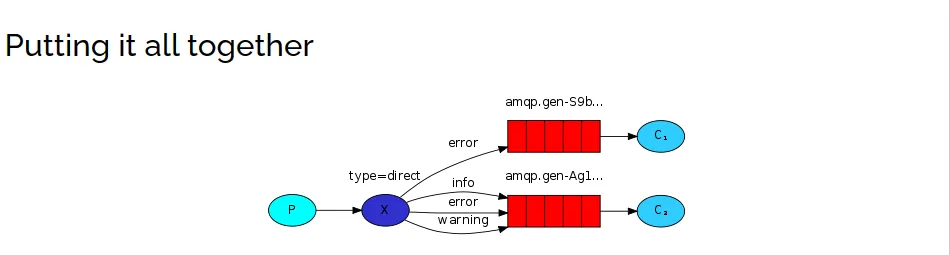
四、第四种模型(Routing)
在fanout模式中,一条消息,会被所有绑定的队列都能消费,但是,在某些场景下,希望不同的消息被不同的队列消费,就需要Direct类型的exchange。
在Direct模型下:队列与交换机的绑定,不是任意绑定的,而是要指定一个RoutingKey(路由key)消息的发送方在向Exchange发送消息时,也必须指定消息的 RoutingKey。Exchange不再把消息交给每一个绑定的队列,而是根据消息的Routing Key进行判断,只有队列的Routingkey与消息的 Routing key完全一致,才会接收到消息。
生产者
package com.duan.rabbitmq.direct;
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Provider
* @since 2023/11/28
*/
public class Provider {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 建立连接
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.exchangeDeclare("logs_direct","direct");
String routingKey = "error";
channel.basicPublish("logs_direct",routingKey,null,("这是direct模型发布的基于route key: ["+routingKey+"] 发送的消息").getBytes());
RabbitMqUtil.closeConnectionAndChannel(channel,connection);
}
}
消费者1
package com.duan.rabbitmq.direct;
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Consumer1
* @since 2023/11/28
*/
public class Consumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 获得连接对象
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 通道绑定交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare("logs_direct","direct");
// 绑定临时队列
String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
// 绑定交换机和队列
channel.queueBind(queue,"logs_direct","error");
// 消费消息
channel.basicConsume(queue,true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者1: "+new String(body));
}
});
}
}
消费者2
package com.duan.rabbitmq.direct;
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Consumer1
* @since 2023/11/28
*/
public class Consumer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 获得连接对象
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 通道绑定交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare("logs_direct","direct");
// 绑定临时队列
String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
// 绑定交换机和队列
channel.queueBind(queue,"logs_direct","info");
channel.queueBind(queue,"logs_direct","error");
channel.queueBind(queue,"logs_direct","warning");
// 消费消息
channel.basicConsume(queue,true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者1: "+new String(body));
}
});
}
}
测试结果
当routingKey为info时,消费者1和消费者2结果如下:
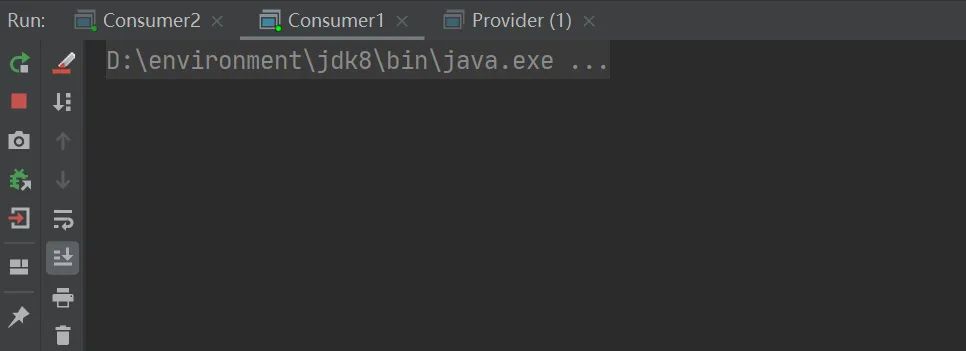
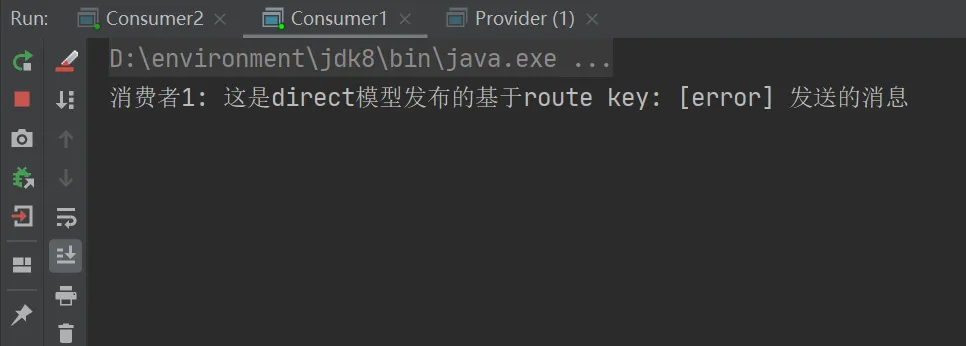
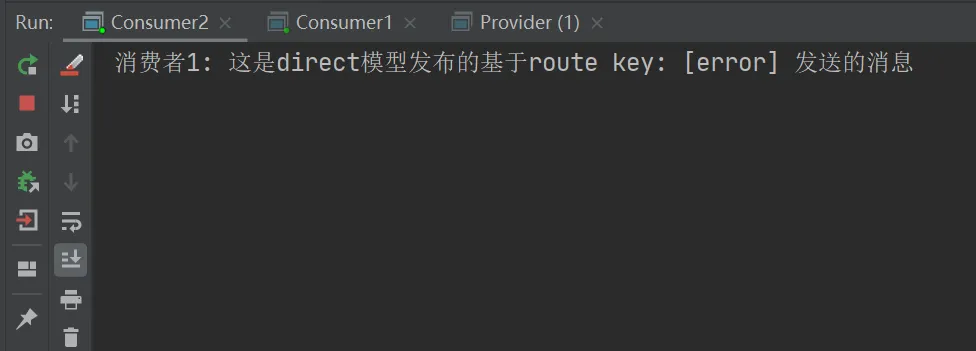
当routingKey为error时,消费者1和消费者2结果如下:
五、第五种模型(topic)
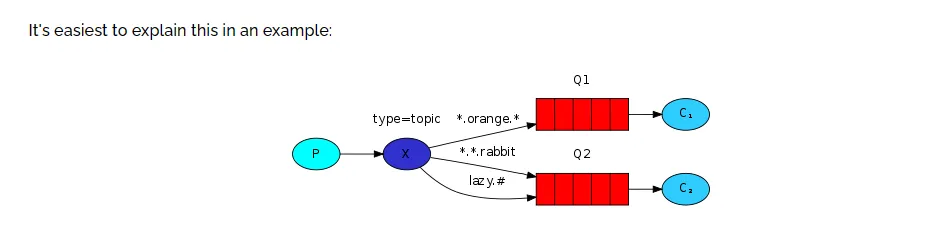
