目录
1.栈
1.1栈的概念及结构
1.2栈的实现
初始化栈
销毁栈
栈的扩容
入栈
出栈
获取栈顶元素
获取栈中有效元素个数
判空
程序代码如下
Stack.h
Stack.c
test.c
2.队列
2.1队列的概念及结构
2.2队列的实现
初始化队列
队尾入队列
队头出队列
获取队列头部元素
获取队列队尾元素
获取队列中有效元素个数
队列打印
队列判空
销毁队列
Queue.h
Queue.c
test.c
1.栈
1.1栈的概念及结构
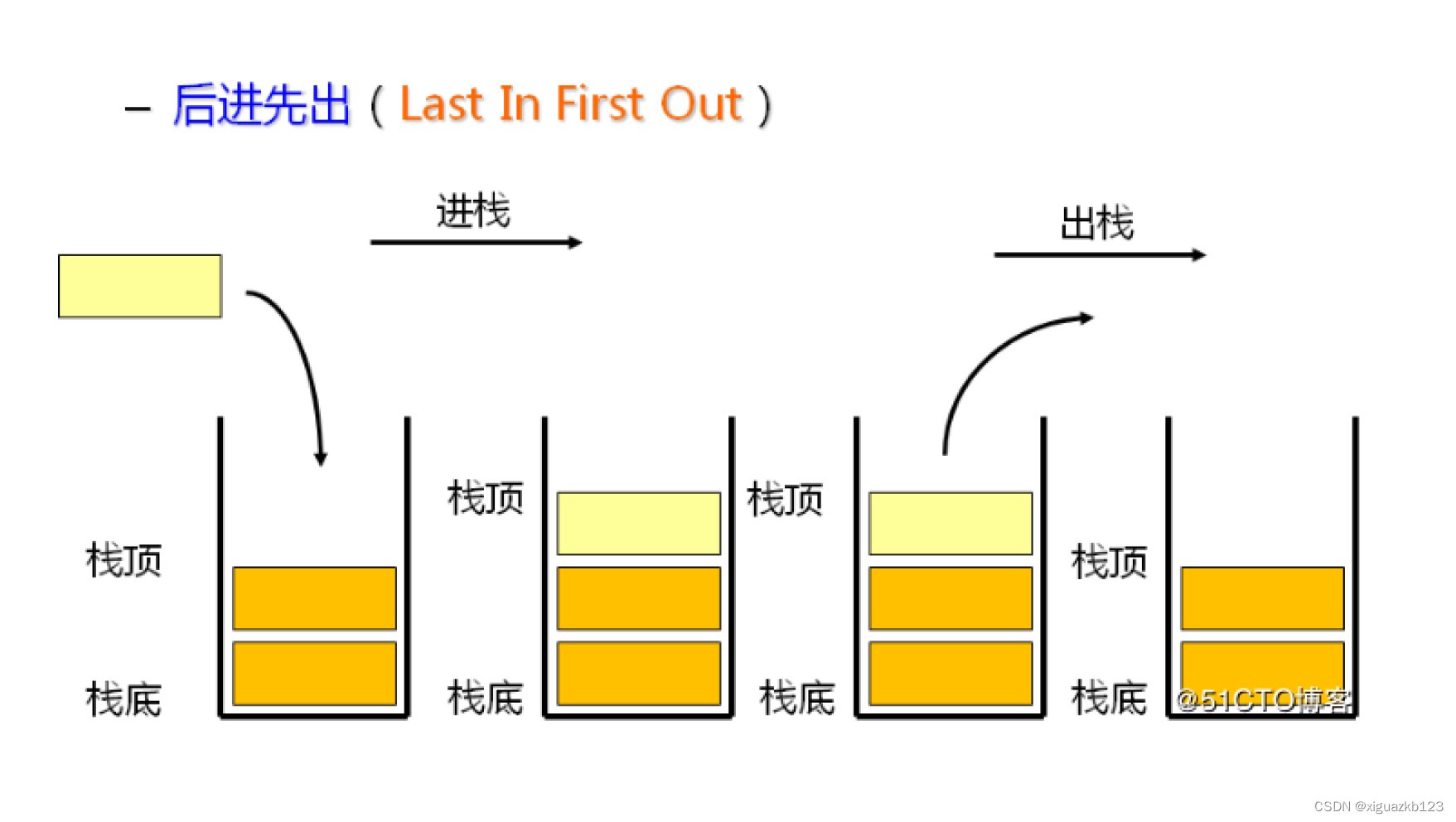
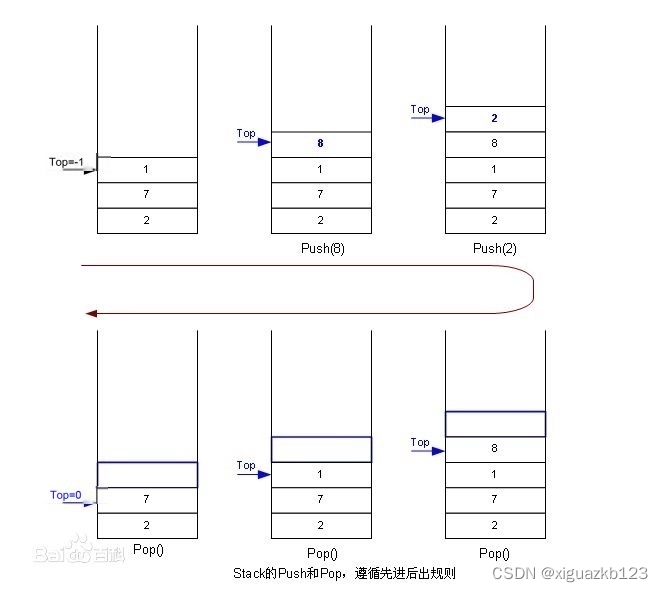
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端 称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶
可以使用数组(数组栈)或者链表(链表栈)实现栈。
数组栈实现更优一些。因为数组栈 尾插尾删效率更高,且缓存利用率高。
单链表,适合头插头删,如果用头作栈顶,可以设计成单链表,但是有点怪。用尾作栈底,要设计成双向链表,否则增删数据效率低。
1.2栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的 代价比较小。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(ST* ps);
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(ST* ps);
// 入栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
// 出栈
void StackPop(ST* ps);
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(ST* ps);
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
初始化栈
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;//ps->top=-1;
}
销毁栈
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}栈的扩容
void StackCheckCapacity(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
}入栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
StackCheckCapacity(ps);
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}出栈
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}判空
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
/*if (ps->top == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}*/
//换成下面语句就行了
return ps->top == 0;
}程序代码如下
Stack.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
void StackInit(ST* ps);
void StackDestroy(ST* ps);
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
void StackPop(ST* ps);
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
int StackSize(ST* ps);
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
Stack.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Stack.h"
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;//ps->top=-1;
}
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
void StackCheckCapacity(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
}
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
StackCheckCapacity(ps);
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
/*if (ps->top == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}*/
