目录
- 写在前面
- Nginx
- Nginx处理用户请求流程
- 虚拟主机
- 虚拟主机的分类
- 基于域名的虚拟主机
- 基于端口的虚拟主机
- 基于IP的虚拟主机
- Nginx日志
- 错误日志
- 案例
- 访问日志
- 访问格式变量
- 案例
- Location规则
- 案例1
- 案例2
- Location规则小结
写在前面
这是Nginx第二篇,内容为Nginx处理用户请求流程、虚拟主机、日志简介、Location简介等。
上篇笔记 Nginx01-HTTP简介与Nginx简介(安装、命令介绍、目录介绍、配置文件介绍)
Nginx
Nginx处理用户请求流程
- DNS解析,域名->IP;
- TCP三次握手,与对应端口建立连接。
- 用户的请求报文:
- GET /index.html
- HOST: game.test.com
- User-Agent: Chrome/xxxx
- Nginx对http请求交给http区域处理。
- 不同的server{ }区域(子配置文件)处理:
- 端口
- 域名:用户的请求将携带
HOST,Nginx根据这个HOST和所有配置文件的server_name进行匹配。 - 匹配成功后,Nginx确定站点目录
root和访问定位location,访问对应的location内的文件。
- 不同的server{ }区域(子配置文件)处理:
- Nginx若找到,回复
200 OK和文件。- 响应报文:
- 状态码:
- server信息
- 其他信息
- 文件内容
- 浏览器处理收到的文件,进行渲染。
- 响应报文:
- Nginx若没找到,根据配置的默认站点,进行访问
default_server;- 若没有默认站点,根据子配置文件字母顺序第一个。
虚拟主机
虚拟主机,相当于一个网站,Nginx中的server{}区域实现。
Nginx中,虚拟主机有不同的类型,配置也不同。
虚拟主机的分类
| 虚拟主机分类 | 说明 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|
基于域名的虚拟主机 | 不同域名访问不同的站点。生产环境最常用的。 | 用于多域名网站,每个域名对应一个站点。 |
基于端口的虚拟主机 | 不同端口访问不同的站点。保护,设置特殊端口(1024以上)。 | 用于多站点共用一个IP地址,通过不同端口来区分。 |
基于IP的虚拟主机 | 不同IP访问不同的站点。保护,用户只能通过某个IP连接进来。 | 用于多站点,每个站点有独立的IP地址,可以提供更好的安全性和隔离性。 |
基于域名的虚拟主机
不同的域名访问不同的虚拟主机
同一个ip,多个域名,访问不同的界面
Linux不修改hosts文件访问不同的域名
curl -H Host:域名 ip
例子:curl -H Host:bird.test.com 192.168.100.148
# 书写子配置文件
[root@front conf.d]# cat bird.test.com.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name bird.test.com;
location / {
root /app/code/bird/;
index index.html;
}
}
#测试并重启
nginx -t
systemctl reload nginx
# 不指定访问文件,报错403
[root@front conf.d]# curl -H Host:bird.test.com 192.168.100.148
<html>
<head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>403 Forbidden</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.26.1</center>
</body>
</html>
# 指定访问文件,报错404
[root@front conf.d]# curl -H Host:bird.test.com 192.168.100.148/index.html
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.26.1</center>
</body>
</html>
# 添加index.html后,访问
[root@front conf.d]# echo bird > /app/code/bird/index.html
[root@front conf.d]# curl -H Host:bird.test.com 192.168.100.148/index.html
bird
基于端口的虚拟主机
仅需将server{}中,
listen字段的端口号修改即可
# 编写子配置文件
[root@front conf.d]# cat live.test.com.conf
server {
listen 8011; #修改此行
server_name live.test.com;
location / {
root /app/code/live/;
index index.html;
}
}
# 访问
[root@front conf.d]# curl -H Host:live.test.com 192.168.100.148:8011
live
基于IP的虚拟主机
同样修改
listen字段,修改为IP:端口的形式
这样就制定了,什么网段能访问这个虚拟主机
若路径错误,会报错 Failed connect to x.x.x.x:yyy; Connection refused
Nginx日志
默认的日志存放是所有虚拟主机在一个日志文件中。
所以可以设置给每个虚拟主机指定一个自己的独立的错误日志和访问日志
| 日志类型 | 使用建议 | 定义 | 使用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 错误日志 | 记录服务器错误信息,有助于故障排查。 | 发生故障时查看,4xx,5xx错误级别。 | error_log |
| 访问日志 | 记录用户访问信息,如访问时间、访问页面、客户端信息等。 | 记录用户访问行为。 | access_log |
错误日志
- error_log指定访问日志位置
- 格式:error_log 文件名 错误日志级别
- 位置:main , http , mail , stream , server , location
- 错误日志级别:debug, info, notice, warn, error, crit, alert, emerg(从左往右,信息记录越来越粗糙)
