2023.1.25
现在已经学习过了,如果我们设置了合适的权重初始值,则各层的激活值分布会呈现适当的广度,从而可以时神经网络模型顺利的进行学习。
而 batch normalization算法 的思想就是为了使得各层有适当的广度,“强制性”地调整激活值的分布。
Batch Normalization算法:
这是一个提出自2015年的方法,但是已经广泛的应用于机器学习......
他的作用是调整各层激活函数进行正规化的层,即Bacth Normalization 层,所以将他插入在Affine层与ReLU层之间;

具体,在神经网络进行学习时,以mini-batch为单位,按mini-batch进行正规化(正规化:就是时数据分布均值为0、反差为1的正规化)
正规化数学公式:
;
;
;其中
是个很小的值,防止除以0的情况 。
之后Batch Normalization层会对正规划的数据进行缩放和平移:
=1和
= 0 是参数,然后经过学习调整到合适的值;
优点:
一、可以使学习快速进行;
二、不那么以来初始值;
三、可以抑制过拟合;
观察Batch Normalization的计算图:

其反向操作比较复杂,并没有推导(教材上也没有推导)
运用MNIST数据集对Bacth Normalization的评估:
观察使用Batch Normalization层和不适用Batch Normalizaton层,会出现什么现象;
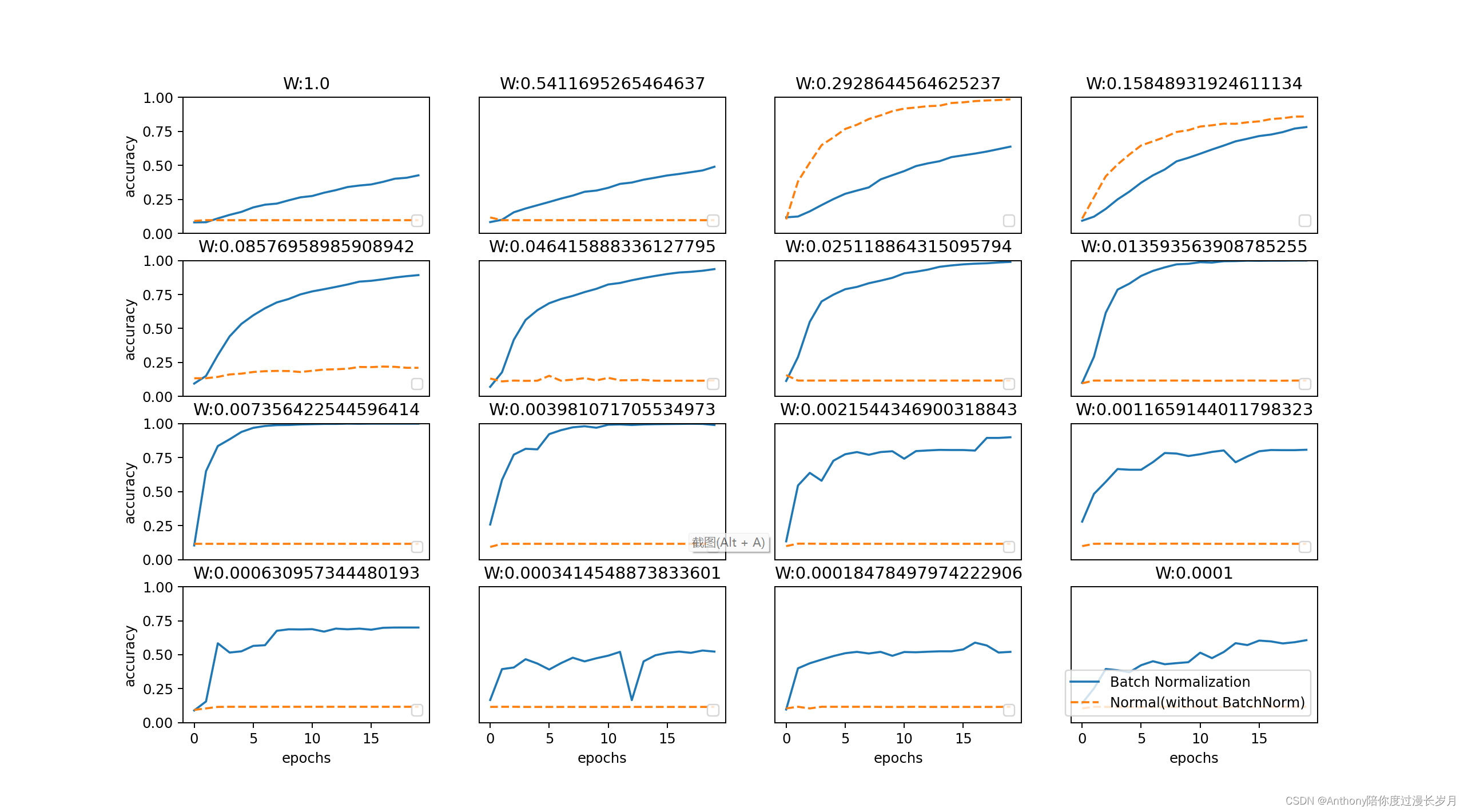
进行了16次的对比,可以说使用了Bacth Normalization后,学习变得更快了。在不同的权重初始值的标准差为各种不同的值的时学习过程也做了实验;
事实是,如果没有一个好的初始值,神经网络的学习将难以进行;
通过使用Batch Norlization层 推动神经网络学习的进行。并且,对权重初始值变得 健壮(使得神经网络模型不那么依赖初始值)
实验代码:
import sys, os
from collections import OrderedDict
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from dataset.mnist import load_mnist
sys.path.append(os.pardir)
def softmax(x):
if x.ndim == 2:
x = x.T
x = x - np.max(x, axis=0)
y = np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x), axis=0)
return y.T
x = x - np.max(x)
return np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x))
def cross_entropy_error(y, t):
if y.ndim == 1:
t = t.reshape(1, t.size)
y = y.reshape(1, y.size)
if t.size == y.size:
t = t.argmax(axis=1)
batch_size = y.shape[0]
return -np.sum(np.log(y[np.arange(batch_size), t] + 1e-7)) / batch_size
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
class Relu:
def __init__(self):
self.mask = None
def forward(self, x):
self.mask = (x <= 0)
out = x.copy()
out[self.mask] = 0
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dout[self.mask] = 0
dx = dout
return dx
class Sigmoid:
def __init__(self):
self.out = None
def forward(self, x):
out = sigmoid(x)
self.out = out
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dx = dout * (1.0 - self.out) * self.out
return dx
class Affine:
def __init__(self, W, b):
self.W = W
self.b = b
self.x = None
self.original_x_shape = None
# 权重和偏置参数的导数
self.dW = None
self.db = None
def forward(self, x):
# 对应张量
self.original_x_shape = x.shape
x = x.reshape(x.shape[0], -1)
self.x = x
out = np.dot(self.x, self.W) + self.b
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dx = np.dot(dout, self.W.T)
self.dW = np.dot(self.x.T, dout)
self.db = np.sum(dout, axis=0)
dx = dx.reshape(*self.original_x_shape) # 还原输入数据的形状(对应张量)
return dx
class SoftmaxWithLoss:
def __init__(self):
self.loss = None
self.y = None # softmax的输出
self.t = None # 监督数据
def forward(self, x, t):
self.t = t
self.y = softmax(x)
self.loss = cross_entropy_error(self.y, self.t)
return self.loss
def backward(self, dout=1):
batch_size = self.t.shape[0]
if self.t.size == self.y.size: # 监督数据是one-hot-vector的情况
dx = (self.y - self.t) / batch_size
else:
dx = self.y.copy()
dx[np.arange(batch_size), self.t] -= 1
dx = dx / batch_size
return dx
class Dropout:
def __init__(self, dropout_ratio=0.5):
self.dropout_ratio = dropout_ratio
self.mask = None
def forward(self, x, train_flg=True):
if train_flg:
self.mask = np.random.rand(*x.shape) > self.dropout_ratio
return x * self.mask
else:
