目录
- 一、复习题
- 二、编程练习
一、复习题
1. 假设String类有如下私有成员:
// String 类声明
class String
{
private:
char* str;
int len;
// ...
};
a. 下述默认构造函数有什么问题?
String::String() { } // 默认构造函数
b. 下述构造函数有什么问题?
String::String(const char* s) // 构造函数
{
str = s;
len = strlen;
}
c. 下述构造函数有什么问题?
String::String(const char* s) // 构造函数
{
strcpy(str, s);
len = strlen(s);
}
答:注意:下面的代码需要包含相应的头文件和using声明。
a. 该默认函数并未进行任何操作,则成员变量str与len的值是未知的(和创建局部变量未初始化一个道理)。而String类涉及动态内存分配,所以需要给str适当初始化(一般初始化为空指针——nullptr)。
修改如下:
String::String() // 默认构造函数
{
str = nullptr;
len = 0
}
b. 该构造函数中语句str = s; 只是单纯地让str和s指向同一个字符串,str只是存储了s指向的字符串的首地址,这是浅拷贝。而我们需要拷贝存储字符串的副本(深拷贝)。
修改如下:
String::String(const char* s)
{
len = strlen(s); // 存储字符串的长度,不包括空字符
str = new char[len + 1]; // 申请空间,别忘了空字符'\0'
strcpy(str, s); // 拷贝字符串内容副本
}
c. 还未在堆上申请空间,str指向的地方是未知的,直接使用函数strcpy()进行内容拷贝会导致不确定的问题。
修改如下:
String::String(const char* s)
{
len = strlen(s); // 存储字符串的长度,不包括空字符
str = new char[len + 1]; // 申请空间,别忘了空字符'\0'
strcpy(str, s); // 拷贝字符串内容副本
}
2. 如果你定义了一个类,其指针成员是使用new初始化的,请指出可能出现的三个问题及如何纠正这些问题?
答:
1)问题:没有定义对应的析构函数,和使用对应的delete运算符的形式。
纠正:使用new为成员指针分配空间需要对应的析构函数来释放空间,使用什么形式申请空间就需要使用什么形式释放空间,如:int * pi = new int; —— delete pi; ,int* pa = new int[5];——delete[5]pa;。而且所有构造函数只能使用上面相同的一种new形式,使之与析构函数中的delete形式对应。
2)问题:没有定义相关的复制构造函数。
纠正:如果没有定义赋值构造函数,编译器会提供默认的复制构造函数,其只能进行浅拷贝,只能复制需要拷贝的内容的地址。需要定义相关的复制构造函数进行深拷贝,为拷贝内容申请空间。
3)问题:没有重载对应的赋值运算符
纠正:和问题2一样,如果没有重载赋值运算符,编译器也会提供默认的,同样是浅拷贝。我们需要定义相关的赋值运算符,来进行深度拷贝。需要先释放前面存储的动态空间,然后根据拷贝大小申请新的空间。
3. 如果没有显示提供类方法,编译器将自动生成哪些类方法?请描述这些隐式生成的函数的行为。
答:
1)若没有提供构造函数,则编译器会提供一个默认构造函数,该函数什么都不做,但允许声明数组和未初始化的对象。
2)若没有提供析构函数,则编译器会提供一个默认析构函数,该函数什么都不做。
3)若没有提供拷贝构造函数,则编译器会提供一个默认的拷贝构造函数,该函数进行浅拷贝。
4)若没有提供赋值运算符重载,则编译器会提供默认的赋值运算符重载,该函数也进行浅拷贝。
5)若没有提供地址运算符重载,则编译器会提供默认的地址运算符重载,该函数返回调用对象的地址,也就是this指针的值。
4. 找出并改正下述类声明中的错误。
// nifty 类声明
class nifty
{
// 数据
char personality[];
int talents;
// 方法
nifty();
nifty(char* s);
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, nifty& n);
};
nifty::nifty()
{
personality = NULL;
talents = 0;
}
nifty::nifty(char* s)
{
personality = new char[strlen(s)];
personality = s;
talents = 0;
}
ostream& nifty::operator<<(ostream& os, nifty& n)
{
os << n;
}
答:首先,类声明中一般成员变量为私有成员(private),而成员函数为公有成员(public)。不显式声明时,类(class)默认为private,而结构(struct)默认为public。所以需要将成员函数声明为public。在默认构造函数中,personality是数组名也是指向第一个元素的char指针,但是其指向不能改变,可以使用strcpy()函数将其初始化为空字符串,参数s最好声明为const。在第二个提供一个参数的构造函数中,也是同样的问题。最后一个重载运算符(<<)函数需要被声明为友元函数,且该函数定义完全就是狗屁,我们都还没定义,你就用上了成品。根据上述问题,我们通过把变量personality修改为char指针,然后添加析构函数进行重写代码。(当然拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符重载也是需要的,读者可以自行编写)
下面是正确的代码:
// nifty 类声明
class nifty
{
private:
// 数据
char* personality;
int talents;
public:
// 方法
nifty();
