pipeline
快速使用
from transformers import pipeline
classifier = pipeline("sentiment-analysis")
classifier(
[
"I've been waiting for a HuggingFace course my whole life.",
"I hate this so much!",
]
)[{'label': 'POSITIVE', 'score': 0.9598047137260437},
{'label': 'NEGATIVE', 'score': 0.9994558095932007}]
3大结构
tokenizer:原始单词—input ids(互相转化)
原始文本被划分为token列表,再为其加上特殊的首位token进行区分,最后根据预训练模型的词表为所有token找到id

transformers提供了autotokenizer API实现该功能
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
checkpoint = "distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)raw_inputs = [
"I've been waiting for a HuggingFace course my whole life.",
"I hate this so much!",
]
# 每个句子的单词数目不同,可以padding用0来把短句补齐
# truncation=True,此时,如果句子的向量长度超过模型可以处理的范围,就会被截断
# return_tensors="pt",这样返回的结果就是tensor类型了,因为transformers只接受tensor输入
inputs = tokenizer(raw_inputs, padding=True, truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
print(inputs){
'input_ids': tensor([
[ 101, 1045, 1005, 2310, 2042, 3403, 2005, 1037, 17662, 12172, 2607, 2026, 2878, 2166, 1012, 102],
[ 101, 1045, 5223, 2023, 2061, 2172, 999, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
]),
# mask可以告诉我们哪里做了padding
'attention_mask': tensor([
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
])
}
b. model:input ids—logits
transformers提供了automodel API:
from transformers import AutoModel
checkpoint = "distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english"
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(checkpoint)# outputs.last_hidden_state获得最后一层隐藏网络的输出的向量
outputs = model(**inputs)
print(outputs.last_hidden_state.shape)
###
1.Batch size: The number of sequences processed at a time (2 in our example).
2.Sequence length: The length of the numerical representation of the sequence (16 in our example).
3.Hidden size: The vector dimension of each model input.
###torch.Size([2, 16, 768])
model的架构
embedding层将输入的input id转换为vector
随后的层使用注意力机制操纵这些向量,以产生句子的最终表示
head是有多个线性层组成的网络,它可以把高纬的hidden states映射到不同的维度
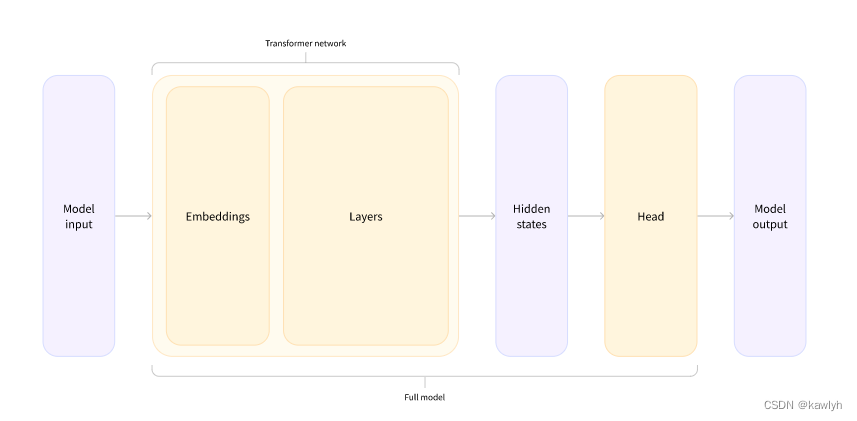
补充:除了model,transformers还有很多head:
*Model (retrieve the hidden states)
*ForCausalLM
*ForMaskedLM
*ForMultipleChoice
*ForQuestionAnswering
*ForSequenceClassification
*ForTokenClassification
# 例如为了区分矩阵的正负情感,我们用AutoModelForSequenceClassification
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
checkpoint = "distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english"
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
outputs = model(**inputs)print(outputs.logits.shape)torch.Size([2, 2])
print(outputs.logits)tensor([[-1.5607, 1.6123],
[ 4.1692, -3.3464]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward>)
c. post processing:预测,得到标签结果和分数
可以发现model层输出的并非概率,而是裸分数logits,我们需要做一个softmax将其转换为概率:(例如这里的输出每个tensor的和都是1了)
import torch
predictions = torch.nn.functional.softmax(outputs.logits, dim=-1)
print(predictions)tensor([[4.0195e-02, 9.5980e-01],
[9.9946e-01, 5.4418e-04]], grad_fn=<SoftmaxBackward>)



![[hive]数仓分层|用户纬度拉链表|维度建模](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/345dab024c1e40b496530982354a0b51.png)