return x * (1.0 - self.dropout_ratio)
def backward(self, dout):
return dout * self.mask
class BatchNormalization:
def __init__(self, gamma, beta, momentum=0.9, running_mean=None, running_var=None):
self.gamma = gamma
self.beta = beta
self.momentum = momentum
self.input_shape = None # Conv层的情况下为4维,全连接层的情况下为2维
# 测试时使用的平均值和方差
self.running_mean = running_mean
self.running_var = running_var
# backward时使用的中间数据
self.batch_size = None
self.xc = None
self.std = None
self.dgamma = None
self.dbeta = None
def forward(self, x, train_flg=True):
self.input_shape = x.shape
if x.ndim != 2:
N, C, H, W = x.shape
x = x.reshape(N, -1)
out = self.__forward(x, train_flg)
return out.reshape(*self.input_shape)
def __forward(self, x, train_flg):
if self.running_mean is None:
N, D = x.shape
self.running_mean = np.zeros(D)
self.running_var = np.zeros(D)
if train_flg:
mu = x.mean(axis=0)
xc = x - mu
var = np.mean(xc ** 2, axis=0)
std = np.sqrt(var + 10e-7)
xn = xc / std
self.batch_size = x.shape[0]
self.xc = xc
self.xn = xn
self.std = std
self.running_mean = self.momentum * self.running_mean + (1 - self.momentum) * mu
self.running_var = self.momentum * self.running_var + (1 - self.momentum) * var
else:
xc = x - self.running_mean
xn = xc / ((np.sqrt(self.running_var + 10e-7)))
out = self.gamma * xn + self.beta
return out
def backward(self, dout):
if dout.ndim != 2:
N, C, H, W = dout.shape
dout = dout.reshape(N, -1)
dx = self.__backward(dout)
dx = dx.reshape(*self.input_shape)
return dx
def __backward(self, dout):
dbeta = dout.sum(axis=0)
dgamma = np.sum(self.xn * dout, axis=0)
dxn = self.gamma * dout
dxc = dxn / self.std
dstd = -np.sum((dxn * self.xc) / (self.std * self.std), axis=0)
dvar = 0.5 * dstd / self.std
dxc += (2.0 / self.batch_size) * self.xc * dvar
dmu = np.sum(dxc, axis=0)
dx = dxc - dmu / self.batch_size
self.dgamma = dgamma
self.dbeta = dbeta
return dx
def numerical_gradient(f, x):
h = 1e-4 # 0.0001
grad = np.zeros_like(x)
it = np.nditer(x, flags=['multi_index'], op_flags=['readwrite'])
while not it.finished:
idx = it.multi_index
tmp_val = x[idx]
x[idx] = float(tmp_val) + h
fxh1 = f(x) # f(x+h)
x[idx] = tmp_val - h
fxh2 = f(x) # f(x-h)
grad[idx] = (fxh1 - fxh2) / (2 * h)
x[idx] = tmp_val # 还原值
it.iternext()
return grad
class MultiLayerNetExtend:
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size_list, output_size,
activation='relu', weight_init_std='relu', weight_decay_lambda=0,
use_dropout=False, dropout_ration=0.5, use_batchnorm=False):
self.input_size = input_size
self.output_size = output_size
self.hidden_size_list = hidden_size_list
self.hidden_layer_num = len(hidden_size_list)
self.use_dropout = use_dropout
self.weight_decay_lambda = weight_decay_lambda
self.use_batchnorm = use_batchnorm
self.params = {}
# 初始化权重
self.__init_weight(weight_init_std)
# 生成层
activation_layer = {'sigmoid': Sigmoid, 'relu': Relu}
self.layers = OrderedDict()
for idx in range(1, self.hidden_layer_num + 1):
self.layers['Affine' + str(idx)] = Affine(self.params['W' + str(idx)],
self.params['b' + str(idx)])
if self.use_batchnorm:
self.params['gamma' + str(idx)] = np.ones(hidden_size_list[idx - 1])
self.params['beta' + str(idx)] = np.zeros(hidden_size_list[idx - 1])
