前言:
学习了pose_graph_2d部分,因为先学习了3维的pose_graph_3d部分,所以这个就比较容易。简单来说就是se2和se3的区别。整个的运行逻辑和3维部分的pose_graph_3d部分是一样的,概括为:
1.设置好两个type,分别是poses和constrains的格式,并重写>>运算符;
2.是对于g2o文件的解析,和分字符输入到不同的容器中,这里部分的内容再read_g2o.h里面;
3.针对二维的角度划定范围[-pi and pi),这部分在normalize_angle.h里面;
4.针对角度的非常规计算,这部分在angle_local_parameterization.h里面;
5.对于残差部分的运算,这部分在pose_graph_2d_error_term.h里面;
6.最后的优化配置计算,main函数部分,在pose_graph_2d.cc里面。
官方doc说的很详细了:
Consider a robot moving in a 2-Dimensional plane. The robot has access to a set of sensors such as wheel odometry or a laser range scanner. From these raw measurements, we want to estimate the trajectory of the robot as well as build a map of the environment. In order to reduce the computational complexity of the problem, the pose graph approach abstracts the raw measurements away. Specifically, it creates a graph of nodes which represent the pose of the robot, and edges which represent the relative transformation (delta position and orientation) between the two nodes. The edges are virtual measurements derived from the raw sensor measurements, e.g. by integrating the raw wheel odometry or aligning the laser range scans acquired from the robot. A visualization of the resulting graph is shown below.

The figure depicts the pose of the robot as the triangles, the measurements are indicated by the connecting lines, and the loop closure measurements are shown as dotted lines. Loop closures are measurements between non-sequential robot states and they reduce the accumulation of error over time. The following will describe the mathematical formulation of the pose graph problem.
下面按前面概括的顺序学习源码。
一、配置poses和constrains数据格式
内容是types.h部分:
首先是Pose2d部分,
// The state for each vertex in the pose graph.
struct Pose2d {
double x;
double y;
double yaw_radians;
// The name of the data type in the g2o file format.
static std::string name() { return "VERTEX_SE2"; }
};数据结构比较简单,
一个x,一个y表示二维坐标;
一个yaw_radians表示旋转的角度,也就是方向;
然后一个成员函数返回"VERTEX_SE2",这是g2o文件中,记录点部分的title。
inline std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& input, Pose2d& pose) {
input >> pose.x >> pose.y >> pose.yaw_radians;
// Normalize the angle between -pi to pi.
pose.yaw_radians = NormalizeAngle(pose.yaw_radians);
return input;
}这是重写了一个>>运算符,将运算符左侧的对象写入Pose2d数据结构生成的对象里面。并且把角度修正到-pi to pi范围内。
接下来是Constrain2d部分,
// The constraint between two vertices in the pose graph. The constraint is the
// transformation from vertex id_begin to vertex id_end.
struct Constraint2d {
int id_begin;
int id_end;
double x;
double y;
double yaw_radians;
// The inverse of the covariance matrix for the measurement. The order of the
// entries are x, y, and yaw.
Eigen::Matrix3d information;
// The name of the data type in the g2o file format.
static std::string name() { return "EDGE_SE2"; }
};两个index,表示两个点的index;
x,y,yaw_radians表示这两个点的差值,在id_begin坐标系下,id_end与id_begin的差值;
信息矩阵information;
一个成员函数,返回"EDGE_SE2",它也是g2o文件中Constraint2d部分的title。
inline std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& input, Constraint2d& constraint) {
input >> constraint.id_begin >> constraint.id_end >> constraint.x >>
constraint.y >> constraint.yaw_radians >> constraint.information(0, 0) >>
constraint.information(0, 1) >> constraint.information(0, 2) >>
constraint.information(1, 1) >> constraint.information(1, 2) >>
constraint.information(2, 2);
// Set the lower triangular part of the information matrix.
constraint.information(1, 0) = constraint.information(0, 1);
constraint.information(2, 0) = constraint.information(0, 2);
constraint.information(2, 1) = constraint.information(1, 2);
// Normalize the angle between -pi to pi.
constraint.yaw_radians = NormalizeAngle(constraint.yaw_radians);
return input;
}同样重写了>>运算符,将左侧的对象写入右侧的Constraint2d生成的对象中。
二、解析读取g2o文件的内容
内容在read_g2o.h中:
阅读点的部分:
// Reads a single pose from the input and inserts it into the map. Returns false
// if there is a duplicate entry.
template <typename Pose, typename Allocator>
bool ReadVertex(std::ifstream* infile,
std::map<int, Pose, std::less<int>, Allocator>* poses) {
int id;
Pose pose;
*infile >> id >> pose;
// Ensure we don't have duplicate poses.