nifty(const char* s);
~nifty();
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const nifty& n);
};
// 类方法定义
nifty::nifty() // 默认构造函数
{
personality = nullptr;
talents = 0;
}
nifty::nifty(const char* s) // 构造函数
{
int len = strlen(s);
personality = new char[len+1];
strcpy(personality, s);
talents = 0;
}
nifty::~nifty() // 析构函数
{
if (personality != nullptr)
delete[]personality;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const nifty& n) // 运算符(<<)重载
{
os << "Personality: " << personality << endl;
os << "Talents: " << talents << endl;
return os;
}
5. 对于下面的类声明,回答下面的问题。
// Golfer 类声明
class Golfer
{
private:
char* fullname; // 指向包含高尔夫的名称的字符串
int games; // 保存玩的高尔夫游戏的个数
int* scores; // 指向高尔夫分数数组的第一个元素
public:
Golfer();
Golfer(const char* name, int g = 0);
Golfer(const Golfer& g);
~Golfer();
};
a. 下列各条语句将调用哪些类方法?
1 Golfer nancy;
2 Golfer lulu(“Little Lulu”);
3 Golfer roy(“Roy Hobbs”, 12);
4 Golfer *par = new Golfer;
5 Golfer next = lulu;
6 Golfer hazzard = “Weed Thwacker”;
7 *par = nancy;
8 nancy = “Nancy Putter”;
b. 很明显,类需要有另外几个方法才能更有用,但是类需要哪些方法才能防止数据被损坏呢?
答:
a.
- 调用默认构造函数。
- 调用一个参数的构造函数。
- 调用两个参数的构造函数。
- 调用默认构造函数。
- 调用编译器提供的默认的复制构造函数。
- 先调用一个参数的构造函数创建临时对象,然后调用编译器提供的默认复制构造函数。
- 调用编译器提供的默认的赋值运算符重载函数。
- 先调用一个参数的构造函数创建临时对象,然后调用编译器提供的默认的赋值运算符重载函数。
b. 由于编译器提供的默认的复制构造函数和赋值运算符重载函数都是浅拷贝,所以需要用户自己定义复制构造函数和赋值运算符重载函数来对对象实行深度拷贝,避免程序出现问题。
二、编程练习
1. 对于下面的类声明,为这个类提供实现,并编写一个使用所有成员函数的小程序。
// Cow 类声明
class Cow
{
private:
char name[20];
char* hobby;
double weight;
public:
Cow(); // 默认构造函数
Cow(const char* nm, const char* ho, double wt);
Cow(const Cow& c); // 复制构造函数
~Cow(); // 析构函数
Cow& operator=(const Cow& c); // 赋值运算符重载
void ShowCow() const; // 显示所有有关于奶牛的数据
};
答:三个文件。
Cow.h头文件
#pragma once
// 头文件
#include <iostream>
// Cow 类声明
class Cow
{
private:
char name[20];
char* hobby;
double weight;
public:
Cow(); // 默认构造函数
Cow(const char* nm, const char* ho, double wt);
Cow(const Cow& c); // 复制构造函数
~Cow(); // 析构函数
Cow& operator=(const Cow& c); // 赋值运算符重载
void ShowCow() const; // 显示所有有关于奶牛的数据
};
main.cpp测试文件
// 头文件
#include "Cow.h"
// using 声明
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
// 默认构造函数
Cow cow1;
cow1.ShowCow();
cout << endl;
// 三个参数的构造函数
Cow cow2("若雪", "干饭", 888.8);
cow2.ShowCow();
cout << endl;
// 复制构造函数
Cow cow3(cow2);
cow3.ShowCow();
cout << endl;
// 赋值运算符
cow3 = cow1;
cow3.ShowCow();
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Cow.cpp方法定义文件
// 头文件
#include "Cow.h"
#include <cstring>
// using 声明
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
Cow::Cow() // 默认构造函数
{
strcpy(name, "小雪");
// 申请空间
hobby = new char[strlen("吃草") + 1];
strcpy(hobby, "吃草");
weight = 888.0;
}
Cow::Cow(const char* nm, const char* ho, double wt)
