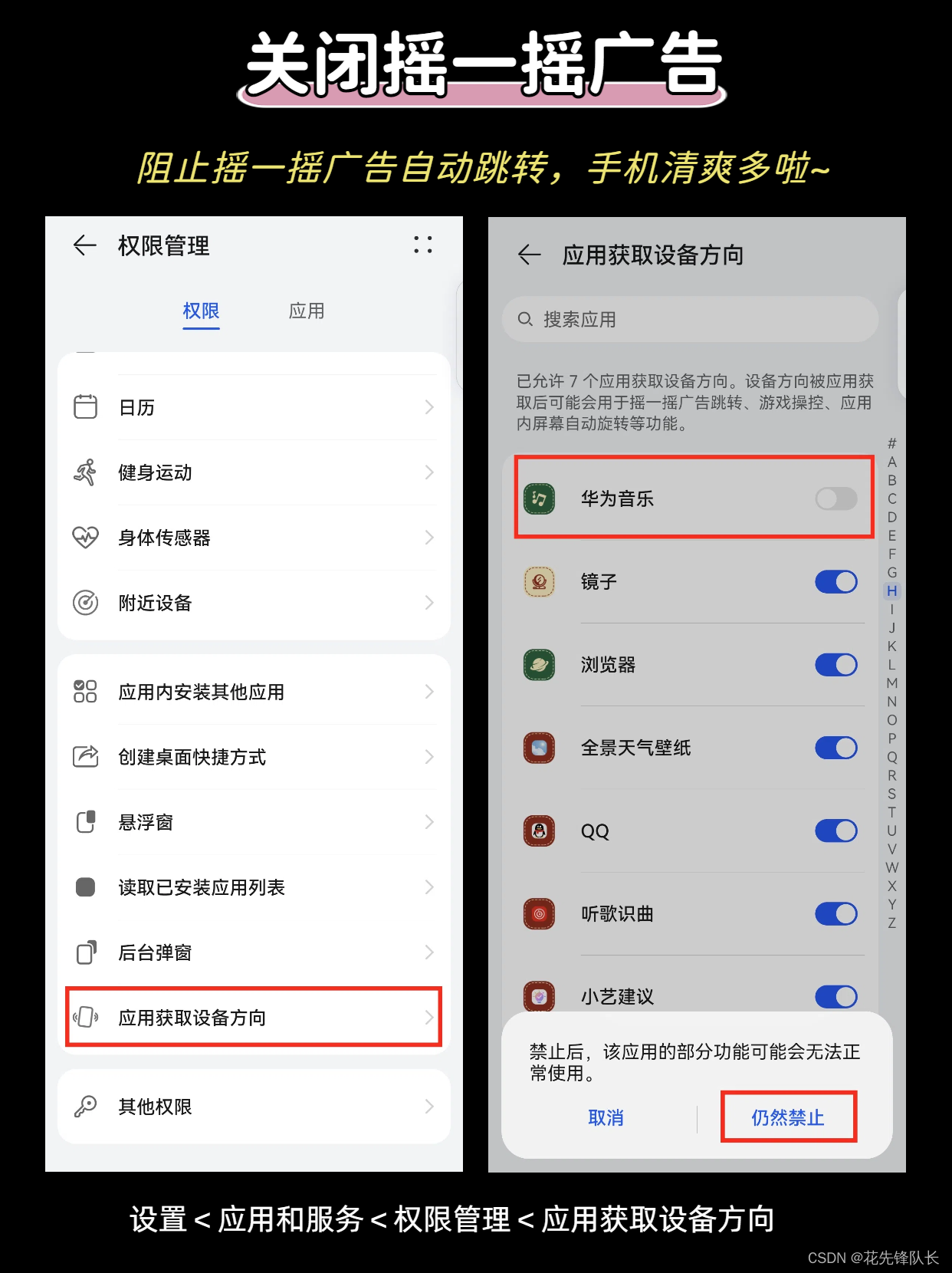
目录
SeqList.h
SeqList.c
头插尾插复用任意位置插入
头删尾删复用任意位置删除
SLtest.c
测试示例
顺序表优劣分析
SeqList.h
//SeqList.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define IN_CY 3
typedef int SLdataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLdataType* a;
int size;
int capacity;
}SeqList;
//初始化函数
void SeqListInit(SeqList* ps);
//销毁函数
void SeqListDestory(SeqList* ps);
//尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* ps, SLdataType x);
//尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* ps);
//打印函数
void print(SeqList* ps);
//头插
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* ps, SLdataType x);
//头删
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* ps);
// 顺序表在pos位置插入x
void SeqListInsert(SeqList* ps, int pos, SLdataType x);
// 顺序表删除pos位置的值
void SeqListErase(SeqList* ps, int pos);SeqList.c
//SeqList.C
#include "SeqList.h"
//初始化顺序表
void SeqListInit(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 3;
ps->a = (SLdataType*)malloc(sizeof(SLdataType) * ps->capacity);
//申请空间失败
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