if (poses->find(id) != poses->end()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Duplicate vertex with ID: " << id;
return false;
}
(*poses)[id] = pose;
return true;
}首先定义了id和pose对象,先利用之前的重载输入运算符写入,然后判断是否有重复id,若没有则再写入到指针poses中去。
阅读边部分:
// Reads the contraints between two vertices in the pose graph
template <typename Constraint, typename Allocator>
void ReadConstraint(std::ifstream* infile,
std::vector<Constraint, Allocator>* constraints) {
Constraint constraint;
*infile >> constraint;
constraints->push_back(constraint);
}写入到constrains容器中去。
然后是整合部分ReadG2oFile函数:
template <typename Pose,
typename Constraint,
typename MapAllocator,
typename VectorAllocator>
bool ReadG2oFile(const std::string& filename,
std::map<int, Pose, std::less<int>, MapAllocator>* poses,
std::vector<Constraint, VectorAllocator>* constraints) {
CHECK(poses != NULL);
CHECK(constraints != NULL);
poses->clear();
constraints->clear();
std::ifstream infile(filename.c_str());
if (!infile) {
return false;
}
std::string data_type;
while (infile.good()) {
// Read whether the type is a node or a constraint.
infile >> data_type;
if (data_type == Pose::name()) {
if (!ReadVertex(&infile, poses)) {
return false;
}
} else if (data_type == Constraint::name()) {
ReadConstraint(&infile, constraints);
} else {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unknown data type: " << data_type;
return false;
}
// Clear any trailing whitespace from the line.
infile >> std::ws;
}
return true;
}这部分内容是就一个判断,是node就用ReadVertex处理,是constraint就用ReadConstraint处理。值得注意的是string中c_str()函数,它的作用是指向一个以空字符结尾的指针。用它返回的对象来进行这个判断。
三、对于旋转角度的规范
在normalize_angle.h中:
// Normalizes the angle in radians between [-pi and pi).
template <typename T>
inline T NormalizeAngle(const T& angle_radians) {
// Use ceres::floor because it is specialized for double and Jet types.
T two_pi(2.0 * M_PI);
return angle_radians -
two_pi * ceres::floor((angle_radians + T(M_PI)) / two_pi);
}这部分就是把角度限制再-pi到pi之间,但这个ceres::floor的作用是什么,我没有找到资料。
四、针对角度的非常规计算
// Defines a local parameterization for updating the angle to be constrained in
// [-pi to pi).
class AngleLocalParameterization {
public:
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T* theta_radians,
const T* delta_theta_radians,
T* theta_radians_plus_delta) const {
*theta_radians_plus_delta =
NormalizeAngle(*theta_radians + *delta_theta_radians);
return true;
}
static ceres::LocalParameterization* Create() {
return (new ceres::AutoDiffLocalParameterization<AngleLocalParameterization,
1,
1>);
}
};构建角度更新,主要作用是theta_radians_plus_delta = theta_radians + delta_theta_radians。
yaw_new = yaw + △yaw
五、对于残差部分构建
这部分内容在pose_graph_2d_error_term.h里面:
首先是对于旋转角度变换成2*2的旋转矩阵的函数实现:
template <typename T>
Eigen::Matrix<T, 2, 2> RotationMatrix2D(T yaw_radians) {
const T cos_yaw = ceres::cos(yaw_radians);
const T sin_yaw = ceres::sin(yaw_radians);
Eigen::Matrix<T, 2, 2> rotation;
rotation << cos_yaw, -sin_yaw, sin_yaw, cos_yaw;
return rotation;
}本来准备手写的,突然发现官方doc里面有?就直接用官方的了,

就是变换成这个矩阵。
然后就是正式的残差构建部分,结构PoseGraph2dErrorTerm:
private:
// The position of B relative to A in the A frame.
const Eigen::Vector2d p_ab_;
// The orientation of frame B relative to frame A.
const double yaw_ab_radians_;
// The inverse square root of the measurement covariance matrix.
const Eigen::Matrix3d sqrt_information_;定义了三个私有的成员变量,
p_ab_是b点在a坐标系下的坐标;
yaw_ab_radians_是b点旋转到a方向的角度变化;
sqrt_information_是协方差矩阵。
PoseGraph2dErrorTerm(double x_ab,
double y_ab,
double yaw_ab_radians,
const Eigen::Matrix3d& sqrt_information)
: p_ab_(x_ab, y_ab),
yaw_ab_radians_(yaw_ab_radians),
sqrt_information_(sqrt_information) {}构造函数没什么好说的。
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T* const x_a,
const T* const y_a,
const T* const yaw_a,
const T* const x_b,
const T* const y_b,
const T* const yaw_b,
T* residuals_ptr) const {
const Eigen::Matrix<T, 2, 1> p_a(*x_a, *y_a);
const Eigen::Matrix<T, 2, 1> p_b(*x_b, *y_b);
Eigen::Map<Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1>> residuals_map(residuals_ptr);
residuals_map.template head<2>() =
RotationMatrix2D(*yaw_a).transpose() * (p_b - p_a) - p_ab_.cast<T>();
residuals_map(2) = ceres::examples::NormalizeAngle(
(*yaw_b - *yaw_a) - static_cast<T>(yaw_ab_radians_));
// Scale the residuals by the square root information matrix to account for
// the measurement uncertainty.
