【多线程开发 2】从代码到实战TransmittableThreadLocal
本文将从以下几个点讲解TransmittableThreadLocal(为了方便写以下简称ttl):
-
前身
-
是什么?
-
可以用来做什么?
-
源码原理
-
实战
前身
ThreadLocal
要了解ttl就要先了解Java自带的类ThreadLocal,threadlocal是作为当前线程中属性ThreadLocalMap集合中的某一个Entry的key值Entry(threadlocl,value),虽然不同的线程之间threadlocal这个key值是一样,但是不同的线程所拥有的ThreadLocalMap是独一无二的,,用于存储一些线程不安全的公共变量,通过“给每一个线程一个线程不安全的变量的拷贝”,来达到线程安全的目的,就不会出现变量多个线程之间共享的问题。
ThreadLocal 变量通常被private static修饰。当一个线程结束时,它所使用的所有 ThreadLocal 相对的实例副本都可被回收。
InheritableThreadLocal
使用ThreadLocal可以解决线程安全问题,但是也有一定的局限性,比如无法在父子线程之间传递信息,因此InheritableThreadLocal就是JDK为了解决这个问题而创建的
TTL是什么?可以做什么?
在现在开发的情况下肯定是需要复用线程的,如果说InheritableThreadLocal在生成子进程的时候会做信息传递,但是在使用线程池或者其他需要复用线程的地方,由于会不产生新的Thread,而是直接使用空闲的已建成的Thread,所以的话InheritableThreadLocal有时候会不能用,此时可以通过使用TTL解决对应问题。
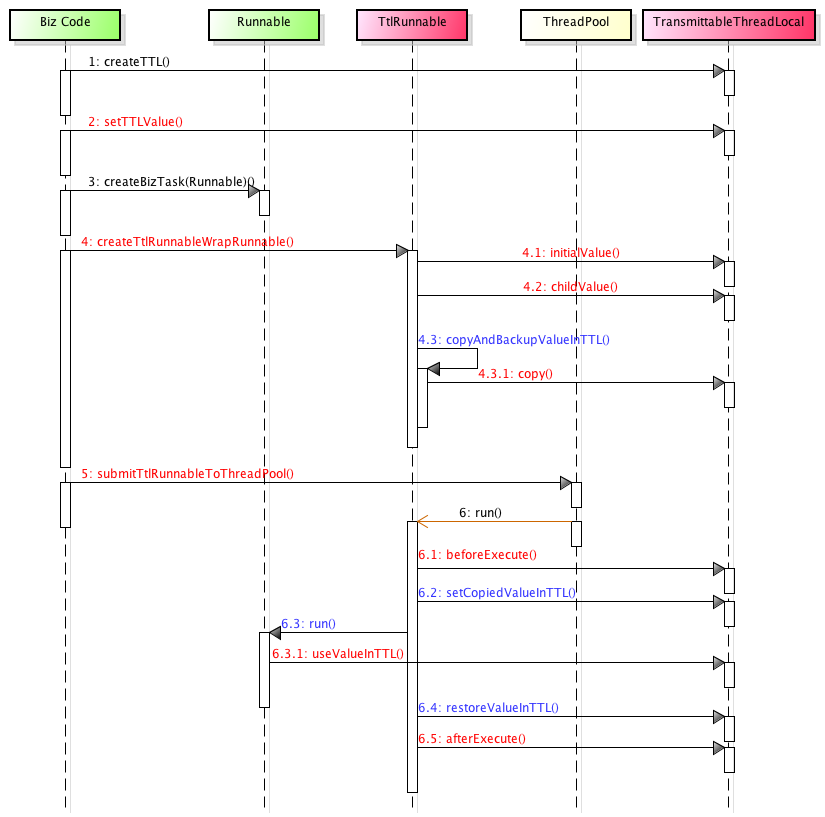
读取线程间传递的ThreadLocal 值比较麻烦,ThreadLocal 和 InheritableThreadLocal 都没有开放内部的 ThreadLocalMap,不能直接读取。所以TTL继承了InheritableThreadLocal,在每次调用 ThreadLocal的 set/get/remove 等接口的时候,为 Thread 记录到底绑定了哪些需要发生线程间传递的 ThreadLocal 对象。
在创建runnable的时候,TTL会通过holder遍历全部的TTLRunnable快照,看出上下文中有哪些线程上的信息需要进行复制。
TTL的GitHub项目地址:https://github.com/alibaba/transmittable-thread-local,感兴趣的话可以查看一下源码,后续有时间的话我会出一篇详细解析TTL源码的项目地址。
实战
其中需要使用拦截器辅助实现,需要读者依据相应技术架构自行实现
使用TTL实现MDC日志在多系统之间的信息传输
public class CustomMdcAdapters implements MDCAdapter {
private static final int WRITE_OPERATION = 1;
private static final int MAP_COPY_OPERATION = 2;
private static CustomMdcAdapters mtcMDCAdapter;
static {
mtcMDCAdapter = new CustomMdcAdapters();
MDC.mdcAdapter = mtcMDCAdapter;
}
private final ThreadLocal<Map<String, String>> copyOnInheritThreadLocal = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>();
private final ThreadLocal<Integer> lastOperation = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static MDCAdapter getInstance() {
return mtcMDCAdapter;
}
private static boolean wasLastOpReadOrNull(Integer lastOp) {
return lastOp == null || lastOp == MAP_COPY_OPERATION;
}
private Integer getAndSetLastOperation(int op) {
Integer lastOp = lastOperation.get();
lastOperation.set(op);
return lastOp;
}
private Map<String, String> duplicateAndInsertNewMap(Map<String, String> oldMap) {
Map<String, String> newMap = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<>(16));
if (oldMap != null) {
// we don't want the parent thread modifying oldMap while we are
// iterating over it
synchronized (oldMap) {
newMap.putAll(oldMap);
}
}
copyOnInheritThreadLocal.set(newMap);
return newMap;
}
@Override
public void put(String key, String val) {
if (key == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("key cannot be null");
}
Map<String, String> oldMap = copyOnInheritThreadLocal.get();