Topic类型的Exchange与Direct相比,都是可以根据RoutingKey把消息路由到不同的队列。只不过Topic类型Exchange可以让队列在绑定BindingKey 的时候使用通配符!BindingKey 一般都是有一个或多个单词组成,多个单词之间以.分割,例如: item.insert通配符规则:
- #:匹配一个或多个词
- *:匹配不多不少恰好1个词
举例:
- item.#:能够匹配
item.spu.insert或者item.spu - item.*:只能匹配
item.spu
生产者
package com.duan.rabbitmq.topic;
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Provider
* @since 2023/11/30
*/
public class Provider {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//获取连接对象
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明交换机以及交换机类型 topic
channel.exchangeDeclare("topics","topic");
//发布消息
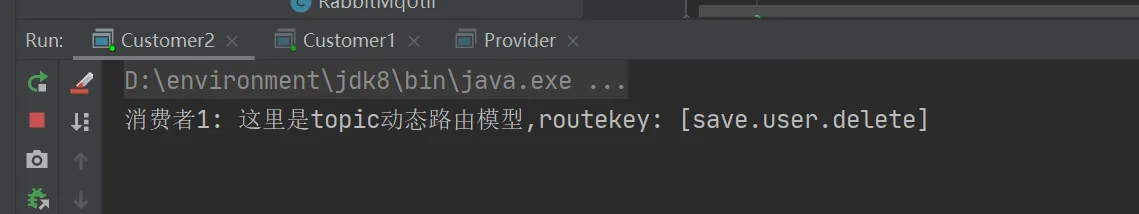
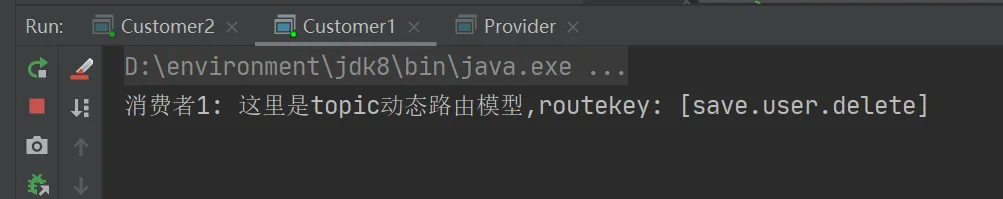
String routekey = "save.user.delete";
channel.basicPublish("topics",routekey,null,("这里是topic动态路由模型,routekey: ["+routekey+"]").getBytes());
//关闭资源
RabbitMqUtil.closeConnectionAndChannel(channel,connection);
}
}
消费者1
package com.duan.rabbitmq.topic;
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Customer1
* @since 2023/11/30
*/
public class Customer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 获得连接对象
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 通道绑定交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare("topics","topic");
// 绑定临时队列
String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
// 绑定交换机和队列
channel.queueBind(queue,"topics","*.user.*");
// 消费消息
channel.basicConsume(queue,true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者1: "+new String(body));
}
});
}
}
消费者2
package com.duan.rabbitmq.topic;
import com.duan.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitMqUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author db
* @version 1.0
* @description Customer1
* @since 2023/11/30
*/
public class Customer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 获得连接对象
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 通道绑定交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare("topics","topic");
// 绑定临时队列
String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
// 绑定交换机和队列
channel.queueBind(queue,"topics","*.user.#");
// 消费消息
channel.basicConsume(queue,true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者1: "+new String(body));
}
});
}
}
测试结果
代码地址:https://gitee.com/duan138/practice-code/tree/dev/rabbitmq-java
六、总结
以上就是rabbitMQ中常见的几种模式,这些模型通过交换机(Exchange)和队列(Queue)的不同组合与绑定方式实现。本文只是初步了解RabbitMQ相关知识。后续会讲解怎么在SpringBoot中应用。
改变你能改变的,接受你不能改变的,关注公众号:程序员康康,一起成长,共同进步。