residuals_map = sqrt_information_.template cast<T>() * residuals_map;
return true;
}前面内容比较简单,解释以下核心部分residuals_map的计算,residuals_map是一个3*1的向量。

它的具体形式如上图所示,下面是推导过程:

是上图中最后矩阵的第一行第二个,t表示p。
这个residuals_map就是残差,所以前两行是计算位移的残差,就是estimated - measures的。后面一行是对于旋转角度的残差。
static ceres::CostFunction* Create(double x_ab,
double y_ab,
double yaw_ab_radians,
const Eigen::Matrix3d& sqrt_information) {
return (new ceres::
AutoDiffCostFunction<PoseGraph2dErrorTerm, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1>(
new PoseGraph2dErrorTerm(
x_ab, y_ab, yaw_ab_radians, sqrt_information)));
}定义了一个create函数,我觉得这里是为了方便优化部分的简洁。
六、优化配置和main函数部分
// Output the poses to the file with format: ID x y yaw_radians.
bool OutputPoses(const std::string& filename,
const std::map<int, Pose2d>& poses) {
std::fstream outfile;
outfile.open(filename.c_str(), std::istream::out);
if (!outfile) {
std::cerr << "Error opening the file: " << filename << '\n';
return false;
}
for (std::map<int, Pose2d>::const_iterator poses_iter = poses.begin();
poses_iter != poses.end();
++poses_iter) {
const std::map<int, Pose2d>::value_type& pair = *poses_iter;
outfile << pair.first << " " << pair.second.x << " " << pair.second.y << ' '
<< pair.second.yaw_radians << '\n';
}
return true;
}生成一个txt文件来保存pose数据,这里的文件读写操作可以借鉴一下。
接下来是优化problem的配置:
// Constructs the nonlinear least squares optimization problem from the pose
// graph constraints.
void BuildOptimizationProblem(const std::vector<Constraint2d>& constraints,
std::map<int, Pose2d>* poses,
ceres::Problem* problem) {
CHECK(poses != NULL);
CHECK(problem != NULL);
if (constraints.empty()) {
LOG(INFO) << "No constraints, no problem to optimize.";
return;
}
ceres::LossFunction* loss_function = NULL;
ceres::LocalParameterization* angle_local_parameterization =
AngleLocalParameterization::Create();
for (std::vector<Constraint2d>::const_iterator constraints_iter =
constraints.begin();
constraints_iter != constraints.end();
++constraints_iter) {
const Constraint2d& constraint = *constraints_iter;
std::map<int, Pose2d>::iterator pose_begin_iter =
poses->find(constraint.id_begin);
CHECK(pose_begin_iter != poses->end())
<< "Pose with ID: " << constraint.id_begin << " not found.";
std::map<int, Pose2d>::iterator pose_end_iter =
poses->find(constraint.id_end);
CHECK(pose_end_iter != poses->end())
<< "Pose with ID: " << constraint.id_end << " not found.";
const Eigen::Matrix3d sqrt_information =
constraint.information.llt().matrixL();
// Ceres will take ownership of the pointer.
ceres::CostFunction* cost_function = PoseGraph2dErrorTerm::Create(
constraint.x, constraint.y, constraint.yaw_radians, sqrt_information);
problem->AddResidualBlock(cost_function,
loss_function,
&pose_begin_iter->second.x,
&pose_begin_iter->second.y,
&pose_begin_iter->second.yaw_radians,
&pose_end_iter->second.x,
&pose_end_iter->second.y,
&pose_end_iter->second.yaw_radians);
problem->SetParameterization(&pose_begin_iter->second.yaw_radians,
angle_local_parameterization);
problem->SetParameterization(&pose_end_iter->second.yaw_radians,
angle_local_parameterization);
}
// The pose graph optimization problem has three DOFs that are not fully
// constrained. This is typically referred to as gauge freedom. You can apply
// a rigid body transformation to all the nodes and the optimization problem
// will still have the exact same cost. The Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm has
// internal damping which mitigate this issue, but it is better to properly
// constrain the gauge freedom. This can be done by setting one of the poses
// as constant so the optimizer cannot change it.