{
strcpy(name, nm);
// 申请空间
hobby = new char[strlen(ho) + 1];
strcpy(hobby, ho);
weight = wt;
}
Cow::Cow(const Cow& c) // 复制构造函数
{
strcpy(name, c.name);
// 申请空间
hobby = new char[strlen(c.hobby) + 1];
strcpy(hobby, c.hobby);
weight = c.weight;
}
Cow::~Cow() // 析构函数
{
// 释放空间
delete[]hobby; // 与申请的格式对应
}
Cow& Cow::operator=(const Cow& c) // 赋值运算符重载
{
if (this == &c) // 检查是否给自己赋值
{
return *this;
}
else
{
strcpy(name, c.name);
// 释放原来的空间
delete[]hobby;
// 申请新的空间
hobby = new char[strlen(c.hobby) + 1];
strcpy(hobby, c.hobby);
weight = c.weight;
return *this;
}
}
void Cow::ShowCow() const // 显示所有有关于奶牛的数据
{
cout << "Name: " << name << endl;
cout << "Hobby: " << hobby << endl;
cout << "Weight: " << weight << endl;
}
2. 通过完成下面的工作来改进String类的声明(即将String1.h升级为String2.h)。
a. 对+运算符进行重载,使之可以将两个字符串合并成一个。
b. 提供一个Stringlow()成员函数,将字符串中所有的字母字符转换为小写(注意cctype系列的字符函数)
c. 提供String()成员函数,将字符串中所有字母字符转换为大写。
d. 提供一个这样的成员函数,它接受一个char参数,返回该字符在字符串中出现的次数。使用下面的程序来测试你的工作。
// 头文件
#include "String2.h"
// using 声明
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
String s1(" and I am a C++ student.");
String s2 = "Please enter your name: ";
String s3;
cout << s2;
cin >> s3;
s2 = "My name is " + s3;
cout << s2 << endl;
s2 = s2 + s1;
s2.Stringupper();
cout << "The string\n" << s2 << "\ncontains " << s2.ch_times('A')
<< " 'A' characters in it.\n";
s1 = "red";
String rgb[3] = { String(s1), String("green"), String("blue") };
cout << "Enter the name of a primary color for mixing light: ";
String ans;
bool success = false;
while (cin >> ans)
{
ans.Stringlow();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
if (ans == rgb[i])
{
cout << "That's right!\n";
success = true;
break;
}
}
if (success)
break;
else
cout << "Try again!\n";
}
cout << "Bye\n";
return 0;
}
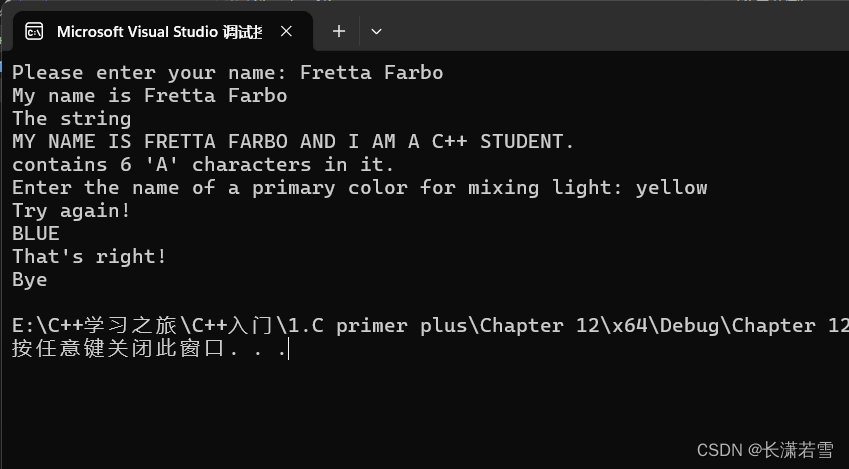
输出应于下面相似。
Please enter your name: Fretta Farbo
My name is Fretta Farbo.
The string
My NAME IS FRETTA FARBO AND I AM A C++ STUDENT.
contains 6 ‘A’ characters in it.
Enter the name of a primary color for misxing light: yellow
Try again!
BLUE
That’s right!
Bye
答:两个文件。
String2.h头文件
#pragma once
// 头文件
#include <iostream>
// String 类声明
class String
{
private:
char* str;
int len; // 字符串长度
static int num_strings; // 目前有多少个String对象
static const int CINLIM = 80; // 输入的限制
public:
String(); // 默认构造函数
String(const char* s);
String(const String& s); // 复制构造函数
~String(); // 析构函数
int lenth() const { return len; } // 返回字符串长度
int ch_times(char key) const; // 返回字符key在字符串中出现的次数
void Stringlow();
void Stringupper();
String& operator=(const char* s);
String& operator=(const String& s);
char& operator[](int i);
const char& operator[](int i) const;
