一、 开发环境
ubuntu20.04
ros版本noetic
参考视频
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ci4y1L7ZZ/?p=52&spm_id_from=333.1007.top_right_bar_window_history.content.click&vd_source=4cd1b6f268e2a29a11bea5d2568836ee
二、 编写msg文件
在功能包下面创建msg文件夹(msg文件夹和src文件夹并列),在msg文件夹中创建Person.msg文件
Person.msg
string name
int32 age
float32 height
三、 编写发布者
main.cpp
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "/home/leon/project/ros/helloworld/ws/devel/include/publisher/Person.h"
#include <sstream>
//发布者
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
//中文支持
setlocale(LC_ALL,"");
//初始化ros节点
//指定节点名称
ros::init(argc,argv,"publisher");
//创建ros节点句柄
ros::NodeHandle n;
//创建发布者对象
ros::Publisher pub = n.advertise<publisher::Person>("fang",10);
//编写发布逻辑
publisher::Person person;
person.name = "张三";
person.age = 10;
person.height = 10.5;
//发布频率
ros::Rate rate(1);
int count = 0;
//如果节点活着循环发布
while(ros::ok)
{
count++;
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "hello:" << count;
pub.publish(person);
ROS_INFO("发布数据:%s,%d,%f",person.name.c_str(),person.age,person.height);
rate.sleep();
ros::spinOnce();
}
return 0;
}
//通过ros工具打印话题消息
//rostopic echo fang
修改配置
package.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<package format="2">
<name>publisher</name>
<version>0.0.0</version>
<description>The publisher package</description>
<!-- One maintainer tag required, multiple allowed, one person per tag -->
<!-- Example: -->
<!-- <maintainer email="jane.doe@example.com">Jane Doe</maintainer> -->
<maintainer email="leon@todo.todo">leon</maintainer>
<!-- One license tag required, multiple allowed, one license per tag -->
<!-- Commonly used license strings: -->
<!-- BSD, MIT, Boost Software License, GPLv2, GPLv3, LGPLv2.1, LGPLv3 -->
<license>TODO</license>
<!-- Url tags are optional, but multiple are allowed, one per tag -->
<!-- Optional attribute type can be: website, bugtracker, or repository -->
<!-- Example: -->
<!-- <url type="website">http://wiki.ros.org/publisher</url> -->
<!-- Author tags are optional, multiple are allowed, one per tag -->
<!-- Authors do not have to be maintainers, but could be -->
<!-- Example: -->
<!-- <author email="jane.doe@example.com">Jane Doe</author> -->
<!-- The *depend tags are used to specify dependencies -->
<!-- Dependencies can be catkin packages or system dependencies -->
<!-- Examples: -->
<!-- Use depend as a shortcut for packages that are both build and exec dependencies -->
<!-- <depend>roscpp</depend> -->
<!-- Note that this is equivalent to the following: -->
<!-- <build_depend>roscpp</build_depend> -->
<!-- <exec_depend>roscpp</exec_depend> -->
<!-- Use build_depend for packages you need at compile time: -->
<!-- <build_depend>message_generation</build_depend> -->
<!-- Use build_export_depend for packages you need in order to build against this package: -->
<!-- <build_export_depend>message_generation</build_export_depend> -->
<!-- Use buildtool_depend for build tool packages: -->
<!-- <buildtool_depend>catkin</buildtool_depend> -->
<!-- Use exec_depend for packages you need at runtime: -->
<!-- <exec_depend>message_runtime</exec_depend> -->
<!-- Use test_depend for packages you need only for testing: -->
<!-- <test_depend>gtest</test_depend> -->
<!-- Use doc_depend for packages you need only for building documentation: -->
<!-- <doc_depend>doxygen</doc_depend> -->
<buildtool_depend>catkin</buildtool_depend>
<build_depend>roscpp</build_depend>
<build_depend>std_msgs</build_depend>
<build_depend>message_generation</build_depend>
<build_export_depend>roscpp</build_export_depend>
<build_export_depend>std_msgs</build_export_depend>
<exec_depend>roscpp</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>std_msgs</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>message_runtime</exec_depend>
<!-- The export tag contains other, unspecified, tags -->
<export>
<!-- Other tools can request additional information be placed here -->
</export>
</package>
修改配置
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0.2)
project(publisher)
## Compile as C++11, supported in ROS Kinetic and newer
# add_compile_options(-std=c++11)
## Find catkin macros and libraries
## if COMPONENTS list like find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS xyz)
## is used, also find other catkin packages
find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS
roscpp
std_msgs
message_generation
)