perror("SeqListInit");
exit(-1);
}
}
//销毁顺序表
void SeqListDestory(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
}
//容量检查
void SLCheckCapacity(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
ps->capacity += IN_CY;
SLdataType* tmp = (SLdataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(SLdataType) * ps->capacity);
//申请空间失败
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("SLCheckCapacity");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
}
}
//尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* ps, SLdataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
ps->a[ps->size++] = x;
}
//尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
ps->size--;
}
//打印顺序表
void print(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//头插
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* ps, SLdataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int end = ps->size;
while (end--)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
}
ps->size++;
ps->a[0] = x;
}
//头删
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
// 顺序表在pos位置插入x
void SeqListInsert(SeqList* ps, int pos, SLdataType x)
{
assert(ps);
//下标合法检查
assert(pos>= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int end = ps->size;
while (end >= pos)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
end--;
}
ps->size++;
ps->a[pos] = x;
}
// 顺序表删除pos位置的值
void SeqListErase(SeqList* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
//下标合法检查
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
int i;
for (i = pos; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}头插尾插复用任意位置插入
// 顺序表在pos位置插入x
void SeqListInsert(SeqList* ps, int pos, SLdataType x)
{
assert(ps);
//下标合法检查
assert(pos>= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int end = ps->size;
while (end >= pos)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
end--;
}
ps->size++;
ps->a[pos] = x;
}
//头插
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* ps, SLdataType x)
{
SeqListInsert(ps, 0, x);
}
//尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* ps, SLdataType x)
{
SeqListInsert(ps, ps->size, x);
}头删尾删复用任意位置删除
// 顺序表删除pos位置的值
