文章目录
- 一、重排列表
- [1. 奇偶链表](https://leetcode.cn/problems/odd-even-linked-list/solutions/)
- 题解
- 二、链表的增、删、改、查
- [203. 移除链表元素](https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/)
- 题解
- 不简洁代码
- 简洁代码
- 707.设计链表
- 题解
- 不简洁代码
- 优化后的简洁代码
- 19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点
- 题解
- 三、反转(交换)链表
- 206.反转链表
- 题解
- 迭代
- 递归
- [24. 两两交换链表中的节点](https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/)
- 题解
- [25. K 个一组翻转链表](https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/)
- 题解
- 四、链表相交-环形链表
- [面试题 02.07. 链表相交](https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/)
- 题解1:O(n)空间
- 题解2:O(1)空间
- [141. 环形链表](https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/)
- 题解
- [142. 环形链表 II](https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/)
- 题解
一、重排列表
1. 奇偶链表
给定单链表的头节点 head ,将所有索引为奇数的节点和索引为偶数的节点分别组合在一起,然后返回重新排序的列表。
第一个节点的索引被认为是 奇数 , 第二个节点的索引为 偶数 ,以此类推。
请注意,偶数组和奇数组内部的相对顺序应该与输入时保持一致。
你必须在 O(1) 的额外空间复杂度和 O(n) 的时间复杂度下解决这个问题。
示例 1:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-QAslc9U9-1674527294574)(https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/03/10/oddeven-linked-list.jpg)]
输入: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出: [1,3,5,2,4]
示例 2:
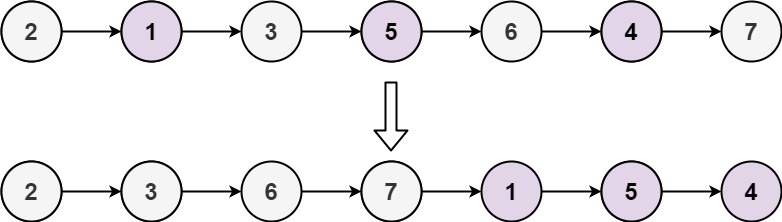
输入: head = [2,1,3,5,6,4,7]
输出: [2,3,6,7,1,5,4]
提示:
n ==链表中的节点数0 <= n <= 104-106 <= Node.val <= 106
题解
- 实质上是将链表拆分,在重组
- 将链表分割成奇链表和偶链表要同时操作,不能用两个循环,因为奇数的指向改变了,找不到下个偶链表位置
注意
- 偶链表最后更新,如果偶链表不为null,奇链表定不为null,最后奇一定不为null
- 不能用奇链表为null作为循环终止,这样,奇链表连接偶链表就没办法了
class Solution {
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return null;
ListNode oddHead = head; // 奇链表头
ListNode evenHead = head.next; // 偶链表的头节点
ListNode oddCur = head, evenCur = evenHead;//改变节点指向指针
// 一个循环内进行拆分
// 偶链表最后更新,如果偶链表不为null,奇链表定不为null,最后奇一定不为null
while(evenCur != null && evenCur.next != null) {
// 先拆开奇链表
oddCur.next = evenCur.next;
oddCur = oddCur.next;
// 再同时拆偶链表-在下个奇链表没有改变前,能找到偶链表位置
evenCur.next = oddCur.next;
evenCur = evenCur.next;
}
// 合并
oddCur.next = evenHead;
return oddHead;
}
}
二、链表的增、删、改、查
203. 移除链表元素
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
示例 1:
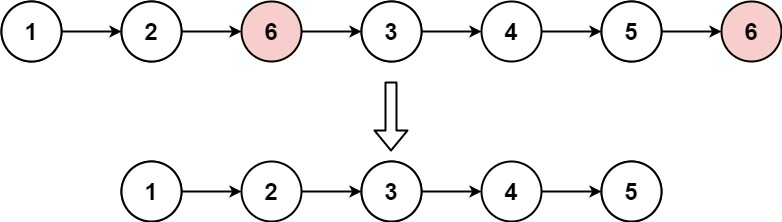
输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [], val = 1
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
输出:[]
提示:
- 列表中的节点数目在范围
[0, 104]内 1 <= Node.val <= 500 <= val <= 50
题解
注意:
- 对重复节点的删除,下个指针一直往下遍历,要用while循环
不简洁代码
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head == null) return null;
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummyHead; // 删除链表,要找到前驱节点
while(pre != null && pre.next != null) {
ListNode cur = pre.next;
while(cur != null && cur.val == val) {// 删除重复节点
pre.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
pre = cur;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
简洁代码
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head == null) return null;
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummyHead; // 删除链表,要找到前驱节点
while(pre.next != null) { // 链表中真实的每个cur
if(pre.next.val == val) {
ListNode cur = pre.next; // 先记录当前节点再删除
pre.next = cur.next; // 指向cur的指针改变
cur.next = null; // 清空cur指向的指针
} else { // 连续等于val的元素全部删除后才移动pre
pre = pre.next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
707.设计链表
设计链表的实现。您可以选择使用单链表或双链表。单链表中的节点应该具有两个属性:val 和 next。val 是当前节点的值,next 是指向下一个节点的指针/引用。如果要使用双向链表,则还需要一个属性 prev 以指示链表中的上一个节点。假设链表中的所有节点都是 0-index 的。
在链表类中实现这些功能:
- get(index):获取链表中第
index个节点的值。如果索引无效,则返回-1。 - addAtHead(val):在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为
val的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点。 - addAtTail(val):将值为
val的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素。 - addAtIndex(index,val):在链表中的第
index个节点之前添加值为val的节点。如果index等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾。如果index大于链表长度,则不会插入节点。如果index小于0,则在头部插入节点。 - deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引
index有效,则删除链表中的第index个节点。