std::map<int, Pose2d>::iterator pose_start_iter = poses->begin();
CHECK(pose_start_iter != poses->end()) << "There are no poses.";
problem->SetParameterBlockConstant(&pose_start_iter->second.x);
problem->SetParameterBlockConstant(&pose_start_iter->second.y);
problem->SetParameterBlockConstant(&pose_start_iter->second.yaw_radians);
}下面来分析,
CHECK(poses != NULL);
CHECK(problem != NULL);
if (constraints.empty()) {
LOG(INFO) << "No constraints, no problem to optimize.";
return;
}判断是否存在,跳过。
ceres::LossFunction* loss_function = NULL;
ceres::LocalParameterization* angle_local_parameterization =
AngleLocalParameterization::Create();设定无核函数,对于角度规范话的设定。
下面是核心部分,对于每个pose和constrains的加入:
for (std::vector<Constraint2d>::const_iterator constraints_iter =
constraints.begin();
constraints_iter != constraints.end();
++constraints_iter) 用for循环遍历Constraint2d的vector容器,里面存放的是边的信息。
const Constraint2d& constraint = *constraints_iter;
std::map<int, Pose2d>::iterator pose_begin_iter =
poses->find(constraint.id_begin);
CHECK(pose_begin_iter != poses->end())
<< "Pose with ID: " << constraint.id_begin << " not found.";
std::map<int, Pose2d>::iterator pose_end_iter =
poses->find(constraint.id_end);
CHECK(pose_end_iter != poses->end())
<< "Pose with ID: " << constraint.id_end << " not found.";使用constraint局部变量来作为循环内的判断赋值等;
pose_begin_iter赋值为开始的index点;
pose_end_iter赋值为结束的index点,并判断是否存在。
const Eigen::Matrix3d sqrt_information =
constraint.information.llt().matrixL();这里是将斜对称矩阵进行Eigen的LLT分解实现了Cholesky 分解,并赋值给sqrt_information变量。
ceres::CostFunction* cost_function = PoseGraph2dErrorTerm::Create(
constraint.x, constraint.y, constraint.yaw_radians, sqrt_information);利用create函数构建costfunction,将上面的局部变量传入进去。
problem->AddResidualBlock(cost_function,
loss_function,
&pose_begin_iter->second.x,
&pose_begin_iter->second.y,
&pose_begin_iter->second.yaw_radians,
&pose_end_iter->second.x,
&pose_end_iter->second.y,
&pose_end_iter->second.yaw_radians);
problem->SetParameterization(&pose_begin_iter->second.yaw_radians,
angle_local_parameterization);
problem->SetParameterization(&pose_end_iter->second.yaw_radians,
angle_local_parameterization);AddResidualBlock进行problem部分的配置,SetParameterization是对于角度的不同要求的配置。
std::map<int, Pose2d>::iterator pose_start_iter = poses->begin();
CHECK(pose_start_iter != poses->end()) << "There are no poses.";
problem->SetParameterBlockConstant(&pose_start_iter->second.x);
problem->SetParameterBlockConstant(&pose_start_iter->second.y);
problem->SetParameterBlockConstant(&pose_start_iter->second.yaw_radians);固定第一个点不动。
最后是SolveOptimizationProblem部分:
// Returns true if the solve was successful.
bool SolveOptimizationProblem(ceres::Problem* problem) {
CHECK(problem != NULL);
ceres::Solver::Options options;
options.max_num_iterations = 100;
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::SPARSE_NORMAL_CHOLESKY;
ceres::Solver::Summary summary;
ceres::Solve(options, problem, &summary);
std::cout << summary.FullReport() << '\n';
return summary.IsSolutionUsable();
}主要是配置options并开始优化计算输出结果等。
七、输出结果
进行修改成,并配置CMakeLists.txt文件,然后输入结果可视化。

选择另一个数据:
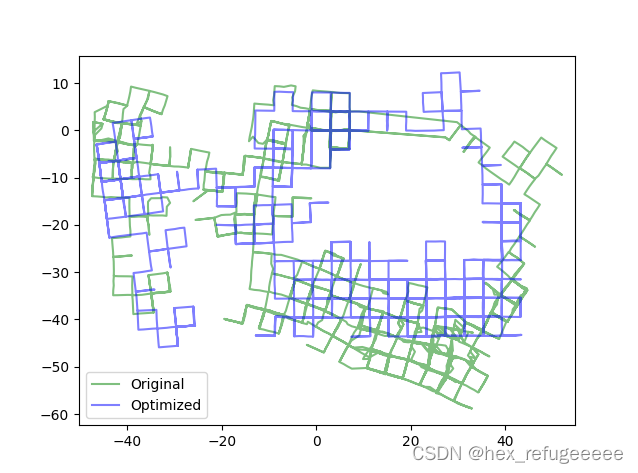
可以看出变化还是比较明显。
对于CMakeLists.txt在多文件夹下的使用配置还是不太熟练,找个时间系统总结一下。