String operator+(const String& s) const;
// 关系运算符重载
friend bool operator<(const String& s1, const String& s2);
friend bool operator>(const String& s1, const String& s2);
friend bool operator==(const String& s1, const String& s2);
friend String operator+(const char* s, const String& str);
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const String& s);
friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& is, String& s);
// 静态成员函数
static int HowMany();
};
String2.cpp方法定义文件
// 头文件
#include "String2.h"
#include <cctype>
#include <cstring>
// using 声明
using std::endl;
// 静态成员变量初始化
int String::num_strings = 0;
String::String() // 默认构造函数
{
str = nullptr;
len = 0;
++num_strings;
}
String::String(const char* s)
{
len = strlen(s);
// 申请空间
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(str, s);
++num_strings;
}
String::String(const String& s) // 复制构造函数
{
len = s.len;
// 申请空间
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(str, s.str);
++num_strings;
}
String::~String() // 析构函数
{
// 释放空间
if (str != nullptr)
delete[]str;
}
int String::ch_times(char key) const // 返回字符key在字符串中出现的次数
{
int times = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
if (str[i] == key)
++times;
}
return times;
}
void String::Stringlow()
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
str[i] = tolower(str[i]);
}
}
void String::Stringupper()
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
str[i] = toupper(str[i]);
}
}
String& String::operator=(const char* s)
{
len = strlen(s);
// 释放之前的空间
delete[]str;
// 申请新的空间
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(str, s);
return *this;
}
String& String::operator=(const String& s)
{
len = s.len;
// 释放之前的空间
delete[]str;
// 申请新的空间
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(str, s.str);
return *this;
}
char& String::operator[](int i)
{
return str[i];
}
const char& String::operator[](int i) const
{
return str[i];
}
String String::operator+(const String& s) const
{
int total = len + s.len;
// 申请空间
char* result = new char[total + 1];
strcpy(result, str);
strcat(result, s.str);
String tmp(result);
// 释放空间
delete[]result;
return tmp;
}
String operator+(const char* s, const String& str)
{
int total = strlen(s) + str.len;
// 申请空间
char* result = new char[total + 1];
strcpy(result, s);
strcat(result, str.str);
String tmp(result);
// 释放空间
delete[]result;
return tmp;
}
// 关系运算符重载
bool operator<(const String& s1, const String& s2)
{
return (strcmp(s1.str, s2.str) < 0);
}
bool operator>(const String& s1, const String& s2)
{
return s2 < s1;
}
bool operator==(const String& s1, const String& s2)
{
return !strcmp(s1.str, s2.str);
}
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const String& s)