## System dependencies are found with CMake's conventions
# find_package(Boost REQUIRED COMPONENTS system)
## Uncomment this if the package has a setup.py. This macro ensures
## modules and global scripts declared therein get installed
## See http://ros.org/doc/api/catkin/html/user_guide/setup_dot_py.html
# catkin_python_setup()
################################################
## Declare ROS messages, services and actions ##
################################################
## To declare and build messages, services or actions from within this
## package, follow these steps:
## * Let MSG_DEP_SET be the set of packages whose message types you use in
## your messages/services/actions (e.g. std_msgs, actionlib_msgs, ...).
## * In the file package.xml:
## * add a build_depend tag for "message_generation"
## * add a build_depend and a exec_depend tag for each package in MSG_DEP_SET
## * If MSG_DEP_SET isn't empty the following dependency has been pulled in
## but can be declared for certainty nonetheless:
## * add a exec_depend tag for "message_runtime"
## * In this file (CMakeLists.txt):
## * add "message_generation" and every package in MSG_DEP_SET to
## find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS ...)
## * add "message_runtime" and every package in MSG_DEP_SET to
## catkin_package(CATKIN_DEPENDS ...)
## * uncomment the add_*_files sections below as needed
## and list every .msg/.srv/.action file to be processed
## * uncomment the generate_messages entry below
## * add every package in MSG_DEP_SET to generate_messages(DEPENDENCIES ...)
## Generate messages in the 'msg' folder
add_message_files(
FILES
Person.msg
)
## Generate services in the 'srv' folder
# add_service_files(
# FILES
# Service1.srv
# Service2.srv
# )
## Generate actions in the 'action' folder
# add_action_files(
# FILES
# Action1.action
# Action2.action
# )
## Generate added messages and services with any dependencies listed here
generate_messages(
DEPENDENCIES
std_msgs
)
################################################
## Declare ROS dynamic reconfigure parameters ##
################################################
## To declare and build dynamic reconfigure parameters within this
## package, follow these steps:
## * In the file package.xml:
## * add a build_depend and a exec_depend tag for "dynamic_reconfigure"
## * In this file (CMakeLists.txt):
## * add "dynamic_reconfigure" to
## find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS ...)
## * uncomment the "generate_dynamic_reconfigure_options" section below
## and list every .cfg file to be processed
## Generate dynamic reconfigure parameters in the 'cfg' folder
# generate_dynamic_reconfigure_options(
# cfg/DynReconf1.cfg
# cfg/DynReconf2.cfg
# )
###################################
## catkin specific configuration ##
###################################
## The catkin_package macro generates cmake config files for your package
## Declare things to be passed to dependent projects
## INCLUDE_DIRS: uncomment this if your package contains header files
## LIBRARIES: libraries you create in this project that dependent projects also need
## CATKIN_DEPENDS: catkin_packages dependent projects also need
## DEPENDS: system dependencies of this project that dependent projects also need
catkin_package(
# INCLUDE_DIRS include
# LIBRARIES publisher
CATKIN_DEPENDS roscpp std_msgs message_runtime
# DEPENDS system_lib
)
###########
## Build ##
###########
## Specify additional locations of header files
## Your package locations should be listed before other locations
include_directories(
# include
${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