self.layers['BatchNorm' + str(idx)] = BatchNormalization(self.params['gamma' + str(idx)],
self.params['beta' + str(idx)])
self.layers['Activation_function' + str(idx)] = activation_layer[activation]()
if self.use_dropout:
self.layers['Dropout' + str(idx)] = Dropout(dropout_ration)
idx = self.hidden_layer_num + 1
self.layers['Affine' + str(idx)] = Affine(self.params['W' + str(idx)], self.params['b' + str(idx)])
self.last_layer = SoftmaxWithLoss()
def __init_weight(self, weight_init_std):
all_size_list = [self.input_size] + self.hidden_size_list + [self.output_size]
for idx in range(1, len(all_size_list)):
scale = weight_init_std
if str(weight_init_std).lower() in ('relu', 'he'):
scale = np.sqrt(2.0 / all_size_list[idx - 1]) # 使用ReLU的情况下推荐的初始值
elif str(weight_init_std).lower() in ('sigmoid', 'xavier'):
scale = np.sqrt(1.0 / all_size_list[idx - 1]) # 使用sigmoid的情况下推荐的初始值
self.params['W' + str(idx)] = scale * np.random.randn(all_size_list[idx - 1], all_size_list[idx])
self.params['b' + str(idx)] = np.zeros(all_size_list[idx])
def predict(self, x, train_flg=False):
for key, layer in self.layers.items():
if "Dropout" in key or "BatchNorm" in key:
x = layer.forward(x, train_flg)
else:
x = layer.forward(x)
return x
def loss(self, x, t, train_flg=False):
y = self.predict(x, train_flg)
weight_decay = 0
for idx in range(1, self.hidden_layer_num + 2):
W = self.params['W' + str(idx)]
weight_decay += 0.5 * self.weight_decay_lambda * np.sum(W ** 2)
return self.last_layer.forward(y, t) + weight_decay
def accuracy(self, X, T):
Y = self.predict(X, train_flg=False)
Y = np.argmax(Y, axis=1)
if T.ndim != 1: T = np.argmax(T, axis=1)
accuracy = np.sum(Y == T) / float(X.shape[0])
return accuracy
def numerical_gradient(self, X, T):
loss_W = lambda W: self.loss(X, T, train_flg=True)
grads = {}
for idx in range(1, self.hidden_layer_num + 2):
grads['W' + str(idx)] = numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['W' + str(idx)])
grads['b' + str(idx)] = numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['b' + str(idx)])
if self.use_batchnorm and idx != self.hidden_layer_num + 1:
grads['gamma' + str(idx)] = numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['gamma' + str(idx)])
grads['beta' + str(idx)] = numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['beta' + str(idx)])
return grads
def gradient(self, x, t):
# forward
self.loss(x, t, train_flg=True)
# backward
dout = 1
dout = self.last_layer.backward(dout)
layers = list(self.layers.values())
layers.reverse()
for layer in layers:
dout = layer.backward(dout)
# 设定
grads = {}
for idx in range(1, self.hidden_layer_num + 2):
grads['W' + str(idx)] = self.layers['Affine' + str(idx)].dW + self.weight_decay_lambda * self.params[
'W' + str(idx)]
grads['b' + str(idx)] = self.layers['Affine' + str(idx)].db
if self.use_batchnorm and idx != self.hidden_layer_num + 1:
grads['gamma' + str(idx)] = self.layers['BatchNorm' + str(idx)].dgamma
grads['beta' + str(idx)] = self.layers['BatchNorm' + str(idx)].dbeta
return grads
class Adam:
def __init__(self, lr=0.001, beta1=0.9, beta2=0.999):
self.lr = lr
self.beta1 = beta1
self.beta2 = beta2
self.iter = 0
self.m = None
self.v = None