{
if (s.str != nullptr)
{
os << s.str;
}
return os;
}
std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& is, String& s)
{
char tmp[String::CINLIM];
is.getline(tmp, String::CINLIM);
if (!is)
{
is.clear();
while (is.get() != '\n')
continue;
return is;
}
s = tmp;
return is;
}
// 静态成员函数
int String::HowMany()
{
return num_strings;
}
运行结果
3. 重写程序清单10.7和程序清单10.8描述的Stock类,使之使用动态分配的内存,而不是string类对象来存储股票名称。另外,使用重载的operator<<()定义代替show()成员函数。再使用程序清单10.9测试新的程序。
答:使用动态内存分配,可以使用char*指针,也可以使用指向string类的指针。在构造函数中申请空间,在析构函数中释放空间,申请和释放的形式需要匹配。
Stock.h头文件
#pragma once
// 头文件
#include <iostream>
// Stock 类声明
class Stock
{
private:
char* company; // 股票公司名称
int shares; // 股票数量
double share_val; // 每份股票
double total_val; // 总值
void set_tot() { total_val = share_val * shares; } // 设置总值
public:
Stock(); // 默认构造函数
Stock(const char* co, int n, double pr);
~Stock(); // 析构函数
void buy(int num, double pr); // 买进
void sell(int num, double pr); // 卖出
void update(double pr); // 更新价格
// 运算符(<<)重载
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Stock& s);
const Stock& topval(const Stock& s) const; // 返回总值大的对象
};
main3.cpp测试文件
// 头文件
#include "Stock.h"
// using 声明
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
// 符号常量声明
const int STKS = 4;
int main()
{
Stock stocks[STKS] = {
Stock("NanoSmart", 12, 20.0),
Stock("Boffo Objects", 200, 2.0),
Stock("Monolithic Obelisks", 130, 3.25),
Stock("Fleep Enterprises", 60, 6.5)
};
// 显示所有股票
cout << "Stock holdings:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < STKS; ++i)
cout << stocks[i];
// 找出总值最大的股票
const Stock* top = &stocks[0];
for (int i = 1; i < STKS; ++i)
top = &top->topval(stocks[i]);
cout << "\nMost valuable holding:\n";
cout << *top << endl;
return 0;
}
Stock.cpp方法定义文件
// 头文件
#include "Stock.h"
#include <cstring>
// using 声明
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
Stock::Stock() // 默认构造函数
{
company = nullptr;
shares = 0;
share_val = 0;
set_tot();
}
Stock::Stock(const char* co, int n, double pr)
{
// 申请空间,拷贝公司名称
int len = (int)strlen(co);
company = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(company, co);
// 赋值其他成员
shares = n;
share_val = pr;
set_tot();
}
Stock::~Stock() // 析构函数
{
// 释放申请空间
if (company != nullptr)
delete[]company;
}
void Stock::buy(int num, double pr) // 买进
{
if (num > 0)
{
shares += num;
share_val = pr;
set_tot();
}
else
{
cout << "买进股票的数量不能为负";
}
}
void Stock::sell(int num, double pr) // 卖出
{
if (num < 0)
{
cout << "卖出股票的数量不能为负";
}
else if (num > shares)
{
cout << "卖出股票的数量不能超过自身拥有的股票数量";
}
else
{
shares -= num;
share_val = pr;
set_tot();
}
}
void Stock::update(double pr) // 更新价格
{
share_val = pr;
}
// 运算符(<<)重载