## Declare a C++ library
# add_library(${PROJECT_NAME}
# src/${PROJECT_NAME}/publisher.cpp
# )
## Add cmake target dependencies of the library
## as an example, code may need to be generated before libraries
## either from message generation or dynamic reconfigure
# add_dependencies(${PROJECT_NAME} ${${PROJECT_NAME}_EXPORTED_TARGETS} ${catkin_EXPORTED_TARGETS})
## Declare a C++ executable
## With catkin_make all packages are built within a single CMake context
## The recommended prefix ensures that target names across packages don't collide
add_executable(pbx src/main.cpp)
## Rename C++ executable without prefix
## The above recommended prefix causes long target names, the following renames the
## target back to the shorter version for ease of user use
## e.g. "rosrun someones_pkg node" instead of "rosrun someones_pkg someones_pkg_node"
# set_target_properties(${PROJECT_NAME}_node PROPERTIES OUTPUT_NAME node PREFIX "")
## Add cmake target dependencies of the executable
## same as for the library above
add_dependencies(pbx ${PROJECT_NAME}_generate_messages_cpp)
## Specify libraries to link a library or executable target against
target_link_libraries(pbx
${catkin_LIBRARIES}
)
#############
## Install ##
#############
# all install targets should use catkin DESTINATION variables
# See http://ros.org/doc/api/catkin/html/adv_user_guide/variables.html
## Mark executable scripts (Python etc.) for installation
## in contrast to setup.py, you can choose the destination
# catkin_install_python(PROGRAMS
# scripts/my_python_script
# DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_BIN_DESTINATION}
# )
## Mark executables for installation
## See http://docs.ros.org/melodic/api/catkin/html/howto/format1/building_executables.html
# install(TARGETS ${PROJECT_NAME}_node
# RUNTIME DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_BIN_DESTINATION}
# )
## Mark libraries for installation
## See http://docs.ros.org/melodic/api/catkin/html/howto/format1/building_libraries.html
# install(TARGETS ${PROJECT_NAME}
# ARCHIVE DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_LIB_DESTINATION}
# LIBRARY DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_LIB_DESTINATION}
# RUNTIME DESTINATION ${CATKIN_GLOBAL_BIN_DESTINATION}
# )
## Mark cpp header files for installation
# install(DIRECTORY include/${PROJECT_NAME}/
# DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_INCLUDE_DESTINATION}
# FILES_MATCHING PATTERN "*.h"
# PATTERN ".svn" EXCLUDE
# )
## Mark other files for installation (e.g. launch and bag files, etc.)
# install(FILES
# # myfile1
# # myfile2
# DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_SHARE_DESTINATION}
# )
#############
## Testing ##
#############
## Add gtest based cpp test target and link libraries
# catkin_add_gtest(${PROJECT_NAME}-test test/test_publisher.cpp)
# if(TARGET ${PROJECT_NAME}-test)
# target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME}-test ${PROJECT_NAME})
# endif()
## Add folders to be run by python nosetests
# catkin_add_nosetests(test)
四、 编写订阅者
main.cpp
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "std_msgs/String.h"
#include "/home/leon/project/ros/helloworld/ws/devel/include/publisher/Person.h"
#include <sstream>
//回调函数
void doMessage(const publisher::Person::ConstPtr &person)
{
ROS_INFO("订阅数据:%s,%d,%f",person->name.c_str(),person->age,person->height);
}
//订阅者
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
//中文支持
setlocale(LC_ALL,"");
//初始化ros节点
//指定节点名称
ros::init(argc,argv,"subscriber");
//创建ros节点句柄
ros::NodeHandle n;
//创建订阅者对象
ros::Subscriber pub = n.subscribe("fang",10,doMessage);
//回头处理回调函数
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
//通过ros工具打印话题消息
//rostopic echo fang
修改配置
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0.2)
project(subscriber)
## Compile as C++11, supported in ROS Kinetic and newer
# add_compile_options(-std=c++11)
## Find catkin macros and libraries
## if COMPONENTS list like find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS xyz)
## is used, also find other catkin packages
find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS
roscpp
std_msgs
)