def update(self, params, grads):
if self.m is None:
self.m, self.v = {}, {}
for key, val in params.items():
self.m[key] = np.zeros_like(val)
self.v[key] = np.zeros_like(val)
self.iter += 1
lr_t = self.lr * np.sqrt(1.0 - self.beta2 ** self.iter) / (1.0 - self.beta1 ** self.iter)
for key in params.keys():
# self.m[key] = self.beta1*self.m[key] + (1-self.beta1)*grads[key]
# self.v[key] = self.beta2*self.v[key] + (1-self.beta2)*(grads[key]**2)
self.m[key] += (1 - self.beta1) * (grads[key] - self.m[key])
self.v[key] += (1 - self.beta2) * (grads[key] ** 2 - self.v[key])
params[key] -= lr_t * self.m[key] / (np.sqrt(self.v[key]) + 1e-7)
class SGD:
def __init__(self, lr=0.01):
self.lr = lr
def update(self, params, grads):
for key in params.keys():
params[key] -= self.lr * grads[key]
(x_train, t_train), (x_test, t_test) = load_mnist(normalize=True)
# 减少学习数据
x_train = x_train[:1000]
t_train = t_train[:1000]
max_epochs = 20
train_size = x_train.shape[0]
batch_size = 100
learning_rate = 0.01
def __train(weight_init_std):
bn_network = MultiLayerNetExtend(input_size=784, hidden_size_list=[100, 100, 100, 100, 100], output_size=10,
weight_init_std=weight_init_std, use_batchnorm=True)
network = MultiLayerNetExtend(input_size=784, hidden_size_list=[100, 100, 100, 100, 100], output_size=10,
weight_init_std=weight_init_std)
optimizer = SGD(lr=learning_rate)
train_acc_list = []
bn_train_acc_list = []
iter_per_epoch = max(train_size / batch_size, 1)
epoch_cnt = 0
for i in range(1000000000):
batch_mask = np.random.choice(train_size, batch_size)
x_batch = x_train[batch_mask]
t_batch = t_train[batch_mask]
for _network in (bn_network, network):
grads = _network.gradient(x_batch, t_batch)
optimizer.update(_network.params, grads)
if i % iter_per_epoch == 0:
train_acc = network.accuracy(x_train, t_train)
bn_train_acc = bn_network.accuracy(x_train, t_train)
train_acc_list.append(train_acc)
bn_train_acc_list.append(bn_train_acc)
print("epoch:" + str(epoch_cnt) + " | " + str(train_acc) + " - " + str(bn_train_acc))
epoch_cnt += 1
if epoch_cnt >= max_epochs:
break
return train_acc_list, bn_train_acc_list
# 3.绘制图形==========
weight_scale_list = np.logspace(0, -4, num=16)
x = np.arange(max_epochs)
for i, w in enumerate(weight_scale_list):
print("============== " + str(i + 1) + "/16" + " ==============")
train_acc_list, bn_train_acc_list = __train(w)
plt.subplot(4, 4, i + 1)
plt.title("W:" + str(w))
if i == 15:
plt.plot(x, bn_train_acc_list, label='Batch Normalization', markevery=2)
plt.plot(x, train_acc_list, linestyle="--", label='Normal(without BatchNorm)', markevery=2)
else:
plt.plot(x, bn_train_acc_list, markevery=2)
plt.plot(x, train_acc_list, linestyle="--", markevery=2)
plt.ylim(0, 1.0)
if i % 4:
plt.yticks([])
else:
plt.ylabel("accuracy")
if i < 12:
plt.xticks([])
else:
plt.xlabel("epochs")
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()
MNIST数据集的导入代码:
代码需要在一个命名为命名为dataset的文件夹下命名为mnist,并且与上个代码在同一个文件夹;
# coding: utf-8
try:
import urllib.request
except ImportError:
raise ImportError('You should use Python 3.x')
import os.path
import gzip
import pickle
import os
import numpy as np
url_base = 'http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/'