官网: nginx.org/en/docs
Modules reference->Alphabetical index of directives->error_log
案例
- 设置让每个虚拟主机有一个自己的独立的错误日志
# 注释主配置文件错误日志
[root@front conf.d]# grep "#error" ../nginx.conf
#error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log notice;
# 在子配置文件中,增加错误日志语句
[root@front conf.d]# cat game.test.com.conf
server {
error_log /var/log/nginx/game.test.com-error.log notice; # 一般添加在server内location外即可
listen 80;
server_name game.test.com;
location / {
root /app/code/game/;
index index.html;
}
}
# 检查语法并查看日志文件
[root@front conf.d]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@front conf.d]# tree /var/log/nginx/
/var/log/nginx/
└── game.test.com-error.log # 检查语法后,会自动添加对应的errorlog
0 directories, 5 files
访问日志
- log_format 指定访问日志的格式
- 格式:log_format 格式名字 格式…;
- 位置:http
- access_log 指定访问日志路径
- 格式:access_log 日志位置 格式
- 位置:http , server , location , if in location , limit_except
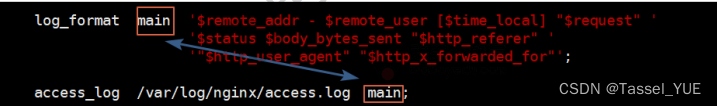
访问格式变量
更多nginx内置变量:http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html
| ngx内置变量 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| $remote_addr | 客户端IP地址 |
| $remote_user | 用户名(空,进行认证的用户) |
| $time_local | 时间(格式:20/Jan/2023:15:04:33 +0800) |
| $request | 请求报文的起始行(请求方法、URI、HTTP/1.1) |
| $status | HTTP状态码 |
| $body_bytes_sent | 响应给客户的文件大小,响应报文的主体大小(文件大小) 单位字节 |
| $http_referer | 从哪里跳转,访问到这个网站的。网站运营分析 |
| $http_user_agent | 客户端代理(浏览器) |
| $http_x_forwarded_for | XFF头,负载均衡器使用,记录用户真实的IP地址 |
案例
- 让每个虚拟主机指定自己的独立的访问日志
# 注释主配置文件的访问日志
[root@front conf.d]# grep "access_log" ../nginx.conf
# access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
# 编辑子配置文件,添加access_log语句
[root@front conf.d]# cat game.test.com.conf
server {
error_log /var/log/nginx/game.test.com-error.log notice;
access_log /var/log/nginx/game.test.com-access.log main; # 添加该行,main为accesslog中记录的语句的格式
listen 80;
server_name game.test.com;
location / {
root /app/code/game/;
index index.html;
}
}
# 检查语法并查看文件
[root@front conf.d]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@front conf.d]# tree /var/log/nginx/
/var/log/nginx/
├── game.test.com-access.log
└── game.test.com-error.log
0 directories, 6 files
| 访问日志说明 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 访问日志进行压缩 | 可以使用gzip压缩访问日志,以节省磁盘空间。压缩后的日志可以通过zcat、zless或zgrep等工具查看。 |
| 进行缓存 | buffer = 32k 先把日志写入到内存中,定期写入到磁盘 |
| 定义刷新时间 | flush=10s, 每10秒,日志缓冲区中的内容会被写入到磁盘,以防止日志丢失 |
access_log /var/log/nginx/game.test.com-access.log main gzip buffer=32k flush=10s ;
Location规则
-
在nginx用于匹配用户请求中的uri进行判断
-
如果用户请求的uri是xxx,则作xxx
-
URL和URI:
- URL:https://nginx.org/en/docs
- URI:/en/docs
-
URI就是URL去除域名之后,
/后的部分
案例1
域名:buy.test.com
站点目录:/app/code/buy
后台管理页面:/app/code/buy/admin/index.html
后台只能内网访问
# 编写子配置文件
[root@front conf.d]# cat buy.test.com.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name buy.test.com;
root /app/code/buy;
location / {
index index.html;
}
location /admin/ {