示例:
MyLinkedList linkedList = new MyLinkedList();
linkedList.addAtHead(1);
linkedList.addAtTail(3);
linkedList.addAtIndex(1,2); //链表变为1-> 2-> 3
linkedList.get(1); //返回2
linkedList.deleteAtIndex(1); //现在链表是1-> 3
linkedList.get(1); //返回3
提示:
0 <= index, val <= 1000- 请不要使用内置的 LinkedList 库。
get,addAtHead,addAtTail,addAtIndex和deleteAtIndex的操作次数不超过2000。
题解
- 注意节点数量的维护,特别是直接调用函数时,要记得
size已经维护过了,不能重复维护
不简洁代码
class MyLinkedList {
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
public Node(){}
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
Node dummyHead; // 保护节点
int size; // 记录节点数量-添加时要记得维护
public MyLinkedList() {
dummyHead = new Node();
this.size = 0;
}
public int get(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= size) return -1;
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
for(int i = 0; i < index; i ++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur.val;
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
Node cur = new Node(val); // 先建立新节点,再连接新节点
Node next = dummyHead.next;
dummyHead.next = cur;
cur.next = next;
size ++;
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
// 先找到最后一个位置
Node cur = dummyHead;
for(int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
System.out.println(cur.val);
cur = cur.next;
}
// 在最后一个位置后再新建一个节点连接上
cur.next = new Node(val);
size ++;
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if(index > size) return;
if(index < 0) addAtHead(val); // 如果调用函数,size已经维护了
else if(index == size) addAtTail(val);
else {
Node cur = dummyHead;
for(int i = 0; i < index; i ++) {
cur = cur.next; // 跑到index-1的位置
}
Node next = cur.next; // 记录下个位置
cur.next = new Node(val); // 创建新节点,并创建连接
cur.next.next = next;
size ++;
}
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= size) return;
// 先找到要删除节点的前一个节点,再断开连接
Node cur = dummyHead;
for(int i = 0; i < index; i ++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
Node next = cur.next;
cur.next = next.next;
next.next = null;
size --;
}
}
优化后的简洁代码
class MyLinkedList {
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
public Node(){}
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
Node dummyHead; // 保护节点
int size; // 记录节点数量-添加时要记得维护
public MyLinkedList() {
dummyHead = new Node();
this.size = 0;
}
public int get(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= size) return -1;
Node cur = dummyHead; // 初始为虚拟头节点,遍历位置与下标相同
for(int i = 0; i <= index; i ++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur.val;
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
addAtIndex(0, val); // 直接复用代码,size已经维护好了
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
addAtIndex(size, val);
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if(index > size) return;
if(index < 0) index = 0; // 重置0,相当于在头部添加节点
// 为了防止忘记维护size,要先进行维护
size ++;
// 找到插入节点的前节点-与get逻辑相同
Node cur = dummyHead;
for(int i = 0; i < index; i ++) cur = cur.next;
// 插入新节点,创建连接
Node next = cur.next; // 改变连接前,要先记录
cur.next = new Node(val);
cur.next.next = next;
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= size) return;
// 先找到要删除节点的前一个节点,再断开连接
Node cur = dummyHead;
for(int i = 0; i < index; i ++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
// 断开连接
Node delNode = cur.next;
cur.next = delNode.next;
delNode.next = null;
size --;
}
}
19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例 1:
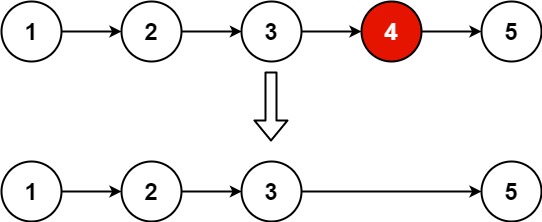
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
输出:[1,2,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1
输出:[1]
提示:
- 链表中结点的数目为
sz 1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
**进阶:**你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
题解
- 因为无法知道链表中一共有多少个元素,如果想使用一趟扫描,需要使用双指针
- 双指针可以利用差值,找到要删除节点的前置节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// 为了实现一遍扫描,需要使用双指针,一个探路,一个找位置
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode slow = dummyHead;
ListNode fast = dummyHead;