## System dependencies are found with CMake's conventions
# find_package(Boost REQUIRED COMPONENTS system)
## Uncomment this if the package has a setup.py. This macro ensures
## modules and global scripts declared therein get installed
## See http://ros.org/doc/api/catkin/html/user_guide/setup_dot_py.html
# catkin_python_setup()
################################################
## Declare ROS messages, services and actions ##
################################################
## To declare and build messages, services or actions from within this
## package, follow these steps:
## * Let MSG_DEP_SET be the set of packages whose message types you use in
## your messages/services/actions (e.g. std_msgs, actionlib_msgs, ...).
## * In the file package.xml:
## * add a build_depend tag for "message_generation"
## * add a build_depend and a exec_depend tag for each package in MSG_DEP_SET
## * If MSG_DEP_SET isn't empty the following dependency has been pulled in
## but can be declared for certainty nonetheless:
## * add a exec_depend tag for "message_runtime"
## * In this file (CMakeLists.txt):
## * add "message_generation" and every package in MSG_DEP_SET to
## find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS ...)
## * add "message_runtime" and every package in MSG_DEP_SET to
## catkin_package(CATKIN_DEPENDS ...)
## * uncomment the add_*_files sections below as needed
## and list every .msg/.srv/.action file to be processed
## * uncomment the generate_messages entry below
## * add every package in MSG_DEP_SET to generate_messages(DEPENDENCIES ...)
## Generate messages in the 'msg' folder
# add_message_files(
# FILES
# Message1.msg
# Message2.msg
# )
## Generate services in the 'srv' folder
# add_service_files(
# FILES
# Service1.srv
# Service2.srv
# )
## Generate actions in the 'action' folder
# add_action_files(
# FILES
# Action1.action
# Action2.action
# )
## Generate added messages and services with any dependencies listed here
# generate_messages(
# DEPENDENCIES
# std_msgs
# )
################################################
## Declare ROS dynamic reconfigure parameters ##
################################################
## To declare and build dynamic reconfigure parameters within this
## package, follow these steps:
## * In the file package.xml:
## * add a build_depend and a exec_depend tag for "dynamic_reconfigure"
## * In this file (CMakeLists.txt):
## * add "dynamic_reconfigure" to
## find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS ...)
## * uncomment the "generate_dynamic_reconfigure_options" section below
## and list every .cfg file to be processed
## Generate dynamic reconfigure parameters in the 'cfg' folder
# generate_dynamic_reconfigure_options(
# cfg/DynReconf1.cfg
# cfg/DynReconf2.cfg
# )
###################################
## catkin specific configuration ##
###################################
## The catkin_package macro generates cmake config files for your package
## Declare things to be passed to dependent projects
## INCLUDE_DIRS: uncomment this if your package contains header files
## LIBRARIES: libraries you create in this project that dependent projects also need
## CATKIN_DEPENDS: catkin_packages dependent projects also need
## DEPENDS: system dependencies of this project that dependent projects also need
catkin_package(
# INCLUDE_DIRS include
# LIBRARIES subscriber
# CATKIN_DEPENDS roscpp std_msgs
# DEPENDS system_lib
)
###########
## Build ##
###########