allow 192.168.100.0/24; # 仅允许192.168.100.0网段
deny all; # 默认拒绝所有
index index.html;
}
}
# 设置目录并重启
[root@front conf.d]# mkdir -p /app/code/buy/admin
[root@front conf.d]# echo buy > /app/code/buy/index.html
[root@front conf.d]# echo buy-admin > /app/code/buy/admin/index.html
[root@front conf.d]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@front conf.d]# systemctl restart nginx
# 测试
## 访问没有限制的
[root@front conf.d]# curl -H Host:buy.test.com 127.0.0.1
buy
## 访问外部有限制,403权限错误
[root@front conf.d]# curl -H Host:buy.test.com http://127.0.0.1/admin/
<html>
<head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>403 Forbidden</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.26.1</center>
</body>
</html>
# 通过allow的网段访问,正常
[root@front conf.d]# curl -H Host:buy.test.com http://192.168.100.148/admin/
buy-admin
案例2
域名:bird.test.com
网站加速,设置缓存。html、js、css文件缓存一天,图片缓存1h
# 配置子配置文件
[root@front conf.d]# cat bird.test.com.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name bird.test.com;
root /app/code/bird/; # 每个location区域都是独立的,如果root写在location内,则在指定缓存时的location中也要添加上root
location / {
index index.html;
#root /app/code/bird/;
}
#uri 包含 html、js、css 结尾的文件缓存一天
#~* 后支持正则表达式
location ~* \.(html|js|css)$ {
expires 1d;
}
location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|bmp)$ {
expires 1h;
}
}
Location规则小结
| location规则 | 说明 |
|---|---|
location / {xxxx} | 默认规则,保底,location规则在进行匹配的时候,其他的规则都匹配失败了,这时候匹配默认的规则。 |
location /image/ {} | 用于匹配请求的uri(路径),例如game.test.com/image/test.txt。 |
location ~ \. (jpg|jpeg)$ {} | 支持正则,区分大小写,例如game.test.com/test/test.jpg。 |
location ~* \. (jpg|jpeg)$ {} | 支持正则,不区分大小写,例如game.test.com/test/test.jpg。 |
location ^~ /test/ | 不支持正则,仅仅匹配普通字符,很少使用,但优先级高。 |
location = /50x.html | 不支持正则,精确匹配,使用较少,例如匹配/50x.html。 |
location @名字 {} | 命名的location,一般用于return或error_log跳转。 |
- 匹配优先级:
| 优先级 | 符号 |
|--------|------|
| 1 = | 精确匹配,如location = /50x.html|
| 2 ^~ | 优先匹配,如location ^~ /test/|
| 3 ~ | 区分大小写的正则匹配,如location ~ \. (jpg|jpeg)$ {}|
| 4 ~* | 不区分大小写的正则匹配,如location ~* \. (jpg|jpeg)$ {}|
| 5 /image/ | 普通字符匹配,如location /image/ {}|
| 6 / | 默认匹配,如location / {}|
# 编辑
server {
listen 80;
server_name l.test.com;
default_type text/html;
location / {
return 200 "location /\n";
}
location = /index.html {
return 200 "location =/\n";
}
location ~ /index.html {
return 200 "location ~/\n";
}
location ^~ /index.html {
return 200 "location ^~\n";
}
}
# 分析?
location = / {
[ configuration A ]
}
location / {
[ configuration B ]
}
location /documents/ {
[ configuration C ]
}
location ^~ /images/ {
[ configuration D ]
}
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
[ configuration E ]
}
#测试与访问
“/” A
“/index.html” B
“/documents/document.html” C
“/images/1.gif” D
“/documents/1.jpg” E













![[数据集][目标检测]剪刀石头布检测数据集VOC+YOLO格式1973张3类别](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/984f8e1eb71b4a17a8ca842aac62d7a3.png)