// 1. fast先走n步
while(n-- > 0) fast = fast.next;
// 2. 同步移动,当fast移动到最后一个位置时,往前n步的slow是前置节点
while(fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
// 3. 通过前置节点删除要删除的下个节点
ListNode del = slow.next;
slow.next = del.next;
del.next = null;
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
三、反转(交换)链表
206.反转链表
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5000] -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
**进阶:**链表可以选用迭代或递归方式完成反转。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
题解
迭代
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return null;
// 需要三个指针,前,中,后,维护指针,改变指向
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode next;
while(cur != null) {
// 1.先记录后面的节点
next = cur.next;
// 2.改变指向
cur.next = pre;
// 3.移动指针,处理下个节点
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
递归
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverse(null, head);
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode pre, ListNode cur) {
if(cur == null) return pre;
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
return reverse(cur, next);
}
}
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:
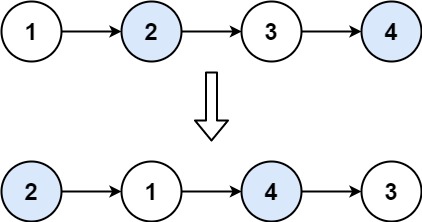
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[2,1,4,3]
示例 2:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1]
输出:[1]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 100]内 0 <= Node.val <= 100
题解
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummyHead;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null && cur.next != null) {
// 1.先记录要改变的节点
ListNode right = cur.next;
ListNode nextHead = null;
if(right.next != null) {
nextHead = right.next;
}
// 2.改变指向
pre.next = right;
right.next = cur;
cur.next = nextHead;
// 3.移动指针,进行下轮循环
pre = cur;
cur = nextHead;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
25. K 个一组翻转链表
给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:
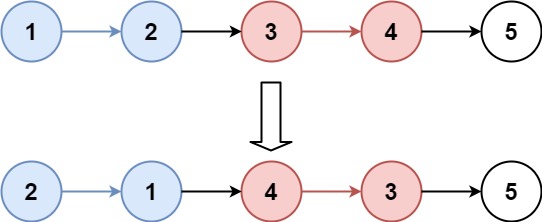
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
示例 2:
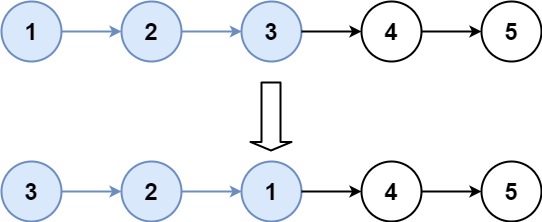
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
输出:[3,2,1,4,5]
提示:
- 链表中的节点数目为
n 1 <= k <= n <= 50000 <= Node.val <= 1000
题解
链表反转,实质上,要记录好三个指针:前一个节点,当前节点,下个节点
分组反转也是,记录好三组:前一组最后一个节点,当前组头一个节点和最后一个节点,下一组头节点
- 1.先分组,找到每组的head,end
- 2.组内进行反转
- 3.处理组与组之间的连接问题,即当前组的边界的前一个、后一个节点
- 注意:
- 注意边界,最后一组不完整
- 设置保护节点-虚拟头节点,不仅可以找到pre,也可以保存新链表头节点的位置
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode preGropuEnd = dummyHead; // 前一组的尾,要连接上当前组的头
ListNode cur = head; // 当前组反转前的头,也是反转后的尾
ListNode end; // 当前组反转前的尾,也是反转后的头
ListNode nextGropuHead; // 后一组的头,要连接上当前组的尾
// 迭代法遍历每个节点进行分组处理
while(cur != null) {
// 1. 分组---已知上一组尾,当前组头,需要找到当前组尾,下组头
end = findEnd(cur, k);
if(end == null) break; // 边界:没有k的长度,不做反转
nextGropuHead = end.next;
// 2. 对当前组进行反转
reverse(cur, nextGropuHead);// 遍历到下组头时停止
// 3. 连接前一组和后一组
preGropuEnd.next = end;
cur.next = nextGropuHead;
// 4. 移动指针,处理下一组
preGropuEnd = cur;
cur = nextGropuHead;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
private ListNode findEnd(ListNode cur, int k) {
// 要防止链表长度小于k的情况
while(cur != null && --k > 0) cur = cur.next;
return cur;
}
private void reverse(ListNode cur, ListNode stop) {
// 第一个节点反转后变成尾节点,指向下组,当前组逻辑不做处理
ListNode pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
ListNode next;
while(cur != stop) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
}
}
四、链表相交-环形链表
面试题 02.07. 链表相交
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交**:**
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ra0b7sRA-1674527294583)(assets/160_statement.png)]
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
示例 1:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ETX9k6ek-1674527294584)(assets/160_example_1.png)]
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Intersected at '8'
解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-B7AXm8J1-1674527294584)(assets/160_example_2.png)]