## Specify additional locations of header files
## Your package locations should be listed before other locations
include_directories(
# include
${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
## Declare a C++ library
# add_library(${PROJECT_NAME}
# src/${PROJECT_NAME}/subscriber.cpp
# )
## Add cmake target dependencies of the library
## as an example, code may need to be generated before libraries
## either from message generation or dynamic reconfigure
# add_dependencies(${PROJECT_NAME} ${${PROJECT_NAME}_EXPORTED_TARGETS} ${catkin_EXPORTED_TARGETS})
## Declare a C++ executable
## With catkin_make all packages are built within a single CMake context
## The recommended prefix ensures that target names across packages don't collide
add_executable(sbx src/main.cpp)
## Rename C++ executable without prefix
## The above recommended prefix causes long target names, the following renames the
## target back to the shorter version for ease of user use
## e.g. "rosrun someones_pkg node" instead of "rosrun someones_pkg someones_pkg_node"
# set_target_properties(${PROJECT_NAME}_node PROPERTIES OUTPUT_NAME node PREFIX "")
## Add cmake target dependencies of the executable
## same as for the library above
add_dependencies(sbx publisher_generate_messages_cpp)
## Specify libraries to link a library or executable target against
target_link_libraries(sbx
${catkin_LIBRARIES}
)
#############
## Install ##
#############
# all install targets should use catkin DESTINATION variables
# See http://ros.org/doc/api/catkin/html/adv_user_guide/variables.html
## Mark executable scripts (Python etc.) for installation
## in contrast to setup.py, you can choose the destination
# catkin_install_python(PROGRAMS
# scripts/my_python_script
# DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_BIN_DESTINATION}
# )
## Mark executables for installation
## See http://docs.ros.org/melodic/api/catkin/html/howto/format1/building_executables.html
# install(TARGETS ${PROJECT_NAME}_node
# RUNTIME DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_BIN_DESTINATION}
# )
## Mark libraries for installation
## See http://docs.ros.org/melodic/api/catkin/html/howto/format1/building_libraries.html
# install(TARGETS ${PROJECT_NAME}
# ARCHIVE DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_LIB_DESTINATION}
# LIBRARY DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_LIB_DESTINATION}
# RUNTIME DESTINATION ${CATKIN_GLOBAL_BIN_DESTINATION}
# )
## Mark cpp header files for installation
# install(DIRECTORY include/${PROJECT_NAME}/
# DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_INCLUDE_DESTINATION}
# FILES_MATCHING PATTERN "*.h"
# PATTERN ".svn" EXCLUDE
# )
## Mark other files for installation (e.g. launch and bag files, etc.)
# install(FILES
# # myfile1
# # myfile2
# DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_SHARE_DESTINATION}
# )
#############
## Testing ##
#############
## Add gtest based cpp test target and link libraries
# catkin_add_gtest(${PROJECT_NAME}-test test/test_subscriber.cpp)
# if(TARGET ${PROJECT_NAME}-test)
# target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME}-test ${PROJECT_NAME})
# endif()
## Add folders to be run by python nosetests
# catkin_add_nosetests(test)
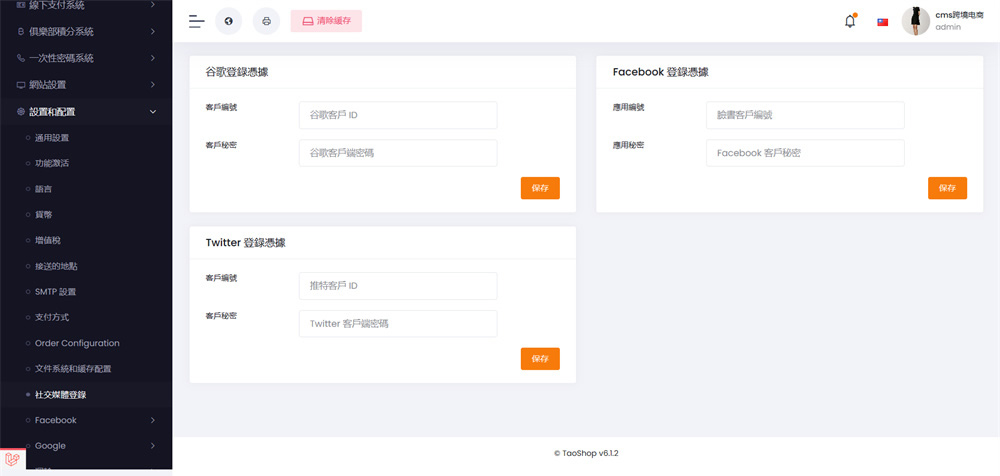
四、 运行截图




![[自动驾驶技术]-5 Tesla自动驾驶方案之算法(AI Day 2021)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/bb38da21cd6a4897a88283f993929ee3.png)



![汇编原理(四)[BX]和loop指令](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/6880f21668b942d9829a7d8e6fb2673d.png)