kprobe其实就是将某个要检测的指令备份,再替换成int3(x86)或者未定义指令(arm)来触发异常,再调用对应体系的异常处理函数来执行我们自定义的hook,执行完我们自定义的hook,再将备份的指令放回原来的位置继续往下执行
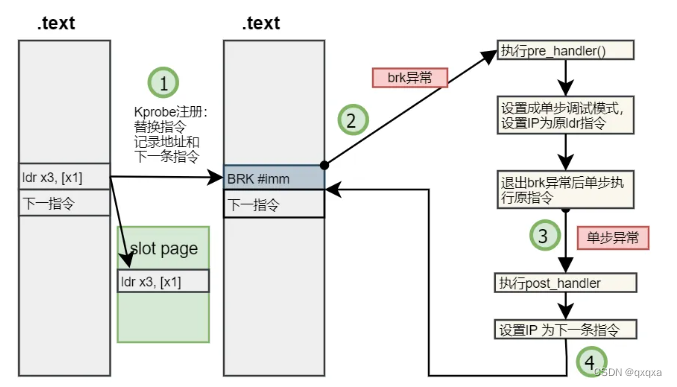
下面我们就来看下linux内核版本为5.17.5的arm64的kprobe代码架构,首先看下probe这个结构体
struct kprobe {
struct hlist_node hlist;
/* list of kprobes for multi-handler support */
struct list_head list;
/*count the number of times this probe was temporarily disarmed */
unsigned long nmissed;
/* location of the probe point */
kprobe_opcode_t *addr;
/* Allow user to indicate symbol name of the probe point */
const char *symbol_name;
/* Offset into the symbol */
unsigned int offset;
/* Called before addr is executed. */
kprobe_pre_handler_t pre_handler;
/* Called after addr is executed, unless... */
kprobe_post_handler_t post_handler;
/* Saved opcode (which has been replaced with breakpoint) */
kprobe_opcode_t opcode;
/* copy of the original instruction */
struct arch_specific_insn ainsn;
/*
* Indicates various status flags.
* Protected by kprobe_mutex after this kprobe is registered.
*/
u32 flags;
};替换成未定义指令后,就会触发的未定义指令异常处理函数
void do_undefinstr(struct pt_regs *regs)
{
/* check for AArch32 breakpoint instructions */
if (!aarch32_break_handler(regs))
return;
if (call_undef_hook(regs) == 0)
return;
BUG_ON(!user_mode(regs));
force_signal_inject(SIGILL, ILL_ILLOPC, regs->pc, 0);
}里面的会调用call_undef_hook,这个函数的参数就是记录在堆栈中的寄存器组,下面一个函数我们也可以看到用到了程序计数器pc
static int call_undef_hook(struct pt_regs *regs)
{
struct undef_hook *hook;
unsigned long flags;
u32 instr;
int (*fn)(struct pt_regs *regs, u32 instr) = NULL;
unsigned long pc = instruction_pointer(regs);
if (!user_mode(regs)) {
__le32 instr_le;
if (get_kernel_nofault(instr_le, (__le32 *)pc))
goto exit;
instr = le32_to_cpu(instr_le);
} else if (compat_thumb_mode(regs)) {
/* 16-bit Thumb instruction */
__le16 instr_le;
if (get_user(instr_le, (__le16 __user *)pc))
goto exit;
instr = le16_to_cpu(instr_le);
if (aarch32_insn_is_wide(instr)) {
u32 instr2;
if (get_user(instr_le, (__le16 __user *)(pc + 2)))
goto exit;
instr2 = le16_to_cpu(instr_le);
instr = (instr << 16) | instr2;
}
} else {
/* 32-bit ARM instruction */
__le32 instr_le;
if (get_user(instr_le, (__le32 __user *)pc))
goto exit;
instr = le32_to_cpu(instr_le);
}
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&undef_lock, flags);
list_for_each_entry(hook, &undef_hook, node)
if ((instr & hook->instr_mask) == hook->instr_val &&
(regs->pstate & hook->pstate_mask) == hook->pstate_val)
fn = hook->fn;
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&undef_lock, flags);
exit:
return fn ? fn(regs, instr) : 1;
}从最后几行我们看到他会便利整个undef_hook,通过对比instr_mask等找到对应的undef_hook的fn:其实也就是 kprobe_trap_handler;
在系统初始化kprobe子系统时
static int __init init_kprobes(void)