void SeqListErase(SeqList* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
//下标合法检查
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
int i;
for (i = pos; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
//头删
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* ps)
{
SeqListErase(ps, 0);
}
//尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* ps)
{
SeqListErase(ps, ps->size - 1);
}SLtest.c
//SLtest.c
#include "SeqList.h"
void SLtest1()
{
SeqList s1;
SeqListInit(&s1);
SeqListPushBack(&s1, 1);
SeqListPushBack(&s1, 2);
SeqListPushBack(&s1, 3);
print(&s1);
SeqListPushBack(&s1, 4);
SeqListPushBack(&s1, 5);
print(&s1);
SeqListPopBack(&s1);
SeqListPopBack(&s1);
SeqListPopBack(&s1);
SeqListPopBack(&s1);
SeqListPopBack(&s1);
print(&s1);
SeqListDestory(&s1);
}
void SLtest2()
{
SeqList s1;
SeqListInit(&s1);
SeqListPushFront(&s1, 1);
SeqListPushFront(&s1, 2);
SeqListPushFront(&s1, 3);
print(&s1);
SeqListPushFront(&s1, 4);
SeqListPushFront(&s1, 5);
print(&s1);
//SeqListPopFront(&s1);
//SeqListPopFront(&s1);
SeqListPopFront(&s1);
print(&s1);
SeqListPopFront(&s1);
print(&s1);
SeqListPopFront(&s1);