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Stock& s)
{
os << "Company: " << s.company;
os << " Shares: " << s.shares << endl;
os << " Share Price: $" << s.share_val;
os << " Total Worth: $" << s.total_val << endl;
return os;
}
const Stock& Stock::topval(const Stock& s) const // 返回总值大的对象
{
if (total_val > s.total_val)
return *this;
else
return s;
}
4. 请看程序清单10.10定义的Stack类的变量。
#pragma once
// 头文件
#include <iostream>
// 类型声明
typedef unsigned long Item;
// Stack 类声明
class Stack
{
private:
enum { MAX = 10 };
Item* pitems;
int size;
int top;
public:
Stack(int n = MAX);
Stack(const Stack& st);
~Stack();
bool isempty() const;
bool isfull() const;
bool push(const Item& item);
bool pop(Item& item);
Stack& operator=(const Stack& st);
void get_info() const;
};
正如私有成员表明的,这个类使用动态分配的数组来保存栈中的项。请重新编写方法,以适应这种新的表示方法,并编写一个程序来演示所有的方法,包括复制构造函数和赋值运算符。
答:头文件上面有,这里就提供测试文件和方法定义文件。
main4.cpp测试文件
// 头文件
#include "Stack.h"
// using 声明
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
// 默认构造函数
Stack stack1;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
stack1.push(i);
}
stack1.get_info();
cout << endl;
// 复制构造函数
Stack stack2(stack1);
stack2.get_info();
cout << endl;
Item tmp;
stack2.pop(tmp);
stack2.pop(tmp);
stack2.get_info();
cout << endl;
// 赋值运算符
stack1 = stack2;
stack1.get_info();
return 0;
}
Stack.cpp方法定义文件
// 头文件
#include "Stack.h"
// using 声明
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
Stack::Stack(int n)
{
if (n > MAX)
{
size = MAX;
}
else if (n > 0)
{
size = n;
}
else
{
cout << "栈的大小不能为非正整数\n";
size = top = 0;
pitems = nullptr;
return;
}
// 申请空间
pitems = new Item[size];
top = 0;
}
Stack::Stack(const Stack& st)
{
size = st.size;
// 申请空间
pitems = new Item[size];
top = st.top;
// 复制每个元素
for (int i = 0; i < top; ++i)
pitems[i] = st.pitems[i];
}
Stack::~Stack()
{
// 释放空间
if (pitems != nullptr)
delete pitems;
}
bool Stack::isempty() const
{
return top == 0;
}
bool Stack::isfull() const
{
return top == size;
}
bool Stack::push(const Item& item)
{
if (!isfull())
{
pitems[top++] = item;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool Stack::pop(Item& item)
{
if (!isempty())
{
item = pitems[--top];
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
Stack& Stack::operator=(const Stack& st)
{
if (&st == this)
{
return *this;
}
else
{
// 释放之前的空间
delete[]pitems;
// 申请新的空间
size = st.size;
pitems = new Item[size];
// 赋值内容
top = st.top;
for (int i = 0; i < top; ++i)
{
pitems[i] = st.pitems[i];
}
return *this;
}
}
void Stack::get_info() const
{
if (pitems != nullptr)
{
for (int i = 0; i < top; ++i)
{
cout << pitems[i] << " ";
}
}
}
后面两题的答案作者没写,因为目前不是很懂,这些编程练习的答案都是我自己写的,然后运行验证的。作者今天就不加班了,偷个懒,明天早上把这两道题补上。