{
int i, err = 0;
/* FIXME allocate the probe table, currently defined statically */
/* initialize all list heads */
for (i = 0; i < KPROBE_TABLE_SIZE; i++)
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&kprobe_table[i]);
err = populate_kprobe_blacklist(__start_kprobe_blacklist,
__stop_kprobe_blacklist);
if (err)
pr_err("Failed to populate blacklist (error %d), kprobes not restricted, be careful using them!\n", err);
if (kretprobe_blacklist_size) {
/* lookup the function address from its name */
for (i = 0; kretprobe_blacklist[i].name != NULL; i++) {
kretprobe_blacklist[i].addr =
kprobe_lookup_name(kretprobe_blacklist[i].name, 0);
if (!kretprobe_blacklist[i].addr)
pr_err("Failed to lookup symbol '%s' for kretprobe blacklist. Maybe the target function is removed or renamed.\n",
kretprobe_blacklist[i].name);
}
}
/* By default, kprobes are armed */
kprobes_all_disarmed = false;
#if defined(CONFIG_OPTPROBES) && defined(__ARCH_WANT_KPROBES_INSN_SLOT)
/* Init 'kprobe_optinsn_slots' for allocation */
kprobe_optinsn_slots.insn_size = MAX_OPTINSN_SIZE;
#endif
err = arch_init_kprobes();
if (!err)
err = register_die_notifier(&kprobe_exceptions_nb);
if (!err)
err = register_module_notifier(&kprobe_module_nb);
kprobes_initialized = (err == 0);
kprobe_sysctls_init();
return err;
}
early_initcall(init_kprobes);会调用arch_init_kprobes来注册体系架构的kprobe的hook
static struct undef_hook kprobes_arm_break_hook = {
.instr_mask = 0x0fffffff,
.instr_val = KPROBE_ARM_BREAKPOINT_INSTRUCTION,
.cpsr_mask = MODE_MASK,
.cpsr_val = SVC_MODE,
.fn = kprobe_trap_handler,
};
#endif /* !CONFIG_THUMB2_KERNEL */
int __init arch_init_kprobes(void)
{
arm_probes_decode_init();
#ifdef CONFIG_THUMB2_KERNEL
register_undef_hook(&kprobes_thumb16_break_hook);
register_undef_hook(&kprobes_thumb32_break_hook);
#else
register_undef_hook(&kprobes_arm_break_hook);
#endif
return 0;
}kprobe_trap_handler会调用kprobe_handler
void __kprobes kprobe_handler(struct pt_regs *regs)
{
struct kprobe *p, *cur;
struct kprobe_ctlblk *kcb;
kcb = get_kprobe_ctlblk();
cur = kprobe_running();
#ifdef CONFIG_THUMB2_KERNEL
/*
* First look for a probe which was registered using an address with
* bit 0 set, this is the usual situation for pointers to Thumb code.
* If not found, fallback to looking for one with bit 0 clear.
*/
p = get_kprobe((kprobe_opcode_t *)(regs->ARM_pc | 1));
if (!p)
p = get_kprobe((kprobe_opcode_t *)regs->ARM_pc);
#else /* ! CONFIG_THUMB2_KERNEL */
p = get_kprobe((kprobe_opcode_t *)regs->ARM_pc);
#endif
if (p) {
if (!p->ainsn.insn_check_cc(regs->ARM_cpsr)) {
/*
* Probe hit but conditional execution check failed,
* so just skip the instruction and continue as if
* nothing had happened.