key_file = {
'train_img':'train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz',
'train_label':'train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz',
'test_img':'t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz',
'test_label':'t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz'
}
dataset_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
save_file = dataset_dir + "/mnist.pkl"
train_num = 60000
test_num = 10000
img_dim = (1, 28, 28)
img_size = 784
def _download(file_name):
file_path = dataset_dir + "/" + file_name
if os.path.exists(file_path):
return
print("Downloading " + file_name + " ... ")
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url_base + file_name, file_path)
print("Done")
def download_mnist():
for v in key_file.values():
_download(v)
def _load_label(file_name):
file_path = dataset_dir + "/" + file_name
print("Converting " + file_name + " to NumPy Array ...")
with gzip.open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
labels = np.frombuffer(f.read(), np.uint8, offset=8)
print("Done")
return labels
def _load_img(file_name):
file_path = dataset_dir + "/" + file_name
print("Converting " + file_name + " to NumPy Array ...")
with gzip.open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
data = np.frombuffer(f.read(), np.uint8, offset=16)
data = data.reshape(-1, img_size)
print("Done")
return data
def _convert_numpy():
dataset = {}
dataset['train_img'] = _load_img(key_file['train_img'])
dataset['train_label'] = _load_label(key_file['train_label'])
dataset['test_img'] = _load_img(key_file['test_img'])
dataset['test_label'] = _load_label(key_file['test_label'])
return dataset
def init_mnist():
download_mnist()
dataset = _convert_numpy()
print("Creating pickle file ...")
with open(save_file, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(dataset, f, -1)
print("Done!")
def _change_one_hot_label(X):
T = np.zeros((X.size, 10))
for idx, row in enumerate(T):
row[X[idx]] = 1
return T
def load_mnist(normalize=True, flatten=True, one_hot_label=False):
"""读入MNIST数据集
Parameters
----------
normalize : 将图像的像素值正规化为0.0~1.0
one_hot_label :
one_hot_label为True的情况下,标签作为one-hot数组返回
one-hot数组是指[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]这样的数组
flatten : 是否将图像展开为一维数组
Returns
-------
(训练图像, 训练标签), (测试图像, 测试标签)
"""
if not os.path.exists(save_file):
init_mnist()
with open(save_file, 'rb') as f:
dataset = pickle.load(f)
if normalize:
for key in ('train_img', 'test_img'):
dataset[key] = dataset[key].astype(np.float32)
dataset[key] /= 255.0
if one_hot_label:
dataset['train_label'] = _change_one_hot_label(dataset['train_label'])
dataset['test_label'] = _change_one_hot_label(dataset['test_label'])
if not flatten:
for key in ('train_img', 'test_img'):
dataset[key] = dataset[key].reshape(-1, 1, 28, 28)
return (dataset['train_img'], dataset['train_label']), (dataset['test_img'], dataset['test_label'])
if __name__ == '__main__':
init_mnist()



![Python信用卡欺诈检测 [TensorFlow]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/70349f16813841b5b33168756e4dec08.png)





![LeetCode[990]等式方程式的可满足性](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/4824c9e643c94d0badf9160c454866a8.png)