Integer lastOp = getAndSetLastOperation(WRITE_OPERATION);
if (wasLastOpReadOrNull(lastOp) || oldMap == null) {
Map<String, String> newMap = duplicateAndInsertNewMap(oldMap);
newMap.put(key, val);
} else {
oldMap.put(key, val);
}
}
@Override
public void remove(String key) {
if (key == null) {
return;
}
Map<String, String> oldMap = copyOnInheritThreadLocal.get();
if (oldMap == null) {
return;
}
Integer lastOp = getAndSetLastOperation(WRITE_OPERATION);
if (wasLastOpReadOrNull(lastOp)) {
Map<String, String> newMap = duplicateAndInsertNewMap(oldMap);
newMap.remove(key);
} else {
oldMap.remove(key);
}
}
@Override
public void clear() {
lastOperation.set(WRITE_OPERATION);
copyOnInheritThreadLocal.remove();
}
@Override
public String get(String key) {
final Map<String, String> map = copyOnInheritThreadLocal.get();
if ((map != null) && (key != null)) {
return map.get(key);
} else {
return null;
}
}
public Map<String, String> getPropertyMap() {
lastOperation.set(MAP_COPY_OPERATION);
return copyOnInheritThreadLocal.get();
}
public Set<String> getKeys() {
Map<String, String> map = getPropertyMap();
if (map != null) {
return map.keySet();
} else {
return null;
}
}
@Override
public Map<String, String> getCopyOfContextMap() {
Map<String, String> hashMap = copyOnInheritThreadLocal.get();
if (hashMap == null) {
return null;
} else {
return new HashMap<>(hashMap);
}
}
@Override
public void setContextMap(Map<String, String> contextMap) {
lastOperation.set(WRITE_OPERATION);
Map<String, String> newMap = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<>(16));
newMap.putAll(contextMap);
copyOnInheritThreadLocal.set(newMap);
}
}
使用TTL帮助实现web服务中的用户信息传输
public final class ContextsUtils {
private ContextsUtils() {
}
private static final ThreadLocal<Map<String, String>> THREAD_LOCAL = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>();
public static void putAll(Map<String, String> map) {
map.forEach(ContextsUtils::set);
}
public static void set(String key, Object value) {
Map<String, String> map = getLocalMap();
map.put(key, value == null ? StrPool.EMPTY : value.toString());
}
public static <T> T get(String key, Class<T> type) {
Map<String, String> map = getLocalMap();
return Convert.convert(type, map.get(key));
}
public static <T> T get(String key, Class<T> type, Object def) {
Map<String, String> map = getLocalMap();
return Convert.convert(type, map.getOrDefault(key, String.valueOf(def == null ? StrPool.EMPTY : def)));
}
public static Map<String, String> getLocalMap() {
Map<String, String> map = THREAD_LOCAL.get();
if (map == null) {
map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(10);
THREAD_LOCAL.set(map);
}
return map;
}
/**
* 其他get/set各种信息需要读者依据业务自行实现。。。
*/
}