* In this case, we can skip recursing check too.
*/
singlestep_skip(p, regs);
} else if (cur) {
/* Kprobe is pending, so we're recursing. */
switch (kcb->kprobe_status) {
case KPROBE_HIT_ACTIVE:
case KPROBE_HIT_SSDONE:
case KPROBE_HIT_SS:
/* A pre- or post-handler probe got us here. */
kprobes_inc_nmissed_count(p);
save_previous_kprobe(kcb);
set_current_kprobe(p);
kcb->kprobe_status = KPROBE_REENTER;
singlestep(p, regs, kcb);
restore_previous_kprobe(kcb);
break;
case KPROBE_REENTER:
/* A nested probe was hit in FIQ, it is a BUG */
pr_warn("Failed to recover from reentered kprobes.\n");
dump_kprobe(p);
fallthrough;
default:
/* impossible cases */
BUG();
}
} else {
/* Probe hit and conditional execution check ok. */
set_current_kprobe(p);
kcb->kprobe_status = KPROBE_HIT_ACTIVE;
/*
* If we have no pre-handler or it returned 0, we
* continue with normal processing. If we have a
* pre-handler and it returned non-zero, it will
* modify the execution path and no need to single
* stepping. Let's just reset current kprobe and exit.
*/
if (!p->pre_handler || !p->pre_handler(p, regs)) {
kcb->kprobe_status = KPROBE_HIT_SS;
singlestep(p, regs, kcb);
if (p->post_handler) {
kcb->kprobe_status = KPROBE_HIT_SSDONE;
p->post_handler(p, regs, 0);
}
}
reset_current_kprobe();
}
} else {
/*
* The probe was removed and a race is in progress.
* There is nothing we can do about it. Let's restart
* the instruction. By the time we can restart, the
* real instruction will be there.
*/
}
}上面这个函数我们可以看到,会调用kprobe的pre_handler和post_handler,这两个函数被我们实现好,装填进kprobe,并用register_kprobe注册到kprobe子系统;当注册好之后,系统执行到这个位置就会陷入异常,异常处理函数就会来处理我们的kprobe
int register_kprobe(struct kprobe *p)
{
int ret;
struct kprobe *old_p;
struct module *probed_mod;
kprobe_opcode_t *addr;
/* Adjust probe address from symbol */
addr = kprobe_addr(p);
if (IS_ERR(addr))
return PTR_ERR(addr);
p->addr = addr;
ret = warn_kprobe_rereg(p);
if (ret)
return ret;
/* User can pass only KPROBE_FLAG_DISABLED to register_kprobe */
p->flags &= KPROBE_FLAG_DISABLED;
p->nmissed = 0;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->list);
ret = check_kprobe_address_safe(p, &probed_mod);
if (ret)
return ret;
mutex_lock(&kprobe_mutex);
old_p = get_kprobe(p->addr);
if (old_p) {
/* Since this may unoptimize 'old_p', locking 'text_mutex'. */
ret = register_aggr_kprobe(old_p, p);
goto out;
}
cpus_read_lock();
/* Prevent text modification */
mutex_lock(&text_mutex);
ret = prepare_kprobe(p);
mutex_unlock(&text_mutex);
cpus_read_unlock();
if (ret)
goto out;
INIT_HLIST_NODE(&p->hlist);
hlist_add_head_rcu(&p->hlist,
&kprobe_table[hash_ptr(p->addr, KPROBE_HASH_BITS)]);
if (!kprobes_all_disarmed && !kprobe_disabled(p)) {
ret = arm_kprobe(p);
if (ret) {
hlist_del_rcu(&p->hlist);
synchronize_rcu();
goto out;
}
}
/* Try to optimize kprobe */
try_to_optimize_kprobe(p);
out:
mutex_unlock(&kprobe_mutex);
if (probed_mod)
module_put(probed_mod);
return ret;
}