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Intersected at '2'
解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-5e68vB7G-1674527294585)(assets/160_example_3.png)]
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。
由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。
提示:
listA中节点数目为mlistB中节点数目为n0 <= m, n <= 3 * 1041 <= Node.val <= 1050 <= skipA <= m0 <= skipB <= n- 如果
listA和listB没有交点,intersectVal为0 - 如果
listA和listB有交点,intersectVal == listA[skipA + 1] == listB[skipB + 1]
**进阶:**你能否设计一个时间复杂度 O(n) 、仅用 O(1) 内存的解决方案?
题解1:O(n)空间
- 可以直接使用集合记录节点,重复的节点就是相交的节点
public class Solution {
// 实际上找重复的第一个节点,可以用set处理
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA == null || headB == null) return null;
HashSet<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
// 1. 先记录a链表的节点
while(headA != null) {
set.add(headA);
headA = headA.next;
}
// 2. 遍历b链表的节点,查找重复的链表
while(headB != null) {
if(set.contains(headB)) return headB;
headB = headB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
题解2:O(1)空间
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-NWx2V70N-1674527294585)(assets/image-20221120214525644.png)]
证明
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-dJkdyJzJ-1674527294586)(assets/image-20221120214712154.png)][外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-s3zhA31x-1674527294586)(assets/image-20221120214733231.png)]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
// 实际上找重复的第一个节点,可以用set处理
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA == null || headB == null) return null;
ListNode pA = headA;
ListNode pB = headB;
while(pA != pB) {
pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next;
pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next;
}
return pA;
}
}
141. 环形链表
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-hP7ImmAN-1674527294587)(assets/circularlinkedlist.png)]
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-4TYoTjYU-1674527294587)(assets/circularlinkedlist_test2.png)]
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-gDHzMTgz-1674527294587)(assets/circularlinkedlist_test3.png)]
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 104] -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5pos为-1或者链表中的一个 有效索引 。
题解
-
1.可以用**哈希表记录链表遍历过的节点,**如果有重复,说明有环,空间O(n)
-
2.也可以原地解决,使用快慢指针,如果有环,快指针一定能与慢指针相遇
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-8hlTeRLd-1674527294588)(assets/34c6bd80278a4c05a713f7aa279d4f31.png)]
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return false;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow) return true;
}
return false;
}
}
142. 环形链表 II
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
示例 1:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ctgBxEol-1674527294588)(assets/circularlinkedlist-166895576765318.png)]
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-jaBUBKSx-1674527294588)(assets/circularlinkedlist_test2-166895576765720.png)]
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:返回索引为 0 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-8qFnrYSa-1674527294588)(assets/circularlinkedlist_test3-166895576765722.png)]
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:返回 null
解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围在范围
[0, 10^4]内 -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5pos的值为-1或者链表中的一个有效索引
题解
-
1.此题若不开额外空间,需要找规律,列数学表达式
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-zRQ4yNKb-1674527294589)(assets/e384a94b6efa48cda6b361c9792a33f8.png)]
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return null;
ListNode slow = head.next; // 先走一步,不然进不了循环
ListNode fast = head.next.next;
// 1. 先找到快慢指针的相遇点
while(fast != slow && fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// 2. 判断是否有环
if(fast != slow) return null;
// 3. 如果有环,根据公式,计算出环的起点
while(head != slow) {
head = head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return head;
}
}