//换成下面语句就行了
return ps->top == 0;
}
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Stack.h"
void test1()
{
ST st;
StackInit(&st);
StackPush(&st, 1);
StackPush(&st, 2);
StackPush(&st, 3);
StackPush(&st, 4);
printf("%d ", StackTop(&st));
StackPop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
//printf("%d ", StackTop(&st));
StackDestroy(&st);
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}2.队列
2.1队列的概念及结构
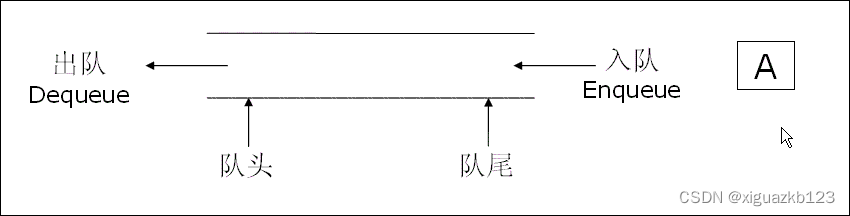
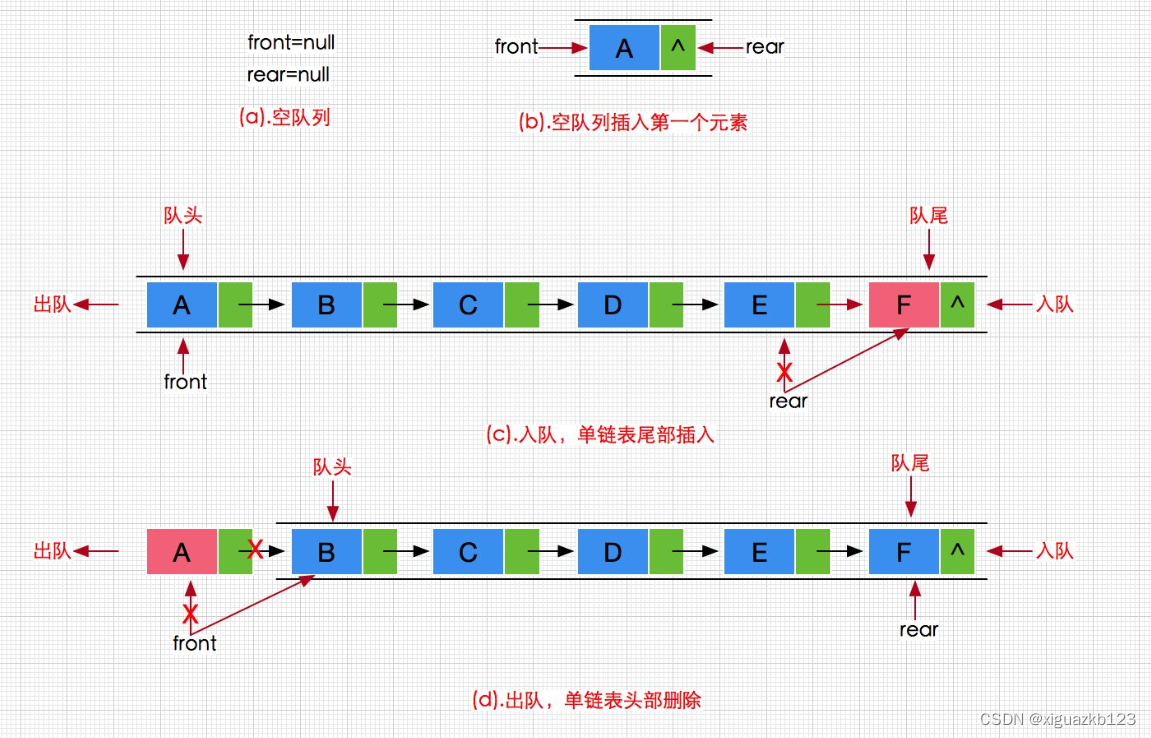
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out)
- 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾
- 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
 2.2队列的实现
2.2队列的实现
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
typedef int QDataType;
//链式结构:表示队列
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;//指针域
QDataType data;//数据域
}QueueNode;
//队列链表的头指针与尾指针
typedef struct Queue
{
QueueNode* head;
QueueNode* tail;
}Queue;
//初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
//队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
//队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
//获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
//获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
//获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
//队列打印
void QueuePrint(Queue* pq);
//队列判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
//销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = NULL;
pq->tail = NULL;
}队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* newnode = BuyQueueNode(x);
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//if (pq->head == NULL)
// return;
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
QueueNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
pq->tail = NULL;
}
}获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->data;
}获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int n = 0;
QueueNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
++n;
cur = cur->next;
}
return n;
}队列打印
void QueuePrint(Queue* pq)
{
QueueNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}队列判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* cur = pq->head;// QueueNode* cur =NULL
while (cur != NULL)
{
QueueNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}Queue.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int QDataType;
//链式结构:表示队列
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;//指针域
QDataType data;//数据域
}QueueNode;
//队列链表的头指针与尾指针
typedef struct Queue
{
QueueNode* head;
QueueNode* tail;
}Queue;
//初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
//队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
//队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
//获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
//获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
//获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
//队列打印
void QueuePrint(Queue* pq);
//队列判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
//销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
Queue.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = NULL;
pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* cur = pq->head;// QueueNode* cur =NULL
while (cur != NULL)
{
QueueNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
QueueNode* BuyQueueNode(QDataType x)
{
QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* newnode = BuyQueueNode(x);
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}
void QueuePrint(Queue* pq)
{
QueueNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//if (pq->head == NULL)
// return;
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
QueueNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
pq->tail = NULL;
}
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int n = 0;
QueueNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
++n;
cur = cur->next;
}
return n;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Queue.h"
void test1()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
QueuePrint(&q);
/*QueuePop(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
QueuePop(&q);*/
QueuePrint(&q);
printf("%d\n", QueueFront(&q));
printf("%d\n", QueueBack(&q));
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
void test2()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
QDataType front = QueueFront(&q);
printf("%d ", front);
QueuePop(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
QDataType front = QueueFront(&q);
printf("%d ", front);
QueuePop(&q);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
//test1();
test2();
return 0;
}