print(&s1);
SeqListPopFront(&s1);
print(&s1);
SeqListDestory(&s1);
}
void SLtest3()
{
SeqList s1;
SeqListInit(&s1);
SeqListInsert(&s1, 0, 1);
SeqListInsert(&s1, 0, 2);
SeqListInsert(&s1, 0, 3);
print(&s1);
SeqListInsert(&s1, s1.size, 4);
SeqListInsert(&s1, s1.size, 5);
SeqListInsert(&s1, s1.size, 6);
print(&s1);
SeqListInsert(&s1, 1, 7);
print(&s1);
SeqListErase(&s1, s1.size - 1);
print(&s1);
}
int main()
{
//测试尾插尾删
//SLtest1();
//测试头插头删
//SLtest2();
//测试任意位置插入删除
SLtest3();
return 0;
}测试示例
尾插:
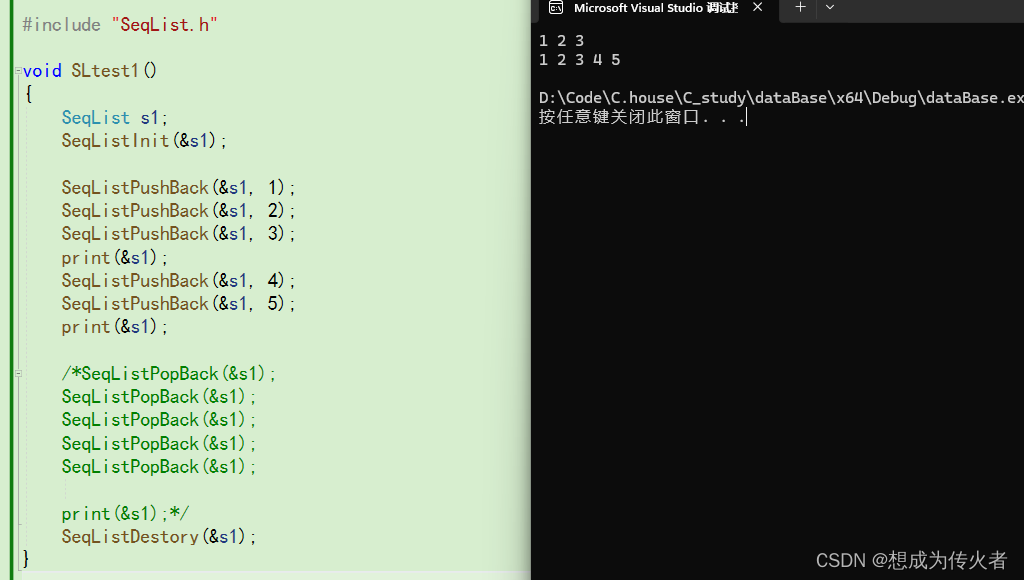
尾删:
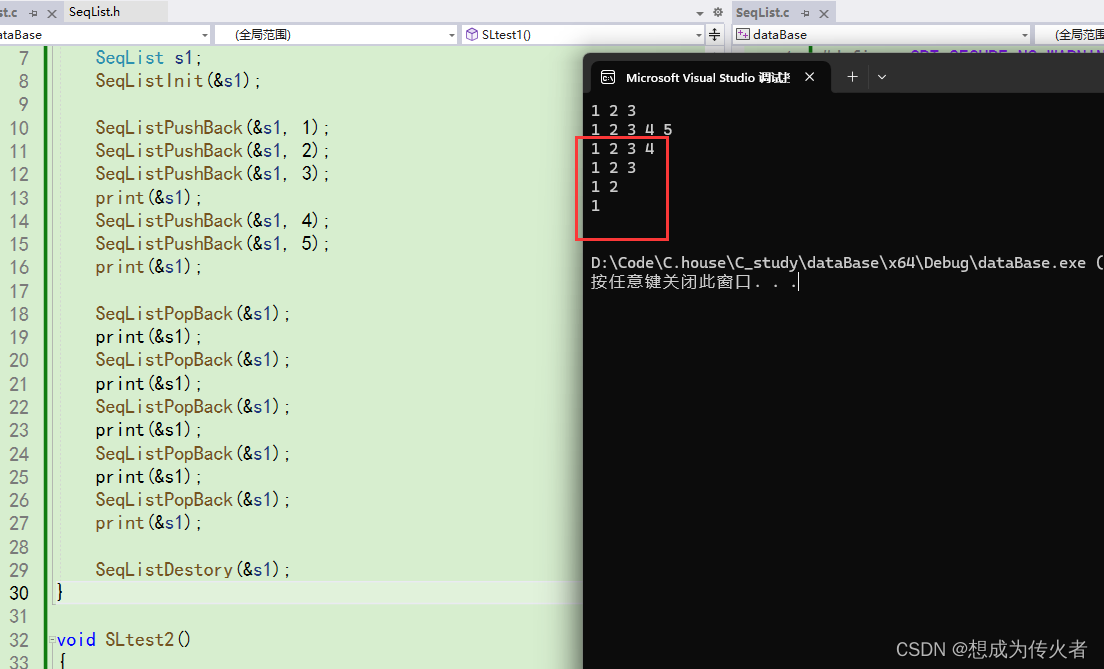
头插:

头删:
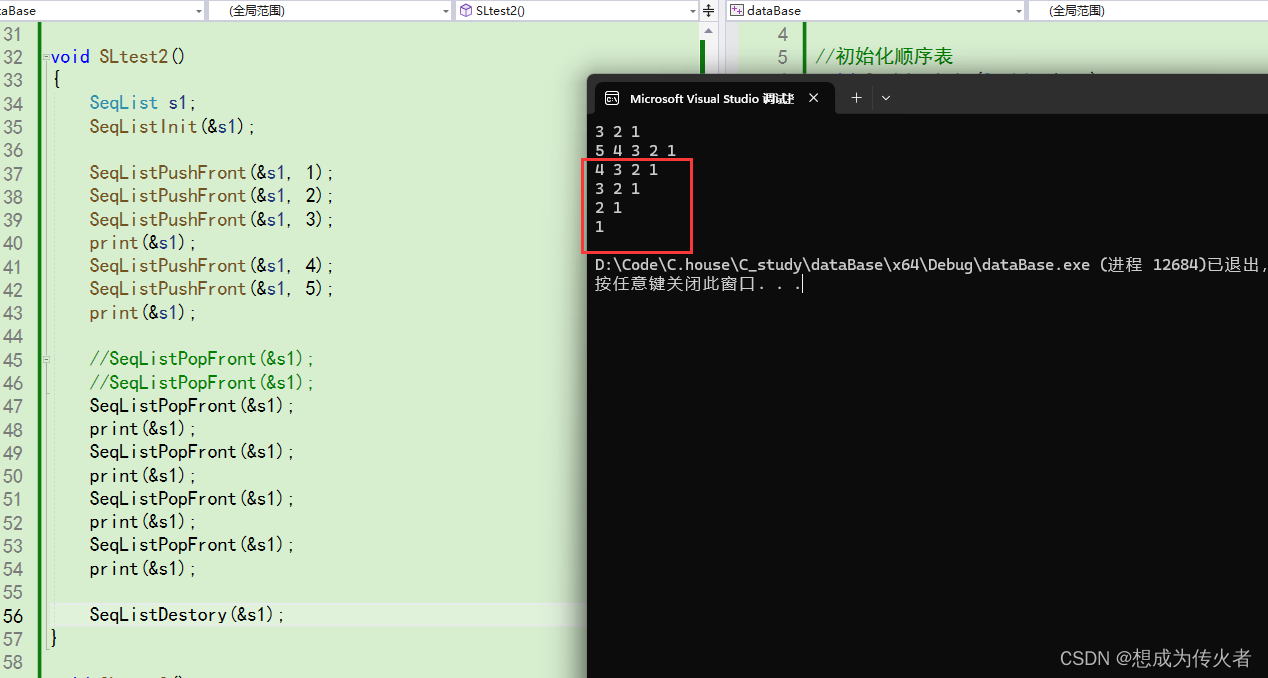
任意位置插入:
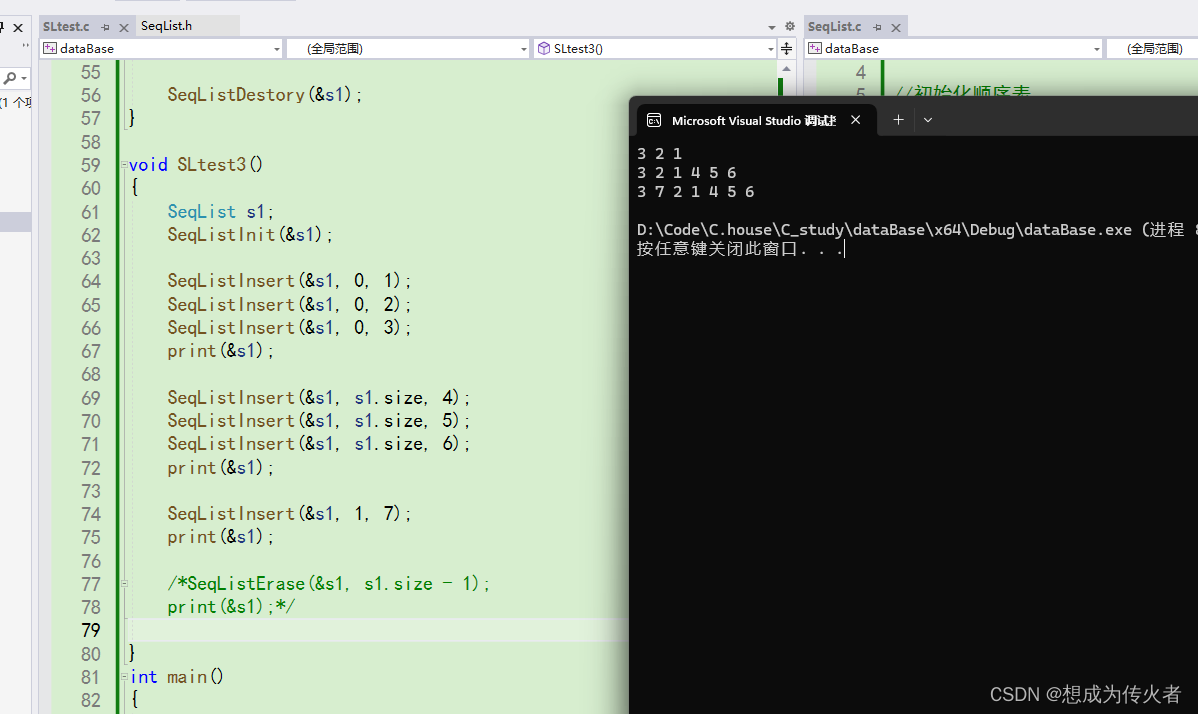
任意位置删除:

顺序表优劣分析
由于顺序表是一块连续的空间,因此可以直接通过下标访问而无需遍历寻找,所以在需要大量访问的程序中具有优势,对缓存的利用率高。而当空间不够扩容时一般是呈2倍的增长,势必会有一定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到200,我们再继续插入了5个数据,后面没有数据插入了,那么就浪费了95个数据空间。且对于异地扩容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间。会有不小的消耗。
尾插和尾删的时间复杂度为O(1),因此适用于只需要尾插尾删的场景。而头插头删和任意位置插入删除为了保证数据的顺序性需要一个一个挪动数据,时间复杂度为0(n),因此对于需要大量随机存取的程序来说开销较大。
因此顺序表通常应用于元素高效存储+频繁访问的场景。